Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2, May 2022 (preprint)
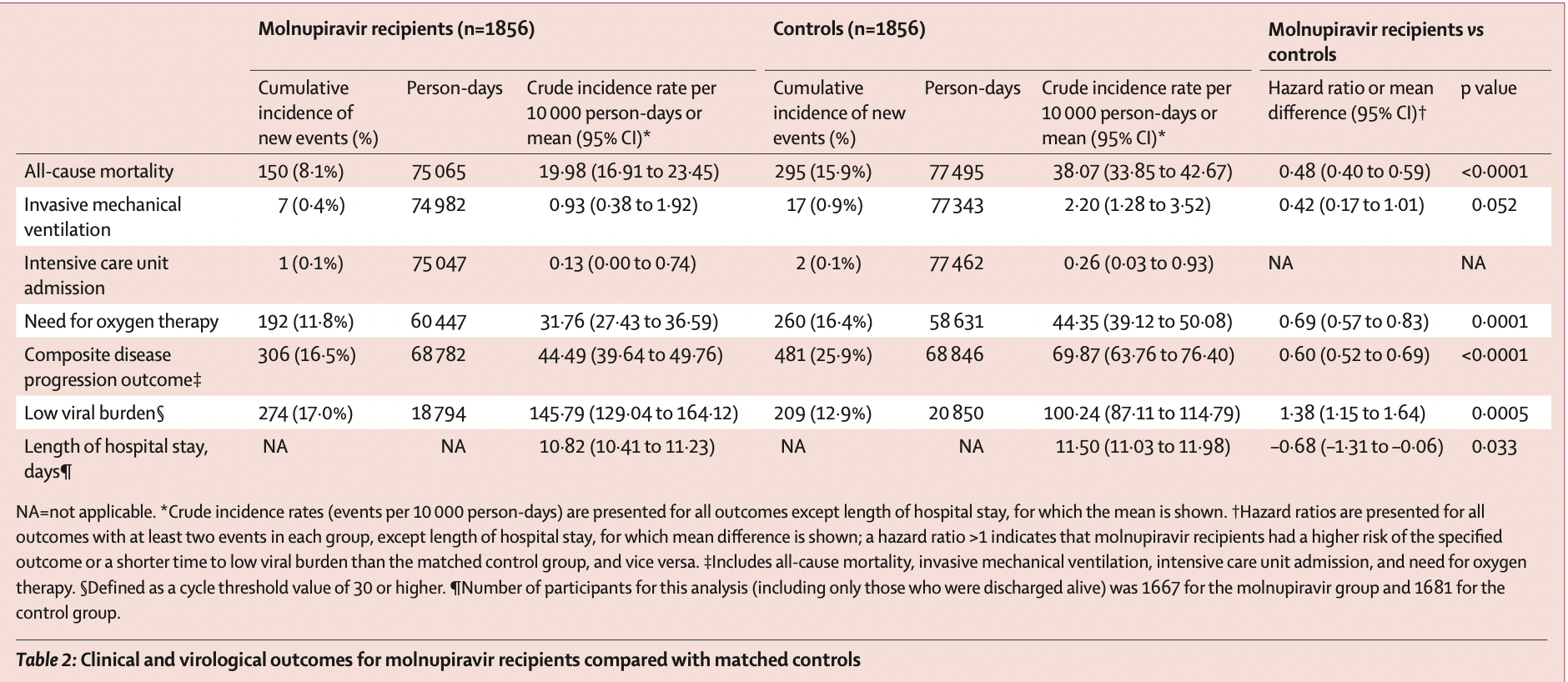
PSM retrospective 40,776 patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality and lower combined mortality, ventilation, ICU, and oxygen therapy with molnupiravir treatment.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments25.
Study covers paxlovid and molnupiravir.
|
risk of death, 52.0% lower, HR 0.48, p < 0.001, treatment 1,856, control 1,856, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 58.0% lower, HR 0.42, p = 0.06, treatment 1,856, control 1,856, propensity score matching.
|
|
combined death/ventilation/ICU/oxygen, 40.0% lower, HR 0.60, p < 0.001, treatment 1,856, control 1,856, propensity score matching.
|
|
hospitalization time, 5.9% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.03, treatment 1,856, control 1,856, propensity score matching.
|
|
Ct<30, 27.5% lower, HR 0.72, p < 0.001, treatment 1,856, control 1,856, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wong et al., 20 May 2022, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 26 February, 2022 - 26 April, 2022.
Contact: carlosho@hku.hk, bcowling@hku.hk.
Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study
The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00507-2
Background Data on the effectiveness of oral antivirals in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 are urgently needed. This retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the clinical and virological outcomes associated with molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir use in hospitalised patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 during a pandemic wave dominated by the omicron BA.2 subvariant. Methods We analysed data from a territory-wide retrospective cohort of patients in Hong Kong who were hospitalised with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection between Feb 26 and April 26, 2022. Data were extracted from the Hospital Authority, the Department of Health, and the Hong Kong Death Registry. Patients were eligible for inclusion if their admission date was within 3 days before or after confirmation of their COVID-19 diagnosis. Those who were admitted to hospital more than 5 days after symptom onset, were younger than 18 years, had a history of oral antiviral use before admission, required supplemental oxygen on admission, had drug-related contraindications to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir use, or had severe renal or severe liver impairment were excluded. Patients who received the oral antivirals molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir were matched with controls using propensity-score matching in a ratio of 1:1. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality and secondary outcomes included a composite outcome of disease progression (all-cause mortality, initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation [IMV], intensive care unit [ICU] admission, or the need for oxygen therapy) and each of these individual disease progression outcomes, and time to reaching a low viral burden (RT-PCR cycle threshold value ≥30). For each event outcome, crude incidence rates were calculated and hazard ratios (HRs) estimated using Cox regression models. Findings We identified 40 776 patients hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection during the study period, with a mean follow-up of 41•3 days (total 925 713 person-days). After exclusions and propensity-score matching, we included 1856 molnupiravir recipients and 1856 matched controls, and 890 nirmatrelvir-ritonavir recipients and 890 matched controls. A lower risk of all-cause mortality was observed in molnupiravir recipients (crude incidence rate per 10 000 person-days 19•98 events [95% CI 16•91-23•45]) versus matched controls (38•07 events [33•85-42•67]; HR 0•48 [95% CI 0•40-0•59], p<0•0001) and in nirmatrelvir-ritonavir recipients (10•28 events [7•03-14•51]) versus matched controls (26•47 events [21•34-32•46]; HR 0•34 [0•23-0•50], p<0•0001). Oral antiviral recipients also had lower risks of the composite disease progression outcome (molnupiravir HR 0•60 [95% CI 0•52-0•69], p<0•0001; nirmatrelvir-ritonavir 0•57 [0•45-0•72], p<0•0001) and need for oxygen therapy (molnupiravir 0•69 [0•57-0•83], p=0•0001; nirmatrelvir-ritonavir 0•73 [0•54-0•97], p=0•032) compared with controls. Time to achieving a low viral burden was..
References
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Oral nirmatrelvir and severe COVID-19 outcomes during the omicron surge, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1705061/v1
Arribas, Bhagani, Lobo, Randomized trial of molnupiravir or placebo in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, NEJM Evidence
Austin, Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations, Biom J
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Bojkova, Widera, Ciesek, Wass, Michaelis et al., Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in omicron variant compared to delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates, Cell Res
Fischer Wa 2nd, Eron, Jr, Holman, A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus, Sci Transl Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Hetero, Hetero announces interim clinical results from phase III clinical trials of molnupiravir conducted in India
Johnson, Puenpatom, Moncada, Effect of molnupiravir on biomarkers, respiratory interventions, and medical services in COVID-19: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/m22-0729
Leyrat, Seaman, White, Propensity score analysis with partially observed covariates: how should multiple imputation be used?, Stat Methods Med Res
Li, Wang, Lavrijsen, SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination, Cell Res
Merck, Merck and Ridgeback to present data demonstrating that treatment with Lagevrio (molnupiravir) was associated with more rapid elimination of infectious SARS-CoV-2 than placebo
Monedero, Gea, Castro, Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study, Crit Care
Mótyán, Mahdi, Hoffka, Tőzsér, Potential resistance of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) against protease inhibitors: lessons learned from HIV-1 protease, Int J Mol Sci
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac443
Renoux, Azoulay, Suissa, Biases in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: designing real-world evidence studies, Am J Epidemiol
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral COVID antiviral drugs, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac180
Singh, Singh, Singh, Misra, Molnupiravir in COVID-19: a systematic review of literature, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Soriano, De-Mendoza, Edagwa, Oral antivirals for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection, AIDS Rev
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against COVID-19 omicron variant, N Engl J Med
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2, N Engl J Med
Ullrich, Ekanayake, Otting, Nitsche, Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir, Bioorg Med Chem Lett
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res
Waters, Warren, Hughes, Lewis, Zhang, Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environ Mol Mutagen
White, Royston, Wood, Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice, Stat Med
Who, Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline
Wong, Lau, Au, Xiong, Lau et al., Clinical improvement, outcomes, antiviral activity, and costs associated with early treatment with remdesivir for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis
Zhou, Hill, Sarkar, β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 through lethal mutagenesis but is also mutagenic to mammalian cells, J Infect Dis
Zou, Peng, Shu, Antiviral efficacy and safety of molnupiravir against omicron variant infection: a randomized controlled clinical trial, Front Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"ISSN": [
"1473-3099"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"alternative-id": [
"S1473309922005072"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00522-9"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Carlos K H",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Au",
"given": "Ivan C H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Kristy T K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Eric H Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowling",
"given": "Benjamin J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Gabriel M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T22:34:53Z",
"timestamp": 1661380493000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T22:35:19Z",
"timestamp": 1661380519000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T23:12:45Z",
"timestamp": 1661382765673
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659312000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309922005072?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309922005072?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.816429",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of antiviral therapy in highly-transmissible variants of SARS-CoV-2: a modeling and simulation study",
"author": "Schöning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib5",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102396",
"article-title": "An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib6",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.855496",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and its antiviral activity against COVID-19",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib7",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o443",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir's authorisation was premature",
"author": "Brophy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o443",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib8",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: FDA expert panel recommends authorising molnupiravir but also voices concerns",
"author": "Dyer",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib9",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o977",
"article-title": "Imbalance in baseline characteristics in molnupiravir trials",
"author": "Hama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o977",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib10",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00119-0",
"article-title": "Availability of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and the requirement for an ethical prescribing approach",
"author": "Dal-Ré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e231",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib11",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100743",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of different therapeutic options for COVID-19 in two Chinese case cohorts: a propensity-score analysis",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib12",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00345-0",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study",
"author": "McMenamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"article-title": "Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib17",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03422-3",
"article-title": "Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "Monedero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib18",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwab028",
"article-title": "Biases in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: designing real-world evidence studies",
"author": "Renoux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1452",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib19",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab631",
"article-title": "Clinical improvement, outcomes, antiviral activity, and costs associated with early treatment with remdesivir for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1450",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib20",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.4067",
"article-title": "Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice",
"author": "White",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib22",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280217713032",
"article-title": "Propensity score analysis with partially observed covariates: how should multiple imputation be used?",
"author": "Leyrat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Stat Methods Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib23",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bimj.200810488",
"article-title": "Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Biom J",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib24",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir–ritonavir: oral COVID antiviral drugs",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib27",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib28",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir and severe COVID-19 outcomes during the omicron surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100044",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of molnupiravir or placebo in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Arribas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evidence",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib31",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-0729",
"article-title": "Effect of molnupiravir on biomarkers, respiratory interventions, and medical services in COVID-19: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9",
"article-title": "Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in omicron variant compared to delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates",
"author": "Bojkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib33",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00618-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib34",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against COVID-19 omicron variant",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib35",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern",
"author": "Vangeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib36",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128629",
"article-title": "Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir",
"author": "Ullrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Bioorg Med Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib37",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib38",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib39",
"series-title": "Hetero announces interim clinical results from phase III clinical trials of molnupiravir conducted in India",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus",
"author": "Fischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib40",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.939573",
"article-title": "Antiviral efficacy and safety of molnupiravir against omicron variant infection: a randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib42",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral antivirals for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Soriano",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "AIDS Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib43",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102329",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir in COVID-19: a systematic review of literature",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib46",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/em.22471",
"article-title": "Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir",
"author": "Waters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Environ Mol Mutagen",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib47",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab247",
"article-title": "β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 through lethal mutagenesis but is also mutagenic to mammalian cells",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib48",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23073507",
"article-title": "Potential resistance of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) against protease inhibitors: lessons learned from HIV-1 protease",
"author": "Mótyán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib49",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1473309922005072"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}