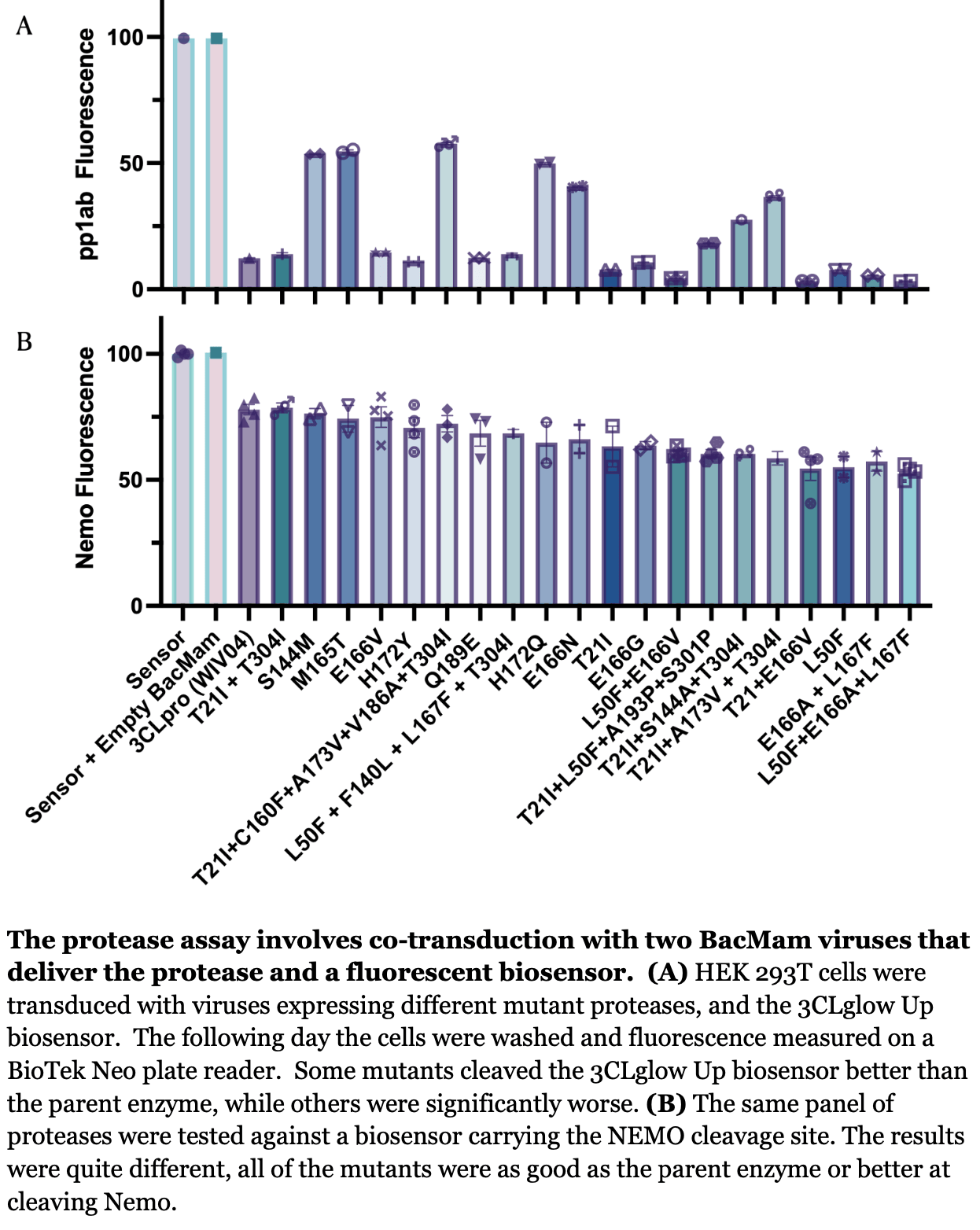
Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137, Oct 2024
In vitro study showing that paxlovid use may promote the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants that can weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID.
Authors show that SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) mutations that confer resistance to nirmatrelvir also enhance cleavage of the host protein NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO), potentially weakening the immune response and contributing to long COVID. Authors developed live cell assays with biosensors containing viral and host cleavage sites. Mpro mutants that were less sensitive to nirmatrelvir inhibition showed equal or greater cleavage of the NEMO-based sensor compared to wildtype Mpro. The results suggest Mpro mutations may be selected for both drug resistance and ability to disarm host immunity.
Thomas et al., 19 Oct 2024, USA, preprint, 2 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator
doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137
Nirmatrelvir is a SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor in Paxlovid. Patients treated with it often produce mutant viruses in which the M pro resists Nirmatrelvir inhibition. A common interpretation is that the mutations allow the virus to escape inhibition, but here we report that these mutations enable the protease to more effectively cleave the host protein NF-kappa-B essential modulator (NEMO), which weakens the immune response, improves viral replication, and may contribute to long COVID.
References
Authorization, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: Emergency use authorization for paxlovidtm
Barretto, The papain-like protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus has deubiquitinating activity, J. Virol
Chathuranga, Negative regulation of NEMO signaling by the ubiquitin E3 ligase MARCH2, EMBO J
Duan, Molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature
Fu, Both Boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease, Nat. Commun
Hameedi, Structural and functional characterization of NEMO cleavage by SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro, Nat. Commun
Hu, Naturally Occurring Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Confer Drug Resistance to Nirmatrelvir, ACS Cent Sci
Huang, A new generation Mpro inhibitor with potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Iketani, Functional map of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease reveals tolerant and immutable sites, Cell Host Microbe
Iketani, Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature
Jochmans, The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, MBio
Luckow, Lee, Barry, Olins, Efficient generation of infectious recombinant baculoviruses by site-specific transposon-mediated insertion of foreign genes into a baculovirus genome propagated in Escherichia coli, J. Virol
Lytras, Xia, Hughes, Jiang, Robertson, The animal origin of SARS-CoV-2, Science
Markov, The evolution of SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Pérez-Vargas, A novel class of broad-spectrum active-site-directed 3C-like protease inhibitors with nanomolar antiviral activity against highly immune-evasive SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants, Emerg. Microbes Infect
Shu, Mccauley, Gisaid, Global initiative on sharing all influenza datafrom vision to reality, Euro Surveill
Tan, Joyce, Tan, Hu, Wang, SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Drug Design, Assay Development, and Drug Resistance Studies, Acc. Chem. Res
Tong, Evaluation of in vitro antiviral activity of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor pomotrelvir and cross-resistance to nirmatrelvir resistance substitutions, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Ullrich, Ekanayake, Otting, Nitsche, Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett
Wenzel, The SARS-CoV-2 main protease Mpro causes microvascular brain pathology by cleaving NEMO in brain endothelial cells, Nat. Neurosci
Xie, The SARS-unique domain (SUD) of SARS-CoV-2 nsp3 protein inhibits the antiviral immune responses through the NF-κB pathway, J. Med. Virol
Zhao, Structural basis for replicase polyprotein cleavage and substrate specificity of main protease from SARS-CoV-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Zhou, Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Sci Adv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.10.18.619137",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.18.619137",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Nirmatrelvir is a SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor in Paxlovid. Patients treated with it often produce mutant viruses in which the Mpro resists Nirmatrelvir inhibition. A common interpretation is that the mutations allow the virus to escape inhibition, but here we report that these mutations enable the protease to more effectively cleave the host protein NF-kappa-B essential modulator (NEMO), which weakens the immune response, improves viral replication, and may contribute to long COVID.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3430-0912",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Merrilee",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "Thom",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-20T07:15:15Z",
"timestamp": 1729408515000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-20T07:15:15Z",
"timestamp": 1729408515000
},
"group-title": "Immunology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-20T07:40:22Z",
"timestamp": 1729410022814,
"version": "3.27.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "bioRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.biorxiv.org/about/FAQ#license",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729296000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2024.10.18.619137",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2024.10.18.619137"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator",
"type": "posted-content"
}