SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination
et al., Cell Death & Differentiation, doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3, Apr 2021
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
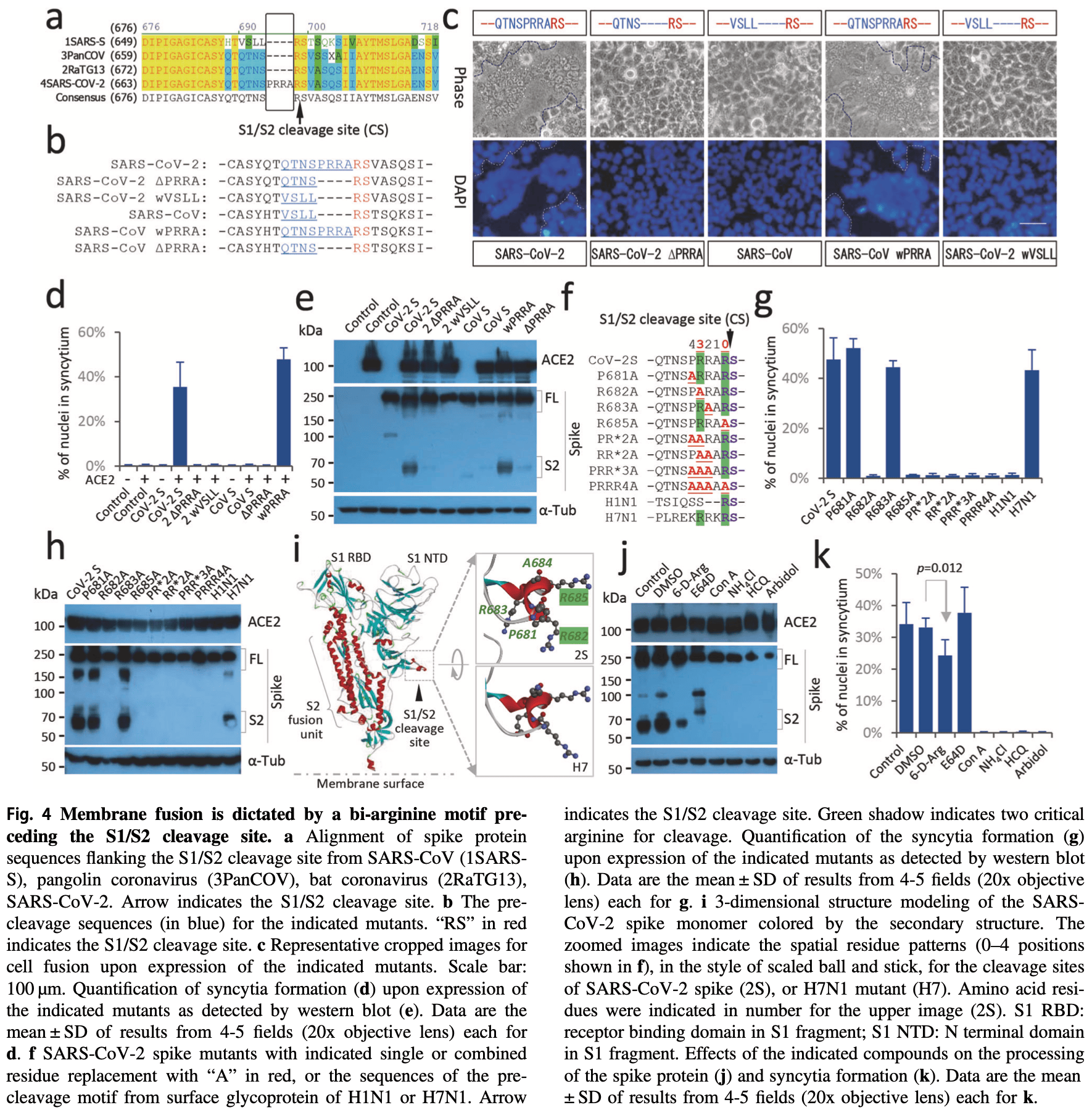
In vitro study showing that SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces rapid cell fusion and formation of syncytia that internalize and kill lymphocytes, potentially contributing to lymphocytopenia in COVID-19 patients. A bi-arginine motif in the spike protein S1/S2 cleavage site was found to control membrane fusion and syncytia formation. Several candidate antiviral compounds, including arbidol, 6-D-Arg, Con A, NH4Cl, and hydroxychloroquine, inhibited spike protein processing, membrane fusion, syncytia formation, and lymphocyte internalization in 293T-ACE2 cells expressing the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
39 preclinical studies support the efficacy of HCQ for COVID-19:
1.
Shang et al., Identification of Cathepsin L as the molecular target of hydroxychloroquine with chemical proteomics, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, doi:10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.101314.
2.
González-Paz et al., Biophysical Analysis of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Recognition and Their Effect on Viral Dynamics in Different Cell Types: A Computational Prediction from In Vitro Experimental Data, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c06968.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Guimarães Silva et al., Are Non-Structural Proteins From SARS-CoV-2 the Target of Hydroxychloroquine? An in Silico Study, ACTA MEDICA IRANICA, doi:10.18502/acta.v61i2.12533.
5.
Nguyen et al., The Potential of Ameliorating COVID-19 and Sequelae From Andrographis paniculata via Bioinformatics, Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, doi:10.1177/11779322221149622.
7.
Yadav et al., Repurposing the Combination Drug of Favipiravir, Hydroxychloroquine and Oseltamivir as a Potential Inhibitor Against SARS-CoV-2: A Computational Study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-628277/v1.
8.
Hussein et al., Molecular Docking Identification for the efficacy of Some Zinc Complexes with Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine against Main Protease of COVID-19, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129979.
9.
Baildya et al., Inhibitory capacity of Chloroquine against SARS-COV-2 by effective binding with Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 receptor: An insight from molecular docking and MD-simulation studies, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129891.
10.
Noureddine et al., Quantum chemical studies on molecular structure, AIM, ELF, RDG and antiviral activities of hybrid hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19: molecular docking and DFT calculations, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2020.101334.
11.
Tarek et al., Pharmacokinetic Basis of the Hydroxychloroquine Response in COVID-19: Implications for Therapy and Prevention, European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, doi:10.1007/s13318-020-00640-6.
12.
Rowland Yeo et al., Impact of Disease on Plasma and Lung Exposure of Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin: Application of PBPK Modeling, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.1955.
13.
Hitti et al., Hydroxychloroquine attenuates double-stranded RNA-stimulated hyper-phosphorylation of tristetraprolin/ZFP36 and AU-rich mRNA stabilization, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13835.
14.
Yan et al., Super-resolution imaging reveals the mechanism of endosomal acidification inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 infection, ChemBioChem, doi:10.1002/cbic.202400404.
15.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
16.
Alsmadi et al., The In Vitro, In Vivo, and PBPK Evaluation of a Novel Lung-Targeted Cardiac-Safe Hydroxychloroquine Inhalation Aerogel, AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-023-02627-3.
17.
Wen et al., Cholinergic α7 nAChR signaling suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection and inflammation in lung epithelial cells, Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjad048.
18.
Kamga Kapchoup et al., In vitro effect of hydroxychloroquine on pluripotent stem cells and their cardiomyocytes derivatives, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1128382.
19.
Milan Bonotto et al., Cathepsin inhibitors nitroxoline and its derivatives inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105655.
20.
Miao et al., SIM imaging resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells, Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001.
21.
Yuan et al., Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8.
22.
Faísca et al., Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Hydroxychloroquine Ionic Liquids against SARS-CoV-2, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14040877.
23.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
24.
Purwati et al., An in vitro study of dual drug combinations of anti-viral agents, antibiotics, and/or hydroxychloroquine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from hospitalized patients in Surabaya, Indonesia, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252302.
25.
Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination, Cell Death & Differentiation, doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3.
26.
Dang et al., Structural basis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of hydroxychloroquine: specific binding to NTD/CTD and disruption of LLPS of N protein, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.16.435741.
27.
Shang (B) et al., Inhibitors of endosomal acidification suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieve viral pneumonia in hACE2 transgenic mice, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-021-01515-1.
28.
Wang et al., Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as ACE2 blockers to inhibit viropexis of 2019-nCoV Spike pseudotyped virus, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153333.
29.
Sheaff, R., A New Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Based on (Hydroxy)Chloroquine Activity, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.02.232892.
30.
Ou et al., Hydroxychloroquine-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry is attenuated by TMPRSS2, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009212.
31.
Andreani et al., In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microbial Pathogenesis, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228.
32.
Clementi et al., Combined Prophylactic and Therapeutic Use Maximizes Hydroxychloroquine Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effects in vitro, Front. Microbiol., 10 July 2020, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01704.
33.
Liu et al., Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discovery 6, 16 (2020), doi:10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0.
34.
Yao et al., In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis., 2020 Mar 9, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237.
Zhang et al., 20 Apr 2021, peer-reviewed, 27 authors.
Contact: liuliang@mails.tjmu.edu.cn, hhongy1999@126.com, sunq@bmi.ac.cn.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination
Cell Death & Differentiation, doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus is highly contagious and causes lymphocytopenia, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. We demonstrate here that heterotypic cell-in-cell structures with lymphocytes inside multinucleate syncytia are prevalent in the lung tissues of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. These unique cellular structures are a direct result of SARS-CoV-2 infection, as the expression of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein is sufficient to induce a rapid (~45.1 nm/s) membrane fusion to produce syncytium, which could readily internalize multiple lines of lymphocytes to form typical cell-in-cell structures, remarkably leading to the death of internalized cells. This membrane fusion is dictated by a bi-arginine motif within the polybasic S1/S2 cleavage site, which is frequently present in the surface glycoprotein of most highly contagious viruses. Moreover, candidate anti-viral drugs could efficiently inhibit spike glycoprotein processing, membrane fusion, and cell-in-cell formation. Together, we delineate a molecular and cellular rationale for SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis and identify novel targets for COVID-19 therapy.
Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Amin, Abbas, Docking study of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein-An in silico insight into the comparative efficacy of repurposing antiviral drugs, J Biomol Struct Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1775703:1-11
Andersen, Rambaut, Lipkin, Holmes, Garry, The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Med
Boonstra, Blijleven, Roos, Onck, Van Der Giessen et al., Hemagglutinin-mediated membrane fusion: a biophysical perspective, Annu Rev Biophys
Braga, Ali, Secco, Chiavacci, Neves et al., Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 Spikeinduced syncytia, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6
Fais, Overholtzer, Cell-in-cell phenomena in cancer, Nat Rev Cancer
Fan, Fang, Yang, Cui, Zhao et al., Role of heterotypic neutrophil-in-tumor structure in the prognosis of patients with Buccal Mucosa squamous cell carcinoma, Front Oncol
Fantini, Scala, Chahinian, Yahi, Structural and molecular modelling studies reveal a new mechanism of action of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Fox, Akmatbekov, Harbert, Li, Brown et al., Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in Covid-19: the first autopsy series from New Orleans, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.06.20050575:2020.04.06.20050575
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Huang, Chen, Sun, Mammalian cell competitions, cell-incell phenomena and their biomedical implications, Curr Mol Med
Huang, Chen, Wang, Wang, Ning et al., Detecting cell-in-cell structures in human tumor samples by E-cadherin/CD68/CD45 triple staining, Oncotarget
Huang, He, Zhang, Zhang, Niu et al., Identification and validation of heterotypic cell-in-cell structure as an adverse prognostic predictor for young patients of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Jiang, Zhang, Wang, Ren, Gao et al., Bimodular effects of D614G mutation on the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 enhance protein processing, membrane fusion, and viral infectivity, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Ledford, Safety fears over drug hyped to treat the coronavirus spark global confusion, Nature
Li, Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins, Annu Rev Virol
Liang, Niu, Zhang, Yu, Zheng et al., p53dependent elimination of aneuploid mitotic offspring by entosis, Cell Death Differ
Liu, Cao, Xu, Wang, Zhang et al., Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Disco
Luo, Yu, Gou, Li, Sun et al., Clinical pathology of critical patient with novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19)
Mackay, Muller, Biological relevance of cell-in-cell in cancers, Biochem Soc Trans
Niu, He, Sun, Molecular mechanisms underlying cell-incell formation: core machineries and beyond, J Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjab015.
Rizzotto, Villunger, P53 clears aneuploid cells by entosis, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-020-00659-x
Ruan, Niu, Jiang, Li, Tai et al., High frequency of cell-in-cell formation in heterogeneous human breast cancer tissue in a patient with poor prognosis: a case report and literature review, Front Oncol
Su, Ren, Tang, Zheng, Zhang et al., Role and dynamics of vacuolar pH during cell-in-cell mediated death, Cell Death Dis
Sun, Cibas, Huang, Hodgson, Overholtzer, Induction of entosis by epithelial cadherin expression, Cell Res
Sun, Luo, Ren, Florey, Shirasawa et al., Competition between human cells by entosis, Cell Res
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Chen, Ruan, Niu, Su et al., PCDH7 inhibits the formation of homotypic cell-in-cell structure, Front Cell Dev Biol
Wang, He, Chen, Wang, Yu et al., Rapid reuptake of granzyme B leads to emperitosis: an apoptotic cell-in-cell death of immune killer cells inside tumor cells, Cell Death Dis
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wang, Niu, Qin, Ruan, Zheng et al., Mechanical ring interfaces between adherens junction and contractile actomyosin to coordinate entotic cell-in-cell formation, Cell Rep
Who, Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation report-174
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Song, A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30076-x
Yurkovetskiy, Wang, Pascal, Tomkins-Tinch, Nyalile et al., Structural and functional analysis of the D614G SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant, Cell
Zhang, Niu, Qin, Wang, Zhang, Subtypebased prognostic analysis of cell-in-cell structures in early breast cancer, Front Oncol
Zhengrong Zhang 1, Del Nonno Franca 5 • Yunyun Wang 6 • Yichao Zhu 1 • Yan Su 1 • Meng Tang 1, Zubiao Niu
Zhou, Niu, Jiang, Zhang, Zheng et al., SARS-CoV-2 targets by the pscRNA profiling of ACE2. TMPRSS2 Furin Proteases iScience
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N. Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3",
"ISSN": [
"1350-9047",
"1476-5403"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3",
"alternative-id": [
"782"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "22 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "7 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "8 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "20 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with ethical standards",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics statement",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The autopsy for COVID-19 death was carried out with informed consent under the approval of Ethics Committee of Wuhan Infectious Diseases Hospital (KY-2020-15.01) and Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Army Medical University (KY2020298)."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zhengrong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "You",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Niu",
"given": "Zubiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Chenxi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Xiaohong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Haoran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franca",
"given": "Del Nonno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yunyun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Yichao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Meng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Xiaoyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ren",
"given": "He",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Meifang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yuqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Lihua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Hanping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Zhaolie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xiaoning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piacentini",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4383-0197",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bian",
"given": "Xiuwu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9428-5972",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Melino",
"given": "Gerry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Hongyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8094-2214",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cell Death & Differentiation",
"container-title-short": "Cell Death Differ",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-20T17:45:22Z",
"timestamp": 1618940722000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T00:26:35Z",
"timestamp": 1630455995000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-16T15:54:00Z",
"timestamp": 1726502040738
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 120,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618876800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618876800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-021-00782-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-021-00782-3",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-021-00782-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2765-2777",
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"author": "P Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "782_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–3.",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR2",
"unstructured": "Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen Y-M, Wang W, Song Z-G, et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl J Med",
"key": "782_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–33.",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-110615-042301",
"author": "F Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Virol",
"key": "782_CR4",
"unstructured": "Li F. Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins. Annu Rev Virol. 2016;3:237–61.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00392-4",
"author": "X Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "782_CR5",
"unstructured": "Jiang X, Zhang Z, Wang C, Ren H, Gao L, Peng H, et al. Bimodular effects of D614G mutation on the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 enhance protein processing, membrane fusion, and viral infectivity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:268–71.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.032",
"author": "L Yurkovetskiy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "739",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "782_CR6",
"unstructured": "Yurkovetskiy L, Wang X, Pascal KE, Tomkins-Tinch C, Nyalile TP, Wang Y, et al. Structural and functional analysis of the D614G SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant. Cell. 2020;183:739–51.e8.",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9",
"author": "C Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "470",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "782_CR7",
"unstructured": "Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet. 2020;395:470–3.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "782_CR8",
"unstructured": "WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation report-174. Situation reports. 2020;doi: 20200318-sitrep-174-covid-19:https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR9",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1566524015666151026101101",
"author": "H Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "852",
"journal-title": "Curr Mol Med",
"key": "782_CR10",
"unstructured": "Huang H, Chen Z, Sun Q. Mammalian cell competitions, cell-in-cell phenomena and their biomedical implications. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15:852–60.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20180618",
"author": "HL Mackay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "725",
"journal-title": "Biochem Soc Trans",
"key": "782_CR11",
"unstructured": "Mackay HL, Muller PAJ. Biological relevance of cell-in-cell in cancers. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019;47:725–32.",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cr.2014.138",
"author": "Q Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1299",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "782_CR12",
"unstructured": "Sun Q, Luo T, Ren Y, Florey O, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, et al. Competition between human cells by entosis. Cell Res. 2014;24:1299–310.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-00659-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR13",
"unstructured": "Rizzotto D, Villunger A. P53 clears aneuploid cells by entosis. Cell Death Differ. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00659-x."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-00645-3",
"author": "J Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "782_CR14",
"unstructured": "Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, Yu X, Zheng Y, Wang C, et al. p53-dependent elimination of aneuploid mitotic offspring by entosis. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28:799–813.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2019.00895",
"author": "X Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "895",
"journal-title": "Front Oncol",
"key": "782_CR15",
"unstructured": "Zhang X, Niu Z, Qin H, Fan J, Wang M, Zhang B, et al. Subtype-based prognostic analysis of cell-in-cell structures in early breast cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:895.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00346-w",
"author": "H Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "782_CR16",
"unstructured": "Huang H, He M, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Niu Z, Zheng Y, et al. Identification and validation of heterotypic cell-in-cell structure as an adverse prognostic predictor for young patients of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:246–8.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2020.541878",
"author": "J Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "541878",
"journal-title": "Front Oncol",
"key": "782_CR17",
"unstructured": "Fan J, Fang Q, Yang Y, Cui M, Zhao M, Qi J, et al. Role of heterotypic neutrophil-in-tumor structure in the prognosis of patients with Buccal Mucosa squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:541878.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108071",
"author": "M Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108071",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "782_CR18",
"unstructured": "Wang M, Niu Z, Qin H, Ruan B, Zheng Y, Ning X, et al. Mechanical ring interfaces between adherens junction and contractile actomyosin to coordinate entotic cell-in-cell formation. Cell Rep. 2020;32:108071.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cr.2014.137",
"author": "Q Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1288",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "782_CR19",
"unstructured": "Sun Q, Cibas ES, Huang H, Hodgson L, Overholtzer M. Induction of entosis by epithelial cadherin expression. Cell Res. 2014;24:1288–98.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jmcb/mjab015.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR20",
"unstructured": "Niu Z, He M, Sun Q. Molecular mechanisms underlying cell-in-cell formation: core machineries and beyond. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjab015."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2019.01444",
"author": "B Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Front Oncol",
"key": "782_CR21",
"unstructured": "Ruan B, Niu Z, Jiang X, Li Z, Tai Y, Huang H, et al. High frequency of cell-in-cell formation in heterogeneous human breast cancer tissue in a patient with poor prognosis: a case report and literature review. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1444.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.4275",
"author": "H Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20278",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "782_CR22",
"unstructured": "Huang H, Chen A, Wang T, Wang M, Ning X, He M, et al. Detecting cell-in-cell structures in human tumor samples by E-cadherin/CD68/CD45 triple staining. Oncotarget. 2015;6:20278–87.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-021-03396-2",
"author": "Y Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "782_CR23",
"unstructured": "Su Y, Ren H, Tang M, Zheng Y, Zhang B, Wang C, et al. Role and dynamics of vacuolar pH during cell-in-cell mediated death. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:119.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41568-018-0073-9",
"author": "S Fais",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "758",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cancer",
"key": "782_CR24",
"unstructured": "Fais S, Overholtzer M. Cell-in-cell phenomena in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18:758–66.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cddis.2013.352",
"author": "S Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e856",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "782_CR25",
"unstructured": "Wang S, He MF, Chen YH, Wang MY, Yu XM, Bai J, et al. Rapid reuptake of granzyme B leads to emperitosis: an apoptotic cell-in-cell death of immune killer cells inside tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e856.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "782_CR26",
"unstructured": "Luo W, Yu H, Gou J, Li X, Sun Y, Li J, et al. Clinical pathology of critical patient with novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Preprint at https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202002.0407/v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30076-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR27",
"unstructured": "Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30076-x."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.06.20050575:2020.04.06.20050575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR28",
"unstructured": "Fox SE, Akmatbekov A, Harbert JL, Li G, Brown JQ, Vander Heide RS. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in Covid-19: the first autopsy series from New Orleans. medRxiv. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.06.20050575:2020.04.06.20050575."
},
{
"author": "L Zhou",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "TMPRSS2 Furin Proteases iScience",
"key": "782_CR29",
"unstructured": "Zhou L, Niu Z, Jiang X, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Wang Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 targets by the pscRNA profiling of ACE2. TMPRSS2 Furin Proteases iScience. 2020;23:1–15.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-biophys-070317-033018",
"author": "S Boonstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Biophys",
"key": "782_CR30",
"unstructured": "Boonstra S, Blijleven JS, Roos WH, Onck PR, van der Giessen E, van Oijen AM. Hemagglutinin-mediated membrane fusion: a biophysical perspective. Annu Rev Biophys. 2018;47:153–73.",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9",
"author": "KG Andersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "782_CR31",
"unstructured": "Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med. 2020;26:450–2.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-020-01599-9",
"author": "H Ledford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "782_CR32",
"unstructured": "Ledford H. Safety fears over drug hyped to treat the coronavirus spark global confusion. Nature 2020;582:18–9.",
"volume": "582",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Cell Disco",
"key": "782_CR33",
"unstructured": "Liu J, Cao R, Xu M, Wang X, Zhang H, Hu H, et al. Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Cell Disco. 2020;6:16.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"author": "M Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "782_CR34",
"unstructured": "Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020;30:269–71.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105960",
"author": "J Fantini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105960",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "782_CR35",
"unstructured": "Fantini J, Di Scala C, Chahinian H, Yahi N. Structural and molecular modelling studies reveal a new mechanism of action of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55:105960.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1775703:1-11",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR36",
"unstructured": "Amin M, Abbas G. Docking study of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein-An in silico insight into the comparative efficacy of repurposing antiviral drugs. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1775703:1-11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "782_CR37",
"unstructured": "Braga L, Ali H, Secco I, Chiavacci E, Neves G, Goldhill D, et al. Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 Spike-induced syncytia. Nature. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00001",
"author": "C Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "782_CR38",
"unstructured": "Wang C, Chen A, Ruan B, Niu Z, Su Y, Qin H, et al. PCDH7 inhibits the formation of homotypic cell-in-cell structure. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:1–12.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 38,
"references-count": 38,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-353991/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-021-00782-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "28"
}
