Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2, May 2022 (preprint)
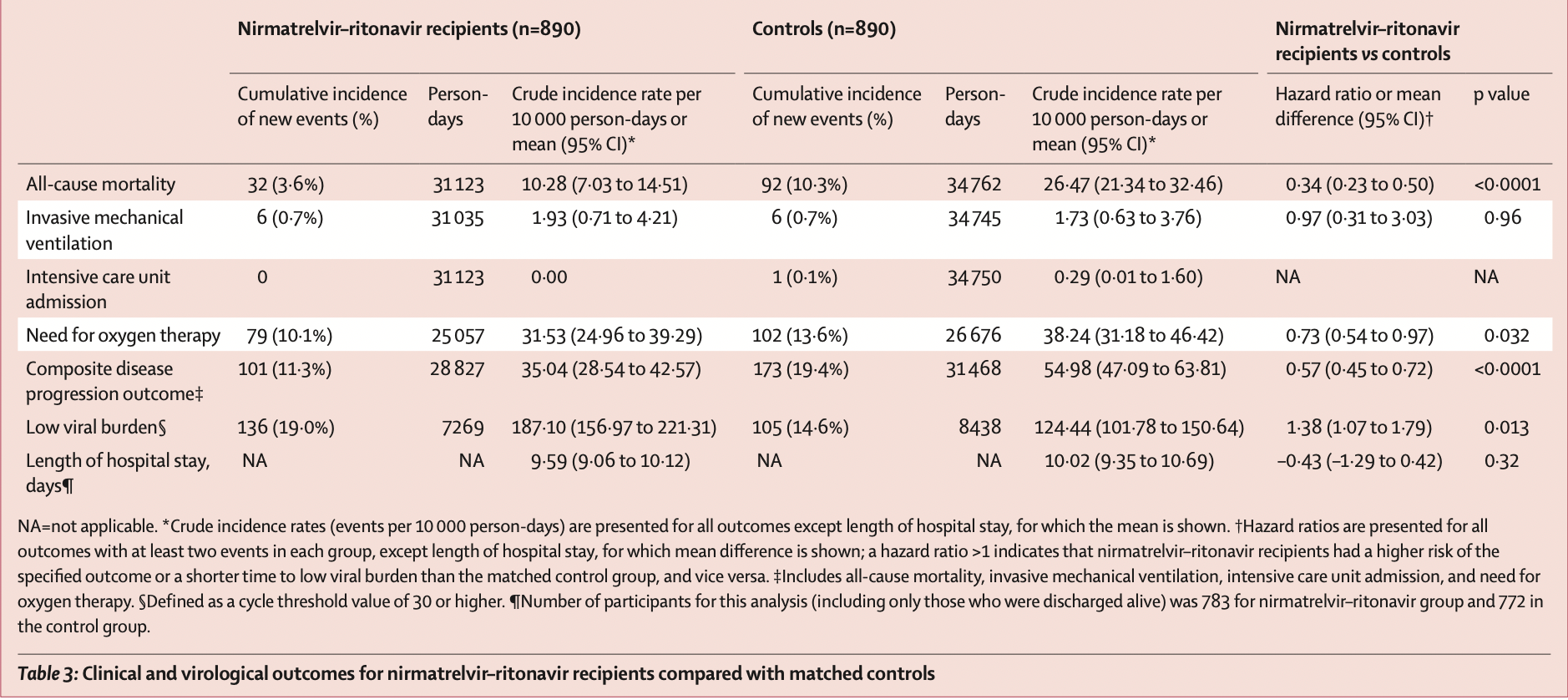
PSM retrospective 40,776 patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality and lower combined mortality, ventilation, ICU, and oxygen therapy with paxlovid treatment.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers paxlovid and molnupiravir.
|
risk of death, 66.0% lower, HR 0.34, p < 0.001, treatment 890, control 890, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 3.0% lower, HR 0.97, p = 0.96, treatment 890, control 890, propensity score matching.
|
|
combined death/ventilation/ICU/oxygen, 43.0% lower, HR 0.57, p < 0.001, treatment 890, control 890, propensity score matching.
|
|
hospitalization time, 4.3% lower, relative time 0.96, p = 0.32, treatment 890, control 890, propensity score matching.
|
|
Ct<30, 27.5% lower, HR 0.72, p = 0.01, treatment 890, control 890, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wong et al., 20 May 2022, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 26 February, 2022 - 26 April, 2022.
Contact: carlosho@hku.hk, bcowling@hku.hk.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"ISSN": [
"1473-3099"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"alternative-id": [
"S1473309922005072"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00522-9"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Carlos K H",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Au",
"given": "Ivan C H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Kristy T K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Eric H Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowling",
"given": "Benjamin J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Gabriel M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T22:34:53Z",
"timestamp": 1661380493000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T22:35:19Z",
"timestamp": 1661380519000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T23:12:45Z",
"timestamp": 1661382765673
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659312000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309922005072?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309922005072?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.816429",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of antiviral therapy in highly-transmissible variants of SARS-CoV-2: a modeling and simulation study",
"author": "Schöning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib5",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102396",
"article-title": "An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib6",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.855496",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and its antiviral activity against COVID-19",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib7",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o443",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir's authorisation was premature",
"author": "Brophy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o443",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib8",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: FDA expert panel recommends authorising molnupiravir but also voices concerns",
"author": "Dyer",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib9",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o977",
"article-title": "Imbalance in baseline characteristics in molnupiravir trials",
"author": "Hama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o977",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib10",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00119-0",
"article-title": "Availability of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and the requirement for an ethical prescribing approach",
"author": "Dal-Ré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e231",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib11",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100743",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of different therapeutic options for COVID-19 in two Chinese case cohorts: a propensity-score analysis",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib12",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00345-0",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study",
"author": "McMenamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"article-title": "Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib17",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03422-3",
"article-title": "Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "Monedero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib18",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwab028",
"article-title": "Biases in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: designing real-world evidence studies",
"author": "Renoux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1452",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib19",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab631",
"article-title": "Clinical improvement, outcomes, antiviral activity, and costs associated with early treatment with remdesivir for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1450",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib20",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.4067",
"article-title": "Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice",
"author": "White",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib22",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280217713032",
"article-title": "Propensity score analysis with partially observed covariates: how should multiple imputation be used?",
"author": "Leyrat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Stat Methods Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib23",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bimj.200810488",
"article-title": "Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Biom J",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib24",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir–ritonavir: oral COVID antiviral drugs",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib27",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib28",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir and severe COVID-19 outcomes during the omicron surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100044",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of molnupiravir or placebo in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Arribas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evidence",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib31",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-0729",
"article-title": "Effect of molnupiravir on biomarkers, respiratory interventions, and medical services in COVID-19: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9",
"article-title": "Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in omicron variant compared to delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates",
"author": "Bojkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib33",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00618-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib34",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against COVID-19 omicron variant",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib35",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern",
"author": "Vangeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib36",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128629",
"article-title": "Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir",
"author": "Ullrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Bioorg Med Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib37",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib38",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib39",
"series-title": "Hetero announces interim clinical results from phase III clinical trials of molnupiravir conducted in India",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus",
"author": "Fischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib40",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.939573",
"article-title": "Antiviral efficacy and safety of molnupiravir against omicron variant infection: a randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib42",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral antivirals for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Soriano",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "AIDS Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib43",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102329",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir in COVID-19: a systematic review of literature",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib46",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/em.22471",
"article-title": "Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir",
"author": "Waters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Environ Mol Mutagen",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib47",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab247",
"article-title": "β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 through lethal mutagenesis but is also mutagenic to mammalian cells",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib48",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23073507",
"article-title": "Potential resistance of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) against protease inhibitors: lessons learned from HIV-1 protease",
"author": "Mótyán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2_bib49",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1473309922005072"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}