The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review
et al., Current Nutrition Reports, doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3, Feb 2025
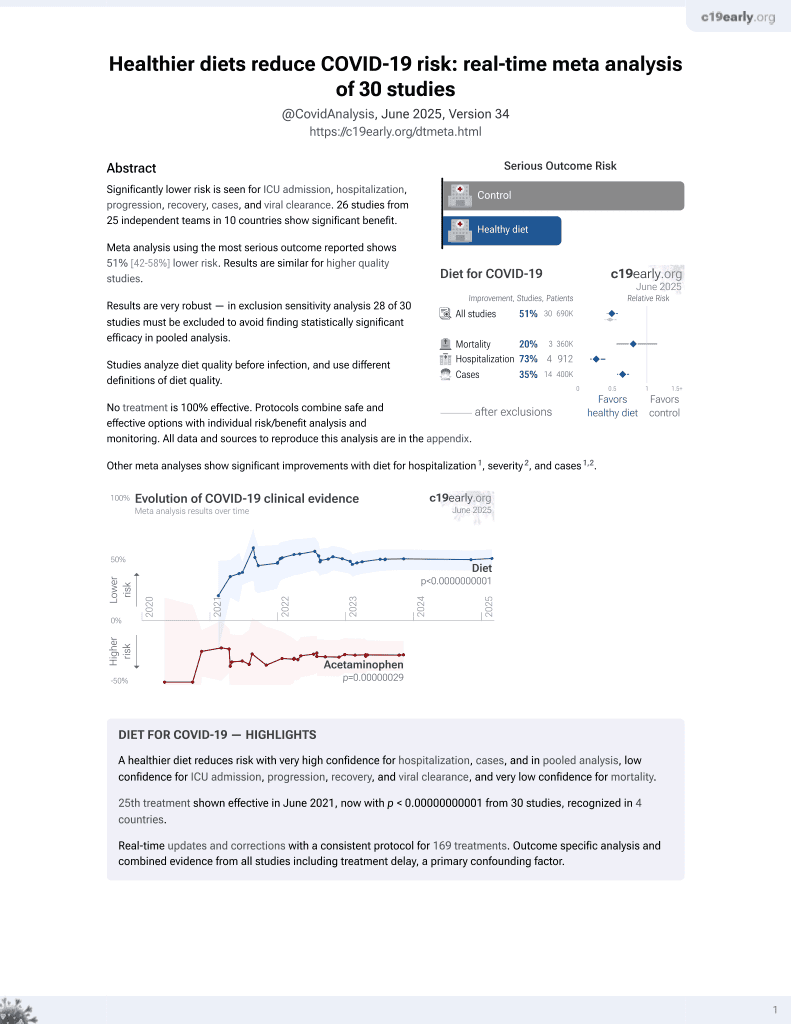
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
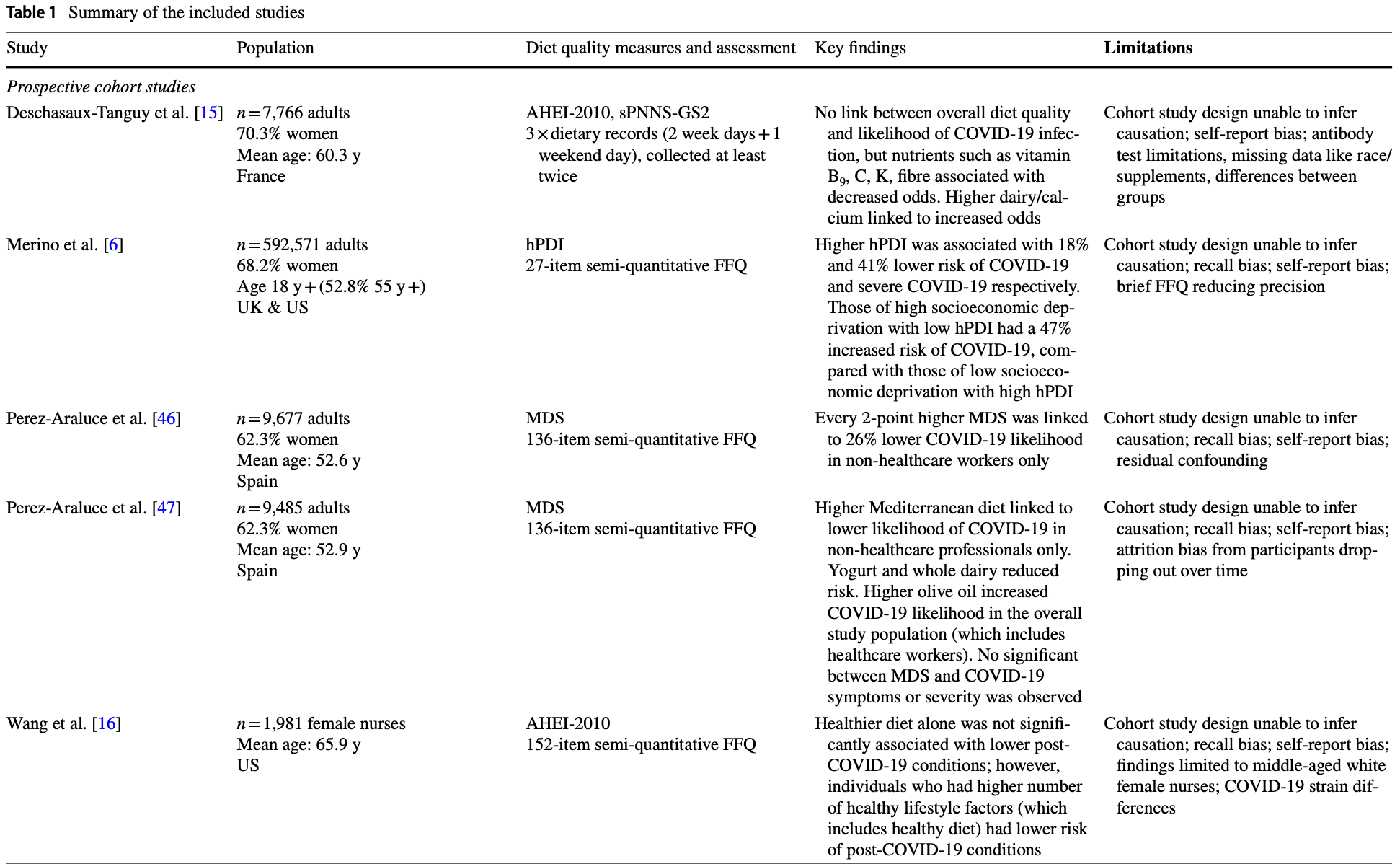
Review of 15 studies examining associations between diet quality and COVID-19 severity and outcomes. Authors found that adherence to high-quality, anti-inflammatory diets like the Mediterranean and DASH diets was generally associated with lower risks of COVID-19 infection and severe illness. Conversely, consumption of processed foods high in saturated fats, sugars, and additives was linked to increased COVID-19 complications.
1.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
2.
Tassakos et al., The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review, Current Nutrition Reports, doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3.
3.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
4.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
Tassakos et al., 1 Feb 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: jimmylouie@swin.edu.au.
The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review
Current Nutrition Reports, doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3
Purpose of Review The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has highlighted the potential role of nutrition in modifying disease susceptibility and severity. This review aims to systematically evaluate the current evidence on associations between dietary patterns, assessed using diet quality scores (DQS), and COVID-19 severity and outcomes. Recent Findings A comprehensive literature search identified 15 studies across diverse populations. Prospective cohort studies generally found higher diet quality associated with lower COVID-19 infection rates. Case-control studies consistently showed reduced odds of COVID-19 infection and severe illness with adherence to anti-inflammatory dietary patterns, particularly the Mediterranean diet. Cross-sectional data revealed associations between higher DQS and reduced COVID-19 symptom burden and improved prognostic biomarkers. An ecological study demonstrated inverse relationships between national-level diet quality and COVID-19 caseloads. Mediterranean, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and plant-based diet scores were notably predictive of favourable outcomes, even after adjusting for confounders. Conversely, consumption of processed foods high in saturated fats, sugars, and additives was linked to increased COVID-19 complications. Despite these findings, research gaps remain, including the impacts of specific dietary components, effect modifiers across populations, and establishing causality through interventional trials. Summary This review highlights the observational evidence supporting the potential integration of optimal nutrition into pandemic preparedness strategies. Further research is needed to strengthen these findings and inform evidence-based dietary recommendations for COVID-19 prevention and management.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Albahrani, Tn, Naam, Alqahtani, Alqahtani et al., The association of body mass index with COVID-19 complications and survival rate at a tertiary Hospital, Life
Anal, Koirala, Umar, Thapa, Immunomodulation and enhancing the immunity: unveiling the potential of designer diets, Future Foods, doi:10.1016/j.fufo.2023.100246
Andrés, De La Lastra, Juan, Plou, Pérez-Lebeña, Antioxidant metabolism pathways in vitamins, polyphenols, and selenium: parallels and divergences, Int J Mol Sci
Bakırhan, Arpa, Uğur, Pehlivan, Saleki et al., Metabolic risks and prognosis of COVID-19: are dietary patterns important?, Nutr Food Sci, doi:10.1108/NFS-10-2022-0360
Berthon, Wood, Nutrition and respiratory health-Feature review, Nutrients
Bromage, Batis, Bhupathiraju, Fawzi, Fung et al., Development and validation of a novel food-based Global Diet Quality Score (GDQS), J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxab244
Cena, Calder, Defining a healthy diet: evidence for the role of contemporary dietary patterns in health and disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12020334
Childs, Calder, Miles, Diet and immune function, Nutrients
Cámara, Sánchez-Mata, Fernández-Ruiz, Cámara, Cebadera et al., A review of the role of micronutrients and bioactive compounds on immune system supporting to fight against the COVID-19 disease, Foods
De Araújo, De Souza, Da Silva-Maia, De, Vale et al., Nutritional status, diet and viral respiratory infections: perspectives for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114520003311
Deschasaux-Tanguy, Srour, Bourhis, Arnault, Druesne-Pecollo et al., Nutritional risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective study within the NutriNet-Santé cohort, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-021-02168-1
Durán-Agüero, Ortiz, Pérez-Armijo, Vinueza-Veloz, Castillo et al., Quality of the diet during the COVID-19 pandemic in 11 Latin-American countries, J Health Popul Nutr, doi:10.1186/s41043-022-00316-8
Firoozi, Masoumi, Ranjbar, Shivappa, Hebert et al., The association between energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index, body composition, and anthropometric indices in COVID-19-infected patients: a case-control study in Shiraz, Iran Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1155/2022/5452488
Govers, Calder, Savelkoul, Albers, Van Neerven, Ingestion, immunity, and infection: nutrition and viral respiratory tract infections, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.841532
Gozzi-Silva, Teixeira, Ajds, Sato, Oliveira, Immunomodulatory role of nutrients: how can pulmonary dysfunctions improve?, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.674258
Greene, Roberts, Frugé, Negative association between Mediterranean diet adherence and COVID-19 cases and related deaths in Spain and 23 OECD countries: an ecological study, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.591964
Hammerton, Munafò, Causal inference with observational data: the need for triangulation of evidence, Psychol Med, doi:10.1017/S0033291720005127
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Kelly, Sacker, Marmot, Nutrition and respiratory health in adults: findings from the Health Survey for Scotland, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/09031936.03.00055702
Khorasanchi, Ahmadihoseini, Hajhoseini, Zare-Feyzabadi, Haghighi et al., Adherence to dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet in relation to psychological function in recovered COVID-19 patients: a case-control study, BMC Nutr, doi:10.1186/s40795-022-00633-5
Khoury, Julien, Inverse association between the Mediterranean diet and COVID-19 risk in Lebanon: a case-control study, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.707359
Kim, Rebholz, Hegde, Lafiura, Raghavan et al., Plant-based diets, pescatarian diets and COVID-19 severity: a population-based case-control study in six countries, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272
Ling, Zabetakis, The role of an anti-inflammatory diet in conjunction to COVID-19, Diseases, doi:10.3390/diseases9040076
Merino, Joshi, Nguyen, Leeming, Mazidi et al., Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325353
Mohammad, Aziz, Mahri, Malik, Haji et al., Obesity and COVID-19: what makes obese host so vulnerable?, Immun Ageing, doi:10.1186/s12979-020-00212-x
Murni, Prawirohartono, Triasih, Potential role of vitamins and zinc on acute respiratory infections including Covid-19, Global Pediatric Health, doi:10.1177/2333794x211021739
Nguyen, Pham, Vu, Do, Nguyen et al., Single and combinative impacts of healthy eating behavior and physical activity on COVID-19-like symptoms among outpatients: a multi-hospital and health center survey, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13093258
Nicklett, Johnson, Troy, Vartak, Reiter, Food access, diet quality, and nutritional status of older adults during COVID-19: a scoping review, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.763994
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, Br Med J, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pan, Lai, Dushenkov, Ho, Modulation of inflammatory genes by natural dietary bioactive compounds, J Agric Food Chem, doi:10.1021/jf900612n
Panagiotakos, Pitsavos, Stefanadis, Dietary patterns: A Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2005.08.006
Perez-Araluce, Martinez-Gonzalez, Fernández-Lázaro, Bes-Rastrollo, Gea et al., Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the "Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra" cohort, Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001
Perez-Araluce, Martínez-González, Gea, Carlos, Components of the Mediterranean diet and risk of COVID-19, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.805533
Petrakis, Margină, Tsarouhas, Tekos, Stan et al., Obesity -a risk factor for increased COVID-19 prevalence, severity and lethality (Review), Mol Med Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11127
Ravelli, Schoeller, Traditional self-reported dietary instruments are prone to inaccuracies and new approaches are needed, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.00090
Rodriguez-Leyva, Pierce, the impact of nutrition on the COVID-19 pandemic and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on nutrition, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061752
Sharma, Castelnuovo, Cerletti, Donati, De Gaetano et al., Diet quality and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19: a systematic review of observational studies, Adv Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.advnut.2023.09.006
Singh, Yau, Leung, El-Nezami, Lee, Interaction of polyphenols as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds in Brain-Liver-Gut Axis, Antioxidants
Sudhakar, Winfred, Meiyazhagan, Venkatachalam, Mechanisms contributing to adverse outcomes of COVID-19 in obesity, Mol Cell Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-022-04356-w
Tavakol, Ghannadi, Tabesh, Halabchi, Noormohammadpour et al., Relationship between physical activity, healthy lifestyle and COVID-19 disease severity; a cross-sectional study, J Public Health Theory Pract, doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01468-9
Thirumdas, Kothakota, Pandiselvam, Bahrami, Barba, Role of food nutrients and supplementation in fighting against viral infections and boosting immunity: a review, Trends Food Sci Technol, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.069
Tong, Khani, Lu, Taylor, Osinski et al., Association between body-mass index, patient characteristics, and obesityrelated comorbidities among COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study, Obes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.orcp.2022.12.003
Tricco, Zarin, Brien, Colquhoun, Levac, PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M18-0850
Wang, Li, Yue, Yuan, Kang et al., Adherence to healthy lifestyle prior to infection and risk of Post-COVID-19 condition, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6555
Yue, Ma, Accorsi, Ding, Hu et al., Longterm diet and risk of severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqac219
Zargarzadeh, Vajargah, Ebrahimzadeh, Mousavi, Khodaveisi et al., Higher adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern is inversely associated with severity of COVID-19 and related symptoms: a cross-sectional study, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.911273
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3",
"ISSN": [
"2161-3311"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Purpose of Review</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has highlighted the potential role of nutrition in modifying disease susceptibility and severity. This review aims to systematically evaluate the current evidence on associations between dietary patterns, assessed using diet quality scores (DQS), and COVID-19 severity and outcomes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Recent Findings</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A comprehensive literature search identified 15 studies across diverse populations. Prospective cohort studies generally found higher diet quality associated with lower COVID-19 infection rates. Case–control studies consistently showed reduced odds of COVID-19 infection and severe illness with adherence to anti-inflammatory dietary patterns, particularly the Mediterranean diet. Cross-sectional data revealed associations between higher DQS and reduced COVID-19 symptom burden and improved prognostic biomarkers. An ecological study demonstrated inverse relationships between national-level diet quality and COVID-19 caseloads. Mediterranean, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and plant-based diet scores were notably predictive of favourable outcomes, even after adjusting for confounders. Conversely, consumption of processed foods high in saturated fats, sugars, and additives was linked to increased COVID-19 complications. Despite these findings, research gaps remain, including the impacts of specific dietary components, effect modifiers across populations, and establishing causality through interventional trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Summary</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This review highlights the observational evidence supporting the potential integration of optimal nutrition into pandemic preparedness strategies. Further research is needed to strengthen these findings and inform evidence-based dietary recommendations for COVID-19 prevention and management.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"618"
],
"article-number": "27",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "23 January 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 2,
"value": "1 February 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with Ethical Standards",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of Interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tassakos",
"given": "Athina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kloppman",
"given": "Alanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7736-605X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Louie",
"given": "Jimmy Chun Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Current Nutrition Reports",
"container-title-short": "Curr Nutr Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T10:05:01Z",
"timestamp": 1738404301000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T10:05:10Z",
"timestamp": 1738404310000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Swinburne University of Technology"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-02T05:24:31Z",
"timestamp": 1738473871099,
"version": "3.35.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "618_CR1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). (2021). https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1. Accessed 30 May 2024"
},
{
"key": "618_CR2",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 dashboard. (2023). https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 30 May 2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"author": "CB Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "618_CR3",
"unstructured": "Jackson CB, Farzan M, Chen B, Choe H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;23(1):3–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "618_CR4",
"unstructured": "Department of Health and Aged Care (Australia). About Coronavirus (COVID-19). (2023). https://www.health.gov.au/topics/covid-19/about. Accessed 30 May 2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diseases9040076",
"author": "V Ling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diseases",
"key": "618_CR5",
"unstructured": "Ling V, Zabetakis I. The role of an anti-inflammatory diet in conjunction to COVID-19. Diseases. 2021;9(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9040076.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325353",
"author": "J Merino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2096",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "618_CR6",
"unstructured": "Merino J, Joshi AD, Nguyen LH, Leeming ER, Mazidi M, Drew DA. Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. Gut. 2021;70(11):2096–104. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325353.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12020334",
"author": "H Cena",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "334",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "618_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cena H, Calder PC. Defining a healthy diet: evidence for the role of contemporary dietary patterns in health and disease. Nutrients. 2020;12(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020334.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.591964",
"author": "MW Greene",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "591964",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "618_CR8",
"unstructured": "Greene MW, Roberts AP, Frugé AD. Negative association between Mediterranean diet adherence and COVID-19 cases and related deaths in Spain and 23 OECD countries: an ecological study. Front Nutr. 2021;8:591964. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.591964.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114520003311",
"author": "AH de Araújo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "851",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "618_CR9",
"unstructured": "de Araújo AH, de Souza AJ, da Silva-Maia JK, de Lima Vale SH, Maciel BLL, Passos TS. Nutritional status, diet and viral respiratory infections: perspectives for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Br J Nutr. 2021;125(8):851–62. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114520003311.",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M18-0850",
"author": "AC Tricco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "467",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "618_CR10",
"unstructured": "Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850.",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"author": "MJ Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n71",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "618_CR11",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. 2021;372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71.",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxab244",
"author": "S Bromage",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75s",
"issue": "12 Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "618_CR12",
"unstructured": "Bromage S, Batis C, Bhupathiraju SN, Fawzi WW, Fung TT, Li Y, Deitchler M, Angulo E, Birk N, Castellanos-Gutiérrez A, He Y, Fang Y, Matsuzaki M, Zhang Y, Moursi M, Gicevic S, Holmes MD, Isanaka S, Kinra S, Sachs SE, Stampfer MJ, Stern D, Willett WC. Development and validation of a novel food-based Global Diet Quality Score (GDQS). J Nutr. 2021;151(12 Suppl 2):75s–92s. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxab244.",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2005.08.006",
"author": "DB Panagiotakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "559",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis",
"key": "618_CR13",
"unstructured": "Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Stefanadis C. Dietary patterns: A Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(8):559–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2005.08.006.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqac219",
"author": "Y Yue",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1672",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "618_CR14",
"unstructured": "Yue Y, Ma W, Accorsi EK, Ding M, Hu FB, Willett WC. Long-term diet and risk of severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022;116:1672–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac219.",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-021-02168-1",
"author": "M Deschasaux-Tanguy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "618_CR15",
"unstructured": "Deschasaux-Tanguy M, Srour B, Bourhis L, Arnault N, Druesne-Pecollo N, Esseddik Y. Nutritional risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective study within the NutriNet-Santé cohort. BMC Med. 2021;19:290. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-021-02168-1.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6555",
"author": "S Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "232",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "618_CR16",
"unstructured": "Wang S, Li Y, Yue Y, Yuan C, Kang JH, Chavarro JE. Adherence to healthy lifestyle prior to infection and risk of Post–COVID-19 condition. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(3):232–41. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6555.",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.707359",
"author": "CN El Khoury",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "707359",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "618_CR17",
"unstructured": "El Khoury CN, Julien SG. Inverse association between the Mediterranean diet and COVID-19 risk in Lebanon: a case-control study. Front Nutr. 2021;8:707359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.707359.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.911273",
"author": "N Zargarzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "911273",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "618_CR18",
"unstructured": "Zargarzadeh N, Tadbir Vajargah K, Ebrahimzadeh A, Mousavi SM, Khodaveisi H, Akhgarjand C. Higher adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern is inversely associated with severity of COVID-19 and related symptoms: a cross-sectional study. Front Med. 2022;9:911273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.911273.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272",
"author": "H Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr Prev Health.",
"key": "618_CR19",
"unstructured": "Kim H, Rebholz CM, Hegde S, LaFiura C, Raghavan M. Lloyd JF (2021) Plant-based diets, pescatarian diets and COVID-19 severity: a population-based case–control study in six countries. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2021;4(1):257. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13093258",
"author": "MH Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3258",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "618_CR20",
"unstructured": "Nguyen MH, Pham TTM, Vu DN, Do BN, Nguyen HC, Duong TH. Single and combinative impacts of healthy eating behavior and physical activity on COVID-19-like symptoms among outpatients: a multi-hospital and health center survey. Nutrients. 2021;13(9):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093258.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10389-020-01468-9",
"author": "Z Tavakol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "267",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Public Health Theory Pract",
"key": "618_CR21",
"unstructured": "Tavakol Z, Ghannadi S, Tabesh MR, Halabchi F, Noormohammadpour P, Akbarpour S. Relationship between physical activity, healthy lifestyle and COVID-19 disease severity; a cross-sectional study. J Public Health Theory Pract. 2021;31(2):267–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01468-9.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1108/NFS-10-2022-0360",
"author": "H Bakırhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "752",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutr Food Sci",
"key": "618_CR22",
"unstructured": "Bakırhan H, Özyürek Arpa F, Uğur H, Pehlivan M, Saleki N, Çelik T. Metabolic risks and prognosis of COVID-19: are dietary patterns important? Nutr Food Sci. 2022;53(4):752–68. https://doi.org/10.1108/NFS-10-2022-0360.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.03.00055702",
"author": "Y Kelly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "664",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "618_CR23",
"unstructured": "Kelly Y, Sacker A, Marmot M. Nutrition and respiratory health in adults: findings from the Health Survey for Scotland. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(4):664–71. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.03.00055702.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7031618",
"author": "BS Berthon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1618",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "618_CR24",
"unstructured": "Berthon BS, Wood LG. Nutrition and respiratory health—Feature review. Nutrients. 2015;7(3):1618–43.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.674258",
"author": "SC Gozzi-Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "674258",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "618_CR25",
"unstructured": "Gozzi-Silva SC, Teixeira FME, Duarte AJdS, Sato MN, Oliveira LdM. Immunomodulatory role of nutrients: how can pulmonary dysfunctions improve? Front Nutr. 2021;8:674258. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.674258.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf900612n",
"author": "M-H Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4467",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "618_CR26",
"unstructured": "Pan M-H, Lai C-S, Dushenkov S, Ho C-T. Modulation of inflammatory genes by natural dietary bioactive compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57(11):4467–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900612n.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11081933",
"author": "CE Childs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1933",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "618_CR27",
"unstructured": "Childs CE, Calder PC, Miles EA. Diet and immune function. Nutrients. 2019;11(8):1933.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2333794x211021739",
"author": "IK Murni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2333794X2110217",
"journal-title": "Global Pediatric Health",
"key": "618_CR28",
"unstructured": "Murni IK, Prawirohartono EP, Triasih R. Potential role of vitamins and zinc on acute respiratory infections including Covid-19. Global Pediatric Health. 2021;8:2333794X211021739. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333794x211021739.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.841532",
"author": "C Govers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "841532",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "618_CR29",
"unstructured": "Govers C, Calder PC, Savelkoul HFJ, Albers R, van Neerven RJJ. Ingestion, immunity, and infection: nutrition and viral respiratory tract infections. Front Immunol. 2022;13:841532. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.841532.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9080669",
"author": "A Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "669",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "618_CR30",
"unstructured": "Singh A, Yau YF, Leung KS, El-Nezami H, Lee JC-Y. Interaction of polyphenols as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds in Brain–Liver–Gut Axis. Antioxidants. 2020;9(8):669.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25052600",
"author": "CMC Andrés",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2600",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "618_CR31",
"unstructured": "Andrés CMC, Pérez de la Lastra JM, Juan CA, Plou FJ, Pérez-Lebeña E. Antioxidant metabolism pathways in vitamins, polyphenols, and selenium: parallels and divergences. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(5):2600.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fufo.2023.100246",
"author": "AK Anal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100246",
"journal-title": "Future Foods",
"key": "618_CR32",
"unstructured": "Anal AK, Koirala S, Karna A, Umar M, Thapa SP. Immunomodulation and enhancing the immunity: unveiling the potential of designer diets. Future Foods. 2023;8:100246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2023.100246.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.069",
"author": "R Thirumdas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Trends Food Sci Technol",
"key": "618_CR33",
"unstructured": "Thirumdas R, Kothakota A, Pandiselvam R, Bahrami A, Barba FJ. Role of food nutrients and supplementation in fighting against viral infections and boosting immunity: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2021;110:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.069.",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods10051088",
"author": "M Cámara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1088",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Foods",
"key": "618_CR34",
"unstructured": "Cámara M, Sánchez-Mata MC, Fernández-Ruiz V, Cámara RM, Cebadera E, Domínguez L. A review of the role of micronutrients and bioactive compounds on immune system supporting to fight against the COVID-19 disease. Foods. 2021;10(5):1088.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2020.11127",
"author": "D Petrakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "618_CR35",
"unstructured": "Petrakis D, Margină D, Tsarouhas K, Tekos F, Stan M, Nikitovic D, Kouretas D, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A. Obesity - a risk factor for increased COVID-19 prevalence, severity and lethality (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(1):9–19. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11127.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12979-020-00212-x",
"author": "S Mohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Immun Ageing",
"key": "618_CR36",
"unstructured": "Mohammad S, Aziz R, Al Mahri S, Malik SS, Haji E, Khan AH, Khatlani TS, Bouchama A. Obesity and COVID-19: what makes obese host so vulnerable? Immun Ageing. 2021;18(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12979-020-00212-x.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-022-04356-w",
"author": "M Sudhakar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1155",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Biochem",
"key": "618_CR37",
"unstructured": "Sudhakar M, Winfred SB, Meiyazhagan G, Venkatachalam DP. Mechanisms contributing to adverse outcomes of COVID-19 in obesity. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(4):1155–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04356-w.",
"volume": "477",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life13071572",
"author": "S AlBahrani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1572",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Life",
"key": "618_CR38",
"unstructured": "AlBahrani S, Al-Maqati TN, Al Naam YA, Alqahtani JS, Alqahtani AS, AlRabeeah S, Aldhahir AM, Alkhalaf F, Alzuraiq HR, Alenezi MH, Alzahrani A, Bakkar M, Albahrani Z, Maawadh RM. The association of body mass index with COVID-19 complications and survival rate at a tertiary Hospital. Life. 2023;13(7):1572.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.orcp.2022.12.003",
"author": "L Tong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Obes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "618_CR39",
"unstructured": "Tong L, Khani M, Lu Q, Taylor B, Osinski K, Luo J. Association between body-mass index, patient characteristics, and obesity-related comorbidities among COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2023;17(1):47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2022.12.003.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061752",
"author": "D Rodriguez-Leyva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1752",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "618_CR40",
"unstructured": "Rodriguez-Leyva D, Pierce GN. the impact of nutrition on the COVID-19 pandemic and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on nutrition. Nutrients. 2021;13(6):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061752.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.763994",
"author": "EJ Nicklett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "763994",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "618_CR41",
"unstructured": "Nicklett EJ, Johnson KE, Troy LM, Vartak M, Reiter A. Food access, diet quality, and nutritional status of older adults during COVID-19: a scoping review. Front Public Health. 2021;9:763994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.763994.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.advnut.2023.09.006",
"author": "S Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1596",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "618_CR42",
"unstructured": "Sharma S, Di Castelnuovo A, Cerletti C, Donati MB, de Gaetano G, Iacoviello L, Bonaccio M. Diet quality and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19: a systematic review of observational studies. Adv Nutr. 2023;14(6):1596–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advnut.2023.09.006.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41043-022-00316-8",
"author": "S Durán-Agüero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Health Popul Nutr",
"key": "618_CR43",
"unstructured": "Durán-Agüero S, Ortiz A, Pérez-Armijo P, Vinueza-Veloz MF, Ríos-Castillo I, Camacho-Lopez S, Cavagnari BM, Nava-González EJ, Carpio-Arias V, Cordón-Arrivillaga K, Mauricio-Alza S, Roncancio JJB, Nuñez-Martínez B, González-Medina G, Ivancovich S, Meza-Miranda ER, Landaeta-Díaz L. Quality of the diet during the COVID-19 pandemic in 11 Latin-American countries. J Health Popul Nutr. 2022;41(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-022-00316-8.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0033291720005127",
"author": "G Hammerton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "563",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Psychol Med",
"key": "618_CR44",
"unstructured": "Hammerton G, Munafò MR. Causal inference with observational data: the need for triangulation of evidence. Psychol Med. 2021;51(4):563–78. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291720005127.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.00090",
"author": "MN Ravelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "618_CR45",
"unstructured": "Ravelli MN, Schoeller DA. Traditional self-reported dietary instruments are prone to inaccuracies and new approaches are needed. Front Nutr. 2020;7:90. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00090.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001",
"author": "R Perez-Araluce",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3061",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "618_CR46",
"unstructured": "Perez-Araluce R, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Fernández-Lázaro CI, Bes-Rastrollo M, Gea A, Carlos S. Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the “Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra” cohort. Clin Nutr. 2022;41(12):3061–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.805533",
"author": "R Perez-Araluce",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "805533",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "618_CR47",
"unstructured": "Perez-Araluce R, Martínez-González MÁ, Gea A, Carlos S. Components of the Mediterranean diet and risk of COVID-19. Front Nutr. 2022;8:805533. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.805533.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/5452488",
"author": "D Firoozi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5452488",
"journal-title": "Iran Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "618_CR48",
"unstructured": "Firoozi D, Masoumi SJ, Ranjbar S, Shivappa N, Hebert JR, Zare M. The association between energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index, body composition, and anthropometric indices in COVID-19-infected patients: a case-control study in Shiraz. Iran Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:5452488. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5452488.",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40795-022-00633-5",
"author": "Z Khorasanchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "130",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Nutr.",
"key": "618_CR49",
"unstructured": "Khorasanchi Z, Ahmadihoseini A, Hajhoseini O, Zare-Feyzabadi R, Haghighi M, Heidari M. Adherence to dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet in relation to psychological function in recovered COVID-19 patients: a case–control study. BMC Nutr. 2022;8(1):130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00633-5.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}