Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective
et al., Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113, Jan 2025
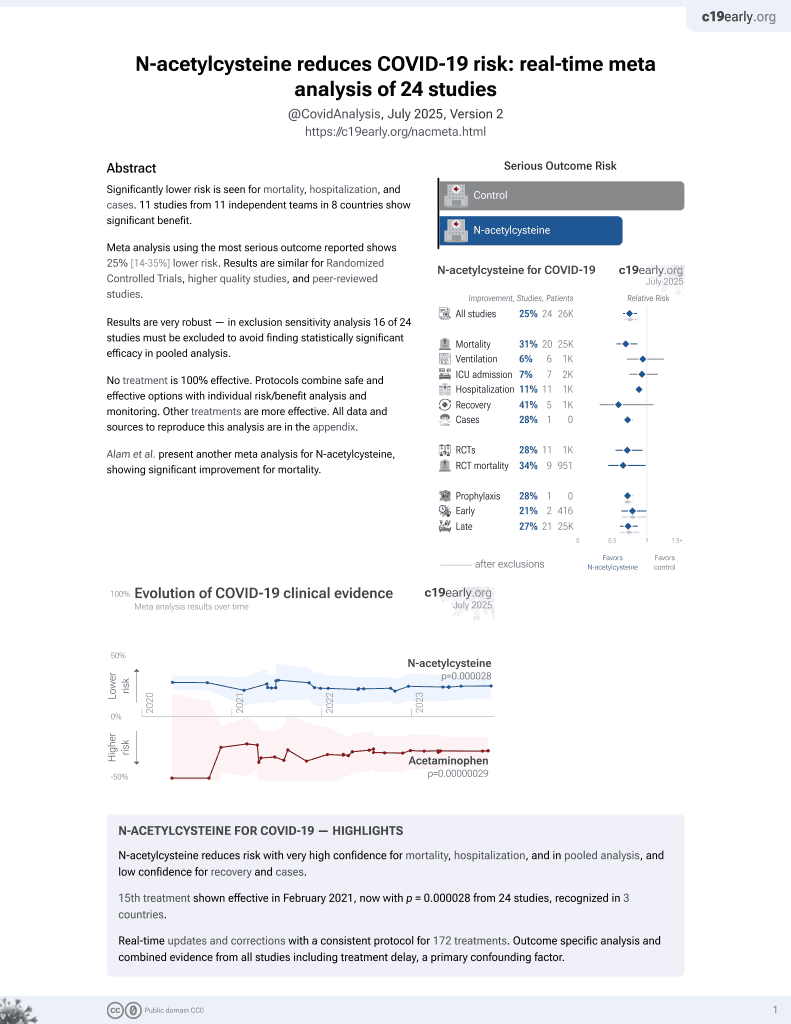
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
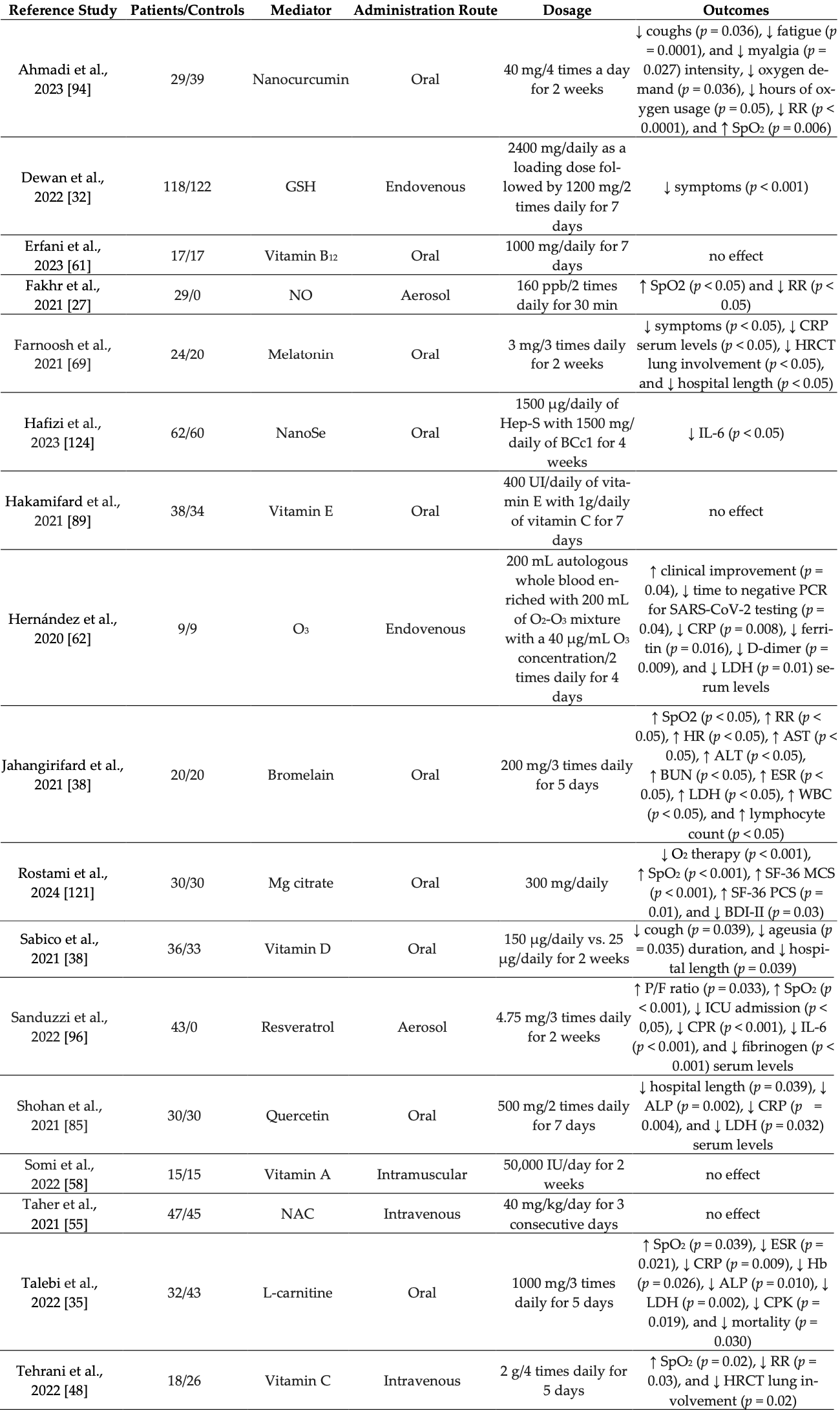
Review of immune-boosting and antiviral effects of antioxidants in COVID-19 pneumonia. Authors provide an overview of the literature on the use of antioxidants, including vitamins, trace elements, ozone, glutathione, L-carnitine, melatonin, bromelain, N-acetylcysteine, and numerous polyphenols, in hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. These molecules support endothelial function, reduce thrombosis risk, and may help mitigate the effects of the cytokine storm through their ROS-scavenging properties. Clinical evidence suggests that antioxidant supplementation may decrease inflammation, support immune cell function, shorten recovery times, and exert direct antiviral effects that inhibit the infection and replication of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells.
Review covers vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, quercetin, curcumin, melatonin, N-acetylcysteine, and selenium.
1.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
2.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
3.
Yuan et al., The role of cell death in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01580-8.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., 16 Jan 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: stefanosanduzzi@gmail.com (corresponding author), sanduzzi@unina.it, marialuisa.bocchino@unina.it.
Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective
Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has profoundly impacted global health, with pneumonia emerging as a major complication in severe cases. The pathogenesis of COVID-19 is marked by the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and an excessive inflammatory response, resulting in oxidative stress and significant tissue damage, particularly in the respiratory system. Antioxidants have garnered considerable attention for their potential role in managing COVID-19 pneumonia by mitigating oxidative stress and modulating immune responses. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the literature on the use of antioxidants in hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. Studies exploring antioxidants, including vitamins, trace elements, nitric oxide (NO), ozone (O3), glutathione (GSH), L-carnitine, melatonin, bromelain, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and numerous polyphenols, have yielded promising outcomes. Through their ROS-scavenging properties, these molecules support endothelial function, reduce the thrombosis risk, and may help mitigate the effects of the cytokine storm, a key contributor to COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Clinical evidence suggests that antioxidant supplementation may improve patient outcomes by decreasing inflammation, supporting immune cell function, and potentially shortening recovery times. Furthermore, these molecules may mitigate the symptoms of COVID-19 by exerting direct antiviral effects that inhibit the infection process and genomic replication of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. Moreover, antioxidants may work synergistically with standard antiviral treatments to reduce viral-induced oxidative damage. By integrating findings from the literature with real-world data from our clinical experience, we gain a more profound understanding of the role of antioxidants in managing COVID-19 pneumonia. Further research combining comprehensive literature reviews with real-world data analysis is crucial to validate the efficacy of antioxidants and establish evidence-based guidelines for their use in clinical practice.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Ahmadi, Mehrabi, Zare, Ghadir, Masoumi, Efficacy of Nanocurcumin as an Add-On Treatment for Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1155/2023/5734675.100
Alshammari, Fatima, Alraya, Khuzaim Alzahrani, Kamal et al., Selenium and COVID-19: A Spotlight on the Clinical Trials, Inventive Compositions, and Patent Literature, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/J.JIPH.2022.09.011.123
Ambrosino, Sanduzzi Zamparelli, Mosella, Formisano, Molino et al., Clinical Assessment of Endothelial Function in Convalescent COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis with Meta-Regressions, Ann. Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2136403
Arabi, Hadi, Gholambareshi, Bahrami, Hazrati et al., The Effect of L-Carnitine Supplementation on Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Ventilator-Dependent Critically Ill Patients with Obesity and COVID-19: Protocol for a Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial, Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun, doi:10.1016/J.CONCTC.2023.101082
Batista, Cintra, Lucena, Manhães-De-Castro, Toscano et al., The Role of Vitamin B12 in Viral Infections: A Comprehensive Review of Its Relationship with the Muscle-Gut-Brain Axis and Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1093/NUTRIT/NUAB092
Bellamine, Pham, Jain, Wilson, Sahin et al., L-Carnitine Tartrate Downregulates the Ace2 Receptor and Limits SARS-Cov-2 Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU13041297
Bertoncini-Silva, Vlad, Ricciarelli, Giacomo Fassini, Suen et al., Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Curcumin for Disease Prevention and Treatment, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/AN-TIOX13030331
Biancatelli, Berrill, Catravas, Marik, Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19), Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2020.01451.103
Bjørklund, Dadar, Chirumbolo, Lysiuk, Flavonoids as Detoxifying and Pro-Survival Agents: What's New?, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/J.FCT.2017.10.039.101
Bocci, The Clinical Application of Ozonetherapy, doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9234-2_9.134
Bohn, Hall, Sepiashvili, Jung, Steele et al., Pathophysiology of COVID-19: Mechanisms Underlying Disease Severity and Progression, Physiology, doi:10.1152/PHYSIOL.00019.2020
Bouillon, Leboff, Neale, Health Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation: Lessons Learned From Randomized Controlled Trials and Mendelian Randomization Studies, J. Bone Miner. Res, doi:10.1002/JBMR.4888
Buchrieser, Dufloo, Hubert, Monel, Planas et al., Syncytia Formation by SARS-CoV-2-infected Cells, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/EMBJ.2020107405.106
Camini, Da Silva Caetano, Almeida, De Brito Magalhães, Implications of Oxidative Stress on Viral Pathogenesis, Arch. Virol, doi:10.1007/S00705-016-3187-Y
Carr, Maggini, Vitamin C and Immune Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU9111211
Carvajal, García-Castillo, Cuellar, Campillay-Véliz, Salazar-Ardiles et al., New Insights into the Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2024.1363572
Carvalho, Araujo, Da Silva, Da Silva, De Araújo et al., Retinol Levels and Severity of Patients with COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU15214642
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcalá Díaz, López Miranda et al., Effect of Calcifediol Treatment and Best Available Therapy versus Best Available Therapy on Intensive Care Unit Admission and Mortality among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/J.JSBMB.2020.105751
Cerullo, Negro, Parimbelli, Pecoraro, Perna et al., The Long History of Vitamin C: From Prevention of the Common Cold to Potential Aid in the Treatment of COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2020.574029
Chalmers, Crichton, Goeminne, Cao, Humbert et al., Management of Hospitalised Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A European Respiratory Society Living Guideline, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00048-2021
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU12072097
Chen, Liu, Gao, Sun, Chao et al., Inhalation of Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome: A Rescue Trial in Beijing, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1086/425357.128
Chong, Ahearn, Cimmino, Reprogramming the Epigenome with Vitamin C. Front, Cell Dev. Biol, doi:10.3389/FCELL.2019.00128
D'agnano, Scialò, Perna, Atripaldi, Sanduzzi et al., Exploring the Role of Krebs von Den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients, Life, doi:10.3390/LIFE12081141
De Wit, Van Doremalen, Falzarano, Munster, SARS and MERS: Recent Insights into Emerging Coronaviruses, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81
Desaki, Takizawa, Kasama, Kobayashi, Morita et al., Nuclear Factor-Kappa b Activation in Silica-Induced Interleukin 8 Production by Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells, Cytokine, doi:10.1006/CYTO.2000.0704
Dewan, Shinde, Glutathione an Effective Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Infection, J. Adv. Med. Med. Res, doi:10.9734/JAMMR/2022/V34I2231583
Dhar, Bhattacharjee, Promising Role of Curcumin against Viral Diseases Emphasizing COVID-19 Management: A Review on the Mechanistic Insights with Reference to Host-Pathogen Interaction and Immunomodulation, J. Funct. Foods, doi:10.1016/J.JFF.2021.104503
Do, Kwon, Park, Lee, Effects of Vitamin D on Expression of Toll-like Receptors of Monocytes from Patients with Behçet's Disease, Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEN109
Dussault, George, Trullinger, Peroxides as Oxidative Enzyme Inhibitors: Mechanism-Based Inhibition of a Cysteine Protease by an Amino Acid Ozonide, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett, doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(99)00563-6.138
Elvis, Ekta, Ozone, Therapy: A Clinical Review, J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med, doi:10.4103/0976-9668.82319.133
Erfani, Alizadeh, Faraji, Teymouri, Vitamin B12 Effectiveness in the Management of Hospitalized COVID-19 and Its Clinical Outcomes and Complications: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Health Sci. Rep, doi:10.1002/HSR2.1509
Essalmani, Jain, Susan-Resiga, Andréo, Evagelidis et al., Distinctive Roles of Furin and TMPRSS2 in SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00128-22.107
Fan, Zhu, Zheng, Zhang, Seidner et al., Magnesium Treatment on Methylation Changes of Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 (TMPRSS2), Nutrition, doi:10.1016/J.NUT.2021.111340.120
Farnoosh, Akbariqomi, Badri, Bagheri, Izadi et al., Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/J.ARC-MED.2021.06.006
Florescu, Stanciu, Zaharia, Kosa, Codreanu et al., Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: Two Harmonized Randomized Clinical Trials, JAMA, doi:10.1001/JAMA.2023.21407
Fowler, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients with Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/JAMA.2019.11825
Frontera, Rahimian, Yaghi, Liu, Lewis et al., Treatment with Zinc Is Associated with Reduced In-Hospital Mortality Among COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Center Cohort Study, Res. Sq, doi:10.21203/RS.3.RS-94509/V1.117
Gain, Song, Angtuaco, Satta, Kelesidis, The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Infections with Coronaviruses, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/FMICB.2022.1111930
Giovinazzo, Gerardi, Uberti-Foppa, Lopalco, Portillo, Potential Usefulness of Mediterranean Diet Polyphenols against COVID-19-Induced Inflammation: A Review of the Current Knowledge, J. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.3390/MOLECULES25245888
Granada-Flor, Sousa, Filipe, Santos, De Almeida, Quercetin Dual Interaction at the Membrane Level, Chem. Commun, doi:10.1039/C8CC09656B.108
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU12040988
Gruber-Bzura, High-Dose Vitamin C Supplementation as a Legitimate Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Prophylaxis in Healthy Subjects-Yes or No?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU14050979
Guerrero-Romero, Micke, Simental-Mendía, Rodríguez-Morán, Vormann et al., Importance of Magnesium Status in COVID-19, Biology, doi:10.3390/BIOLOGY12050735.121
Guloyan, Oganesian, Baghdasaryan, Yeh, Singh et al., Glutathione Supplementation as an Adjunctive Therapy in COVID-19, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/ANTIOX9100914
Hafizi, Kalanaky, Fakharzadeh, Karimi, Fakharian et al., Beneficial Effects of the Combination of BCc1 and Hep-S Nanochelating-Based Medicines on IL-6 in Hospitalized Moderate COVID-19 Adult Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/S13063-023-07624-2.125
Hakamifard, Soltani, Maghsoudi, Rismanbaf, Aalinezhad et al., The Effect of Vitamin E and Vitamin C in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia; a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial, Immunopathol. Persa, doi:10.34172/ipp.2022.08
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C Reduces the Severity of Common Colds: A Meta-Analysis, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/S12889-023-17229-8
Hernández, Viñals, Pablos, Vilás, Papadakos et al., Ozone Therapy for Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: Preliminary Report of a Prospective Case-Control Study, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/J.INTIMP.2020.107261
Herold, Becker, Ridge, Budinger, Influenza Virus-Induced Lung Injury: Pathogenesis and Implications for Treatment, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.00186214
Huo, Tang, Li, Han, Gu et al., Melatonin Alleviates Lung Injury in H1N1-Infected Mice by Mast Cell Inactivation and Cytokine Storm Suppression, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PPAT.1011406
Ichinose, Roberts, Zapol, Inhaled Nitric Oxide: A Selective Pulmonary Vasodilator: Current Uses and Therapeutic Potential, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62.129
Ignarro, Inhaled NO and COVID-19, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/BPH.15085.126
Jahangirifard, Omidi, Sharifzadeh, Mirtajani, Peyravian et al., The Effect of Bromelain (Anaheal) on Clinical and Para-Clinical Parameters in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Acta Med. Iran, doi:10.18502/ACTA.V59I12.8066
Jakovac, COVID-19 and Vitamin D-Is There a Link and an Opportunity for Intervention?, Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/AJPENDO.00138.2020
Jeeva, Sunitha, Ananthalakshmi, Rajkumari, Ramesh et al., Enzymatic Antioxidants and Its Role in Oral Diseases, J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci, doi:10.4103/0975-7406.163438
Jnk, Kinase, ROS, reactive oxygen species; O2 -, anion superoxide; OH -, hydroxyl radicals; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NQO1, NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1; PLpro, papain-like protease; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; GGH, glutathione; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; LTB4, leukotriene B4; NOX, NADPH oxidase; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase, G6PD, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; MIF-1, macrophage inhibitory factor-1; HNF4-α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-α; Mg, magnesium; TLR, Toll-like receptor; PAF, platelet-aggregating factor; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; NLRP3, NOD-like receptors family pyrin group containing 3; SIRT-1, sirtuin-1; O3, ozone; CAT, catalase; HO-1, hemeoxygenase; NAC, n-acetylcysteine; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; NO, nitric oxide; INF-1, infermeron-1; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling; γ-GCS, γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase; IRF-1, and interferon regulatory factor 1; Th1, helper T cells; 3CLpro, 3-chymotrypsin-like protease; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IP-10, interferon-γ-induced protein-10; RANTES, regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and secreted; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; G-CSF, granulocyte colonystimulating factor; XO, xanthine oxidase; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; RHA, RNA helicase; FGF-2, fibroblastic growth factor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; N, nucleocapsid; Se, selenium; CRP, C-reactive protein; GPx, GSH peroxidase; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; RXR, retinoid receptor X; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PRKCB, protein kinase C-β; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; hAPN, human aminopeptidase N; NAPDH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; JAK/STAT, janus kinase/signal transducers and activators
Kabir, Uddin, Hossain, Abdulhakim, Alam et al., NCOVID-19 Pandemic: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Potential Investigational Therapeutics, Front. Cell Dev. Biol, doi:10.3389/FCELL.2020.00616
Kansakar, Trimarco, Manzi, Cervi, Mone et al., Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bromelain: Applications, Benefits, and Mechanisms, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU16132060
Keyaerts, Vijgen, Chen, Maes, Hedenstierna et al., Inhibition of SARS-Coronavirus Infection in Vitro by S-Nitroso-N-Acetylpenicillamine, a Nitric Oxide Donor Compound, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012.127
Kornberg, Bhargava, Kim, Putluri, Snowman et al., Dimethyl Fumarate Targets GAPDH and Aerobic Glycolysis to Modulate Immunity, Science, doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.AAN4665
Labarrere, Kassab, Glutathione Deficiency in the Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Its Effects upon the Host Immune Response in Severe COVID-19 Disease, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/FMICB.2022.979719
Lahaye, Parant, Haesebaert, Goldet, Bendim'red et al., Minerals and Antioxidant Micronutrients Levels and Clinical Outcome in Older Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 during the First Wave of the Pandemic, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU15061516
Lamers, Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0
Levy, Delvin, Marcil, Spahis, Can Phytotherapy with Polyphenols Serve as a Powerful Approach for the Prevention and Therapy Tool of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)?, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/AJPENDO.00298.2020
Li, Wu, Li, Liang, Fai Tse et al., Revealing the Targets and Mechanisms of Vitamin A in the Treatment of COVID-19, Aging, doi:10.18632/AGING.103888
Linster, Van Schaftingen, Vitamin, Biosynthesis, Recycling and Degradation in Mammals, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/J.1742-4658.2006.05607.X
Malek Mahdavi, A Brief Review of Interplay between Vitamin D and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: Implications for a Potential Treatment for COVID-19, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/RMV.2119
Mandal, Nitric Oxide Mediated Hypoxia Dynamics in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/J.NIOX.2023.02.002
Marín-Corral, Rodríguez-Morató, Gomez-Gomez, Pascual-Guardia, Muñoz-Bermúdez et al., Metabolic Signatures Associated with Severity in Hospitalized Covid-19 Patients, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/IJMS22094794.104
Mata, Morcillo, Gimeno, Cortijo, N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine (NAC) Inhibit Mucin Synthesis and pro-Inflammatory Mediators in Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells Infected with Influenza Virus A and B and with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Biochem. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/J.BCP.2011.05.014
Mccreary, Schnell, Rhoda, Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Proof-of-Concept Trial of Resveratrol for Outpatient Treatment of Mild Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19), Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9.113
Merad, Blish, Sallusto, Iwasaki, The Immunology and Immunopathology of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.ABM8108
Midha, Kumar, Kumar, Madan, Mega Doses of Retinol: A Possible Immunomodulation in Covid-19 Illness in Resource-Limited Settings, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/RMV.2204
Minakshi, Padhan, Rani, Khan, Ahmad et al., The SARS Coronavirus 3a Protein Causes Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Induces Ligand-Independent Downregulation of the Type 1 Interferon Receptor, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0008342
Moatasim, Kutkat, Osman, Gomaa, Okda et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/MICROOR-GANISMS11112777
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D Insufficiency as a Potential Culprit in Critical COVID-19 Patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/JMV.26360
Musavi, Abazari, Barartabar, Kalaki-Jouybari, Hemmati-Dinarvand et al., The Benefits of Vitamin D in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Biochemical and Immunological Mechanisms, Arch. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1826530
Nascimento Marreiro, Cruz, Oliveira, Morais, Freitas et al., Antiviral and Immunological Activity of Zinc and Possible Role in COVID-19, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521002099.116
Nicoliche, Bartolomeo, Lemes, Pereira, Nunes et al., Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Curcumin and Curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y Cells Infected by SARS-CoV-2, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7
Nioi, Mcmahon, Itoh, Yamamoto, Hayes, Identification of a Novel Nrf2-Regulated Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) in the Mouse NAD(P)H:Quinone Oxidoreductase 1 Gene: Reassessment of the ARE Consensus Sequence, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/BJ20030754
Olczak-Pruc, Szarpak, Navolokina, Chmielewski, Panasiuk et al., The Effect of Zinc Supplementation on the Course of COVID-19-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Ann. Agric. Environ. Med, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.115
Padayatty, Sun, Wang, Riordan, Hewitt et al., Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics: Implications for Oral and Intravenous Use, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010
Pallath, Ahirwar, Tripathi, Asia, Sakarde et al., COVID-19 and Nutritional Deficiency: A Review of Existing Knowledge, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1515/HMBCI-2020-0074
Pan, Fang, Zhang, Pan, Liu et al., Chinese Herbal Compounds against SARS-CoV-2: Puerarin and Quercetin Impair the Binding of Viral S-Protein to ACE2 Receptor, Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J, doi:10.1016/J.CSBJ.2020.11.010.105
Pecoraro, Martini, Salvottini, Carbonare, Piacentini et al., The Potential Role of Zinc, Magnesium and Selenium against COVID-19: A Pragmatic Review, Child Adolesc. Obes, doi:10.1080/2574254X.2021.1941706.119
Pecorelli, Bocci, Acquaviva, Belmonte, Gardi et al., NRF2 Activation Is Involved in Ozonated Human Serum Upregulation of HO-1 in Endothelial Cells, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/J.TAAP.2012.12.001.137
Peña, Rincon, Pedreanez, Viera, Mosquera, Chemotactic Effect of Melatonin on Leukocytes, J. Pineal Res, doi:10.1111/J.1600-079X.2007.00471.X
Poland, Ovsyannikova, Kennedy, SARS-CoV-2 Immunity: Review and Applications to Phase 3 Vaccine Candidates, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32137-1
Prakash, Kaur, Kaur, Prabha, Bhatacharya et al., Efficacy and Safety of Inhaled Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of Severe/Critical COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review, Indian J. Pharmacol, doi:10.4103/IJP.IJP_382_21.131
Rahban, Habibi-Rezaei, Mazaheri, Saso, Moosavi-Movahedi, Anti-Viral Potential and Modulation of Nrf2 by Curcumin: Pharmacological Implications, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/ANTIOX9121228
Rajendran, Chathambath, Al-Sehemi, Pannipara, Unnikrishnan et al., Critical Role of Nitric Oxide in Impeding COVID-19 Transmission and Prevention: A Promising Possibility, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1007/S11356-022-19148-4.130
Rederstorff, Krol, Lescure, Understanding the Importance of Selenium and Selenoproteins in Muscle Function, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/S00018-005-5313-Y
Ricevuti, Franzini, Valdenassi, Oxygen-Ozone Immunoceutical Therapy in COVID-19 Outbreak: Facts and Figures, Ozone Ther, doi:10.4081/ozone.2020.9014.135
Rocksén, Lilliehöök, Larsson, Johansson, Bucht, Differential Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of Dexamethasone and N-Acetylcysteine in Endotoxin-Induced Lung Inflammation, Clin. Exp. Immunol, doi:10.1046/J.1365-2249.2000.01373.X
Rostami, Alavi, Daghagheleh, Maraghi, Hosseini, A Randomized Clinical Trial Investigating the Impact of Magnesium Supplementation on Clinical and Biochemical Measures in COVID-19 Patients, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/S12985-024-02362-6.122
Rudenko, Vetoshkina, Marenkova, Borisova-Mubarakshina, Antioxidants of Non-Enzymatic Nature: Their Function in Higher Plant Cells and the Ways of Boosting Their Biosynthesis, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/ANTIOX12112014
Sabico, Enani, Sheshah, Aljohani, Aldisi et al., Effects of a 2-Week 5000 Iu versus 1000 Iu Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU13072170
Sadeghi, Dehnavi, Asadirad, Xu, Majeed et al., Curcumin and Chemokines: Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Potential in Inflammatory Diseases, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/S10787-023-01136-W
Safaee Fakhr, Di Fenza, Gianni, Wiegand, Miyazaki et al., Inhaled High Dose Nitric Oxide Is a Safe and Effective Respiratory Treatment in Spontaneous Breathing Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/J.NIOX.2021.08.003.132
Sahebkar, Serban, Ursoniu, Banach, Effect of Curcuminoids on Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, J. Funct. Foods, doi:10.1016/J.JFF.2015.01.005
Samad, Dutta, Sodunke, Fairuz, Sapkota et al., Fat-Soluble Vitamins and the Current Global Pandemic of COVID-19: Evidence-Based Efficacy from Literature Review, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S307333
Sanduzzi Zamparelli, Fucci, Rea, Perna, Bocchino et al., The Role of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsidic Antigen and Krebs von Den Lungen 6 Serum Levels in Predicting COVID-19 Pneumonia Outcome, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/DIAGNOSTICS14060642
Sanduzzi, Zamparelli, Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal Swabs, And/Or Serology for SARS COVID-19: What Are We Looking For?, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/IJERPH17093289
Saptarini, Rahayu, Herawati, Antioxidant Activity of Crude Bromelain of Pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr) Crown from Subang District, Indonesia, J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci, doi:10.4103/JPBS.JPBS_200_19
Shi, Puyo, N-Acetylcysteine to Combat COVID-19: An Evidence Review, Ther. Clin. Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/TCRM.S273700
Shohan, Nashibi, Mahmoudian-Sani, Abolnezhadian, Ghafourian et al., The Therapeutic Efficacy of Quercetin in Combination with Antiviral Drugs in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/J.EJPHAR.2021.174615.110
Shrivastava, Sahu, Cecchi, Shrestha, Shah et al., An Emerging Natural Antioxidant Therapy for COVID-19 Infection Patients: Current and Future Directions, Food Front, doi:10.1002/FFT2.207
Silvestri, Rossi, Melatonin: Its Possible Role in the Management of Viral Infections-a Brief Review, Ital. J. Pediatr, doi:10.1186/1824-7288-39-61
Singh, Gautam, Chandel, Ghosh, Dey et al., Protease Inhibitory Effect of Natural Polyphenolic Compounds on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, Molecules, doi:10.3390/MOLE-CULES25204604.102
Sinopoli, Caminada, Isonne, Santoro, Baccolini, What Are the Effects of Vitamin A Oral Supplementation in the Prevention and Management of Viral Infections? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU14194081
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and Respiratory Tract Infections: Perspectives for COVID-19 (Review), Int. J. Mol. Med, doi:10.3892/IJMM.2020.4575
Smith, Wilson, Gandhi, Vatsia, Khan, Ozone Therapy: An Overview of Pharmacodynamics, Current Research, and Clinical Utility, Med. Gas Res, doi:10.4103/2045-9912.215752.136
Soltan-Sharifi, Mojtahedzadeh, Najafi, Khajavi, Rouini et al., Improvement by N-Acetylcysteine of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome through Increasing Intracellular Glutathione, and Extracellular Thiol Molecules and Anti-Oxidant Power: Evidence for Underlying Toxicological Mechanisms, Hum. Exp. Toxicol, doi:10.1177/0960327107083452
Somi, Faghih Dinevari, Taghizadieh, Varshochi, Sadeghi Majd et al., Effect of Vitamin A Supplementation on the Outcome Severity of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial, Nutr. Health, doi:10.1177/02601060221129144
Song, Nair, Oh, Vitamin C Enhances the Expression of IL17 in a Jmjd2-Dependent Manner, BMB Rep, doi:10.5483/BMBREP.2017.50.1.193
Taher, Lashgari, Sedighi, Rahimi-Bashar, Poorolajal et al., A Pilot Study on Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Treatment in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1007/S43440-021-00296-2
Talebi, Ghasemi, Etminani-Esfahani, Mohammadi, Haddadi, Effects of L-Carnitine Supplementation in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 Disease: A Pilot Study, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1007/S43440-022-00402-Y
Tan, Manchester, Esteban-Zubero, Zhou, Reiter, Melatonin as a Potent and Inducible Endogenous Antioxidant: Synthesis and Metabolism, Molecules, doi:10.3390/MOLECULES201018886
Tavassolifar, Aghdaei, Sadatpour, Maleknia, Fayazzadeh et al., New Insights into Extracellular and Intracellular Redox Status in COVID-19 Patients, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/J.REDOX.2022.102563
Tehrani, Yadegarynia, Abrishami, Moradi, Gharaei et al., An Investigation into the Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Pulmonary CT Findings and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with COVID 19 Pneumonia A Randomized Clinical Trial, Urol. J, doi:10.22037/UJ.V18I.6863
Tepasse, Vollenberg, Fobker, Kabar, Schmidt et al., Vitamin a Plasma Levels in Covid-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU13072173
Tomaszewska, Rustecka, Lipińska-Opałka, Piprek, Kloc et al., The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 and the Impact of Pandemic Restrictions on Vitamin D Blood Content, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/FPHAR.2022.836738
Tomo, Saikiran, Banerjee, Paul, Selenium to Selenoproteins-Role in COVID-19, Excli J, doi:10.17179/EXCLI2021-3530.124
Vahedian-Azimi, Abbasifard, Rahimi-Bashar, Guest, Majeed et al., Effectiveness of Curcumin on Outcomes of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/NU14020256
Wong, Rinaldi, Ho, Zinc Deficiency Enhanced Inflammatory Response by Increasing Immune Cell Activation and Inducing IL6 Promoter Demethylation, Mol. Nutr. Food Res, doi:10.1002/MNFR.201400761
Wu, Yin, Jiang, Xu, Structure Genomics of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Omicron Variant: Drug Design Templates for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacol. Sin, doi:10.1038/s41401-021-00851-w
Xie, Choi, Al-Aly, Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 vs Influenza in Fall-Winter 2023-2024, JAMA, doi:10.1001/JAMA.2024.7395
Xu, Baylink, Chen, Reeves, Xiao et al., The Importance of Vitamin D Metabolism as a Potential Prophylactic, Immunoregulatory and Neuroprotective Treatment for COVID-19, J. Transl. Med, doi:10.1186/S12967-020-02488-5
Yang, Wang, Long, Li, Quercetin: Its Main Pharmacological Activity and Potential Application in Clinical Medicine, Oxid. Med. Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2020/8825387.109
Yao, Paguio, Dee, Tan, Moulick et al., The Minimal Effect of Zinc on the Survival of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: An Observational Study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082.118
Zafarullah, Li, Sylvester, Ahmad, Molecular Mechanisms of N-Acetylcysteine Actions, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/S000180300001
Zamparelli, Capitelli, Coppola, Venditto, Santoro et al., A Phase II Study on the Effect of Taurisolo ® Administered via AEROsol in Hospitalized Patients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia: The TAEROVID-19 Study, Cells, doi:10.3390/CELLS11091499.114
Zeng, Ma, Zhou, Liu, Huang et al., Spectrum and Clinical Characteristics of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) with and Without Pneumonia, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/FMED.2021.645651
Zhang, Wu, Li, Zhao, Wang, Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonist Tocilizumab May Be the Key to Reduce Mortality, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.105954
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMOA2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life15010113",
"ISSN": [
"2075-1729"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/life15010113",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The COVID-19 pandemic caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has profoundly impacted global health, with pneumonia emerging as a major complication in severe cases. The pathogenesis of COVID-19 is marked by the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and an excessive inflammatory response, resulting in oxidative stress and significant tissue damage, particularly in the respiratory system. Antioxidants have garnered considerable attention for their potential role in managing COVID-19 pneumonia by mitigating oxidative stress and modulating immune responses. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the literature on the use of antioxidants in hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. Studies exploring antioxidants, including vitamins, trace elements, nitric oxide (NO), ozone (O3), glutathione (GSH), L-carnitine, melatonin, bromelain, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and numerous polyphenols, have yielded promising outcomes. Through their ROS-scavenging properties, these molecules support endothelial function, reduce the thrombosis risk, and may help mitigate the effects of the cytokine storm, a key contributor to COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Clinical evidence suggests that antioxidant supplementation may improve patient outcomes by decreasing inflammation, supporting immune cell function, and potentially shortening recovery times. Furthermore, these molecules may mitigate the symptoms of COVID-19 by exerting direct antiviral effects that inhibit the infection process and genomic replication of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. Moreover, antioxidants may work synergistically with standard antiviral treatments to reduce viral-induced oxidative damage. By integrating findings from the literature with real-world data from our clinical experience, we gain a more profound understanding of the role of antioxidants in managing COVID-19 pneumonia. Further research combining comprehensive literature reviews with real-world data analysis is crucial to validate the efficacy of antioxidants and establish evidence-based guidelines for their use in clinical practice.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"life15010113"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3336-7290",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pneumology and Semi-intensive Respiratory Therapy, A. Cardarelli Hospital, 80131 Naples, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sanduzzi Zamparelli",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0977-2643",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, University of Naples “Federico II”, 80131 Naples, Italy"
},
{
"name": "UNESCO Chair for Health Education and Sustainable Development, University of Naples “Federico II”, 80131 Naples, Italy"
},
{
"name": "ERN Lung, 60596 Frankfurt am Main, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sanduzzi Zamparelli",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, University of Naples “Federico II”, 80131 Naples, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bocchino",
"given": "Marialuisa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Life",
"container-title-short": "Life",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-16T15:44:23Z",
"timestamp": 1737042263000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-16T16:03:24Z",
"timestamp": 1737043404000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-16T16:40:31Z",
"timestamp": 1737045631787,
"version": "3.33.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1736985600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/15/1/113/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "113",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/15/1/113"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
sanduzzizamparelli