Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029, Feb 2023
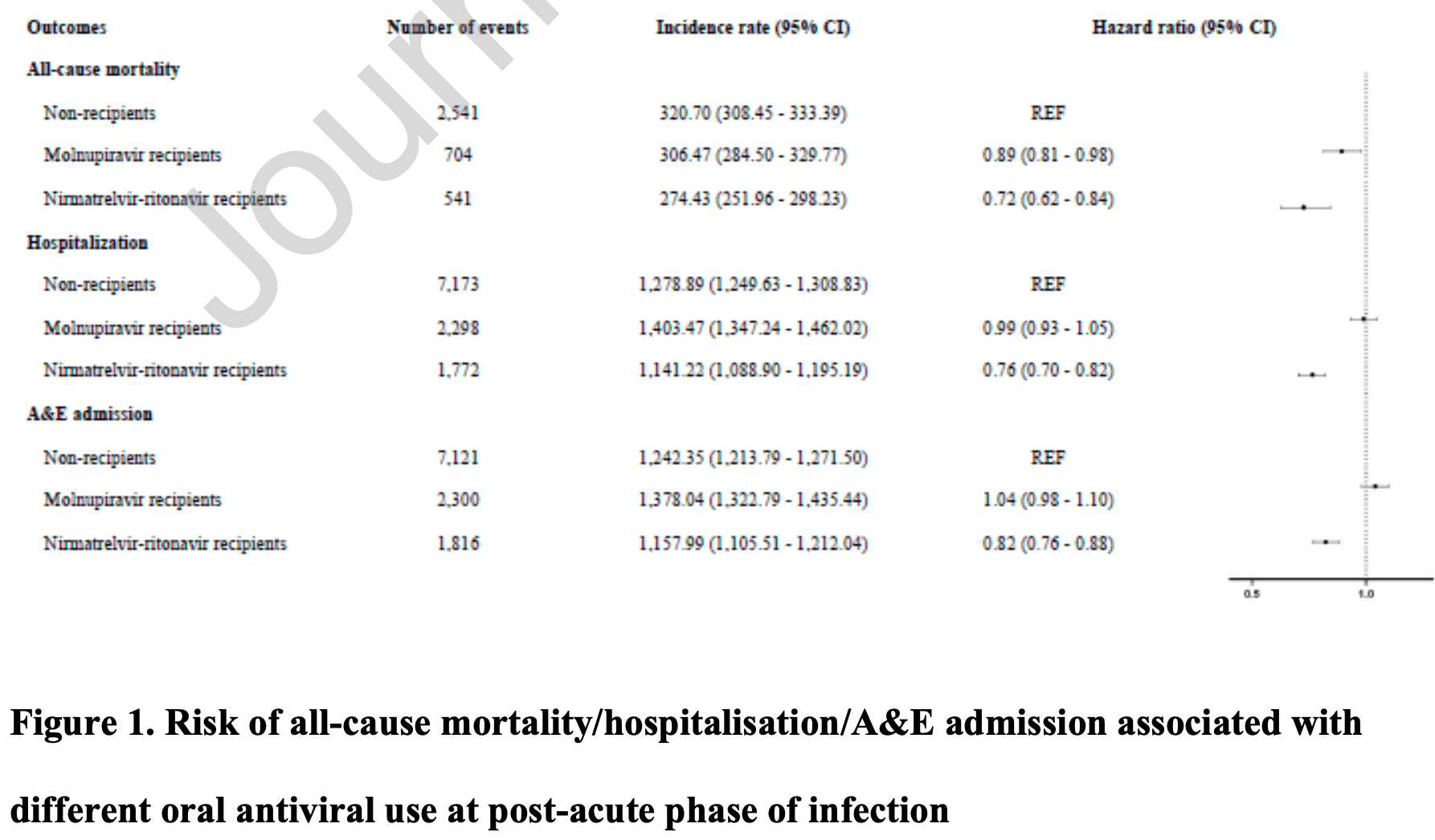
Retrospective 30,040 hospitalized patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality with molnupiravir treatment.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments25.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 11.0% lower, HR 0.89, p = 0.02, treatment 704 of 6,153 (11.4%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 1.0% lower, HR 0.99, p = 0.76, treatment 2,298 of 6,153 (37.3%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 4.0% higher, HR 1.04, p = 0.18, treatment 2,300 of 6,153 (37.4%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, A&E admission, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wan et al., 22 Feb 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 26 February, 2022 - 30 September, 2022.
Contact: ewchan@hku.hk, wongick@hku.hk.
Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase
Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Ethics approval This study was approved by the Central Institutional Review Board of the Hospital Authority of Hong Kong (CIRB-2021-005-4) and the DH Ethics Committee (LM171/2021).
Data sharing Data will not be made available to others because the data custodians have not given permission.
Sources of funding
References
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Evans, Qi, Adebayo, Underwood, Coulson et al., among higher-risk patients with COVID-19 in Wales: a retrospective cohort study
Ledford, Long-COVID treatments: why the world is still waiting, Nature
Wan, Chui, Lai, Chan, Li et al., Bell's palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested casecontrol study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Wan, Mok, Yan, Wang, Zhang et al., Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study, Journal of Infection
Wan, Mok, Yan, Wang, Zhang et al., Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study, Journal of Infection
Wan, Wang, Chui, Mok, Xu et al., Safety of an inactivated, wholevirion COVID-19 vaccine (CoronaVac) in people aged 60 years or older in Hong Kong: a modified selfcontrolled case series, The Lancet Healthy Longevity
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: a, Beta-blockers
Yan, Wan, Ye, Mok, Lai et al., Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccinations against mortality and severe complications after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection: a case-control study, Emerging Microbes & Infections
Yip, Lui, Lai, Wong, Tse et al., Impact of the Use of Oral Antiviral Agents on the Risk of Hospitalization in Community Coronavirus Disease, Clinical Infectious Diseases
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4453"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029",
"alternative-id": [
"S0163445323001172"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The British Infection Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Eric Yuk Fai",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Boyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6261-5674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mathur",
"given": "Sukriti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Cheyenne I Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Vincent Ka Chun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Francisco Tsz Tsun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chui",
"given": "Celine Sze Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4836-7808",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Carlos King Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Philip Hei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Chak Sing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Ian Chi Kei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Esther Wai Yin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"journalofinfection.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T02:35:54Z",
"timestamp": 1677033354000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T02:35:59Z",
"timestamp": 1677033359000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T05:32:13Z",
"timestamp": 1677043933737
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675209600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001172?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001172?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.012",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and sotrovimab on preventing hospital admission among higher-risk patients with COVID-19 in Wales: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib1",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19",
"author": "Agarwal",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib2",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-022-02140-w",
"article-title": "Long-COVID treatments: why the world is still waiting",
"author": "Ledford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "258",
"issue": "7922",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib3",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00125-8",
"article-title": "Safety of an inactivated, whole-virion COVID-19 vaccine (CoronaVac) in people aged 60 years or older in Hong Kong: a modified self-controlled case series",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e491",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Healthy Longevity",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib4",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00451-5",
"article-title": "Bell's palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested case-control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "64",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib5",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.008",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e140",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib6",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2114854",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccinations against mortality and severe complications after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection: a case-control study",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Emerging Microbes & Infections",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.008",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of the Use of Oral Antiviral Agents on the Risk of Hospitalization in Community Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients (COVID-19)",
"author": "Yip",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: a",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1213",
"issue": "10359",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib10",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0163445323001172"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
wan