An in vitro study of dual drug combinations of anti-viral agents, antibiotics, and/or hydroxychloroquine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from hospitalized patients in Surabaya, Indonesia
et al., PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252302, Jun 2021
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
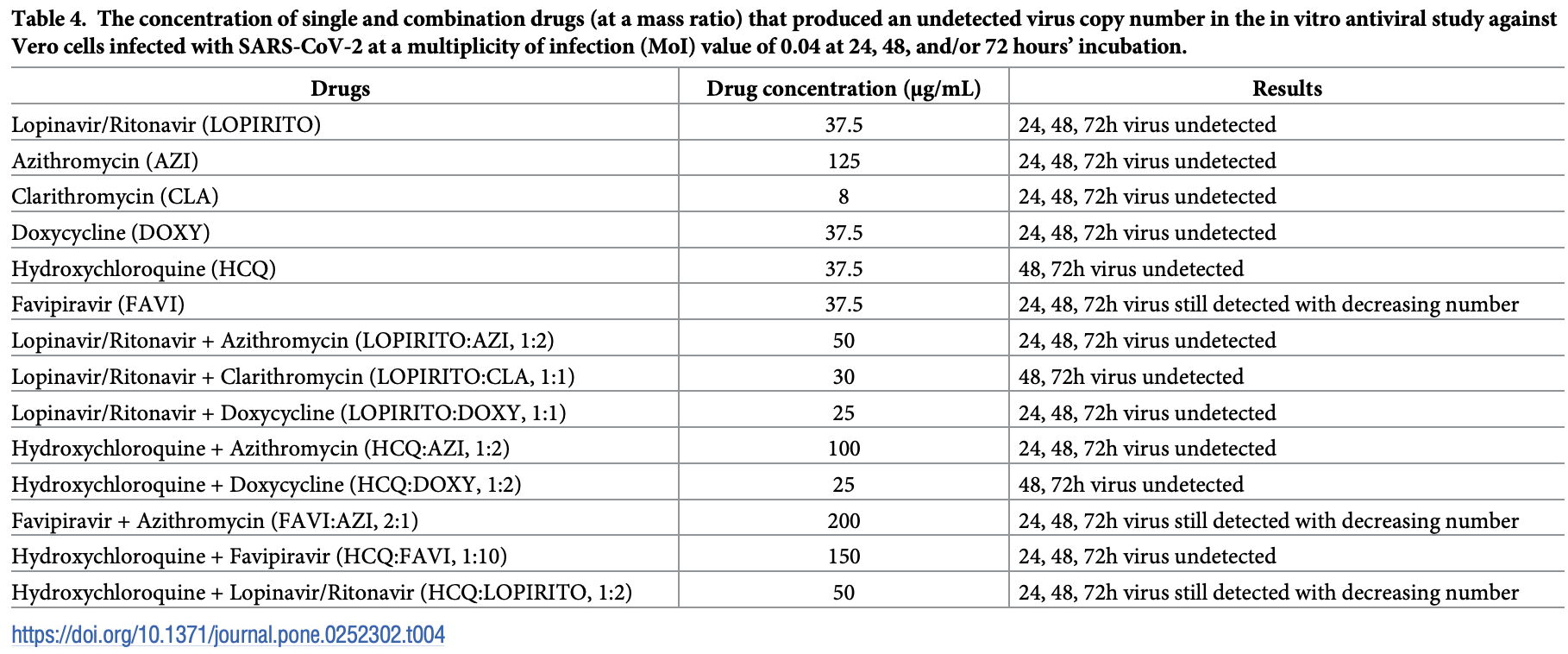
In vitro study of combinations of drugs showing antiviral efficacy of HCQ alone and in combination with AZ, favipiravir, and doxycycline. No high levels of cytotoxicity were observed, and authors conclude that using a combination of drugs can reduce the degree of cytotoxicity, increase antiviral activity, reduce the effect on pro-inflammatory markers, and increase anti-inflammatory response.
39 preclinical studies support the efficacy of HCQ for COVID-19:
Study covers HCQ and favipiravir.
1.
Shang et al., Identification of Cathepsin L as the molecular target of hydroxychloroquine with chemical proteomics, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, doi:10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.101314.
2.
González-Paz et al., Biophysical Analysis of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Recognition and Their Effect on Viral Dynamics in Different Cell Types: A Computational Prediction from In Vitro Experimental Data, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c06968.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Guimarães Silva et al., Are Non-Structural Proteins From SARS-CoV-2 the Target of Hydroxychloroquine? An in Silico Study, ACTA MEDICA IRANICA, doi:10.18502/acta.v61i2.12533.
5.
Nguyen et al., The Potential of Ameliorating COVID-19 and Sequelae From Andrographis paniculata via Bioinformatics, Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, doi:10.1177/11779322221149622.
7.
Yadav et al., Repurposing the Combination Drug of Favipiravir, Hydroxychloroquine and Oseltamivir as a Potential Inhibitor Against SARS-CoV-2: A Computational Study, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-628277/v1.
8.
Hussein et al., Molecular Docking Identification for the efficacy of Some Zinc Complexes with Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine against Main Protease of COVID-19, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129979.
9.
Baildya et al., Inhibitory capacity of Chloroquine against SARS-COV-2 by effective binding with Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 receptor: An insight from molecular docking and MD-simulation studies, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129891.
10.
Noureddine et al., Quantum chemical studies on molecular structure, AIM, ELF, RDG and antiviral activities of hybrid hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19: molecular docking and DFT calculations, Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2020.101334.
11.
Tarek et al., Pharmacokinetic Basis of the Hydroxychloroquine Response in COVID-19: Implications for Therapy and Prevention, European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, doi:10.1007/s13318-020-00640-6.
12.
Rowland Yeo et al., Impact of Disease on Plasma and Lung Exposure of Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin: Application of PBPK Modeling, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.1955.
13.
Hitti et al., Hydroxychloroquine attenuates double-stranded RNA-stimulated hyper-phosphorylation of tristetraprolin/ZFP36 and AU-rich mRNA stabilization, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13835.
14.
Yan et al., Super-resolution imaging reveals the mechanism of endosomal acidification inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 infection, ChemBioChem, doi:10.1002/cbic.202400404.
15.
Mohd Abd Razak et al., In Vitro Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activities of Curcumin and Selected Phenolic Compounds, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231188861.
16.
Alsmadi et al., The In Vitro, In Vivo, and PBPK Evaluation of a Novel Lung-Targeted Cardiac-Safe Hydroxychloroquine Inhalation Aerogel, AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-023-02627-3.
17.
Wen et al., Cholinergic α7 nAChR signaling suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection and inflammation in lung epithelial cells, Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjad048.
18.
Kamga Kapchoup et al., In vitro effect of hydroxychloroquine on pluripotent stem cells and their cardiomyocytes derivatives, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1128382.
19.
Milan Bonotto et al., Cathepsin inhibitors nitroxoline and its derivatives inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105655.
20.
Miao et al., SIM imaging resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells, Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001.
21.
Yuan et al., Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture, Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8.
22.
Faísca et al., Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Hydroxychloroquine Ionic Liquids against SARS-CoV-2, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14040877.
23.
Delandre et al., Antiviral Activity of Repurposing Ivermectin against a Panel of 30 Clinical SARS-CoV-2 Strains Belonging to 14 Variants, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15040445.
24.
Purwati et al., An in vitro study of dual drug combinations of anti-viral agents, antibiotics, and/or hydroxychloroquine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from hospitalized patients in Surabaya, Indonesia, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252302.
25.
Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination, Cell Death & Differentiation, doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3.
26.
Dang et al., Structural basis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of hydroxychloroquine: specific binding to NTD/CTD and disruption of LLPS of N protein, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.16.435741.
27.
Shang (B) et al., Inhibitors of endosomal acidification suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieve viral pneumonia in hACE2 transgenic mice, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-021-01515-1.
28.
Wang et al., Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as ACE2 blockers to inhibit viropexis of 2019-nCoV Spike pseudotyped virus, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153333.
29.
Sheaff, R., A New Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Based on (Hydroxy)Chloroquine Activity, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.02.232892.
30.
Ou et al., Hydroxychloroquine-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry is attenuated by TMPRSS2, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009212.
31.
Andreani et al., In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microbial Pathogenesis, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228.
32.
Clementi et al., Combined Prophylactic and Therapeutic Use Maximizes Hydroxychloroquine Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effects in vitro, Front. Microbiol., 10 July 2020, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01704.
33.
Liu et al., Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discovery 6, 16 (2020), doi:10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0.
34.
Yao et al., In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis., 2020 Mar 9, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237.
Purwati et al., 18 Jun 2021, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
An in vitro study of dual drug combinations of anti-viral agents, antibiotics, and/or hydroxychloroquine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from hospitalized patients in Surabaya, Indonesia
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252302
A potent therapy for the infectious coronavirus disease COVID-19 is urgently required with, at the time of writing, research in this area still ongoing. This study aims to evaluate the in vitro anti-viral activities of combinations of certain commercially available drugs that have recently formed part of COVID-19 therapy. Dual combinatory drugs, namely; Lopinavir-Ritonavir (LOPIRITO)-Clarithromycin (CLA), LOPIRITO-Azithromycin (AZI), LOPIRITO-Doxycycline (DOXY), Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)-AZI, HCQ-DOXY, Favipiravir (FAVI)-AZI, HCQ-FAVI, and HCQ-LOPIRITO, were prepared. These drugs were mixed at specific ratios and evaluated for their safe use based on the cytotoxicity concentration (CC 50 ) values of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The anti-viral efficacy of these combinations in relation to Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from a patient in Universitas Airlangga hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia and evaluated for IC 50 24, 48, and 72 hours after viral inoculation was subsequently determined. Observation of the viral load in qRT-PCR was undertaken, the results of which indicated the absence of high levels of cytotoxicity in any samples and that dual combinatory drugs produced lower cytotoxicity than single drugs. In addition, these combinations demonstrated considerable effectiveness in reducing the copy number of the virus at 48 and 72 hours, while even at 24 hours, post-drug incubation resulted in low IC 50 values. Most combination drugs reduced pro-inflammatory markers, i.e. IL-6 and TNF-α, while increasing the anti-inflammatory response of IL-10. According to these results, the descending order of effective dual combinatory drugs is one of
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Drugs
References
Agrawal, Raju, Udwadia, Favipiravir: A new and emerging antiviral option in COVID-19, Med J Armed Forces India, doi:10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.08.004
Allen, Balius, Mukherjee, Brozell, Moustakas et al., DOCK 6: Impact of new features and current docking performance, J Comput Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.23905
Arabi, Deeb, Al-Hameed, Mandourah, Almekhla et al., Macrolides in critically ill patients with middle east respiratory syndrome, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2019.01.041
Bacharier, Guilbert, Mauger, Boehmer, Beigelman et al., Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Bacharier, Guilbert, Mauger, Boehmer, Beigelman et al., Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2015.13896
Chan, Yao, Yeung, Deng, Bao et al., Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-β1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiv392
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Wong, Chan et al., Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thorax.2003.012658
Covas, Siufi, Silva, Orellana, Isolation and culture of umbilical vein mesenchymal stem cells, Brazilian J Med Biol Res, doi:10.1590/s0100-879x2003000900006
Damle, Vourvahis, Wang, Leaney, Corrigan, Clinical pharmacology perspectives on the antiviral activity of azithromycin and use in COVID-19, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.1857
Dayer, Old drugs for newly emerging viral disease
Dayer, Taleb-Gassabi, Dayer, Lopinavir; a potent drug against coronavirus infection: insight from molecular docking study, Arch Clin Infect Dis
Devaux, Rolain, Colson, Raoult, New insights on the antiviral effects of chloroquine against coronavirus: what to expect for COVID-19?, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938
Dinos, The macrolide antibiotic renaissance, Br J Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.13936
Dong, Hu, Gao, Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Drug Discov Ther, doi:10.5582/ddt.2020.01012
Du, Chen, Favipiravir: pharmacokinetics and concerns about clinical trials for 2019-nCoV infection, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.1844
Du, Li, Xia, Ai, Liang et al., Insights into protein-ligand interactions: mechanisms, models, and methods, Int J Mol Sci
Fraschini, Scaglione, Demartini, Clarithromycin clinical pharmacokinetics, Drug Dispos, doi:10.2165/00003088-199325030-00003
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2930183-5
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Cheng, Deng et al., A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-0233-6
Jin, Du, Xu, Deng, Liu et al., Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y
Kg, AluviaH-W-764: Summary of Product Characteristics
Lim, Im, Cho, Bae, Klein et al., Pharmacokinetics of Hydroxychloroquine and its clinical implications in chemoprophylaxis against malaria caused by plasmodium vivax, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00339-08
Liu, Wan, Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically approved medicines, J Genet Genomics, doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2020.02.001
Lu, Liu, Yang, Zhao, Wang et al., Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials, Haematologica
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2930251-8
Maier, Martinez, Kasavajhala, Wickstrom, Hauser et al., ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB, J Chem Theory Comput, doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00255
Manusubroto, Wicaksono, Tamba, Sudiharto, Pramusinto et al., Neurosurgery services in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, during COVID-19 pandemic: an experience from a developing country, World Neurosurg, doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2020.05.124
Meng, Zhang, Mezei, Cui, Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery, Curr Comput Aided Drug Des, doi:10.2174/157340911795677602
Mennan, Wright, Bhattacharjee, Balain, Richardson et al., Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from different regions of the human umbilical cord, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2013/916136
Meyerowitz, Vannier, Friesen, Schoenfeld, Gelfand et al., Rethinking the role of hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202000919
Nelson, Levy, The history of the tetracyclines, Ann N Y Acad Sci, doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06354.x
Newton, Brockman, Chierakul, Dondorp, Ruangveerayuth et al., Pharmacokinetics of oral doxycycline during combination treatment of severe falciparum malaria, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.49.4.1622-1625.2005
Retallack, Di, Arias, Knopp, Laurie, Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1618029113
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Wilberschied, Kumar et al., Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York state, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8630
Rothan, Inhibitory effect of doxycycline against dengue virus replication in vitro, Arch Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1880-7
Sahraei, Shabani, Shokouhi, Saffaei, Aminoquinolines against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105945
Sargiacomo, Sotgia, Lisanti, COVID-19 and chronological aging: senolytics and other antiaging drugs for the treatment or prevention of corona virus infection?, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103001
Savarino, Boelaert, Cassone, Majori, Cauda, Antiviral effects of chloroquine: Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today's diseases?, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099%2803%2900806-5
Singlas, Clinical pharmacokinetics of azithromycin
Toyama, None, Avigan Tablets
Wang, Sun, Yao, Li, Xu et al., Comprehensive evaluation of ten docking programs on a diverse set of protein-ligand complexes: The prediction accuracy of sampling power and scoring power, Phys Chem Chem Phys, doi:10.1039/c6cp01555g
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0252302",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252302",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A potent therapy for the infectious coronavirus disease COVID-19 is urgently required with, at the time of writing, research in this area still ongoing. This study aims to evaluate the in vitro anti-viral activities of combinations of certain commercially available drugs that have recently formed part of COVID-19 therapy. Dual combinatory drugs, namely; Lopinavir-Ritonavir (LOPIRITO)-Clarithromycin (CLA), LOPIRITO-Azithromycin (AZI), LOPIRITO-Doxycycline (DOXY), Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)-AZI, HCQ-DOXY, Favipiravir (FAVI)-AZI, HCQ-FAVI, and HCQ-LOPIRITO, were prepared. These drugs were mixed at specific ratios and evaluated for their safe use based on the cytotoxicity concentration (CC<jats:sub>50</jats:sub>) values of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The anti-viral efficacy of these combinations in relation to Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from a patient in Universitas Airlangga hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia and evaluated for IC<jats:sub>50</jats:sub> 24, 48, and 72 hours after viral inoculation was subsequently determined. Observation of the viral load in qRT-PCR was undertaken, the results of which indicated the absence of high levels of cytotoxicity in any samples and that dual combinatory drugs produced lower cytotoxicity than single drugs. In addition, these combinations demonstrated considerable effectiveness in reducing the copy number of the virus at 48 and 72 hours, while even at 24 hours, post-drug incubation resulted in low IC<jats:sub>50</jats:sub> values. Most combination drugs reduced pro-inflammatory markers, i.e. IL-6 and TNF-α, while increasing the anti-inflammatory response of IL-10. According to these results, the descending order of effective dual combinatory drugs is one of LOPIRITO-AZI>LOPIRITO-DOXY>HCQ-AZI>HCQ-FAVI>LOPIRITO-CLA>HCQ-DOX. It can be suggested that dual combinatory drugs, e.g. LOPIRITO-AZI, can potentially be used in the treatment of COVID-19 infectious diseases.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6144-2481",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Purwati",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miatmoko",
"given": "Andang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasronudin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hendrianto",
"given": "Eryk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karsari",
"given": "Deya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dinaryanti",
"given": "Aristika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ertanti",
"given": "Nora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ihsan",
"given": "Igo Syaiful",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purnama",
"given": "Disca Sandyakala",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asmarawati",
"given": "Tri Pudy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marfiani",
"given": "Erika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yulistiani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosyid",
"given": "Alfian Nur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wulaningrum",
"given": "Prastuti Asta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Setiawan",
"given": "Herley Windo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siswanto",
"given": "Imam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tri Puspaningsih",
"given": "Ni Nyoman",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-18T17:31:45Z",
"timestamp": 1624037505000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-18T17:32:36Z",
"timestamp": 1624037556000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanyal",
"given": "Mrinmoy",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"name": "State Intelligence Agency (BIN) of Republic of Indonesia"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-09T02:58:01Z",
"timestamp": 1715223481108
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 17,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1623974400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252302",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0252302",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref001",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "R Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"issue": "10224",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref002",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref003",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.wneu.2020.05.124",
"article-title": "Neurosurgery services in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, during COVID-19 pandemic: an experience from a developing country",
"author": "W Manusubroto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e360",
"journal-title": "World Neurosurg",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref004",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/archcid.13823",
"article-title": "Lopinavir; a potent drug against coronavirus infection: insight from molecular docking study",
"author": "MR Dayer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13823",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref005",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/ddt.2020.01012",
"article-title": "Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "L Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov Ther",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref006",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version)",
"author": "Y-H Jin",
"first-page": "4",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref007",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref008",
"volume-title": "KG. AluviaH-W-764: Summary of Product Characteristics",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "[Clinical pharmacokinetics of azithromycin]",
"author": "E Singlas",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pathol Biol (Paris)",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref009",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"article-title": "Clarithromycin clinical pharmacokinetics",
"author": "F Fraschini",
"first-page": "189",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Drug Dispos",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref010",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.49.4.1622-1625.2005",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of oral doxycycline during combination treatment of severe falciparum malaria",
"author": "PN Newton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1622",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref011",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00339-08",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of Hydroxychloroquine and its clinical implications in chemoprophylaxis against malaria caused by plasmodium vivax",
"author": "H Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1468",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref012",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"key": "pone.0252302.ref013",
"unstructured": "Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical. Avigan Tablets 200 mg. 2017 [cited 15 March 2021]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/File/Get/ht8jUiB_MI-aKnlwstwzvw."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1618029113",
"article-title": "Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin",
"author": "H Retallack",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14408",
"issue": "50",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref014",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Old drugs for newly emerging viral disease, COVID-19: bioinformatic prospectivearXiv:2003.04524",
"author": "MR Dayer",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref015",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2019.01.041",
"article-title": "Macrolides in critically ill patients with middle east respiratory syndrome",
"author": "YM Arabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref016",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-013-1880-7",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effect of doxycycline against dengue virus replication in vitro",
"author": "HA Rothan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "711",
"journal-title": "Arch Virol",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref017",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgg.2020.02.001",
"article-title": "Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically approved medicines",
"author": "X Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J Genet Genomics. 2020",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref018",
"volume": "47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13896",
"article-title": "Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "LB Bacharier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2034",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref019",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105945",
"article-title": "Aminoquinolines against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine",
"author": "Z Sahraei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105945",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref020",
"volume": "202055"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938",
"article-title": "New insights on the antiviral effects of chloroquine against coronavirus: what to expect for COVID-19?",
"author": "CA Devaux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105938",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref021",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(03)00806-5",
"article-title": "Antiviral effects of chloroquine: Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today’s diseases?",
"author": "A Savarino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "722",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref022",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103001",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and chronological aging: senolytics and other anti-aging drugs for the treatment or prevention of corona virus infection?",
"author": "C Sargiacomo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6511",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref023",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"article-title": "Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings",
"author": "CM Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref024",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y",
"article-title": "Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors",
"author": "Z Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"issue": "7811",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref025",
"volume": "582",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C6CP01555G",
"article-title": "Comprehensive evaluation of ten docking programs on a diverse set of protein-ligand complexes: The prediction accuracy of sampling power and scoring power",
"author": "Z Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12964",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Phys Chem Chem Phys",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref026",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00255",
"article-title": "ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB",
"author": "JA Maier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3696",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Chem Theory Comput",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref027",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.23905",
"article-title": "DOCK 6: Impact of new features and current docking performance",
"author": "WJ Allen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "J Comput Chem",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref028",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S0100-879X2003000900006",
"article-title": "Isolation and culture of umbilical vein mesenchymal stem cells",
"author": "D Covas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1179",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Brazilian J Med Biol Res",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref029",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials",
"author": "L Lu",
"first-page": "1017",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Haematologica",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref030",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/916136",
"article-title": "Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from different regions of the human umbilical cord",
"author": "C Mennan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref031",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiv392",
"article-title": "Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-β1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset",
"author": "JF-W Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1904",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref032",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1857",
"article-title": "Clinical pharmacology perspectives on the antiviral activity of azithromycin and use in COVID‐19",
"author": "B Damle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref033",
"volume": "108"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York state",
"author": "ES Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2493",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref034",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.13936",
"article-title": "The macrolide antibiotic renaissance",
"author": "GP Dinos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2967",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref035",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1844",
"article-title": "Favipiravir: pharmacokinetics and concerns about clinical trials for 2019‐nCoV infection",
"author": "Y Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "242",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref036",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.08.004",
"article-title": "Favipiravir: A new and emerging antiviral option in COVID-19",
"author": "U Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "370",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Med J Armed Forces India",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref037",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13896",
"article-title": "Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "LB Bacharier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2034",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref038",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06354.x",
"article-title": "The history of the tetracyclines",
"author": "ML Nelson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Ann N Y Acad Sci",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref039",
"volume": "1241",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202000919",
"article-title": "Rethinking the role of hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID‐19",
"author": "EA Meyerowitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6027",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "FASEB J",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref040",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157340911795677602",
"article-title": "Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery",
"author": "X-Y Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Comput Aided Drug Des",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref041",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Insights into protein–ligand interactions: mechanisms, models, and methods",
"author": "X Du",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "144",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "pone.0252302.ref042",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252302"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "An in vitro study of dual drug combinations of anti-viral agents, antibiotics, and/or hydroxychloroquine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus isolated from hospitalized patients in Surabaya, Indonesia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "16"
}
