Vitamin A Plasma Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072173, Jun 2021
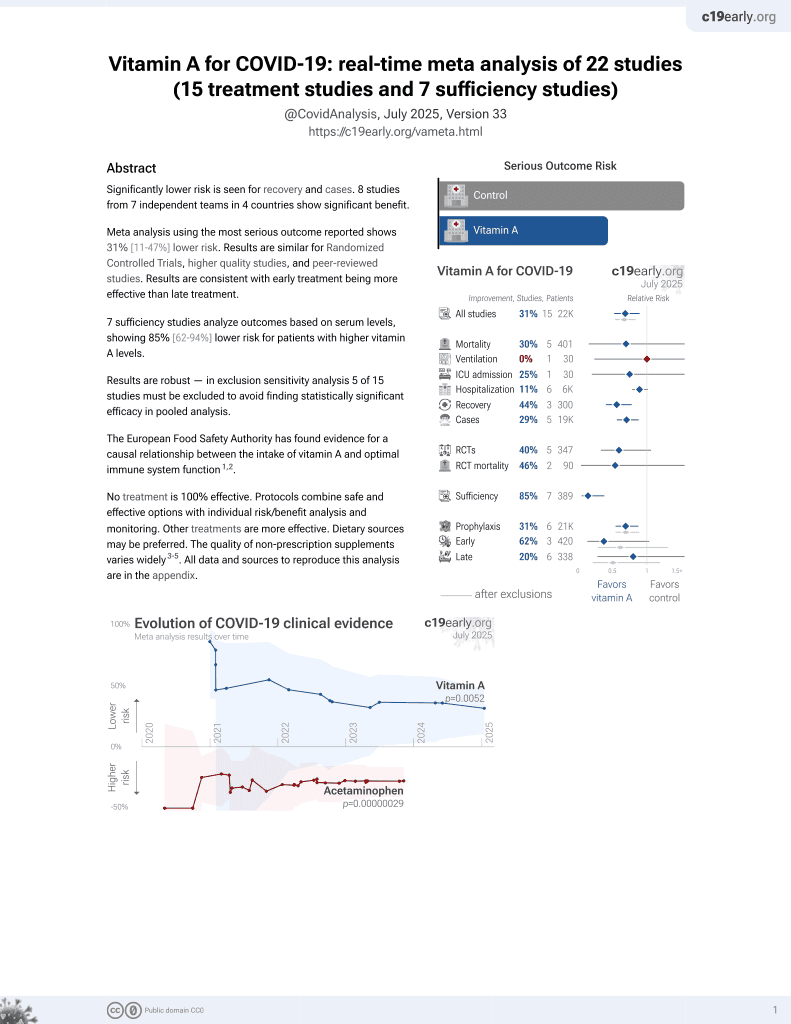
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
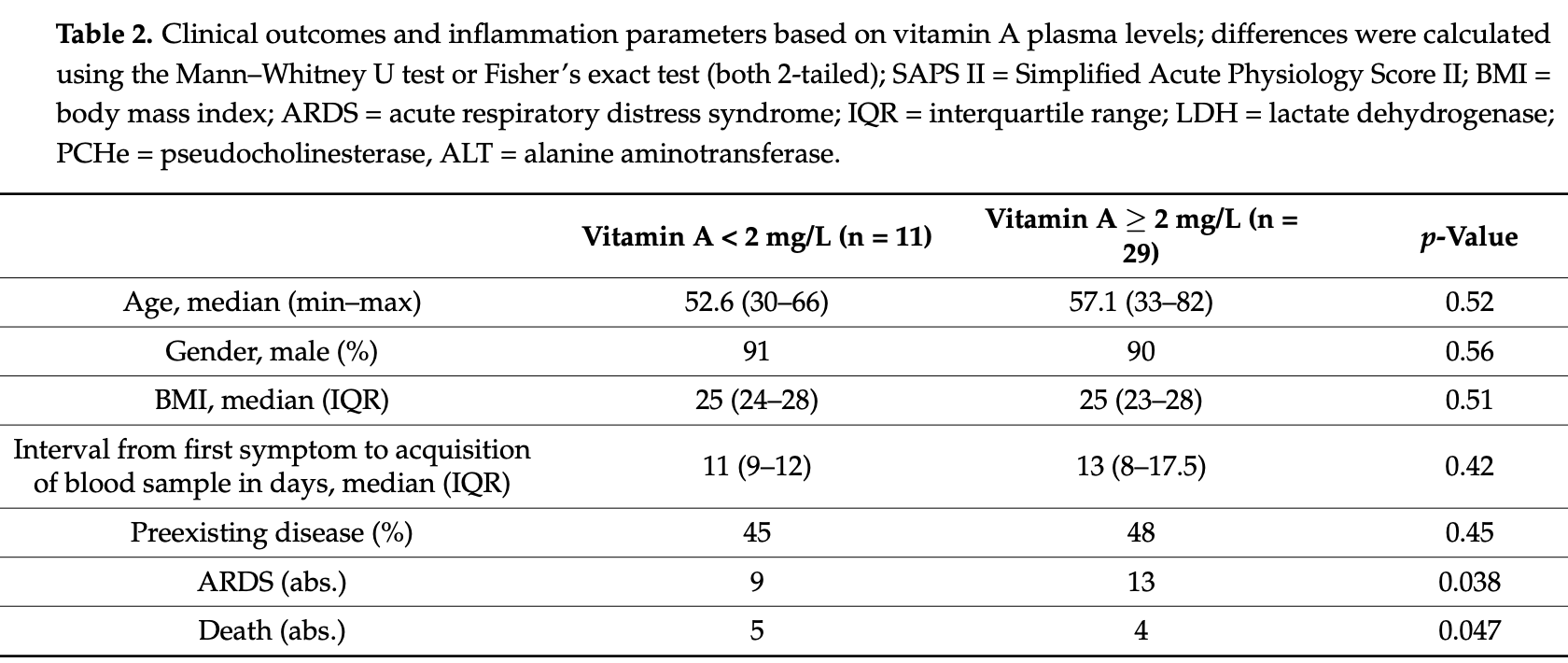
Prospective analysis of 40 hospitalized patients and 47 age-matched convalescent patients, showing significantly lower vitamin A levels in critical patients, and significantly lower vitamin A levels in hospitalized patients vs. controls. Low vitamin A levels were significantly associated with ARDS and mortality in hospitalized patients.
|
risk of death, 69.7% lower, RR 0.30, p = 0.04, high vitamin A levels 4 of 29 (13.8%), low vitamin A levels 5 of 11 (45.5%), NNT 3.2, inverted to make RR<1 favor high vitamin A levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >2mg/L, logistic regression.
|
|
risk of progression, 45.2% lower, RR 0.55, p = 0.048, high vitamin A levels 13 of 29 (44.8%), low vitamin A levels 9 of 11 (81.8%), NNT 2.7, inverted to make RR<1 favor high vitamin A levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, progression to ARDS, >2mg/L, logistic regression.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tepasse et al., 24 Jun 2021, prospective, Germany, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Vitamin A Plasma Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072173
COVID-19 is a pandemic disease that causes severe pulmonary damage and hyperinflammation. Vitamin A is a crucial factor in the development of immune functions and is known to be reduced in cases of acute inflammation. This prospective, multicenter observational cross-sectional study analyzed vitamin A plasma levels in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals, and 40 hospitalized patients were included. Of these, 22 developed critical disease (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [ARDS]/Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO]), 9 developed severe disease (oxygen supplementation), and 9 developed moderate disease (no oxygen supplementation). A total of 47 age-matched convalescent persons that had been earlier infected with SARS-CoV-2 were included as the control group. Vitamin A plasma levels were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Reduced vitamin A plasma levels correlated significantly with increased levels of inflammatory markers (CRP, ferritin) and with markers of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection (reduced lymphocyte count, LDH). Vitamin A levels were significantly lower in hospitalized patients than in convalescent persons (p < 0.01). Of the hospitalized patients, those who were critically ill showed significantly lower vitamin A levels than those who were moderately ill (p < 0.05). Vitamin A plasma levels below 0.2 mg/L were significantly associated with the development of ARDS ]; p = 0.048) and mortality ], p = 0.042). Taken together, we conclude that vitamin A plasma levels in COVID-19 patients are reduced during acute inflammation and that severely reduced plasma levels of vitamin A are significantly associated with ARDS and mortality.
Supplementary Materials: The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10 .3390/nu13072173/s1, Supplementary Figure S1 Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement: Data cannot be made public as personal patient data are included.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Aklamati, Mulenga, Dueker, Buchholz, Peerson et al., Accelerator mass spectrometry can be used to assess vitamin A metabolism quantitatively in boys in a community setting, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.110.125500
Aziz, Fatima, Lee-Smith, Assaly, The association of low serum albumin level with severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02995-3
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary Report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Biesalski, Nohr, Importance of vitamin-A for lung function and development, Mol. Aspects Med
Biolo, Toigo, Ciocchi, Situlin, Iscra et al., Metabolic response to injury and sepsis: Changes in protein metabolism, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00206-2
Chen, Ross, Retinoic acid promotes mouse splenic B cell surface IgG expression and maturation stimulated by CD40 and IL-4, Cell Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.11.001
Chew, Park, Carotenoid action on the immune response, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/134.1.257S
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Jacobson, Meyer et al., Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: A prospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2
Force, Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5669
Gieng, Green, Green, Rosales, Model-based compartmental analysis indicates a reduced mobilization of hepatic vitamin A during inflammation in rats, J. Lipid Res, doi:10.1194/jlr.M600528-JLR200
Glasziou, Mackerras, Vitamin A supplementation in infectious diseases: A meta-analysis, BMJ
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19-Preliminary Report, N. Engl. J. Med
Hall, Cannons, Grainger, Dos Santos, Hand et al., Essential role for retinoic acid in the promotion of CD4(+) T cell effector responses via retinoic acid receptor alpha, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.003
Huang, Liu, Qi, Brand, Zheng, Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm7090258
Hussey, Klein, A randomized, controlled trial of vitamin A in children with severe measles, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM199007193230304
Iwata, Hirakiyama, Eshima, Kagechika, Kato et al., Retinoic acid imprints gut-homing specificity on T cells, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.08.011
Jose, Manuel, COVID-19 cytokine storm: The interplay between inflammation and coagulation, Lancet Respir. Med
Kang, Lim, Andrisani, Broxmeyer, Kim, Vitamin A metabolites induce gut-homing FoxP3+ regulatory T cells, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3724
Karagiannidis, Mostert, Hentschker, Voshaar, Malzahn et al., Case characteristics, resource use, and outcomes of 10 021 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 920 German hospitals: An observational study, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30316-7
Lucena, Alegre, Martinez-Urbistondo, Landecho, Huerta et al., Performance of SAPS II and SAPS 3 in intermediate care, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077229
Ma, Chen, Ross, Retinoic acid and polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid stimulate robust anti-tetanus antibody production while differentially regulating type 1/type 2 cytokines and lymphocyte populations, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.7961
Manicassamy, Ravindran, Deng, Oluoch, Denning et al., Toll-like receptor 2-dependent induction of vitamin A-metabolizing enzymes in dendritic cells promotes T regulatory responses and inhibits autoimmunity, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm.1925
Mcgonagle, Sharif, O'regan, Bridgewood, The Role of Cytokines including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537
Penkert, Smith, Hrincius, Mccullers, Vogel et al., Vitamin A deficiency dysregulates immune responses toward influenza virus and increases mortality after bacterial coinfections, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa597
Raverdeau, Mills, Modulation of T cell and innate immune responses by retinoic Acid, J. Immunol
Ruane, Brane, Reis, Cheong, Poles et al., Lung dendritic cells induce migration of protective T cells to the gastrointestinal tract, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20122762
Sommer, Tarwotjo, Hussaini, Susanto, Increased mortality in children with mild vitamin A deficiency, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90677-3
Sommer, Vitamin a deficiency and clinical disease: An historical overview, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/138.10.1835
Stephensen, Vitamin A, infection, and immune function, Annu. Rev. Nutr, doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167
Surman, Rudraraju, Sealy, Jones, Hurwitz, Vitamin A deficiency disrupts vaccine-induced antibody-forming cells and the balance of IgA/IgG isotypes in the upper and lower respiratory tract, Viral Immunol, doi:10.1089/vim.2012.0023
Tan, Liu, Zhou, Deng, Li et al., Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13223
Timoneda, Rodriguez-Fernandez, Zaragoza, Marin, Cabezuelo et al., Vitamin A Deficiency and the Lung, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10091132
Wang, Liu, Liu, Li, Lin et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002
Weiskopf, Schmitz, Raadsen, Grifoni, Okba et al., Phenotype and kinetics of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Sci. Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abd2071
Who, Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995-2005
Zhang, Lee, Ang, Leo, Young, Risk Factors for Severe Disease and Efficacy of Treatment in Patients Infected With COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa576
Zhang, Yan, Fan, Liu, Liu et al., D-dimer levels on admission to predict in-hospital mortality in patients with Covid-19, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14859
Zhao, Meng, Kumar, Wu, Huang et al., Lymphopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A systemic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.086
Zheng, Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Wang et al., Elevated exhaustion levels and reduced functional diversity of T cells in peripheral blood may predict severe progression in COVID-19 patients, Cell Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0401-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072173",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13072173",
"abstract": "<jats:p>COVID-19 is a pandemic disease that causes severe pulmonary damage and hyperinflammation. Vitamin A is a crucial factor in the development of immune functions and is known to be reduced in cases of acute inflammation. This prospective, multicenter observational cross-sectional study analyzed vitamin A plasma levels in SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals, and 40 hospitalized patients were included. Of these, 22 developed critical disease (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [ARDS]/Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO]), 9 developed severe disease (oxygen supplementation), and 9 developed moderate disease (no oxygen supplementation). A total of 47 age-matched convalescent persons that had been earlier infected with SARS-CoV-2 were included as the control group. Vitamin A plasma levels were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Reduced vitamin A plasma levels correlated significantly with increased levels of inflammatory markers (CRP, ferritin) and with markers of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection (reduced lymphocyte count, LDH). Vitamin A levels were significantly lower in hospitalized patients than in convalescent persons (p < 0.01). Of the hospitalized patients, those who were critically ill showed significantly lower vitamin A levels than those who were moderately ill (p < 0.05). Vitamin A plasma levels below 0.2 mg/L were significantly associated with the development of ARDS (OR = 5.54 [1.01–30.26]; p = 0.048) and mortality (OR 5.21 [1.06–25.5], p = 0.042). Taken together, we conclude that vitamin A plasma levels in COVID-19 patients are reduced during acute inflammation and that severely reduced plasma levels of vitamin A are significantly associated with ARDS and mortality.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13072173"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2757-4755",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tepasse",
"given": "Phil-Robin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3208-7924",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vollenberg",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fobker",
"given": "Manfred",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kabar",
"given": "Iyad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmidt",
"given": "Hartmut",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meier",
"given": "Jörn Arne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4530-5786",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nowacki",
"given": "Tobias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hüsing-Kabar",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-24T15:01:38Z",
"timestamp": 1624546898000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-24T15:53:02Z",
"timestamp": 1624549982000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T09:53:01Z",
"timestamp": 1712569981479
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 40,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624492800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/7/2173/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2173",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30316-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/134.1.257S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm7090258",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1303245",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2012.0023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.306.6874.366",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199007193230304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.M600528-JLR200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.110.125500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2012.5669",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"article-title": "Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995–2005",
"key": "ref19",
"series-title": "WHO Global Database on Vitamin A Deficiency",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0077229",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14859",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02995-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa576",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90677-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0098-2997(03)00039-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/138.10.1835",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.1925",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20122762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2004.08.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.11.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.7961",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3724",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abd2071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0401-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13223",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00206-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/7/2173"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin A Plasma Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}