Real‐World Evaluation Study of Azvudine for the Treatment of Patients With COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
et al., Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, doi:10.1155/cjid/3645253, NCT04425772, Jan 2025
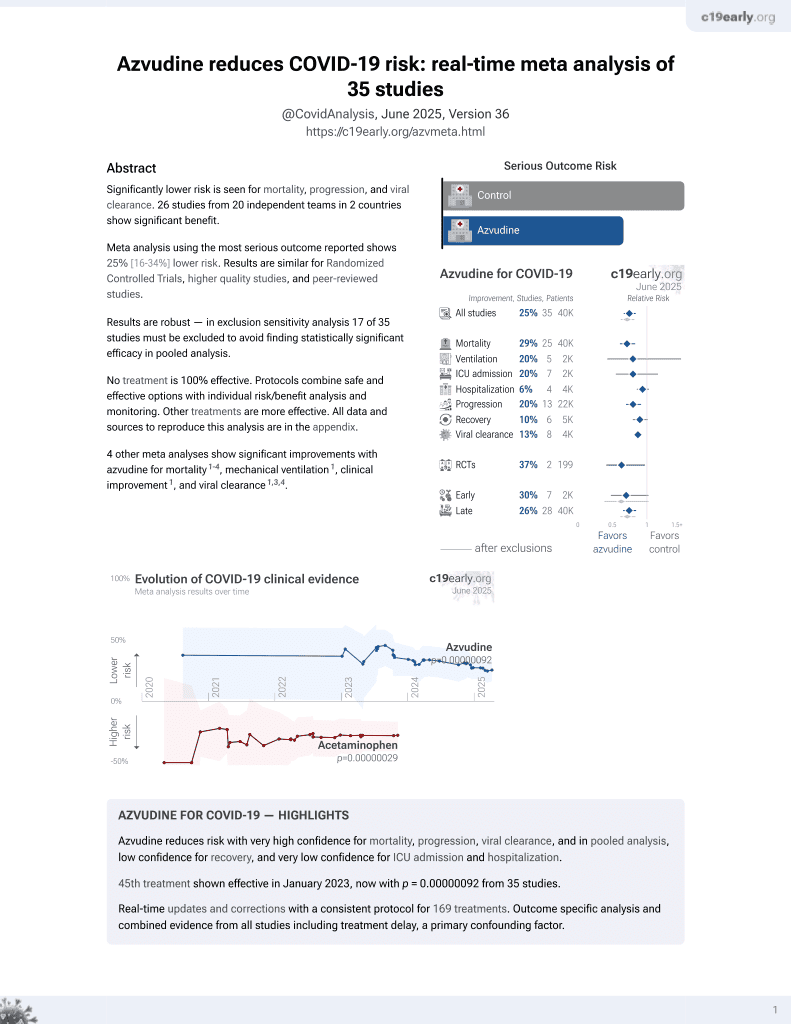
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.000000017 from 39 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 studies (5 RCTs with 1,142 patients and 14 retrospective studies with 6,602 patients) showing significantly lower mortality and progression with azvudine treatment for COVID-19.
5 meta-analyses show significant improvements with azvudine for mortality1-5,
mechanical ventilation1,
improvement1,
progression5, and
viral clearance1,3,4 .
Currently there are 39 azvudine for COVID-19 studies, showing 30% lower mortality [20‑39%], 18% lower ventilation [-10‑39%], 21% lower ICU admission [5‑34%], and 10% lower hospitalization [0‑19%].
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments6.
|
risk of death, 51.0% lower, OR 0.49, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of progression, 52.0% lower, OR 0.48, p = 0.002, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zheng et al., Small-molecule antivirals treatment for COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107096.
2.
Wang et al., Effectiveness of azvudine in reducing mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02316-y.
3.
Amani et al., Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772.
4.
Dong et al., Efficacy and Safety of Azvudine in Patients With COVID‐19 in China: A Meta‐Analysis of Observational Studies, The Clinical Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1111/crj.13798.
Kapar et al., 31 Jan 2025, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, trial NCT04425772 (history).
Contact: wangkaimath@sina.com.
Real‐World Evaluation Study of Azvudine for the Treatment of Patients With COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, doi:10.1155/cjid/3645253
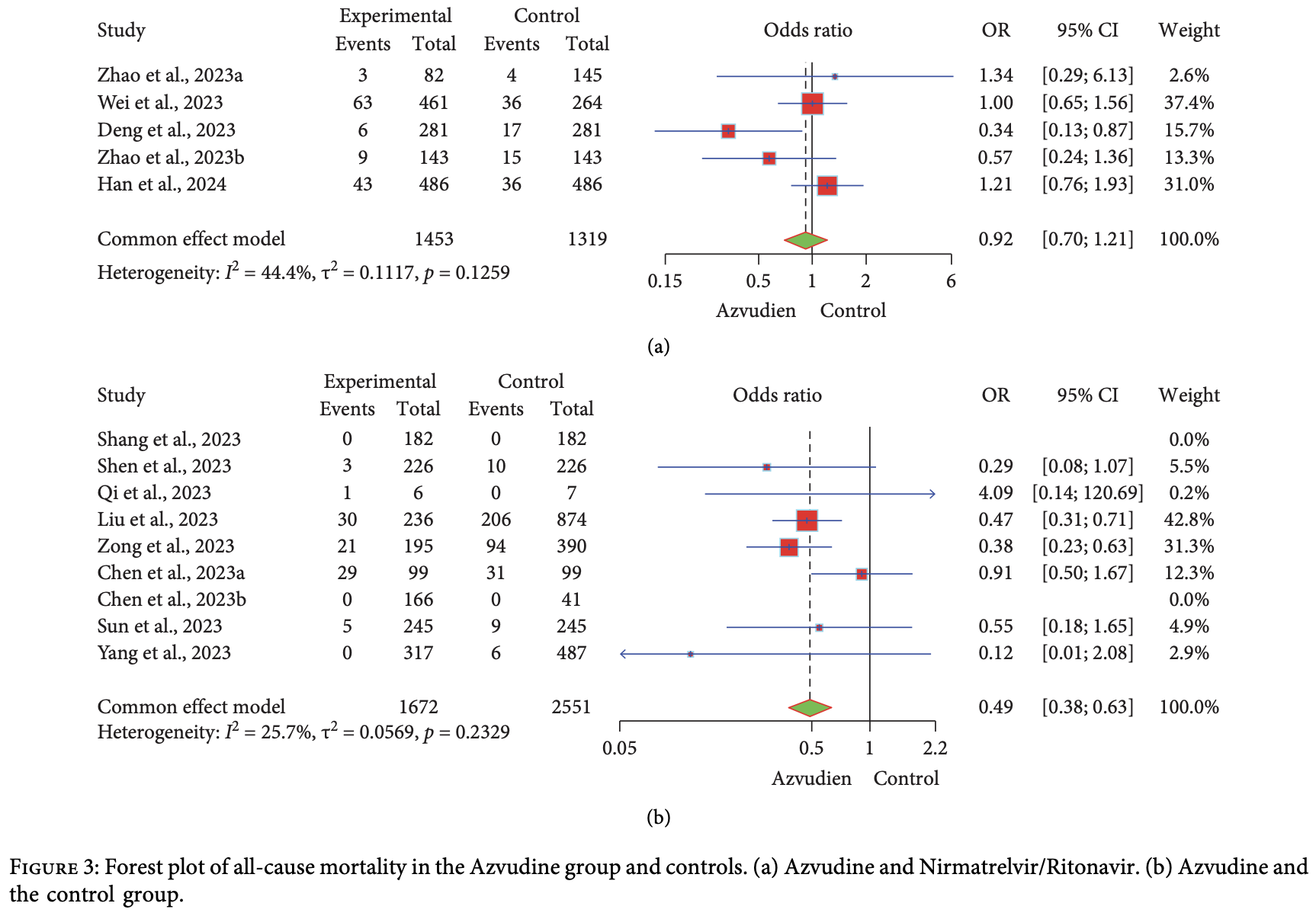
Background: Azvudine, as an antiviral drug, has been approved for the treatment of COVID-19, and multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and retrospective cohort studies have been conducted. Tis study aimed to systematically evaluate the efcacy and safety of Azvudine in treating COVID-19 patients. Methods: As of December 1, 2023, we searched databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Ovid, ICTRP, Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, MedRxiv, and Springer Link for relevant RCTs and retrospective cohort studies. EndNote X9 was used for literature screening and management, and R software was employed for meta-analysis. Results: A total of 1142 COVID-19 patients from fve RCTs were included, with 575 patients receiving Azvudine treatment. Azvudine signifcantly reduced the hospitalization time and the time to nucleic acid conversion to negative in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. However, compared to the control group, Azvudine did not signifcantly reduce the incidence of adverse events (AEs) (risk ratio: 0.89, 95% confdence interval [CI]: 0.80, 1.00). Additionally, eight ongoing clinical trials were included to evaluate the efcacy and safety of Azvudine. In fourteen retrospective cohort studies, a total of 6602 COVID-19 patients were analyzed, with 3118 patients receiving Azvudine treatment. Azvudine signifcantly reduced all-cause mortality (odds ratio [OR]: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.38, 0.63). Te incidence of AEs in the Azvudine group and the Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir group was 4.13% (60/1453) and 5.08% (67/1319), respectively, indicating that Azvudine signifcantly reduced the incidence of AEs compared to Nirmatrelvir/ Ritonavir (OR: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.47, 0.98). Conclusions: Azvudine signifcantly reduced the hospitalization time and the time to nucleic acid conversion to negative in COVID-19 patients and signifcantly lowered all-cause mortality (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation [GRADE]: high-certainty evidence). In terms of safety, Azvudine demonstrated a favorable safety profle (GRADE: moderate-certainty evidence because of suspected publication bias and residual confounding). Further large-scale studies are needed to validate its efcacy and safety.
Ethics Statement Te authors have nothing to report.
Consent Te authors have nothing to report.
Conflicts of Interest Te authors declare no conficts of interest.
Author Contributions Kai Wang, Huling Li, Qian He, Dandan Tang, and Dandan Lin conceived and designed the study. Abiden Kapar, Kai Peng, and Yida Wang performed the main data collection and analyses under the supervision of Huling Li, Qian He, and Dandan Lin. Kai Wang, Qian He, and Huling Li helped with the analyses. Abiden Kapar wrote the draft of the manuscript. All authors have contributed to, seen, and approved the fnal, submitted version of the manuscript.
Supporting Information Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section. (Supporting Information) Figure S1 -S5. Sensitivity analysis of adverse events in RCTs. Figure S6 -S10. Sensitivity analysis of serious adverse events in RCTs. Figure S11 -S24. Sensitivity analysis of all-cause mortality in retrospective cohort studies. Figure S25 -S38. Sensitivity analysis of composite disease progression in retrospective cohort studies. Figure S39 -S52. Sensitivity analysis of adverse events in retrospective cohort studies. Figure S53 -S71. Sensitivity analysis of adverse events in all included studies. Table S1 . Quality assessment of included RCTs. Table S2 . Quality assessment of included retrospective cohort studies. Table S3 . Severity of COVID-19 upon admission of patients. Figure S72 . Stacked graph of..
References
Agarwal, Hunt, Stegemann, A Living WHO Guideline on Drugs for covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Amani, Amani, Azvudine Versus Paxlovid in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2551
Amani, Amani, Efectiveness and Safety of Azvudine in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772
Chang, 4′-Modifed Nucleosides for Antiviral Drug Discovery: Achievements and Perspectives, Accounts of Chemical Research, doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00697
Chen, Guo, Deng, All-Cause Mortality in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Patients with Myocardial Injury Receiving Versus Not Receiving Azvudine: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis, Cardiology, doi:10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049
Chen, Tian, Efcacy and Safety of Azvudine in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153
Chen, Xu, Hong, Oral Azvudine (FNC) Tablets in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: A Retrospective Cohort Study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.05.23284180
Da Silva, Abreu Cabral, De Souza, Serial Viral Load Analysis by DDPCR to Evaluate FNC Efcacy and Safety in the Treatment of Mild Cases of COVID-19, Frontiers of Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485
De Souza, Cabral, Da Silva, Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study: A Study on the Safety and Clinical Efcacy of AZVUDINE in Moderate COVID-19 Patients, Frontiers of Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916
Deng, Li, Sun, Real-World Efectiveness of Azvudine Versus Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Gao, Luo, Hu, Ma, Real-World Efectiveness of Azvudine: Elixir or Equivocal Answer?, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28940
Han, Gao, Li, Real-World Efectiveness of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Versus Azvudine in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 During the Omicron Wave in Beijing: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8
Han, Gao, Li, Yuan, Cui et al., Real-world efectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in Beijing: a multicenter retrospective cohort study, BMC Infect Dis
Jiang, Sun, Zhao, Zhang, Liu et al., Presence of the M184I Mutation After Short-Term Exposure to Azvudine for COVID-19 in People Living with HIV, AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564
Kapar, Xie, Guo, Efectiveness of Azvudine Against Severe Outcomes Among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in Xinjiang, China: A Single-Center, Retrospective, Matched Cohort Study, Expert Review of Anti-infective Terapy, doi:10.1080/14787210.2024.2362900
Khoo, Fitzgerald, Saunders, Molnupiravir Versus Placebo in Unvaccinated and Vaccinated Patients With Early SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): A Randomised, placebo-controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 2 Trial, Te Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2
Lan, Li, Li, Zhou, Lin, 112 Cases of Adverse Drug Reactions Induced by Azvudine Tablets in Patients With COVID-19, Zhongnan Pharmacy, doi:10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2024.06.040
Lei, Chen, Wu, Duan, Men, Small Molecules in the Treatment of COVID-19, Signal Transduction and Targeted Terapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8
Liu, Liang, Gao, Separation and Quantifcation of Azvudine in Plasma of Patients with COVID-19 Using LC-MS/ MS, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115736
Liu, Yang, Xu, Azvudine and Mortality in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110824
Liu, Yang, Xu, Li, Cai et al., Azvudine and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study, Int Immunopharmacol
Mao, Dian, Sun, Chen, Zhu et al., Lactate Dehydrogenase Predicts Disease Progression Outcome in COVID-19 Patients Treated With Azvudine, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1237277
Qi, Yang, Gong, Li, Liang, Real-World Efectiveness of Azvudine for Patients Infected With the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.5 in an Intensive Care Unit, Journal of Toracic Disease, doi:10.21037/jtd-23-1093
Qi, Yang, Gong, Li, Liang, Real-world efectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.5 in an intensive care unit, J Torac Dis
Ren, Luo, Yu, A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, A Pilot Study, Advanced Science, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Sarkar, Mondal, Islam, Potential Terapeutic Options for COVID-19: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.572870
Schöley, Aburto, Kashnitsky, Life Expectancy Changes Since COVID-19, Nature Human Behaviour, doi:10.1038/s41562-022-01450-3
Shang, Fu, Geng, Azvudine Terapy of Common COVID-19 in Hemodialysis Patients, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29007
Shang, Fu, Geng, Zhang, Zhang et al., Azvudine therapy of common COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients, J Med Virol
Shen, Xiao, Sun, Li, Wu et al., Real-world efectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
Shen, Xiao, Sun, Real-World Efectiveness of Azvudine in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899
Sun, Jin, Dian, Oral Azvudine for Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-Existing Conditions: A Retrospective Cohort Study, eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981
Wei, Zeng, Wang, Head-to-Head Comparison of Azvudine and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for the Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study with Propensity Score Matching, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-World Efectiveness of Early Molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 Without Supplemental Oxygen Requirement on Admission During Hong Kong's Omicron BA.2 Wave: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2
Yang, Wang, Bench-To-Bedside: Innovation of Small Molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drugs in China, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115503
Yang, Wang, Jiang, Oral Azvudine for Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 in High Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults: Results of a Real-World Study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947
Yu, Chang, A Nearly 20-Year Journey to Success of Azvudine for Antiviral Terapy, Chinese Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.1002/cjoc.202300361
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): A Promising Clinical Candidate for COVID-19 Treatment, Signal Transduction and Targeted Terapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, Te First Chinese Oral Anti-COVID-19 Drug Azvudine Launched, Innovation, doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Zhang, -H Luo, Chen, Te Study of Azvudine Activity Against Dengue Viruses in Vitro, Yaoxue Xuebao, doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2018-0245
Zhang, Jiao, Li, Elevated INR in a COVID-19 Patient After Concomitant Administration of Azvudine and Anticoagulants, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1191608
Zhang, Li, Wang, Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drug Efective in Treating COVID-19 Patients, Signal Transduction and Targeted Terapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Efcacy of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Versus Azvudine for COVID-19 Treatment in Tibet: A Retrospective Study, Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S423725
Zhao, Zheng, Han, Is Azvudine Comparable to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in Real-World Efcacy and Safety for Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19? A Retrospective Cohort Study, Infectious Disease and Terapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7
Zhong, Zhao, Peng, Zou, Yang, Recent Advances in Small-Molecular Terapeutics for COVID-19, Precision Clinical Medicine, doi:10.1093/pcmedi/pbac024
Zhu, Efcacy and Safety Evaluation of Azvudine in the Prospective Treatment of COVID-19 Based on Four Phase III Clinical Trials, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548
Zong, Zhou, Li, Jiang, Liu et al., Azvudine Reduces the In-Hospital Mortality of COVID-19 Patients: a Retrospective Cohort Study, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007
Zong, Zhou, Li, Jiang, Liu et al., Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study, Acta Pharm Sin B
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1155/cjid/3645253",
"ISSN": [
"1712-9532",
"1918-1493"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/cjid/3645253",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> Azvudine, as an antiviral drug, has been approved for the treatment of COVID‐19, and multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and retrospective cohort studies have been conducted. This study aimed to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of Azvudine in treating COVID‐19 patients.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> As of December 1, 2023, we searched databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Ovid, ICTRP, Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, MedRxiv, and Springer Link for relevant RCTs and retrospective cohort studies. EndNote X9 was used for literature screening and management, and R software was employed for meta‐analysis.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> A total of 1142 COVID‐19 patients from five RCTs were included, with 575 patients receiving Azvudine treatment. Azvudine significantly reduced the hospitalization time and the time to nucleic acid conversion to negative in patients with mild to moderate COVID‐19. However, compared to the control group, Azvudine did not significantly reduce the incidence of adverse events (AEs) (risk ratio: 0.89, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.80, 1.00). Additionally, eight ongoing clinical trials were included to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Azvudine. In fourteen retrospective cohort studies, a total of 6602 COVID‐19 patients were analyzed, with 3118 patients receiving Azvudine treatment. Azvudine significantly reduced all‐cause mortality (odds ratio [OR]: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.38, 0.63). The incidence of AEs in the Azvudine group and the Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir group was 4.13% (60/1453) and 5.08% (67/1319), respectively, indicating that Azvudine significantly reduced the incidence of AEs compared to Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (OR: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.47, 0.98).</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusions:</jats:bold> Azvudine significantly reduced the hospitalization time and the time to nucleic acid conversion to negative in COVID‐19 patients and significantly lowered all‐cause mortality (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation [GRADE]: high‐certainty evidence). In terms of safety, Azvudine demonstrated a favorable safety profile (GRADE: moderate‐certainty evidence because of suspected publication bias and residual confounding). Further large‐scale studies are needed to validate its efficacy and safety.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1155/cjid/3645253"
],
"article-number": "3645253",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2025-02-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-09-08"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-09-26"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0007-6891-4756",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kapar",
"given": "Abiden",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Huling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Qian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Dandan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Dandan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Kai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6224-8453",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Kai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T13:53:08Z",
"timestamp": 1758894788000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T13:53:13Z",
"timestamp": 1758894793000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hariyanto",
"given": "Timotius Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-27T00:09:21Z",
"timestamp": 1758931761686,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 268,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1758844800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1155/cjid/3645253",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_1_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_15_2_2",
"unstructured": "Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 2023 https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---27-april-2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cjoc.202300361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41562-022-01450-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.572870",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pcmedi/pbac024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1191608",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00697",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.16438/j.0513-4870.2018-0245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2023.1237277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28940",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115736",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115503",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0000000000003564",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_19_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_15_20_2",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVlD-19 (Tenth Trial Edition) 2023 http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ylyjs/pqt/202301/32de5b2ff9bf4eaa88e75bdf7223a65a.shtml."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/jtd-23-1093",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110824",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.01.05.23284180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28947",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0298772",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2551",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2024.06.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2024.2362900",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_15_44_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/cjid/3645253"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real‐World Evaluation Study of Azvudine for the Treatment of Patients With COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "2025"
}