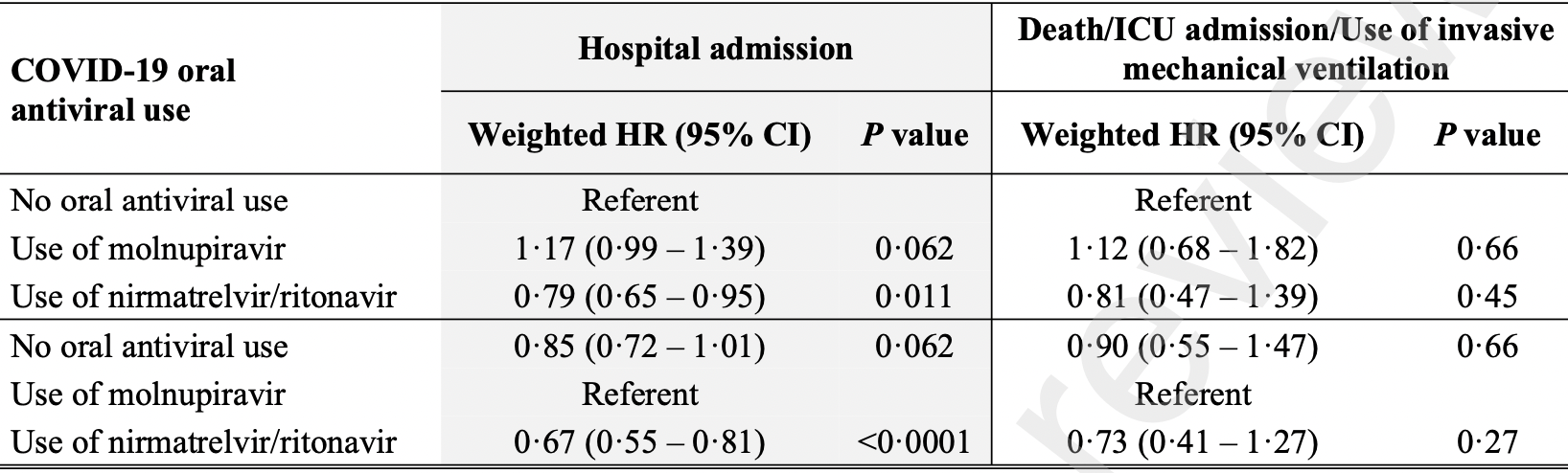
Impact of the use of oral antiviral agents on the risk of hospitalization in community COVID-19 patients
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac687, May 2022 (preprint)
Propensity score weighted retrospective of 93,883 outpatients in Hong Kong, 5,808 treated with molnupiravir and 4,921 treated with paxlovid, showing higher hospitalization and higher combined mortality/mechanical ventilation/ICU admission with molnupiravir, without statistical significance; and lower hospitalization and combined mortality/mechanical ventilation/ICU admission with paxlovid, statistically significant only for hospitalization.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments25.
Study covers paxlovid and molnupiravir.
|
combined death/ventilation/ICU, 12.0% higher, HR 1.12, p = 0.66, treatment 53 of 5,808 (0.9%), control 151 of 83,154 (0.2%), propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards, day 30.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 17.0% higher, HR 1.17, p = 0.06, treatment 437 of 5,808 (7.5%), control 1,322 of 83,154 (1.6%), propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards, day 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Yip et al., 24 May 2022, retrospective, placebo-controlled, China, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 16 February, 2022 - 31 March, 2022.
Contact: wonglaihung@cuhk.edu.hk.
Impact of the use of oral antiviral agents on the risk of hospitalization in community COVID-19 patients
References
Ahmad, Batool, Ain, Kim, Choi, Exploring the Binding Mechanism of PF-07321332 SARS-CoV-2 Protease Inhibitor through Molecular Dynamics and Binding Free Energy Simulations, Int J Mol Sci
Balint, Voros-Horvath, Szechenyi, Omicron: increased transmissibility and decreased pathogenicity, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis
Bloomberg, Hong Kong's Nursing Homes Are Unvaccinated Hotbeds of Covid
Cheung, Fung, Chow, Tung, Structured data entry of clinical information for documentation and data collection, Stud Health Technol Inform
Consortium, Whost, Pan, Peto, Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 -Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J Med
Dal-Re, Becker, Bottieau, Holm, Availability of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and the requirement for an ethical prescribing approach, Lancet Infect Dis
De Anda, Johnson, Pedley, Molnupiravir for Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. Reply, N Engl J Med
Gandhi, Malani, Rio, COVID-19 Therapeutics for Nonhospitalized Patients, JAMA
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hksar Government, Overall first-dose COVID-19 vaccination rate of RCHEs and RCHDs rises to 84 per cent on 11
Hui, Zumla, Advances in the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, clinical management and prevention of coronavirus disease 2019, Curr Opin Pulm Med
Jo, Kim, Radnaabaatar, Model-based cost-effectiveness analysis of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 in Korea, Epidemiol Health
Kabinger, Stiller, Schmitzova, Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis, Nat Struct Mol Biol
Krammer, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development, Nature
Lui, Yip, Wong, Significantly Lower Case-fatality Ratio of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) than Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in Hong Kong-A Territory-Wide Cohort Study, Clin Infect Dis
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of Paxlovid in Reducing Severe COVID-19 and Mortality in High Risk Patients, Clin Infect Dis
Pfizer, Evaluation of Protease Inhibition for COVID-19 in Standard-Risk Patients (EPIC-SR
Roth, Emmons-Bell, Alger, Trends in Patient Characteristics and COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in the United States During the COVID-19 Pandemic, JAMA Netw Open
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral COVID Antiviral Drugs, Clin Infect Dis
Thorlund, Sheldrick, Meyerowitz-Katz, Singh, Hill, Making Statistical Sense of the Molnupiravir MOVe-OUT Clinical Trial, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., community-dwelling, ambulatory COVID-19 patients during the BA.2.2 wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, doi:10.1101/2022.05.26.22275631
Yip, Wong, Lui, Current and Past Infections of HBV Do Not Increase Mortality in Patients With COVID-19, Hepatology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac687",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac687",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We examined the effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in reducing hospitalization and deaths in a real-world cohort of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This was a territory-wide retrospective cohort study in Hong Kong. Non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients who attended designated outpatient clinics between 16 February and 31 March 2022 were identified. Patients hospitalized on the day of the first clinic appointment or used both oral antivirals were excluded. The primary endpoint was hospitalization. The secondary endpoint was a composite of intensive care unit admission, invasive mechanical ventilation use, and/or death.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Of 93,883 patients, 83,154 (88.6%), 5,808 (6.2%), and 4,921 (5.2%) were oral antiviral non-users, molnupiravir users, and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir users respectively. Compared to non-users, oral antiviral users were older and had more comorbidities, lower complete vaccination rate, and more hospitalizations in the previous year. Molnupiravir users were older, and had more comorbidities, lower complete vaccination rate, and more hospitalizations in the previous year than nirmatrelvir/ritonavir users. At a median follow-up of 30 days, 1,931 (2.1%) patients were hospitalized and 225 (0.2%) patients developed the secondary endpoint. After propensity score weighting, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir use (weighted hazard ratio 0.79, 95%CI 0.65-0.95, P = 0.011) but not molnupiravir use (weighted hazard ratio 1.17, 95%CI 0.99-1.39, P = 0.062) was associated with a reduced risk of hospitalization than non-users. The use of molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was not associated with a lower risk of the secondary endpoint as compared to non-users.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir but not molnupiravir was associated with a reduced risk of hospitalization in real-world non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1819-2464",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Digestive Disease"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yip",
"given": "Terry Cheuk Fung",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Jockey Club School of Public Health & Primary Care"
}
],
"family": "Lui",
"given": "Grace Chung Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Mandy Sze Man",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Jockey Club School of Public Health & Primary Care"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Vincent Wai Sun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Digestive Disease"
}
],
"family": "Tse",
"given": "Yee Kit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
}
],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Bosco Hon Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
}
],
"family": "Hui",
"given": "Elsie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine, Prince of Wales Hospital, Hospital Authority , Hong Kong"
}
],
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Maria KW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong ; Hong Kong"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Union Hospital , Hong Kong"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Henry Lik Yuen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Jockey Club School of Public Health & Primary Care"
}
],
"family": "Hui",
"given": "David Shu Cheong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2863-9389",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics"
},
{
"name": "Medical Data Analytics Centre (MDAC)"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Digestive Disease"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Grace Lai Hung",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-29T01:48:15Z",
"timestamp": 1661737695000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-29T01:48:16Z",
"timestamp": 1661737696000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-29T02:11:14Z",
"timestamp": 1661739074182
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661731200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac687/45601511/ciac687.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac687/45601511/ciac687.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac687/6678124"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of the use of oral antiviral agents on the risk of hospitalization in community COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article"
}