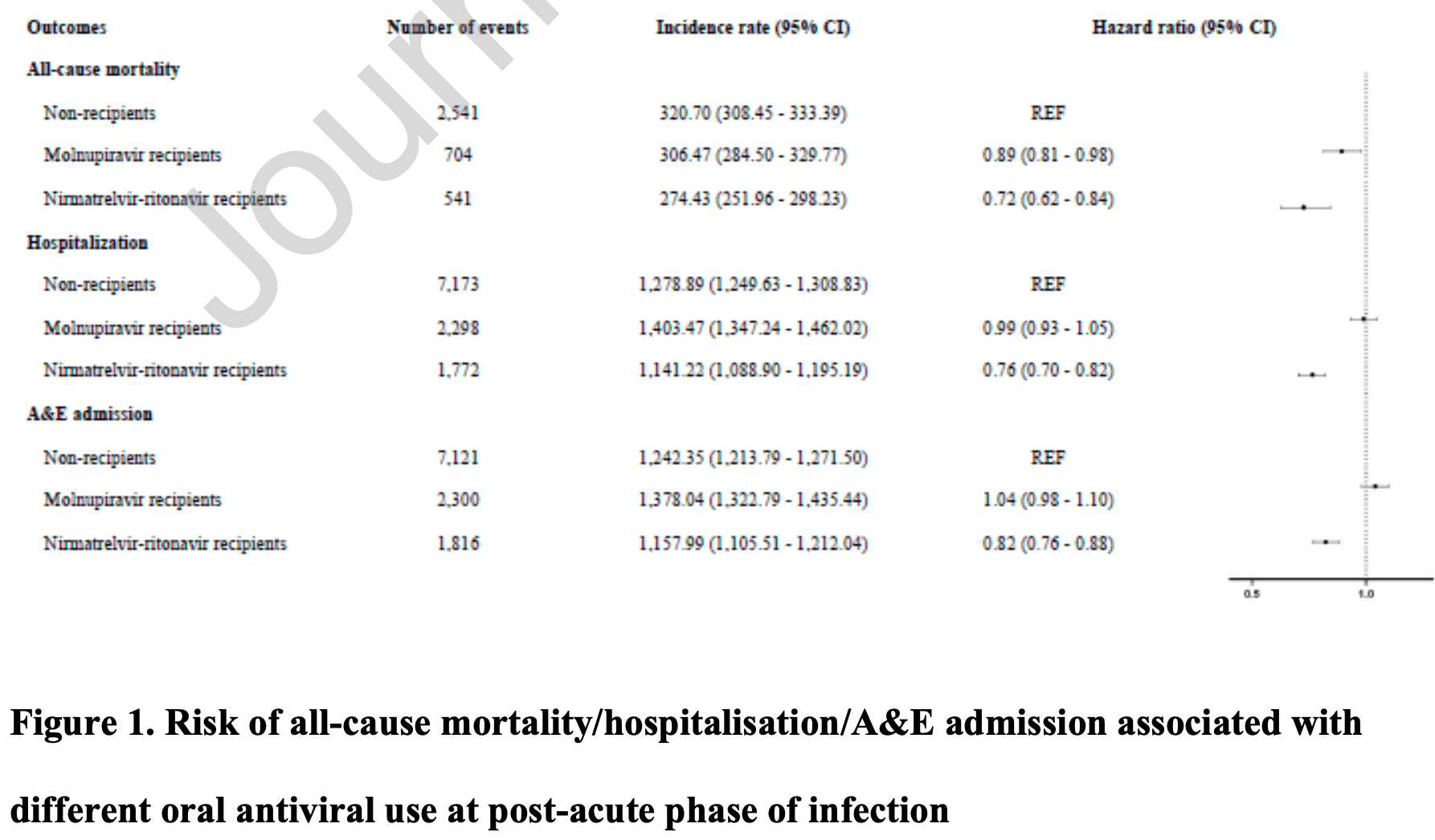
Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029, Feb 2023
Retrospective 30,040 hospitalized patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality with paxlovid treatment. Patients with contraindications to paxlovid were not excluded.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 28.0% lower, HR 0.72, p < 0.001, treatment 541 of 6,604 (8.2%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 24.0% lower, HR 0.76, p < 0.001, treatment 1,772 of 6,604 (26.8%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 18.0% lower, HR 0.82, p < 0.001, treatment 1,816 of 6,604 (27.5%), control 2,541 of 17,283 (14.7%), adjusted per study, A&E admission, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wan et al., 22 Feb 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 26 February, 2022 - 30 September, 2022.
Contact: ewchan@hku.hk, wongick@hku.hk.
Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase
Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Ethics approval This study was approved by the Central Institutional Review Board of the Hospital Authority of Hong Kong (CIRB-2021-005-4) and the DH Ethics Committee (LM171/2021).
Data sharing Data will not be made available to others because the data custodians have not given permission.
Sources of funding
References
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Evans, Qi, Adebayo, Underwood, Coulson et al., among higher-risk patients with COVID-19 in Wales: a retrospective cohort study
Ledford, Long-COVID treatments: why the world is still waiting, Nature
Wan, Chui, Lai, Chan, Li et al., Bell's palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested casecontrol study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Wan, Mok, Yan, Wang, Zhang et al., Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study, Journal of Infection
Wan, Mok, Yan, Wang, Zhang et al., Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study, Journal of Infection
Wan, Wang, Chui, Mok, Xu et al., Safety of an inactivated, wholevirion COVID-19 vaccine (CoronaVac) in people aged 60 years or older in Hong Kong: a modified selfcontrolled case series, The Lancet Healthy Longevity
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: a, Beta-blockers
Yan, Wan, Ye, Mok, Lai et al., Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccinations against mortality and severe complications after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection: a case-control study, Emerging Microbes & Infections
Yip, Lui, Lai, Wong, Tse et al., Impact of the Use of Oral Antiviral Agents on the Risk of Hospitalization in Community Coronavirus Disease, Clinical Infectious Diseases
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4453"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029",
"alternative-id": [
"S0163445323001172"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The British Infection Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Eric Yuk Fai",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Boyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6261-5674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mathur",
"given": "Sukriti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Cheyenne I Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Vincent Ka Chun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Francisco Tsz Tsun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chui",
"given": "Celine Sze Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4836-7808",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Carlos King Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Philip Hei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Chak Sing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Ian Chi Kei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Esther Wai Yin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"journalofinfection.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T02:35:54Z",
"timestamp": 1677033354000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T02:35:59Z",
"timestamp": 1677033359000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-22T05:32:13Z",
"timestamp": 1677043933737
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675209600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001172?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001172?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.012",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and sotrovimab on preventing hospital admission among higher-risk patients with COVID-19 in Wales: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib1",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19",
"author": "Agarwal",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib2",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-022-02140-w",
"article-title": "Long-COVID treatments: why the world is still waiting",
"author": "Ledford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "258",
"issue": "7922",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib3",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00125-8",
"article-title": "Safety of an inactivated, whole-virion COVID-19 vaccine (CoronaVac) in people aged 60 years or older in Hong Kong: a modified self-controlled case series",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e491",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Healthy Longevity",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib4",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00451-5",
"article-title": "Bell's palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested case-control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "64",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib5",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.008",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e140",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib6",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2114854",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccinations against mortality and severe complications after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection: a case-control study",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Emerging Microbes & Infections",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.008",
"article-title": "Vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 infection, hospitalisation, severe complications, cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of the Use of Oral Antiviral Agents on the Risk of Hospitalization in Community Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients (COVID-19)",
"author": "Yip",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: a",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1213",
"issue": "10359",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029_bib10",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0163445323001172"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}