Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1, Mar 2025
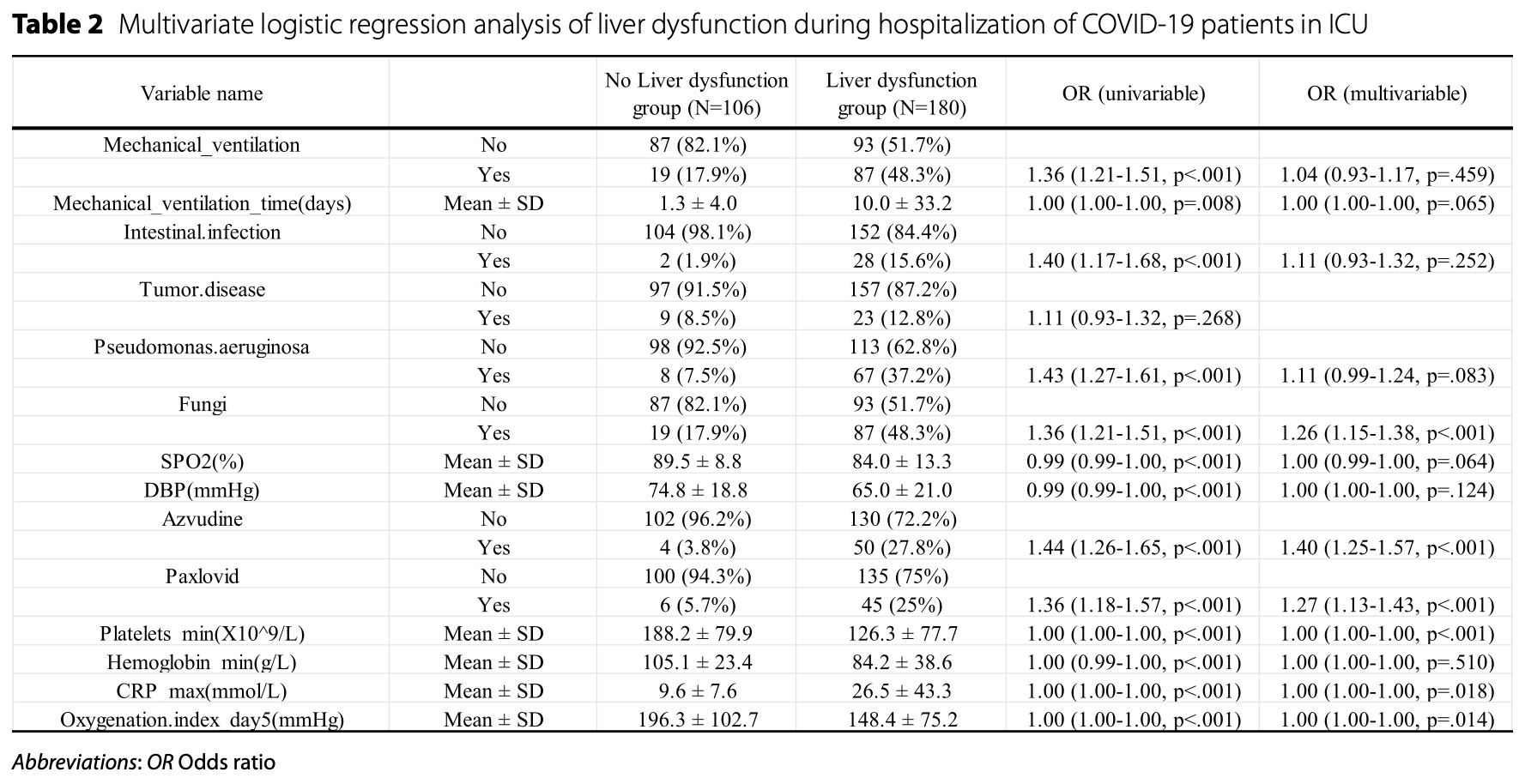
Retrospective 286 critically ill COVID-19 ICU patients developing a predictive model for liver dysfunction, showing significantly higher risk with azvudine and paxlovid use.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers azvudine and paxlovid.
|
liver dysfunction, 27.0% higher, OR 1.27, p < 0.001, treatment 51, control 235, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wang et al., 10 Mar 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period November 2022 - February 2023.
Contact: xiekeliang2009@hotmail.com.
Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU
BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1
The global pandemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) has resulted in millions of deaths over the past three years. As one of the most commonly affected extra-pulmonary organs, numerous studies have reported varying degrees of liver injury in a significant proportion of patients with COVID-19, particularly in severe and critically ill patients. Early prediction of liver dysfunction in hospitalized patients would facilitate the clinical management of COVID-19 and improve clinical prognosis, but reliable and valid predictive models are still lacking.
Methods We collected data from 286 patients with RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 admitted to various ICUs from the case system. These patients were randomly divided into a training cohort (50%) and a validation cohort (50%). In the training cohort, we first used ROC curves to measure the predictive efficiency of each of the variables for the development of liver damage during hospitalization in patients with COVID-19, followed by LASSO regression analysis to screen the variables for predictive models and logistic regression analysis to identify relevant risk factors. A nomogram based on these variables was created following the above model. Finally, the efficiency of the prediction models in the training and validation cohorts was assessed using AUC, consistency index (C index), calibration curves and Decision Curve Analysis.
Results Out of a total of 80 parameters for COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICUs, 10 were determined to be significantly associated with the occurrence of liver dysfunction during hospitalization. Based on these predictors, further prediction models were used to construct and develop a nomogram that was offered for practical clinical application. The C-index of the column line graphs for the training and validation cohorts was 0.956 and 0.844 respectively. in addition, the calibration curves for the model showed a high degree of agreement between the predicted and actual incidence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19.
Conclusion By developing a predictive model and associated nomogram, we predicted the incidence of liver dysfunction during hospitalization in patients with COVID-19 in the ICU. The model's predictive performance was determined in both the training and validation cohorts, contributing to the clinical management of COVID-19.
Abbreviations
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital (Approval Number: IRB2022-YX-268-01) on December 29, 2022. All procedures involving human participants adhered to the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Given the retrospective nature of this study and the use of anonymized medical records, the Medical Ethics Committee approved a waiver of written informed consent for patients with COVID-19. The waiver was granted as the research involved no more than minimal risk to the participants, and the data were anonymized to ensure privacy and confidentiality.
Consent for publication Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Bertolini, Van De Peppel, Bodewes, Moshage, Fantin et al., Abnormal Liver Function Tests in Patients With COVID-19: Relevance and Potential Pathogenesis, Hepatology
Bonaventura, Vecchié, Dagna, Martinod, Dixon et al., Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Cai, Huang, Yu, Zhu, Xia et al., COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests, J Hepatol
Chen, Chu, Bai, Tu, Wei et al., Liver damage at admission is an independent prognostic factor for COVID-19, J Dig Dis
Chen, Wu, Chen, Yang, Chen et al., Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study, BMJ (Clinical research
Chen, Zhou, Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 in Patients With Liver Injury, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, The Journal of infection
Ding, Li, Chen, Shu, Song et al., Association of liver abnormalities with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19, J Hepatol
Falcone, Tiseo, Giordano, Leonildi, Menichini et al., Predictors of hospitalacquired bacterial and fungal superinfections in COVID-19: a prospective observational study, J Antimicrob Chemother
Fan, Chen, Li, Cheng, Yang et al., Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Ferm, Fisher, Pakala, Tong, Shah et al., Analysis of Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in 892 Patients in Queens, NY, Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle et al., Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Huang, Chen, Li, Zhou, Dai et al., The association between markers of liver injury and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Jothimani, Venugopal, Abedin, Kaliamoorthy, Rela, COVID-19 and the liver, J Hepatol
Kulkarni, Kumar, Tevethia, Premkumar, Arab et al., Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Kumar, Delu, Shukla, Singh, Ulasov et al., Safety assessment of a nucleoside analogue FNC (2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine ) in Balb/c Mice: acute toxicity study, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev
Kumar, Delu, Ulasov, Kumar, Singh et al., Pharmacological Insights: Mitochondrial ROS Generation by FNC (Azvudine) in Dalton's Lymphoma Cells Revealed by Super Resolution Imaging, Cell Biochem Biophys
Lai, Chen, Ko, Hsueh, Increased antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Lamb, Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval, Drugs
Lansbury, Lim, Baskaran, Lim, Co-infections in people with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Infect
Lei, Liu, Zhou, Qin, Zhang et al., Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China, Hepatology
Loos, Beijnen, Schinkel, The mechanism-based inactivation of CYP3A4 by Ritonavir: what mechanism?, Int J Mol Sci
Mao, Qiu, He, Tan, Li et al., Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Boyle, Gibbons et al., Recommendations for the Management of Drug-Drug Interactions Between the COVID-19 Antiviral Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) and Comedications, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mokhtari, Hassani, Ghaffari, Ebrahimi, Yarahmadi et al., COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: A narrative review on potential mechanisms, J Mol Histol
Ning, Wu, Wang, Xi, Chen et al., The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Phipps, Barraza, Lasota, Sobieszczyk, Pereira et al., Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U.S. Cohort, Hepatology
Qi, Liu, Jiang, Gu, Zhang et al., Multicenter analysis of clinical characteristics and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 who develop liver injury, J Hepatol
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study, Adv Sci
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area, JAMA
Sathish, Bhatt, Dasilva, Flynn, Jenkinson et al., Comprehensive Nonclinical Safety Assessment of Nirmatrelvir Supporting Timely Development of the SARS-COV-2 Antiviral Therapeutic, Paxlovid ™, Int J Toxicol
Seeto, Fenn, Rockey, Ischemic hepatitis: clinical presentation and pathogenesis, Am J Med
Sun, Aghemo, Forner, Valenti, COVID-19 and liver disease, Liver Int
Tibshirani, Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), doi:10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, The Lancet
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wang, Liu, Liu, Li, Lin et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19, J Hepatol
Wang, Yan, Qi, Wu, Zhu et al., Clinical characteristics and risk factors of liver injury in COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study from Wuhan, China, Hepatol Int
Xie, Zhao, Lian, Lin, Xie et al., Clinical characteristics of non-ICU hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and liver injury: A retrospective study, Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver
Xiong, Liu, Cao, Wang, Guo et al., Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients, Emerg Microbes Infect
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Zaim, Chong, Sankaranarayanan, Harky, COVID-19 and Multiorgan Response, Curr Probl Cardiol
Zhang, Cheng, Yan, Fang, Wang et al., An ALOX12-12-HETE-GPR31 signaling axis is a key mediator of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury, Nat Med
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2334"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1",
"alternative-id": [
"10684"
],
"article-number": "332",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "12 August 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "18 February 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital (Approval Number: IRB2022-YX-268–01) on December 29, 2022. All procedures involving human participants adhered to the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.Given the retrospective nature of this study and the use of anonymized medical records, the Medical Ethics Committee approved a waiver of written informed consent for patients with COVID-19. The waiver was granted as the research involved no more than minimal risk to the participants, and the data were anonymized to ensure privacy and confidentiality."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Zhiwei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Lina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Keliang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "BMC Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T11:37:28Z",
"timestamp": 1741606648000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T12:25:30Z",
"timestamp": 1741609530000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-18T04:21:23Z",
"timestamp": 1742271683344,
"version": "3.40.1"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1741564800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1741564800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10684_CR1",
"unstructured": "WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00907-1",
"author": "Q Ning",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10684_CR2",
"unstructured": "Ning Q, Wu D, Wang X, Xi D, Chen T, Chen G, Wang H, Lu H, Wang M, Zhu L, et al. The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):57.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "T Chen",
"journal-title": "BMJ (Clinical research ed)",
"key": "10684_CR3",
"unstructured": "Chen T, Wu D, Chen H, Yan W, Yang D, Chen G, Ma K, Xu D, Yu H, Wang H, et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2020;368: m1091.",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"author": "WJ Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10684_CR4",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–20.",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "10684_CR5",
"unstructured": "Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10229):1054–62.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006",
"author": "Q Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "566",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR6",
"unstructured": "Cai Q, Huang D, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Su Y, Li Z, Zhou G, Gou J, Qu J, et al. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J Hepatol. 2020;73(3):566–74.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10684_CR7",
"unstructured": "Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, Cohen SL, et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 2020;323(20):2052–9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31480",
"author": "A Bertolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1864",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Hepatology (Baltimore, MD)",
"key": "10684_CR8",
"unstructured": "Bertolini A, van de Peppel IP, Bodewes F, Moshage H, Fantin A, Farinati F, Fiorotto R, Jonker JW, Strazzabosco M, Verkade HJ, et al. Abnormal Liver Function Tests in Patients With COVID-19: Relevance and Potential Pathogenesis. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD). 2020;72(5):1864–72.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31301",
"author": "F Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "389",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Hepatology (Baltimore, MD)",
"key": "10684_CR9",
"unstructured": "Lei F, Liu YM, Zhou F, Qin JJ, Zhang P, Zhu L, Zhang XJ, Cai J, Lin L, Ouyang S, et al. Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD). 2020;72(2):389–98.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.05.049",
"author": "S Ferm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2378",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology",
"key": "10684_CR10",
"unstructured": "Ferm S, Fisher C, Pakala T, Tong M, Shah D, Schwarzbaum D, Cooley V, Hussain S, Kim SH. Analysis of Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in 892 Patients in Queens, NY. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology. 2020;18(10):2378-2379.e2371.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31404",
"author": "MM Phipps",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "807",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Hepatology (Baltimore, Md)",
"key": "10684_CR11",
"unstructured": "Phipps MM, Barraza LH, LaSota ED, Sobieszczyk ME, Pereira MR, Zheng EX, Fox AN, Zucker J, Verna EC. Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U.S. Cohort. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2020;72(3):807–17.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"author": "D Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10684_CR12",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061–9.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002",
"author": "Z Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1561",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR13",
"unstructured": "Fan Z, Chen L, Li J, Cheng X, Yang J, Tian C, Zhang Y, Huang S, Liu Z, Cheng J. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(7):1561–6.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12072-020-10075-5",
"author": "M Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "723",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Int",
"key": "10684_CR14",
"unstructured": "Wang M, Yan W, Qi W, Wu D, Zhu L, Li W, Wang X, Ma K, Ni M, Xu D, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of liver injury in COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study from Wuhan, China. Hepatol Int. 2020;14(5):723–32.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.14449",
"author": "H Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1321",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "10684_CR15",
"unstructured": "Xie H, Zhao J, Lian N, Lin S, Xie Q, Zhuo H. Clinical characteristics of non-ICU hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and liver injury: A retrospective study. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2020;40(6):1321–6.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.010",
"author": "X Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "455",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR16",
"unstructured": "Qi X, Liu C, Jiang Z, Gu Y, Zhang G, Shao C, Yue H, Chen Z, Ma B, Liu D, et al. Multicenter analysis of clinical characteristics and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 who develop liver injury. J Hepatol. 2020;73(2):455–8.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10684_CR17",
"unstructured": "Tibshirani R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological). 1996;58(1):267–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x."
},
{
"key": "10684_CR18",
"unstructured": "The COVID-19 Map. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618",
"author": "S Zaim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Curr Probl Cardiol",
"key": "10684_CR19",
"unstructured": "Zaim S, Chong JH, Sankaranarayanan V, Harky A. COVID-19 and Multiorgan Response. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2020;45(8): 100618.",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10735-020-09915-3",
"author": "T Mokhtari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "613",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Mol Histol",
"key": "10684_CR20",
"unstructured": "Mokhtari T, Hassani F, Ghaffari N, Ebrahimi B, Yarahmadi A, Hassanzadeh G. COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: A narrative review on potential mechanisms. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(6):613–28.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.006",
"author": "D Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1231",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR21",
"unstructured": "Jothimani D, Venugopal R, Abedin MF, Kaliamoorthy I, Rela M. COVID-19 and the liver. J Hepatol. 2020;73(5):1231–40.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.14470",
"author": "J Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1278",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "10684_CR22",
"unstructured": "Sun J, Aghemo A, Forner A, Valenti L. COVID-19 and liver disease. Liver Int. 2020;40(6):1278–81.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5",
"author": "Z Varga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1417",
"issue": "10234",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "10684_CR23",
"unstructured": "Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS, Mehra MR, Schuepbach RA, Ruschitzka F, Moch H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. The Lancet. 2020;395(10234):1417–8.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9",
"author": "A Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10684_CR24",
"unstructured": "Bonaventura A, Vecchié A, Dagna L, Martinod K, Dixon DL, Van Tassell BW, Dentali F, Montecucco F, Massberg S, Levi M, et al. Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(5):319–29.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00461-7",
"author": "RK Seeto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am J Med",
"key": "10684_CR25",
"unstructured": "Seeto RK, Fenn B, Rockey DC. Ischemic hepatitis: clinical presentation and pathogenesis. Am J Med. 2000;109(2):109–13.",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"author": "X Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "475",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10684_CR26",
"unstructured": "Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475–81.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.4451",
"author": "X-J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10684_CR27",
"unstructured": "Zhang X-J, Cheng X, Yan Z-Z, Fang J, Wang X, Wang W, Liu Z-Y, Shen L-J, Zhang P, Wang P-X, et al. An ALOX12–12-HETE–GPR31 signaling axis is a key mediator of hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):73–83.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.043",
"author": "P Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2846",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR28",
"unstructured": "Chen P, Zhou B. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 in Patients With Liver Injury. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(12):2846–7.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "10684_CR29",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10223):497–506.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1747363",
"author": "Y Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "761",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "10684_CR30",
"unstructured": "Xiong Y, Liu Y, Cao L, Wang D, Guo M, Jiang A, Guo D, Hu W, Yang J, Tang Z, et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9(1):761–70.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"author": "C Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "762",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10684_CR31",
"unstructured": "Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang S, Yang S, Tao Y, Xie C, Ma K, Shang K, Wang W, et al. Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):762–8.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "10684_CR32",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10229):1033–4.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa530",
"author": "M Falcone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1078",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10684_CR33",
"unstructured": "Falcone M, Tiseo G, Giordano C, Leonildi A, Menichini M, Vecchione A, Pistello M, Guarracino F, Ghiadoni L, Forfori F, et al. Predictors of hospital-acquired bacterial and fungal superinfections in COVID-19: a prospective observational study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;76(4):1078–84.",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.046",
"author": "L Lansbury",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "266",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10684_CR34",
"unstructured": "Lansbury L, Lim B, Baskaran V, Lim WS. Co-infections in people with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020;81(2):266–75.",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106324",
"author": "CC Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10684_CR35",
"unstructured": "Lai CC, Chen SY, Ko WC, Hsueh PR. Increased antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2021;57(4): 106324.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15916",
"author": "AV Kulkarni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "584",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10684_CR36",
"unstructured": "Kulkarni AV, Kumar P, Tevethia HV, Premkumar M, Arab JP, Candia R, Talukdar R, Sharma M, Qi X, Rao PN, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52(4):584–99.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10684_CR37",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, Baniecki M, Hendrick VM, Damle B, Simón-Campos A, et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10684_CR38",
"unstructured": "Pfizer Inc. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovidtm [PDF]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2021. Revised November 2024. Retrieved from https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=17109. Accessed 20 Dec 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10684_CR39",
"unstructured": "Dian Y, Meng Y, Sun Y, Deng G, Zeng F. Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities. The Journal of infection. 2023;87(2):e24-e27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"author": "JL Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10684_CR40",
"unstructured": "Zhang JL, Li YH, Wang LL, Liu HQ, Lu SY, Liu Y, Li K, Liu B, Li SY, Shao FM, et al. Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):414.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Z Ren",
"first-page": "e2001435",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Adv Sci (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany)",
"key": "10684_CR41",
"unstructured": "Ren Z, Luo H, Yu Z, Song J, Liang L, Wang L, Wang H, Cui G, Liu Y, Wang J, et al. A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study. Adv Sci (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). 2020;7(19):e2001435.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12013-024-01238-4",
"author": "N Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "873",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem Biophys",
"key": "10684_CR42",
"unstructured": "Kumar N, Delu V, Ulasov I, Kumar S, Singh RK, Kumar S, Shukla A, Patel AK, Yadav L, Tiwari R, et al. Pharmacological Insights: Mitochondrial ROS Generation by FNC (Azvudine) in Dalton’s Lymphoma Cells Revealed by Super Resolution Imaging. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024;82(2):873–83.",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.6.2157",
"author": "N Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2157",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Cancer Prev",
"key": "10684_CR43",
"unstructured": "Kumar N, Delu V, Shukla A, Singh RK, Ulasov I, Fayzullina D, Kumar S, Patel AK, Yadav L, Tiwari R, et al. Safety assessment of a nucleoside analogue FNC (2’-deoxy-2’- β-fluoro-4’-azidocytidine ) in Balb/c Mice: acute toxicity study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023;24(6):2157–70.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23179866",
"author": "NHC Loos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9866",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10684_CR44",
"unstructured": "Loos NHC, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH. The mechanism-based inactivation of CYP3A4 by Ritonavir: what mechanism? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9866.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10915818221095489",
"author": "JG Sathish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int J Toxicol",
"key": "10684_CR45",
"unstructured": "Sathish JG, Bhatt S, DaSilva JK, Flynn D, Jenkinson S, Kalgutkar AS, Liu M, Manickam B, Pinkstaff J, Reagan WJ, et al. Comprehensive Nonclinical Safety Assessment of Nirmatrelvir Supporting Timely Development of the SARS-COV-2 Antiviral Therapeutic, Paxlovid™. Int J Toxicol. 2022;41(4):276–90.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2646",
"author": "C Marzolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1191",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10684_CR46",
"unstructured": "Marzolini C, Kuritzkes DR, Marra F, Boyle A, Gibbons S, Flexner C, Pozniak A, Boffito M, Waters L, Burger D, et al. Recommendations for the Management of Drug-Drug Interactions Between the COVID-19 Antiviral Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) and Comedications. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;112(6):1191–200.",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5",
"author": "YN Lamb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "585",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10684_CR47",
"unstructured": "Lamb YN. Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval. Drugs. 2022;82(5):585–91.",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "807",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR48",
"unstructured": "Wang Y, Liu S, Liu H, Li W, Lin F, Jiang L, Li X, Xu P, Zhang L, Zhao L, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19. J Hepatol. 2020;73(4):807–16.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.012",
"author": "ZY Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1295",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR49",
"unstructured": "Ding ZY, Li GX, Chen L, Shu C, Song J, Wang W, Wang YW, Chen Q, Jin GN, Liu TT, et al. Association of liver abnormalities with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. J Hepatol. 2021;74(6):1295–302.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1751-2980.12925",
"author": "LY Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Dig Dis",
"key": "10684_CR50",
"unstructured": "Chen LY, Chu HK, Bai T, Tu SJ, Wei Y, Li ZL, Hu LL, Zhu R, Zhang L, Han CQ, et al. Liver damage at admission is an independent prognostic factor for COVID-19. J Dig Dis. 2020;21(9):512–8.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15962",
"author": "H Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1051",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10684_CR51",
"unstructured": "Huang H, Chen S, Li H, Zhou XL, Dai Y, Wu J, Zhang J, Shao L, Yan R, Wang M, et al. The association between markers of liver injury and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52(6):1051–9.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6",
"author": "R Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "667",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10684_CR52",
"unstructured": "Mao R, Qiu Y, He JS, Tan JY, Li XH, Liang J, Shen J, Zhu LR, Chen Y, Iacucci M, et al. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(7):667–78.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 52,
"references-count": 52,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-4896966/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "25"
}
wang43