Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors
et al., npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0, Aug 2023
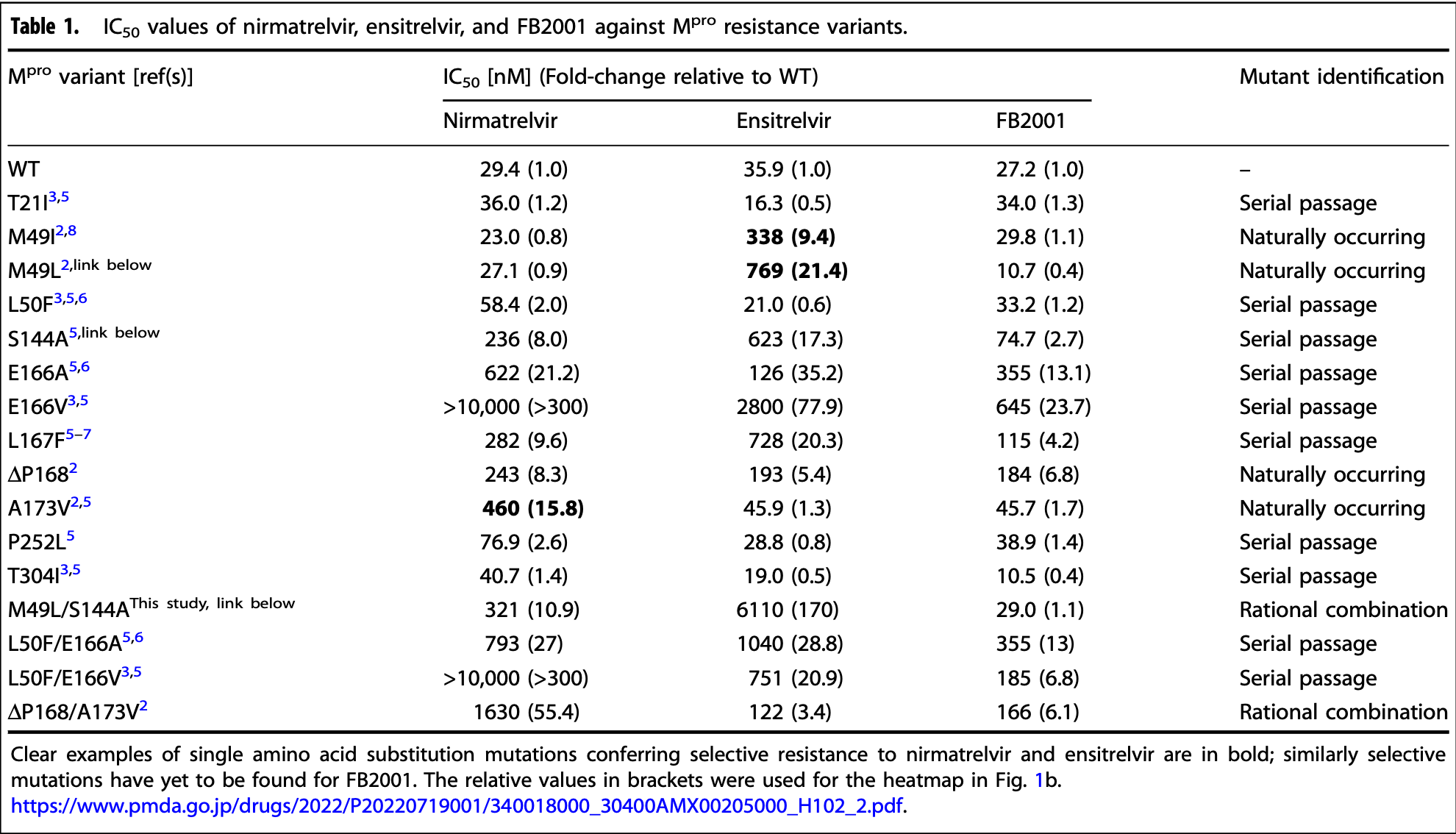
In vitro study of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) variants showing distinct resistance profiles for the Mpro inhibitors nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and FB2001. Results show significant resistance for multiple variants for nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir, with the lowest resistance concerns for FB2001.
Study covers paxlovid and ensitrelvir.
Moghadasi et al., 20 Aug 2023, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: rsh@uthscsa.edu.
Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors
npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0
Resistance to nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) has been shown by multiple groups and may already exist in clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Here a robust cell-based assay is used to determine the relative potencies of nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and FB2001 against a panel of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro ) variants. The results reveal that these three drugs have at least partly distinct resistance mutation profiles and raise the possibility that the latter compounds may be effective in some instances of Paxlovid resistance and vice versa.
Reporting summary Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
COMPETING INTERESTS The M pro gain-of-signal system is the subject of U.S. Provisional Application Serial No. 63/108,611, filed on November 2, 2020, with R.S.H. and S.A.M. as inventors. The authors declare no additional competing interests.
ETHICS
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0 . Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Reuben S. Harris. Reprints and permission information is available at http://www.nature.com/ reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Dai, Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Science
Gordon, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature
Heilmann, SARS-CoV-2 3CL(pro) mutations selected in a VSV-based system confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and GC376, Sci. Transl. Med
Iketani, Functional map of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease reveals tolerant and immutable sites, Cell Host Microbe
Iketani, Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature
Jochmans, The substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro are selected by a protease inhibitor in vitro and confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, mBio
Lan, Nirmatrelvir resistance in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron_BA.1 and WA1 replicons and escape strategies, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.31.522389
Majerova, Konvalinka, Viral proteases as therapeutic targets, Mol. Aspects Med
Meyers, The proximal proteome of 17 SARS-CoV-2 proteins links to disrupted antiviral signaling and host translation, PLoS Pathog
Moghadasi, Gain-of-signal assays for probing inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro)/3CL(pro) in living cells, mBio
Moghadasi, Transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors, Sci. Adv
Noske, Structural basis of nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir activity against naturally occurring polymorphisms of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease, J. Biol. Chem
Unoh, Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19, J. Med. Chem
Zhou, Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Sci. Adv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0",
"ISSN": [
"2731-8745"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Resistance to nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) has been shown by multiple groups and may already exist in clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Here a robust cell-based assay is used to determine the relative potencies of nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and FB2001 against a panel of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M<jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>) variants. The results reveal that these three drugs have at least partly distinct resistance mutation profiles and raise the possibility that the latter compounds may be effective in some instances of Paxlovid resistance and <jats:italic>vice versa</jats:italic>.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"9"
],
"article-number": "9",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "25 February 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "23 June 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "20 August 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The M<sup>pro</sup> gain-of-signal system is the subject of U.S. Provisional Application Serial No. 63/108,611, filed on November 2, 2020, with R.S.H. and S.A.M. as inventors. The authors declare no additional competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Studies here were performed under University of Minnesota IBC protocol 1902-36822H to R.S.H., University of Minnesota IBC protocol 2111-39591H to D.A.H., and University of Texas Health. San Antonio IBC B-00000013853 to R.S.H."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moghadasi",
"given": "Seyed Arad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9656-9175",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Biswas",
"given": "Rayhan G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5950-931X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Harki",
"given": "Daniel A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9034-9112",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Reuben S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "npj Antimicrobials and Resistance",
"container-title-short": "npj Antimicrob Resist",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-20T22:01:44Z",
"timestamp": 1692568904000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-20T22:01:46Z",
"timestamp": 1692568906000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"U19-AI171954"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-14T15:13:36Z",
"timestamp": 1726326816818
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 18,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1692489600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1692489600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44259-023-00009-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44259-023-00009-0",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44259-023-00009-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2022.101159",
"author": "T Majerova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101159",
"journal-title": "Mol. Aspects Med.",
"key": "9_CR1",
"unstructured": "Majerova, T. & Konvalinka, J. Viral proteases as therapeutic targets. Mol. Aspects Med. 88, 101159 (2022).",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.ade8778",
"author": "SA Moghadasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eade8778",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "9_CR2",
"unstructured": "Moghadasi, S. A. et al. Transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 9, eade8778 (2023).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.add7197",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eadd7197",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "9_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zhou, Y. et al. Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system. Sci. Adv. 8, eadd7197 (2022).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2022.08.003",
"author": "S Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1354",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "9_CR4",
"unstructured": "Iketani, S. et al. Functional map of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease reveals tolerant and immutable sites. Cell Host Microbe 30, 1354–1362.e1356 (2022).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2",
"author": "S Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "558",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9_CR5",
"unstructured": "Iketani, S. et al. Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir. Nature 613, 558–564 (2023).",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.02815-22",
"author": "D Jochmans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0281522",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "9_CR6",
"unstructured": "Jochmans, D. et al. The substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro are selected by a protease inhibitor in vitro and confer resistance to nirmatrelvir. mBio 14, e0281522 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abq7360",
"author": "E Heilmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabq7360",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "9_CR7",
"unstructured": "Heilmann, E. et al. SARS-CoV-2 3CL(pro) mutations selected in a VSV-based system confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and GC376. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eabq7360 (2023).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2023.103004",
"author": "GD Noske",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103004",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "9_CR8",
"unstructured": "Noske, G. D. et al. Structural basis of nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir activity against naturally occurring polymorphisms of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. J. Biol. Chem. 299, 103004 (2023).",
"volume": "299",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.12.31.522389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9_CR9",
"unstructured": "Lan, S. et al. Nirmatrelvir resistance in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron_BA.1 and WA1 replicons and escape strategies. BioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.31.522389 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb4489",
"author": "W Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1331",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9_CR10",
"unstructured": "Dai, W. et al. Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Science 368, 1331–1335 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117",
"author": "Y Unoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6499",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "9_CR11",
"unstructured": "Unoh, Y. et al. Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19. J. Med. Chem. 65, 6499–6512 (2022).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00784-22",
"author": "SA Moghadasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0078422",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "9_CR12",
"unstructured": "Moghadasi, S. A. et al. Gain-of-signal assays for probing inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro)/3CL(pro) in living cells. mBio 13, e0078422 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009412",
"author": "JM Meyers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1009412",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "9_CR13",
"unstructured": "Meyers, J. M. et al. The proximal proteome of 17 SARS-CoV-2 proteins links to disrupted antiviral signaling and host translation. PLoS Pathog. 17, e1009412 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9_CR14",
"unstructured": "Gordon, D. E. et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 583, 459–468 (2020).",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2023.02.25.530000",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44259-023-00009-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "1"
}