Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772, PROSPERO CRD42023449248, Jun 2024
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
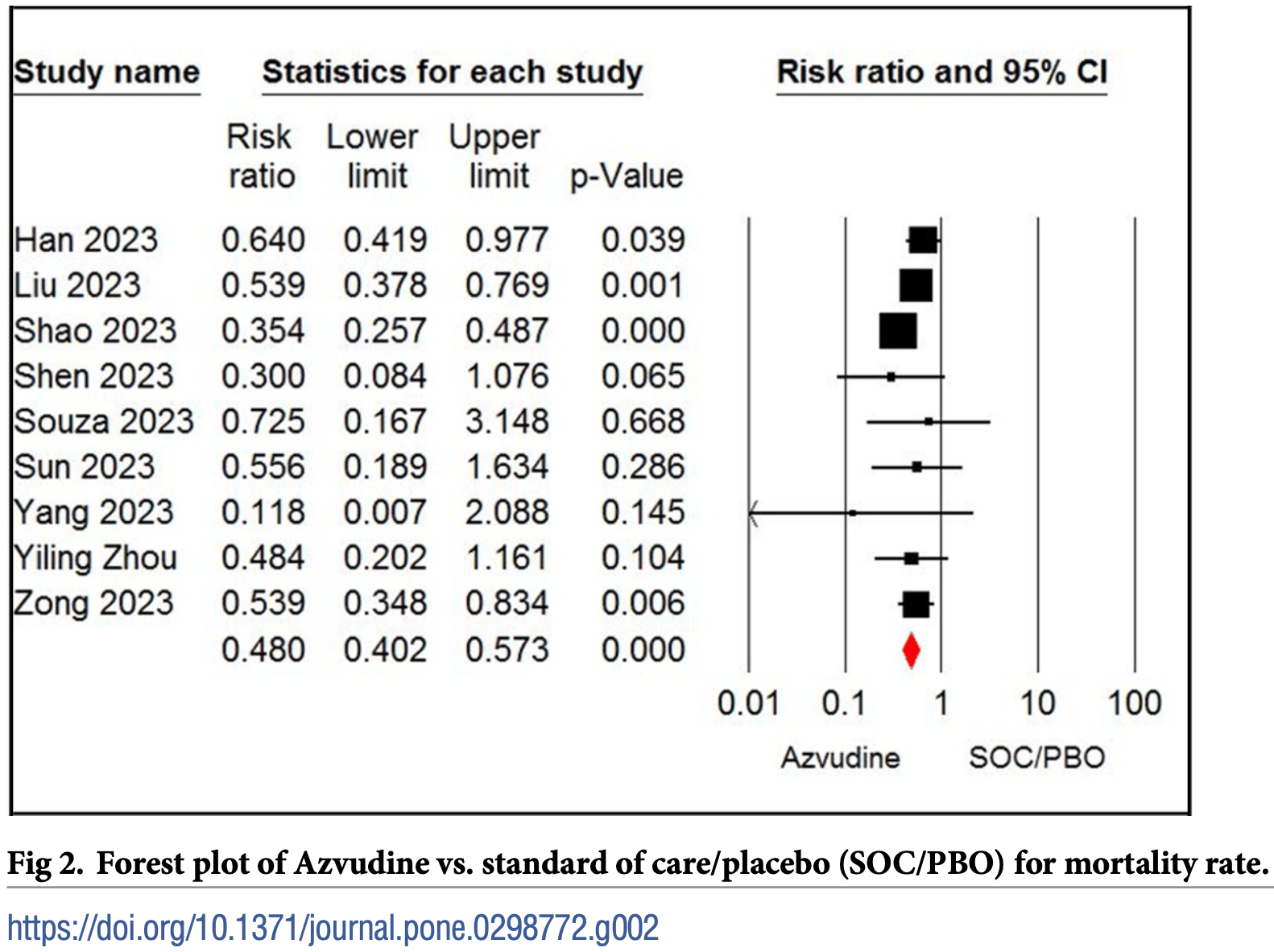
Meta analysis of 21 studies (7 studies have no control, comparing with paxlovid) with 10,011 COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality and faster viral clearance with azvudine treatment compared to standard of care or placebo, while there were no significant differences for length of hospitalization, ICU admission, or need for mechanical ventilation. Compared to paxlovid, azvudine was associated with lower mortality, ICU admission, and need for mechanical ventilation, while there were no significant differences in viral clearance or hospitalization time. Authors rated the certainty of evidence as low or moderate.
5 meta-analyses show significant improvements with azvudine for mortality1-5,
mechanical ventilation1,
improvement1,
progression5, and
viral clearance1,3,4 .
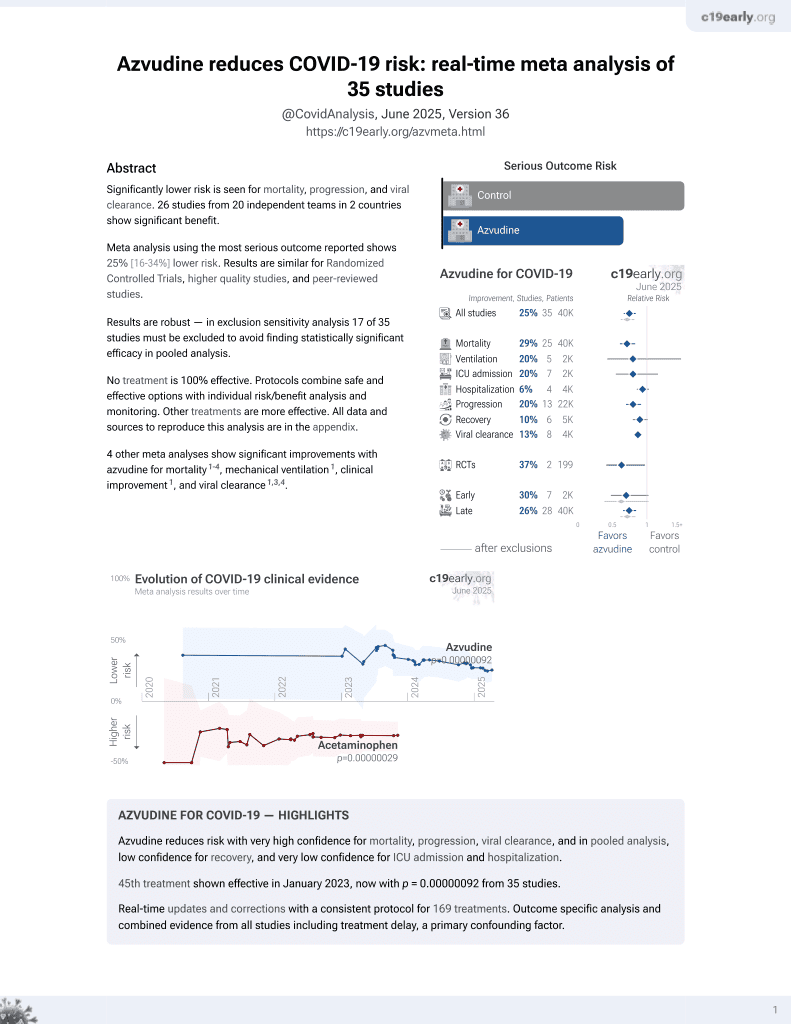
Currently there are 40 azvudine for COVID-19 studies, showing 30% lower mortality [20‑39%], 18% lower ventilation [-10‑39%], 21% lower ICU admission [5‑34%], and 10% lower hospitalization [0‑19%].
|
risk of death, 52.0% lower, RR 0.48, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 9.7% lower, RR 0.90, p = 0.71.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 31.3% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.51.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zheng et al., Small-molecule antivirals treatment for COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107096.
2.
Wang et al., Effectiveness of azvudine in reducing mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02316-y.
3.
Amani et al., Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772.
Amani et al., 13 Jun 2024, peer-reviewed, 2 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023449248.
Contact: b_amani@alumnus.tums.ac.ir.
Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772
Objective The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of azvudine in treating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2).
Methods A search was carried out in PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, medRxiv, and Google Scholar until October 20, 2023. The Cochrane risk of bias tools were used to assess the quality of included studies. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software was used to analyze data.
Results Twenty-one studies including 10,011 patients were examined. The meta-analysis results showed that azvudine and standard of care/placebo (SOC/PBO) were significantly different concerning mortality rate (risk ratio [RR] = 0.48, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.40 to 0.57) and negative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) conversion time (standard mean difference = -0.75, 95% CI: -1.29 to-0.21). However, the two groups did not show significant differences concerning hospital stay, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and need for mechanical ventilation (P > 0.05). On the other hand, azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir were significantly different in mortality rate (RR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.58 to 0.92), ICU admission (RR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.21 to 0.78), and need for mechanical ventilation (RR = 0.67, 95% CI: 0.51 to 0.89), but the two treatments were not significantly different in negative PCR conversion time, and hospital stay (P > 0.05). The incidence of adverse events between groups was not significant (P > 0.05). The certainty of evidence was rated as low or moderate.
Conclusions The antiviral effectiveness of azvudine against SARS-COV-2 is questionable with regard to the certainty of evidence. Further research should be conducted to establish the effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19.
Supporting information S1
Author Contributions Conceptualization: Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani. Formal analysis: Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani. Methodology: Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani. Project administration: Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani. Writing -original draft: Behnam Amani. Writing -review & editing: Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani.
References
Amani, Amani, Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a rapid review and meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28441
Amstutz, Speich, Mentre, Effects of remdesivir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00528-8
Anhua, Lu, Gong, Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294
Benaicha, Khenhrani, Veer, Efficacy of Molnupiravir for the Treatment of Mild or Moderate COVID-19 in Adults: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.38586
Cegolon, Pol, Simonetti, Filon, Luzzati, Molnupiravir, Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, or Sotrovimab for High-Risk COVID-19 Patients Infected by the Omicron Variant: Hospitalization, Mortality, and Time until Negative Swab Test in Real Life, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16050721
Cheema, Jafar, Sohail, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28471
Chen, Guo, Deng, All-cause mortality in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: a propensity score-matched analysis, Cardiology plus, doi:10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049
Chen, Tian, Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153
Chen, Xu, Hong, Oral azvudine (FNC) tablets in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: a retrospective cohort study, medRxiv
Da Silva, Abreu Cabral, Souza, Serial viral load analysis by DDPCR to evaluate FNC efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of COVID-19, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485
Deng, Li, Sun, Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012
Fu, Chen, Comparison of the Different Medications for COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients, Authorea
Gao, Luo, Hu, Ma, Real-world effectiveness of azvudine: Elixir or equivocal answer?, Journal of medical virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28940
Gao, Luo, Ren, Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Han, Han, Wang, Effectiveness and Optimal Timing of Azvudine in COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-center Retrospective Study in Beijing
Higgins, Savović, Page, Elbers, Sterne, Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions
Li, Liu, Shen, Deng, Evaluate clinical effectiveness of Azvudine with data rather than speculation, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28926
Liu, Yang, Xu, Azvudine and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110824
Moher, Shamseer, Clarke, Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement, Systematic reviews, doi:10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Qi, Yang, Gong, Li, Liang, Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA. 5 in an intensive care unit, Journal of Thoracic Disease, doi:10.21037/jtd-23-1093
Raman, Patel, Ranjan, COVID-19: unmasking emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, vaccines and therapeutic strategies, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11070993
Ren, Luo, Yu, A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Advanced Science, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Shang, Fu, Geng, Azvudine therapy of common COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29007
Shao, Fan, Guo, Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11071859
Shen, Xiao, Sun, Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, medRxiv
Souza, Cabral, Da Silva, None, PLA-CEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL STUDY: STUDY ON SAFETY AND CLINICAL EFFICACY OF AZVUDINE (FNC) IN MODERATE COVID-19 PATIENTS. Frontiers in Medicine
Souza, Cg, Rojas-Corte ´s, Barbosa, Bambirra et al., Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 and at high risk of hospitalization: Systematic review and meta-analyses of observational studies, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0284006
Sterne, Herna ´n, Reeves, ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions, doi:10.1136/bmj.i4919
Sun, Dian, Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Tian, Chen, Feng, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir compared with other antiviral drugs for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28732
Tian, Yang, Song, Efficacy and safety of paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) in the treatment of COVID-19: An updated meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2473
Wang, Yang, Luo, Azvudine, a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105617
Yang, Wang, Jiang, Oral azvudine for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real-world study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation (Camb), doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Zhang, Coello, Guyatt, GRADE guidelines: 20. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences-inconsistency, imprecision, and other domains, Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.05.011
Zhang, Li, Wang, Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhang, Yang, Chen, Yue, Zhang et al., Why does COVID-19 continue to spread despite mass vaccination? Frontiers in public health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.938108
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Efficacy of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir versus Azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: A retrospective study, Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S423725
Zhao, Zheng, Han, Is Azvudine Comparable to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in Real-World Efficacy and Safety for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19? A Retrospective Cohort Study, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7
Zhou, Liu, Jiang, Azvudine and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in Hospitalised Patients with Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: Emulation of a Randomised Target Trial
Zong, Zhou, Li, Jiang, Liu et al., Azvudine Reduce the In-Hospital Mortality of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0298772",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0298772",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of azvudine in treating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2).</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n<jats:p>A search was carried out in PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, medRxiv, and Google Scholar until October 20, 2023. The Cochrane risk of bias tools were used to assess the quality of included studies. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software was used to analyze data.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Twenty-one studies including 10,011 patients were examined. The meta-analysis results showed that azvudine and standard of care/placebo (SOC/PBO) were significantly different concerning mortality rate (risk ratio [RR] = 0.48, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.40 to 0.57) and negative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) conversion time (standard mean difference = - 0.75, 95% CI: -1.29 to—0.21). However, the two groups did not show significant differences concerning hospital stay, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and need for mechanical ventilation (P > 0.05). On the other hand, azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir were significantly different in mortality rate (RR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.58 to 0.92), ICU admission (RR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.21 to 0.78), and need for mechanical ventilation (RR = 0.67, 95% CI: 0.51 to 0.89), but the two treatments were not significantly different in negative PCR conversion time, and hospital stay (P > 0.05). The incidence of adverse events between groups was not significant (P > 0.05). The certainty of evidence was rated as low or moderate.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The antiviral effectiveness of azvudine against SARS-COV-2 is questionable with regard to the certainty of evidence. Further research should be conducted to establish the effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amani",
"given": "Bahman",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4298-1807",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Amani",
"given": "Behnam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-13T17:33:23Z",
"timestamp": 1718300003000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-13T17:33:52Z",
"timestamp": 1718300032000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Octavius",
"given": "Gilbert Sterling",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-14T00:35:01Z",
"timestamp": 1718325301700
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1718236800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0298772",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0298772",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.938108",
"article-title": "Why does COVID-19 continue to spread despite mass vaccination?",
"author": "S Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "938108",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in public health",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref001",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28441",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID‐19: a rapid review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "B Amani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28441",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref002",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00528-8",
"article-title": "Effects of remdesivir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials",
"author": "A Amstutz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref003",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of Molnupiravir for the Treatment of Mild or Moderate COVID-19 in Adults: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "K Benaicha",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref004",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph16050721",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir, Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, or Sotrovimab for High-Risk COVID-19 Patients Infected by the Omicron Variant: Hospitalization, Mortality, and Time until Negative Swab Test in Real Life",
"author": "L Cegolon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "721",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref005",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real‐world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID‐19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "G Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28756",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref006",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Y Dian",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref007",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open‐label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID‐19, a pilot study",
"author": "Z Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2001435",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Advanced Science",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref008",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0105617",
"article-title": "Azvudine, a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro",
"author": "R-R Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e105617",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref009",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "B Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref010",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched",
"author": "B Yu",
"first-page": "100321",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Innovation (Camb)",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref011",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "J-L Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref012",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral azvudine (FNC) tablets in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "W Chen",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref013",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Y Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e158",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref014",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2046-4053-4-1",
"article-title": "Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement",
"author": "D Moher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Systematic reviews",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref015",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions",
"author": "JA Sterne",
"journal-title": "bmj",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref016",
"volume": "355",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9781119536604.ch8",
"article-title": "Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial",
"author": "JP Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref017",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.05.011",
"article-title": "GRADE guidelines: 20. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences—inconsistency, imprecision, and other domains",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Epidemiology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref018",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "M Shen",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref019",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Y Sun",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref020",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049",
"article-title": "All-cause mortality in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: a propensity score-matched analysis",
"author": "R Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cardiology plus",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref021",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Z Chen",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref022",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28940",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine: Elixir or equivocal answer?",
"author": "Y Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28940",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of medical virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref023",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28926",
"article-title": "Evaluate clinical effectiveness of Azvudine with data rather than speculation",
"author": "D Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28926",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref024",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "W Anhua",
"first-page": "1274294",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref025",
"volume": "14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485",
"article-title": "Serial viral load analysis by DDPCR to evaluate FNC efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of COVID-19",
"author": "RM da Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1143485",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref026",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916",
"article-title": "PHASE III, RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL STUDY: STUDY ON SAFETY AND CLINICAL EFFICACY OF AZVUDINE (FNC) IN MODERATE COVID-19 PATIENTS",
"author": "SB De Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1215916",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref027",
"volume": "10"
},
{
"author": "X Han",
"journal-title": "Effectiveness and Optimal Timing of Azvudine in COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-center Retrospective Study in Beijing, China",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref028",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110824",
"article-title": "Azvudine and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "B Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110824",
"journal-title": "International Immunopharmacology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref029",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/jtd-23-1093",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA. 5 in an intensive care unit",
"author": "X Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4925",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Journal of Thoracic Disease",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref030",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29007",
"article-title": "Azvudine therapy of common COVID‐19 in hemodialysis patients",
"author": "S Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29007",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref031",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China",
"author": "J Shao",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref032",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28947",
"article-title": "Oral azvudine for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real‐world study",
"author": "H Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28947",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref033",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparison of the Different Medications for COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Authorea",
"author": "JP Yingxin Fu",
"first-page": "2023",
"journal-title": "June",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref034",
"volume": "26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7",
"article-title": "Is Azvudine Comparable to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in Real-World Efficacy and Safety for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19? A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Q Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2087",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref035",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir versus Azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: A retrospective study",
"author": "X Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6053",
"journal-title": "Infection and Drug Resistance",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref036",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "Y Zhou",
"journal-title": "Azvudine and Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir in Hospitalised Patients with Moderate–To–Severe COVID–19: Emulation of a Randomised Target Trial",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref037",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Azvudine Reduce the In-Hospital Mortality of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"author": "K Zong",
"journal-title": "Available at SSRN 4380058",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref038",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11070993",
"article-title": "COVID-19: unmasking emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, vaccines and therapeutic strategies",
"author": "R Raman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "993",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref039",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28471",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir–ritonavir for the treatment of COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "HA Cheema",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28471",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref040",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28732",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir–ritonavir compared with other antiviral drugs for the treatment of COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "F Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28732",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref041",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0284006",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 and at high risk of hospitalization: Systematic review and meta-analyses of observational studies",
"author": "CG Souza KM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0284006",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref042",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2473",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) in the treatment of COVID‐19: An updated meta‐analysis and trial sequential analysis",
"author": "H Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2473",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Reviews in Medical Virology",
"key": "pone.0298772.ref043",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0298772"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "19"
}