A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome
et al., Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2, Jun 2021
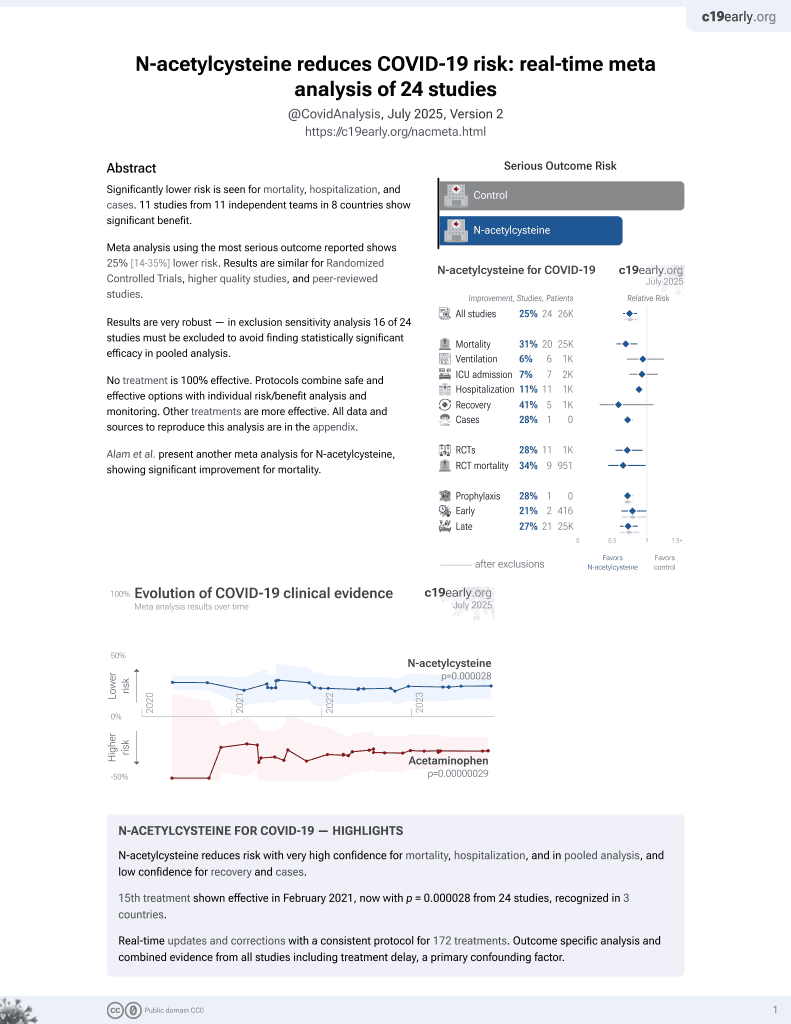
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
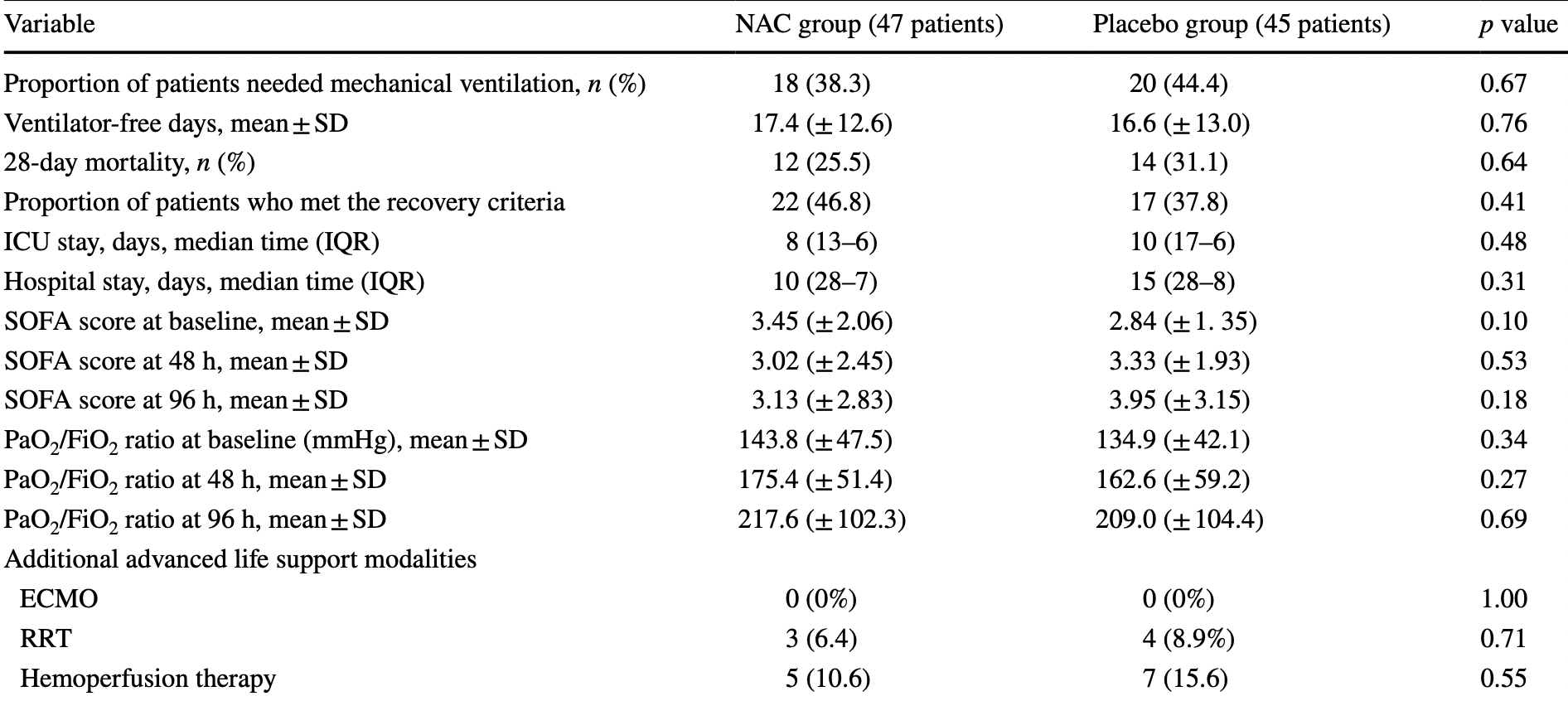
RCT 92 hospitalized patients, 47 treated with NAC, showing non-significant improvements in outcomes. IRCT20120215009014N355. NAC 40mg/kg/day intravenous for 3 days.
|
risk of death, 17.9% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.65, treatment 12 of 47 (25.5%), control 14 of 45 (31.1%), NNT 18.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 13.8% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.67, treatment 18 of 47 (38.3%), control 20 of 45 (44.4%), NNT 16.
|
|
ICU time, 20.0% lower, relative time 0.80, p = 0.48, treatment 47, control 45.
|
|
hospitalization time, 33.3% lower, relative time 0.67, p = 0.31, treatment 47, control 45.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 14.5% lower, RR 0.85, p = 0.41, treatment 25 of 47 (53.2%), control 28 of 45 (62.2%), NNT 11.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Taher et al., 10 Jun 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period June 2020 - February 2021, average treatment delay 7.0 days.
A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome
Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2
Background We designed this single-centre clinical trial to assess the potential benefits of N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) in patients with COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Methods Ninety-two patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated ARDS were allocated to the placebo (45-cases) or NAC groups (47-cases). Besides standard-of-care treatment, the patients received either intravenous NAC at a dose of 40 mg/kg/day or the placebo for three consecutive days. The efficacy outcomes were overall mortality over 28-day, clinical status on day 28, based on the WHO Master Protocol, the proportion of patients requiring mechanical ventilation, changes in ARDS-severity (based on the PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio), and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores 48 and 96 h after intervention, Results No differences were found in the 28-day mortality rate between the two groups (25.5% vs. 31.1% in the NAC and placebo groups, respectively). Although the distribution of the clinical status at day 28 shifted towards better outcomes in the NAC-treated group, it did not reach a statistical significance level (p value = 0.83). Similar results were achieved in terms of the proportion of patients who required invasive ventilator support (38.3% vs. 44.4%), the number of ventilator-free days (17.4 vs. 16.6), and median time of ICU and hospital stay. Results regarding the change in PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio and SOFA scores also showed no significant differences between the groups. Conclusions Our pilot study did not support the potential benefits of intravenous NAC in treating patients with COVID-19-associated ARDS. More studies are needed to determine which COVID-19 patients benefit from the NAC administration. Trial registration The trial was registered at Clinicaltrials.gov (identifier code: IRCT20120215009014N355). Registration date: 2020-05-18.
Author contributions Conceptualisation: AT, MM; methodology: AT, MM, JP; data acquisition: AT, LS, ML, FR-B; statistical analysis: MM, JP; writing-original draft preparation: LS; writing-review and editing: MM, AT; all authors contributed to the interpretation of the results and read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate The trial protocol was according to the Declaration of Helsinki as revised in 1989, and the study protocol was approved by the research and ethics committee at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSHA. REC.13999.153).
Consent for publication All authors have given consent for publication.
References
Ahmad, Rathore, Neurological manifestations and complications of COVID-19: a literature review, J Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2020.05.017
Alamdari, Moghaddam, Amini, Keramati, Zarmehri et al., Application of methylene blue-vitamin C-N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial, Eur J Pharmacol
Bernard, Wheeler, Arons, Morris, Paz et al., A trial of antioxidants N-acetylcysteine and procysteine in ARDS, Chest
Chertoff, N-acetylcysteine's role in sepsis and potential benefit in patients with microcirculatory derangements, J Intensive Care Med
Cpere Novel, Xue, Zhi, The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing
Dass, Brief review of N-acetylcysteine as antiviral agent: potential application in COVID-19, J Biomed Pharm Res
Domenighetti, Suter, Schaller, Ritz, Perret, Treatment with N-acetylcysteine during acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, J Crit Care
Flora, Balansky, Maestra, Rationale for the use of N-acetylcysteine in both prevention and adjuvant therapy of COVID-19, FASEB J
Flora, Grassi, Carati, Attenuation of influenza-like symptomatology and improvement of cell-mediated immunity with long-term N-acetylcysteine treatment, Eur Respir J
Force, Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome, JAMA
Fu, Cheng, Wu, Understanding SARS-CoV-2-mediated inflammatory responses: from mechanisms to potential therapeutic tools, Virol Sin
García, Immune response, inflammation, and the clinical spectrum of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Geiler, Michaelis, Naczk, Leutz, Langer et al., N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) inhibits virus replication and expression of pro-inflammatory molecules in A549 cells infected with highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus, Biochem Pharmacol
Ghezzi, Ungheri, Synergistic combination of N-acetylcysteine and ribavirin to protect from lethal influenza viral infection in a mouse model, Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol
Holdiness, Clinical pharmacokinetics of N-acetylcysteine, Clin Pharmacokinet
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Ibrahim, Smith, Lewis, Kon, Goldenberg, Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous N-acetylcysteine, Clin Immunol
Jaiswal, Bhatnagar, Shah, N-acetylcysteine: a potential therapeutic agent in COVID-19 infection, Med Hypotheses
Jepsen, Herlevsen, Knudsen, Bud, Klausen, Antioxidant treatment with N-acetylcysteine during adult respiratory distress syndrome: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study, Crit Care Med
Kearns, 'briain, Sheehan, Kelly, Bouchier-Hayes, N-acetylcysteine protects striated muscle in a model of compartment syndrome, Clin Orthop Relat Res
Lapenna, Antioxidant therapy in COVID-19: the crucial role of early treatment and antioxidant typology, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab055
Lariccia, Magi, Serfilippi, Toujani, Gratteri et al., Challenges and opportunities from targeting inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection: a narrative review, J Clin Med
Liu, Wang, Luo, Qian, Wu et al., Experience of N-acetylcysteine airway management in the successful treatment of one case of critical condition with COVID-19: a case report, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000022577
Lugrin, Rosenblatt-Velin, Parapanov, Liaudet, The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes, Biol Chem
Mata, Morcillo, Gimeno, Cortijo, N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) inhibit mucin synthesis and pro-inflammatory mediators in alveolar type II epithelial cells infected with influenza virus A and B and with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), Biochem Pharmacol
Mata, Sarrion, Armengot, Carda, Martinez et al., Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits ciliagenesis in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells: effectiveness of N-acetylcysteine, PLoS ONE
Meri, Koutsogiannis, Kerr, How safe is intravenous N-Acetylcysteine for the treatment of paracetamolpoisoning?, Hong Kong J Emerg Med
Millea, N-acetylcysteine: multiple clinical applications, Am Fam Physician
Mohanty, Padhy, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in preventing cytokine storm in COVID-19: review of current evidence, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Moradi, Mojtahedzadeh, Mandegari, Soltan-Sharifi, Najafi et al., The role of glutathione-S-transferase polymorphisms on clinical outcome of ALI/ARDS patient treated with N-acetylcysteine, Respir Med
Nasi, Mcardle, Gaudernack, Westman, Melief et al., Reactive oxygen species as an initiator of toxic innate immune responses in retort to SARS-CoV-2 in an ageing population, consider N-acetylcysteine as early therapeutic intervention, Toxicol Rep
Nicholls, Poon, Lee, Ng, Lai et al., Lung pathology of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome, Lancet
Ortolani, Conti, Gaudio, Masoni, Novelli, Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine and rutin on the lipid peroxidation of the lung epithelium during the adult respiratory distress syndrome, Shock
Poppe, Wittig, Jurida, Bartkuhn, Wilhelm et al., The NF-κB-dependent and-independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells, PLoS Pathog
Puyo, Kreig, Saddi, Ansari, Prince, Case report: Use of hydroxychloroquine and N-acetylcysteine for treatment of a COVID-19 positive patient
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Radomska-Leśniewska, Skopiński, Review paper N-acetylcysteine as an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory drug and its some clinical applications, Cent Eur J Immunol
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Villamizar-Peña, Holguin-Rivera et al., Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel Med Infect Dis
Sabetghadam, Mazdeh, Abolfathi, Mohammadi, Mehrpooya, Evidence for a beneficial effect of oral N-acetylcysteine on functional outcomes and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with acute ischemic stroke, Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat
Sadowska, Manuel-Y-Keenoy, Vertongen, Schippers, Radomska-Lesniewska et al., Effect of N-acetylcysteine on neutrophil activation markers in healthy volunteers: in vivo and in vitro study, Pharmacol Res
Samidurai, Das, Cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19 and potential therapeutic ~ strategies, Int J Mol Sci
Shi, Puyo, N-acetylcysteine to combat COVID-19: an evidence review, Ther Clin Risk Manag
Sochman, N-acetylcysteine in acute cardiology: 10 years later: what do we know and what would we like to know?!, J Am Coll Cardiol
Soltan-Sharifi, Mojtahedzadeh, Najafi, Khajavi, Rouini et al., Improvement by N-acetylcysteine of acute respiratory distress syndrome through increasing intracellular glutathione, and extracellular thiol molecules and anti-oxidant power: evidence for underlying toxicological mechanisms, Hum Exp Toxicol
Suter, Domenighetti, Schaller, Laverrière, Ritz et al., N-acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Chest
Van Hecke, Lee, N-acetylcysteine: a rapid review of the evidence for effectiveness in treating COVID-19
Who, Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020
Who, WHO director-general's remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11
Wu, Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Liu et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the 'Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19, J Infect
Zafarullah, Li, Sylvester, Ahmad, Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions, Cell Mol Life Sci
Zhang, Ding, Li, Wang, Chen et al., Effects of N-acetylcysteine treatment in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis, Exp Ther Med
Zhang, Wu, Li, Zhao, Wang, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality, Int J Antimicrob Agents
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2",
"ISSN": [
"1734-1140",
"2299-5684"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2",
"alternative-id": [
"296"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "14 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "31 May 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "3 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "10 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The trial protocol was according to the Declaration of Helsinki as revised in 1989, and the study protocol was approved by the research and ethics committee at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSHA.REC.13999.153)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "All authors have given consent for publication."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taher",
"given": "Abbas",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lashgari",
"given": "Marjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sedighi",
"given": "Ladan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimi-bashar",
"given": "Farshid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poorolajal",
"given": "Jalal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4119-1600",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mehrpooya",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "irct20120215009014n355",
"registry": "10.18810/irct"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Pharmacological Reports"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-10T18:02:48Z",
"timestamp": 1623348168000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-18T05:15:49Z",
"timestamp": 1637212549000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-13T13:18:15Z",
"timestamp": 1639401495833
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1734-1140"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2299-5684"
}
],
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1623283200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1623283200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1650-1659",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "296_CR1",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO director-general’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. WHO; 2020.",
"volume-title": "WHO director-general’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "CPERE Novel",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "296_CR2",
"unstructured": "CPERE Novel. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41:145.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"author": "X Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "296_CR3",
"unstructured": "Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Liu H, Wu Y, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:475–81.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "ADT Force",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "296_CR4",
"unstructured": "Force ADT, Ranieri V, Rubenfeld G, Thompson B, Ferguson N, Caldwell E. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 2012;307:2526–33.",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623",
"author": "AJ Rodriguez-Morales",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101623",
"journal-title": "Travel Med Infect Dis",
"key": "296_CR5",
"unstructured": "Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Gutiérrez-Ocampo E, Villamizar-Peña R, Holguin-Rivera Y, Escalera-Antezana JP, et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;34:101623.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hsz-2013-0241",
"author": "J Lugrin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Biol Chem",
"key": "296_CR6",
"unstructured": "Lugrin J, Rosenblatt-Velin N, Parapanov R, Liaudet L. The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes. Biol Chem. 2014;395:203–30.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002",
"author": "J Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "296_CR7",
"unstructured": "Wu J. Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19. Nitric Oxide. 2020;102:39–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002. Accessed 17 June 2020.",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954",
"author": "C Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105954",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "296_CR8",
"unstructured": "Zhang C, Wu Z, Li J-W, Zhao H, Wang G-Q. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55:105954.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12250-020-00207-4",
"author": "Y Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Virol Sin",
"key": "296_CR9",
"unstructured": "Fu Y, Cheng Y, Wu Y. Understanding SARS-CoV-2-mediated inflammatory responses: from mechanisms to potential therapeutic tools. Virol Sin. 2020;35:266–71.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"author": "Q Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "296_CR10",
"unstructured": "Ye Q, Wang B, Mao J. The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J Infect. 2020;80:607–13.",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab055",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "296_CR11",
"unstructured": "Lapenna D Antioxidant therapy in COVID-19: the crucial role of early treatment and antioxidant typology. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab055."
},
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "296_CR12",
"unstructured": "WHO. Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020. World Health Organization; 2020.",
"volume-title": "Corticosteroids for COVID-19: living guidance, 2 September 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s000180300001",
"author": "M Zafarullah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Life Sci",
"key": "296_CR13",
"unstructured": "Zafarullah M, Li W, Sylvester J, Ahmad M. Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:6–20.",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"author": "PJ Millea",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Am Fam Physician",
"key": "296_CR14",
"unstructured": "Millea PJ. N-acetylcysteine: multiple clinical applications. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80:265–9.",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"author": "E Dass",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "3–",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Pharm Res",
"key": "296_CR15",
"unstructured": "Dass E. Brief review of N-acetylcysteine as antiviral agent: potential application in COVID-19. J Biomed Pharm Res. 2020;9(3):69–73.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.97.10071535",
"author": "S De Flora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1535",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "296_CR16",
"unstructured": "De Flora S, Grassi C, Carati L. Attenuation of influenza-like symptomatology and improvement of cell-mediated immunity with long-term N-acetylcysteine treatment. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:1535–41.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.014",
"author": "M Mata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "548",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "296_CR17",
"unstructured": "Mata M, Morcillo E, Gimeno C, Cortijo J. N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) inhibit mucin synthesis and pro-inflammatory mediators in alveolar type II epithelial cells infected with influenza virus A and B and with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82:548–55.",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.112.1.164",
"author": "GR Bernard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "296_CR18",
"unstructured": "Bernard GR, Wheeler AP, Arons MM, Morris PE, Paz HL, Russell JA, et al. A trial of antioxidants N-acetylcysteine and procysteine in ARDS. Chest. 1997;112:164–72.",
"volume": "112",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0960327107083452",
"author": "MS Soltan-Sharifi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Hum Exp Toxicol",
"key": "296_CR19",
"unstructured": "Soltan-Sharifi MS, Mojtahedzadeh M, Najafi A, Khajavi MR, Rouini MR, Moradi M, et al. Improvement by N-acetylcysteine of acute respiratory distress syndrome through increasing intracellular glutathione, and extracellular thiol molecules and anti-oxidant power: evidence for underlying toxicological mechanisms. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007;26:697–703.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"author": "R Mohanty",
"first-page": "2802",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "296_CR20",
"unstructured": "Mohanty R, Padhy B, Das S, Meher B. Therapeutic potential of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in preventing cytokine storm in COVID-19: review of current evidence. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25:2802–7.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "C Puyo",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "F1000Research",
"key": "296_CR21",
"unstructured": "Puyo C, Kreig D, Saddi V, Ansari E, Prince O. Case report: Use of hydroxychloroquine and N-acetylcysteine for treatment of a COVID-19 positive patient. F1000Research. 2020;9:491.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000022577",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e22577",
"issue": "42",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "296_CR22",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Wang M, Luo G, Qian X, Wu C, Zhang Y, et al. Experience of N-acetylcysteine airway management in the successful treatment of one case of critical condition with COVID-19: a case report. Medicine. 2020;99(42):e22577. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000022577.",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.003",
"author": "A Nasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Rep",
"key": "296_CR23",
"unstructured": "Nasi A, McArdle S, Gaudernack G, Westman G, Melief C, Rockberg J, et al. Reactive oxygen species as an initiator of toxic innate immune responses in retort to SARS-CoV-2 in an ageing population, consider N-acetylcysteine as early therapeutic intervention. Toxicol Rep. 2020;7:768–71.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108544",
"author": "H Ibrahim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108544",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "296_CR24",
"unstructured": "Ibrahim H, Perl A, Smith D, Lewis T, Kon Z, Goldenberg R, et al. Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous N-acetylcysteine. Clin Immunol. 2020;219:108544.",
"volume": "219",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.105.1.190",
"author": "PM Suter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "296_CR25",
"unstructured": "Suter PM, Domenighetti G, Schaller M-D, Laverrière M-C, Ritz R, Perret C. N-acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Chest. 1994;105:190–4.",
"volume": "105",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"author": "DM Radomska-Leśniewska",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Cent Eur J Immunol",
"key": "296_CR26",
"unstructured": "Radomska-Leśniewska DM, Skopiński P. Review paper N-acetylcysteine as an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory drug and its some clinical applications. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2012;37:57–66.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0885066617696850",
"author": "J Chertoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "J Intensive Care Med",
"key": "296_CR27",
"unstructured": "Chertoff J. N-acetylcysteine’s role in sepsis and potential benefit in patients with microcirculatory derangements. J Intensive Care Med. 2018;33:87–96.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006286",
"author": "M Poppe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1006286",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "296_CR28",
"unstructured": "Poppe M, Wittig S, Jurida L, Bartkuhn M, Wilhelm J, Müller H, et al. The NF-κB-dependent and-independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006286.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/039463200401700114",
"author": "P Ghezzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol",
"key": "296_CR29",
"unstructured": "Ghezzi P, Ungheri D. Synergistic combination of N-acetylcysteine and ribavirin to protect from lethal influenza viral infection in a mouse model. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004;17:99–102.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0048037",
"author": "M Mata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e48037",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "296_CR30",
"unstructured": "Mata M, Sarrion I, Armengot M, Carda C, Martinez I, Melero JA, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits ciliagenesis in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells: effectiveness of N-acetylcysteine. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e48037.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2009.08.025",
"author": "J Geiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "296_CR31",
"unstructured": "Geiler J, Michaelis M, Naczk P, Leutz A, Langer K, Doerr H-W, et al. N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) inhibits virus replication and expression of pro-inflammatory molecules in A549 cells infected with highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79:413–20.",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"author": "C Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "296_CR32",
"unstructured": "Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang S, Yang S, Tao Y, et al. Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:762–8.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001807",
"author": "S De Flora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13185",
"journal-title": "FASEB J",
"key": "296_CR33",
"unstructured": "De Flora S, Balansky R, La Maestra S. Rationale for the use of N-acetylcysteine in both prevention and adjuvant therapy of COVID-19. FASEB J. 2020;34:13185–93.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110133",
"author": "N Jaiswal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110133",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "296_CR34",
"unstructured": "Jaiswal N, Bhatnagar M, Shah H. N-acetylcysteine: a potential therapeutic agent in COVID-19 infection. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144:110133.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "296_CR35",
"unstructured": "Van Hecke O, Lee J. N-acetylcysteine: a rapid review of the evidence for effectiveness in treating COVID-19. 2020. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12663/1089."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "296_CR36",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13413-7",
"author": "JM Nicholls",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1773",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "296_CR37",
"unstructured": "Nicholls JM, Poon LL, Lee KC, Ng WF, Lai ST, Leung CY, et al. Lung pathology of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;361:1773–8.",
"volume": "361",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S273700",
"author": "Z Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1047",
"journal-title": "Ther Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "296_CR38",
"unstructured": "Shi Z, Puyo CA. N-acetylcysteine to combat COVID-19: an evidence review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:1047.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2008.09.013",
"author": "M Moradi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "434",
"journal-title": "Respir Med",
"key": "296_CR39",
"unstructured": "Moradi M, Mojtahedzadeh M, Mandegari A, Soltan-Sharifi MS, Najafi A, Khajavi MR, et al. The role of glutathione-S-transferase polymorphisms on clinical outcome of ALI/ARDS patient treated with N-acetylcysteine. Respir Med. 2009;103:434–41.",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00024382-200013010-00003",
"author": "O Ortolani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Shock",
"key": "296_CR40",
"unstructured": "Ortolani O, Conti A, De Gaudio AR, Masoni M, Novelli G. Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine and rutin on the lipid peroxidation of the lung epithelium during the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Shock. 2000;13:14–8.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0883-9441(97)90029-0",
"author": "G Domenighetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "296_CR41",
"unstructured": "Domenighetti G, Suter PM, Schaller M-D, Ritz R, Perret C. Treatment with N-acetylcysteine during acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. J Crit Care. 1997;12:177–82.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199207000-00004",
"author": "S Jepsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "918",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "296_CR42",
"unstructured": "Jepsen S, Herlevsen P, Knudsen P, Bud MI, Klausen N. Antioxidant treatment with N-acetylcysteine during adult respiratory distress syndrome: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Crit Care Med. 1992;20:918–23.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2017.4891",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2863",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "296_CR43",
"unstructured": "Zhang Y, Ding S, Li C, Wang Y, Chen Z, Wang Z. Effects of N-acetylcysteine treatment in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14:2863–8.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494",
"author": "DH Alamdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173494",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "296_CR44",
"unstructured": "Alamdari DH, Moghaddam AB, Amini S, Keramati MR, Zarmehri AM, Alamdari AH, et al. Application of methylene blue-vitamin C–N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173494.",
"volume": "885",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01441",
"author": "LF García",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1441",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "296_CR45",
"unstructured": "García LF. Immune response, inflammation, and the clinical spectrum of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1441.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9124021",
"author": "V Lariccia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4021",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "296_CR46",
"unstructured": "Lariccia V, Magi S, Serfilippi T, Toujani M, Gratteri S, Amoroso S. Challenges and opportunities from targeting inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection: a narrative review. J Clin Med. 2020;9:4021.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0735-1097(02)01797-7",
"author": "J Sochman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1422",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Cardiol",
"key": "296_CR47",
"unstructured": "Sochman J. N-acetylcysteine in acute cardiology: 10 years later: what do we know and what would we like to know?! J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1422–8.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/NDT.S241497",
"author": "M Sabetghadam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1265",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat",
"key": "296_CR48",
"unstructured": "Sabetghadam M, Mazdeh M, Abolfathi P, Mohammadi Y, Mehrpooya M. Evidence for a beneficial effect of oral N-acetylcysteine on functional outcomes and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020;16:1265.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21186790",
"author": "A Samidurai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6790",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "296_CR49",
"unstructured": "Samidurai A, Das A. Cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19 and potential therapeutic ~ strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6790.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jocn.2020.05.017",
"author": "I Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "J Clin Neurosci",
"key": "296_CR50",
"unstructured": "Ahmad I, Rathore FA. Neurological manifestations and complications of COVID-19: a literature review. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;77:8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2020.05.017. Accessed 6 May 2020.",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/102490790701400402",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "296_CR51",
"unstructured": "Meri W, Koutsogiannis Z, Kerr D, Kelly. How safe is intravenous N-Acetylcysteine for the treatment of paracetamol\npoisoning?. Hong Kong J Emerg Med 2007, 14(4):198–203."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2005.11.003",
"author": "AM Sadowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "296_CR52",
"unstructured": "Sadowska AM, Manuel-y-Keenoy B, Vertongen T, Schippers G, Radomska-Lesniewska D, Heytens E, et al. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on neutrophil activation markers in healthy volunteers: in vivo and in vitro study. Pharmacol Res. 2006;53:216–25.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-199120020-00004",
"author": "MR Holdiness",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacokinet",
"key": "296_CR53",
"unstructured": "Holdiness MR. Clinical pharmacokinetics of N-acetylcysteine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991;20:123–34.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11999-010-1287-7",
"author": "SR Kearns",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2251",
"journal-title": "Clin Orthop Relat Res",
"key": "296_CR54",
"unstructured": "Kearns SR, O’Briain DE, Sheehan KM, Kelly C, Bouchier-Hayes D. N-acetylcysteine protects striated muscle in a model of compartment syndrome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:2251–9.",
"volume": "468",
"year": "2010"
}
],
"reference-count": 54,
"references-count": 54,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Pharmacol. Rep"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "73"
}