Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults
et al., British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733, Aug 2022
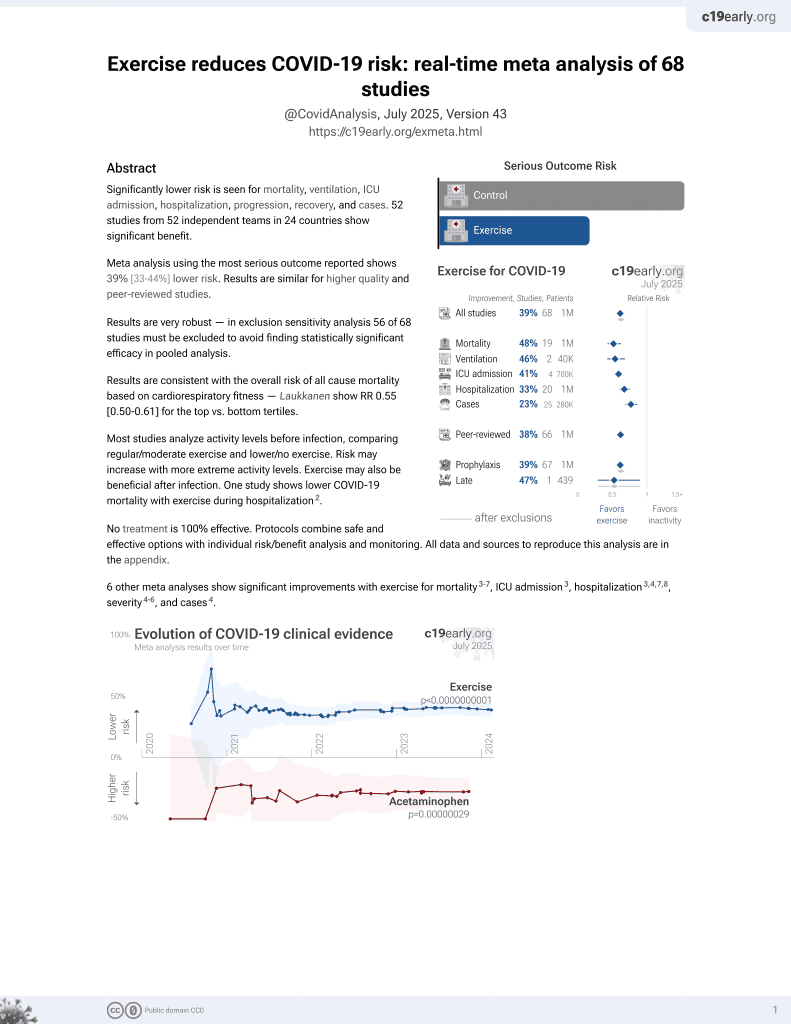
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
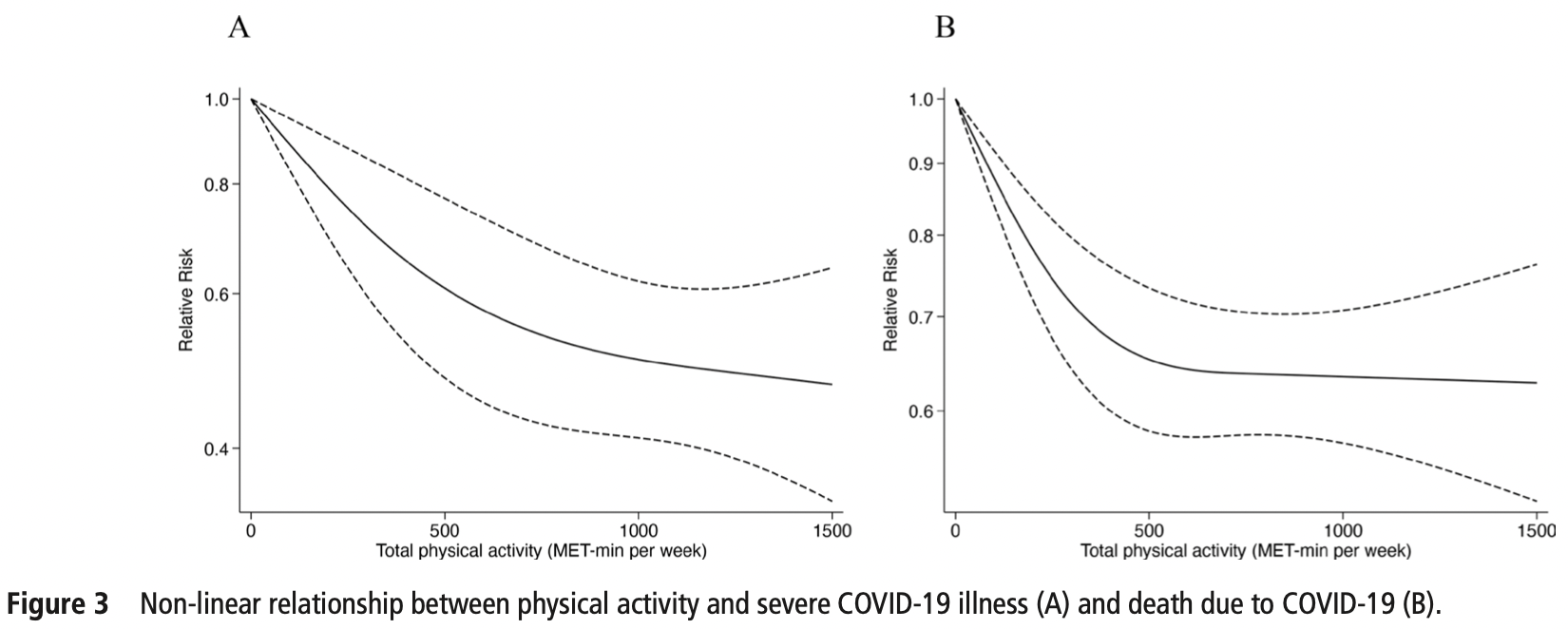
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies, showing lower risk of cases, hospitalization, severe cases, and mortality with regular physical activity. A non-linear dose-response relationship was seen with benefits reducing above 500 MET-min/week.
6 meta-analyses show significant improvements with exercise for mortality1-5,
ICU admission1,
hospitalization1,2,5,6 ,
severity2-4, and
cases2.
Currently there are 68 exercise for COVID-19 studies, showing 48% lower mortality [38‑57%], 46% lower ventilation [32‑57%], 41% lower ICU admission [35‑47%], 33% lower hospitalization [25‑40%], and 23% fewer cases [14‑31%].
|
risk of death, 43.0% lower, RR 0.57, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of severe case, 34.0% lower, RR 0.66, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 36.0% lower, RR 0.64, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of case, 11.0% lower, RR 0.89, p < 0.001.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Rahmati et al., Baseline physical activity is associated with reduced mortality and disease outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2349.
2.
Ezzatvar et al., Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults, British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733.
3.
Sittichai et al., Effects of physical activity on the severity of illness and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Physiology, doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.1030568.
4.
Liu et al., Baseline physical activity and the risk of severe illness and mortality from COVID-19: A dose–response meta-analysis, Preventive Medicine Reports, doi:10.1016/j.pmedr.2023.102130.
Ezzatvar et al., 22 Aug 2022, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults
British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733
Objective To quantify the association between physical activity and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19associated hospitalisation, severe illness and death due to COVID-19 in adults. Design A systematic review and meta-analysis. Data sources Three databases were systematically searched through March 2022. Eligibility criteria for selecting studies Peerreviewed articles reporting the association between regular physical activity and at least one COVID-19 outcome in adults were included. Risk estimates (ORs, relative risk (RR) ratios or HRs) were extracted and pooled using a random-effects inverse-variance model. Results Sixteen studies were included (n=1 853 610). Overall, those who engaged in regular physical activity had a lower risk of infection (RR=0.89; 95% CI 0.84 to 0.95; I 2 =0%), hospitalisation (RR=0.64; 95% CI 0.54 to 0.76; I 2 =48.01%), severe COVID-19 illness (RR=0.66; 95% CI 0.58 to 0.77; I 2 =50.93%) and COVID-19-related death (RR=0.57; 95% CI 0.46 to 0.71; I 2 =26.63%) as compared with their inactive peers. The results indicated a non-linear dose-response relationship between physical activity presented in metabolic equivalent of task (MET)-min per week and severe COVID-19 illness and death (p for non-linearity <0.001) with a flattening of the dose-response curve at around 500 MET-min per week. Conclusions Regular physical activity seems to be related to a lower likelihood of adverse COVID-19 outcomes. Our findings highlight the protective effects of engaging in sufficient physical activity as a public health strategy, with potential benefits to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19. Given the heterogeneity and risk of publication bias, further studies with standardised methodology and outcome reporting are now needed. PROSPERO registration number CRD42022313629. Contributors AG-H and YE conceptualised and designed the study, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. RR-V and YE designed the data collection instruments, collected data, carried out the initial analyses and reviewed and revised the manuscript. MI and AG-H conceptualised and designed the study, coordinated and supervised data collection, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. AG-H is responsible for the integrity of the work as a whole.
Competing interests None declared. Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Patient consent for publication Not applicable. Ethics approval Not applicable. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise. Online supplemental eTable 2. Results Online supplemental eFigure 1. Doi plot for hospitalisation. Relative Risk was transferred to natural logarithm form. BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance Supplemental material placed on this supplemental material which has been supplied by the author(s)
References
Ahmadi, Huang, Inan-Eroglu, Lifestyle risk factors and infectious disease mortality, including COVID-19, among middle aged and older adults: evidence from a community-based cohort study in the United Kingdom, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.04.022
Ainsworth, Haskell, Whitt, Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and met intensities, Med Sci Sports Exerc, doi:10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009
Arem, Moore, Patel, Leisure time physical activity and mortality, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0533
Brandenburg, Lesser, Thomson, Does higher self-reported cardiorespiratory fitness reduce the odds of hospitalization from COVID-19?, J Phys Act Health, doi:10.1123/jpah.2020-0817
Brandenburg, Lesser, Thomson, Giles, Does higher self-reported cardiorespiratory fitness reduce the odds of hospitalization from COVID-19?, J Phys Act Heal, doi:10.1123/jpah.2020-0817
Brandenburg, Lesser, Thomson, Giles, Does higher self-reported cardiorespiratory fitness reduce the odds of hospitalization from COVID-19?, J Phys Act Heal, doi:10.1123/jpah.2020-0817
Bull, Ss, Biddle, World Health organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2020-102955
Chastin, Abaraogu, Bourgois, Effects of regular physical activity on the immune system, vaccination and risk of community-acquired infectious disease in the general population: systematic review and meta-analysis, Sports Med, doi:10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1
Cho, Lee, Physical activity and the risk of covid-19 infection and mortality: a nationwide population-based case-control study, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10071539
Christensen, Arneja, Cyr, Sturrock, Brooks, The association of estimated cardiorespiratory fitness with COVID-19 incidence and mortality: A cohort study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0250508
Christensen, Arneja, Cyr, Sturrock, Brooks, The association of estimated cardiorespiratory fitness with COVID-19 incidence and mortality: A cohort study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0250508
Christensen, Arneja, Cyr, The association of estimated cardiorespiratory fitness with COVID-19 incidence and mortality: a cohort study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0250508
Clerkin, Fried, Raikhelkar, COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046941
Cunningham, Physical activity and its relationship with COVID-19 cases and deaths: analysis of U.S. counties, J Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2021.03.008
De Souza, Motta-Santos, Soares, Association of physical activity levels and the prevalence of COVID-19-associated hospitalization, J Sci Med Sport, doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2021.05.011
Després, Severe COVID-19 outcomes -the role of physical activity, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-021-00521-1
Duggal, Niemiro, Harridge, Can physical activity ameliorate immunosenescence and thereby reduce age-related multi-morbidity?, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-019-0177-9
Dwyer, Pasini, Dominicis, Physical activity: benefits and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, Scand J Med Sci Sports, doi:10.1111/sms.13710
Ekblom-Bak, Väisänen, Ekblom, Cardiorespiratory fitness and lifestyle on severe COVID-19 risk in 279,455 adults: a case control study, Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act, doi:10.1186/s12966-021-01198-5
Fierens, Goossens, Exercise versus no exercise for the occurrence, severity and duration of acute respiratory infections, Int J Nurs Pract, doi:10.1111/ijn.12891
Furuya-Kanamori, Barendregt, Doi, A new improved graphical and quantitative method for detecting bias in meta-analysis, Int J Evid Based Healthc, doi:10.1097/XEB.0000000000000141
Geijerstam, Mehlig, Börjesson, Fitness, strength and severity of COVID-19: a prospective register study of 1 559 187 Swedish conscripts, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051316
Greenland, Longnecker, Methods for trend estimation from summarized doseresponse data, with applications to meta-analysis, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116237
Greenland, Model-based estimation of relative risks and other epidemiologic measures in studies of common outcomes and in case-control studies, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwh221
Gualano, Fitness, strength and severity of COVID-19: A prospective register study of 1 559 187 Swedish conscripts, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105426
Guyatt, Oxman, Schünemann, Grade guidelines: a new series of articles in the journal of clinical epidemiology, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.011
Hallam, Jones, Alley, Exercise after influenza or COVID-19 vaccination increases serum antibody without an increase in side effects, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.005
Hamdan, Badrasawi, Zidan, Risk factors associated with hospitalization owing to COVID-19: a cross-sectional study in palestine, J Int Med Res, doi:10.1177/03000605211064405
Hamer, 'donovan, Stamatakis, Lifestyle risk factors, obesity and infectious disease mortality in the general population: linkage study of 97,844 adults from England and Scotland, Prev Med, doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2019.03.002
Hamer, Kivimäki, Gale, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: a community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059
Hamling, Lee, Weitkunat, Facilitating meta-analyses by deriving relative effect and precision estimates for alternative comparisons from a set of estimates presented by exposure level or disease category, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.3013
Hamrouni, Roberts, Thackray, Associations of obesity, physical activity level, inflammation and cardiometabolic health with COVID-19 mortality: A prospective analysis of the UK Biobank cohort, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055003
Hamrouni, Roberts, Thackray, Associations of obesity, physical activity level, inflammation and cardiometabolic health with COVID-19 mortality: A prospective analysis of the UK Biobank cohort, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055003
Hamrouni, Roberts, Thackray, Associations of obesity, physical activity level, inflammation and cardiometabolic health with COVID-19 mortality: a prospective analysis of the UK biobank cohort, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055003
Heart, Undefined, Health, and BI. Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies
Higgins, Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Inthout, Ioannidis, Borm, The hartung-knapp-sidik-jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard derSimonian-laird method, BMC Med Res Methodol, doi:10.1186/1471-2288-14-25
Jeong, Kim, Kang, Mortality reduction with physical activity in patients with and without cardiovascular disease, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehz564
Kohl, Craig, Lambert, The pandemic of physical inactivity: global action for public health, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60898-8
Latorre-Román, Ángel, Guzmán-Guzmán, Delgado-Floody, Protective role of physical activity patterns prior to COVID-19 confinement with the severity/ duration of respiratory pathologies consistent with COVID-19 symptoms in Spanish populations, Res Sports Med, doi:10.1080/15438627.2021.1937166
Leandro, Ferreira, Silva, Ae, Covid-19 and exercise-induced immunomodulation, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000508951
Lee, Lee, Moon, Physical activity and the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, severe COVID-19 illness and COVID-19 related mortality in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-104203
Li, Hua, Modifiable lifestyle factors and severe COVID-19 risk: a mendelian randomisation study, BMC Med Genomics, doi:10.1186/s12920-021-00887-1
Localio, Margolis, Berlin, Relative risks and confidence intervals were easily computed indirectly from multivariable logistic regression, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.12.001
Maltagliati, Sieber, Sarrazin, Muscle strength explains the protective effect of physical activity against COVID-19 hospitalization among adults aged 50 years and older, J Sports Sci, doi:10.1080/02640414.2021.1964721
Maltagliati, Sieber, Sarrazin, Muscle strength explains the protective effect of physical activity against COVID-19 hospitalization among adults aged 50 years and older, J Sports Sci, doi:10.1080/02640414.2021
Maltagliati, Sieber, Sarrazin, Muscle strength explains the protective effect of physical activity against COVID-19 hospitalization among adults aged 50 years and older, J Sports Sci, doi:10.1080/02640414.2021
Mcnutt, Wu, Xue, Estimating the relative risk in cohort studies and clinical trials of common outcomes, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwg074
Mehlig, Börjesson, Online supplemental emethod 2. Excluded studies and reasons for exclusion. Did not include physical activity data: Af Geijerstam A, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051316
Nieman, Henson, Austin, Upper respiratory tract infection is reduced in physically fit and active adults, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsm.2010.077875
Nieman, Wentz, The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system, J Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009
Orsini, Li, Wolk, Meta-analysis for linear and nonlinear dose-response relations: examples, an evaluation of approximations, and software, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwr265
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pinto, Goessler, Fernandes, No independent associations between physical activity and clinical outcomes among hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, J Sport Heal Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2021.08.001
Pinto, Goessler, Fernandes, No independent associations between physical activity and clinical outcomes among hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, J Sport Heal Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2021.08.001
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Rothman, Greenland, Lash, Modern epidemiology
Rowlands, Dempsey, Gillies, Association between accelerometerassessed physical activity and severity of COVID-19 in UK biobank, Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes, doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2021.08.011
Salgado-Aranda, Pérez-Castellano, Núñez-Gil, Influence of Baseline Physical Activity as a Modifying Factor on COVID-19 Mortality: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00418-6
Salgado-Aranda, Pérez-Castellano, Núñez-Gil, Influence of Baseline Physical Activity as a Modifying Factor on COVID-19 Mortality: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00418-6
Sallis, Young, Tartof, Physical inactivity is associated with a higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes: a study in 48 440 adult patients, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-104080
Sellami, Gasmi, Denham, Effects of acute and chronic exercise on immunological parameters in the elderly aged: can physical activity counteract the effects of aging?, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02187
Senna, Torres, Lopes, Moderate physical training attenuates perinatal low-protein-induced spleen lymphocyte apoptosis in endotoxemic adult offspring rats, Eur J Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-015-0925-y
Simpson, Katsanis, The immunological case for staying active during the COVID-19 pandemic, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.041
Simpson, Kunz, Agha, Exercise and the regulation of immune functions, Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci, doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001
Steenkamp, Saggers, Bandini, Small steps, strong shield: directly measured, moderate physical activity in 65 361 adults is associated with significant protective effects from severe COVID-19 outcomes, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159
Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting, J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Tavakol, Ghannadi, Tabesh, Relationship between physical activity, healthy lifestyle and COVID-19 disease severity; a cross-sectional study, J Public Health, doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01468-9
Wong, Lai, Ou, Is exercise protective against influenza-associated mortality?, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002108
Zhang, Kf, What's the relative risk? a method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes, J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.280.19.1690
Zhang, Li, Sun, Physical activity and COVID-19: an observational and Mendelian randomisation study, J Glob Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.10.020514
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733",
"ISSN": [
"0306-3674",
"1473-0480"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To quantify the association between physical activity and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19-associated hospitalisation, severe illness and death due to COVID-19 in adults.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>A systematic review and meta-analysis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Data sources</jats:title><jats:p>Three databases were systematically searched through March 2022.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Eligibility criteria for selecting studies</jats:title><jats:p>Peer-reviewed articles reporting the association between regular physical activity and at least one COVID-19 outcome in adults were included. Risk estimates (ORs, relative risk (RR) ratios or HRs) were extracted and pooled using a random-effects inverse-variance model.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Sixteen studies were included (n=1 853 610). Overall, those who engaged in regular physical activity had a lower risk of infection (RR=0.89; 95% CI 0.84 to 0.95; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>=0%), hospitalisation (RR=0.64; 95% CI 0.54 to 0.76; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>=48.01%), severe COVID-19 illness (RR=0.66; 95% CI 0.58 to 0.77; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>=50.93%) and COVID-19-related death (RR=0.57; 95% CI 0.46 to 0.71; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>=26.63%) as compared with their inactive peers. The results indicated a non-linear dose–response relationship between physical activity presented in metabolic equivalent of task (MET)-min per week and severe COVID-19 illness and death (p for non-linearity <0.001) with a flattening of the dose–response curve at around 500 MET-min per week.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Regular physical activity seems to be related to a lower likelihood of adverse COVID-19 outcomes. Our findings highlight the protective effects of engaging in sufficient physical activity as a public health strategy, with potential benefits to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19. Given the heterogeneity and risk of publication bias, further studies with standardised methodology and outcome reporting are now needed.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>PROSPERO registration number</jats:title><jats:p>CRD42022313629.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9691-5998",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ezzatvar",
"given": "Yasmin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3075-6960",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramírez-Vélez",
"given": "Robinson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1506-4272",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Izquierdo",
"given": "Mikel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1397-7182",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Garcia-Hermoso",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Sports Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Br J Sports Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-23T00:00:14Z",
"timestamp": 1661212814000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-23T00:00:48Z",
"timestamp": 1661212848000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2017-2020",
"PID2020-113098RB-I00"
],
"name": "Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"CP18/0150"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-23T00:41:53Z",
"timestamp": 1661215313836
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "bjsports-2022-105733",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.19759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046941",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2020-102955",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/sms.13710",
"article-title": "Physical activity: benefits and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Dwyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1291",
"journal-title": "Scand J Med Sci Sports",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.5",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-019-0177-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ypmed.2019.03.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-104203",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00521-1",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 outcomes - the role of physical activity",
"author": "Després",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.11",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.12",
"unstructured": "Page MJ , McKenzie JE , Bossuyt PM . The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372.doi:10.1136/bmj.n71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.283.15.2008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.13"
},
{
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.14",
"unstructured": "Heart N, Lung undefined, Health and BI . Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.280.19.1690",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwh221",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwg074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-14-25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-104080",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.23"
},
{
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwr265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwr265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.27",
"unstructured": "Steenkamp L , Saggers RT , Bandini R . Small steps, strong shield: directly measured, moderate physical activity in 65 361 adults is associated with significant protective effects from severe COVID-19 outcomes. Br J Sports Med 2022:1–10.doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2021.04.022",
"article-title": "Lifestyle risk factors and infectious disease mortality, including COVID-19, among middle aged and older adults: evidence from a community-based cohort study in the United Kingdom",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.28",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15438627.2021.1937166",
"article-title": "Protective role of physical activity patterns prior to COVID-19 confinement with the severity/duration of respiratory pathologies consistent with COVID-19 symptoms in Spanish populations",
"author": "Latorre-Román",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Res Sports Med",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.29",
"volume": "00",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009",
"article-title": "Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and met intensities",
"author": "Ainsworth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S498",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Sports Exerc",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.31",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2021.08.011",
"article-title": "Association between accelerometer-assessed physical activity and severity of COVID-19 in UK biobank",
"author": "Rowlands",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "997",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.32",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1123/jpah.2020-0817",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211064405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605211064405",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with hospitalization owing to COVID-19: a cross-sectional study in palestine",
"author": "Hamdan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Int Med Res",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.35",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Relationship between physical activity, healthy lifestyle and COVID-19 disease severity; a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Tavakol",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Public Health",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.36",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsams.2021.05.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12966-020-01065-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12966-021-01198-5",
"article-title": "Cardiorespiratory fitness and lifestyle on severe COVID-19 risk in 279,455 adults: a case control study",
"author": "Ekblom-Bak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.39",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12920-021-00887-1",
"article-title": "Modifiable lifestyle factors and severe COVID-19 risk: a mendelian randomisation study",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med Genomics",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.40",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsm.2010.077875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsm.2010.077875",
"article-title": "Upper respiratory tract infection is reduced in physically fit and active adults",
"author": "Nieman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "987",
"journal-title": "Br J Sports Med",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.42",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.041",
"article-title": "The immunological case for staying active during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.43",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0002108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001",
"article-title": "Exercise and the regulation of immune functions",
"author": "Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.46",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055003",
"article-title": "Associations of obesity, physical activity level, inflammation and cardiometabolic health with COVID-19 mortality: a prospective analysis of the UK biobank cohort",
"author": "Hamrouni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.47",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0533",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.48",
"unstructured": "Arem H , Moore SC , Patel A , et al . Leisure time physical activity and mortality. JAMA Intern Med 2015;175:959.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0533"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehz564",
"article-title": "Mortality reduction with physical activity in patients with and without cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Jeong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3547",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.49",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02187",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02187",
"article-title": "Effects of acute and chronic exercise on immunological parameters in the elderly aged: can physical activity counteract the effects of aging?",
"author": "Sellami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.51",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051316",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051316",
"article-title": "Fitness, strength and severity of COVID-19: a prospective register study of 1 559 187 Swedish conscripts",
"author": "Af Geijerstam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.53",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60898-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60898-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.55"
},
{
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.56",
"unstructured": "Rothman K , Greenland S , Lash T . Modern epidemiology, 2008. Available: https://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(08)01394-2/abstract [Accessed 01 Jun 2022]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.12.001",
"article-title": "Relative risks and confidence intervals were easily computed indirectly from multivariable logistic regression",
"author": "Localio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "874",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.57",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2022-105426",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2022-105426",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022082217000754000_bjsports-2022-105733v1.59"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bjsm.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Physical Therapy, Sports Therapy and Rehabilitation",
"Orthopedics and Sports Medicine",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy"
}