Real-world nirmatrelvir-ritonavir outpatient treatment in reducing hospitalization for high-risk patients with COVID-19 during Omicron BA.4, BA.5 and XBB subvariants dominance in Malaysia: A retrospective cohort study
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003, Oct 2023
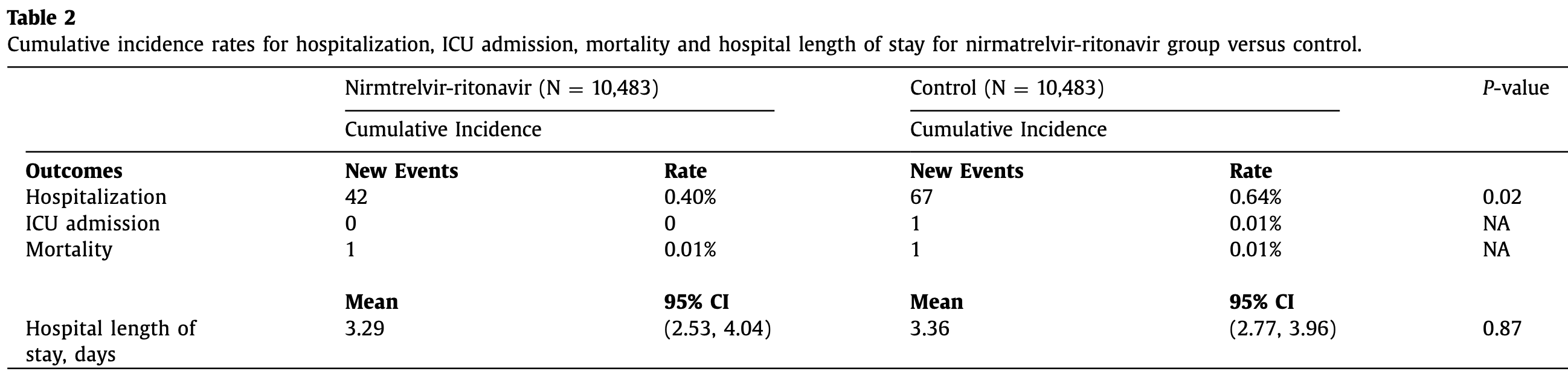
Retrospective 31,483 high-risk COVID-19 outpatients in Malaysia showing lower risk of hospitalization with paxlovid.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending paxlovid also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out paxlovid is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Malden et al. confirm significant bias in the use of paxlovid, showing that treated
patients are more likely to be from affluent neighborhoods, be more health-conscious, and
have better access to care. Campion et al. also show that female patients were more
likely to receive paxlovid, and studies show that female patients are significantly more
likely to be health-conscious, for example being more likely to take additional
non-prescription treatments.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid6-13. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID14. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid15. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid16. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury17 and liver injury18,19. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound20-22.
|
risk of death, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 10,483 (0.0%), control 1 of 10,483 (0.0%), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 10,483 (0.0%), control 1 of 10,483 (0.0%), NNT 10483, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 36.0% lower, HR 0.64, p = 0.03, treatment 42 of 10,483 (0.4%), control 67 of 10,483 (0.6%), NNT 419, propensity score matching, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Malden et al., Predictors of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir receipt among COVID-19 patients in a large US health system, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57633-7.
5.
Campion et al., Disparities in the Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1809.
6.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
7.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
8.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
9.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
10.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
11.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
12.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
13.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
14.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
15.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
16.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
17.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
18.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
19.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
20.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Low et al., 31 Oct 2023, retrospective, Malaysia, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 14 July, 2022 - 14 November, 2022.
Contact: evlow@moh.gov.my, evienlow@gmail.com.
Real-world nirmatrelvir-ritonavir outpatient treatment in reducing hospitalization for high-risk patients with COVID-19 during Omicron BA.4, BA.5 and XBB subvariants dominance in Malaysia: A retrospective cohort study
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003
Objective: To determine if nirmatrelvir-ritonavir 30 0mg/10 0mg treatment for 5 days in high-risk outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms was associated with a reduction in hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and death. Methods: This 1:1 propensity score matched cohort study from 647 public health clinics in Malaysia included all patients with COVID-19 with positive tests aged 18 years and older, who were eligible for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment within 5 days of illness from July 14, 2022, to November 14, 2022. The exposed group was patients with COVID-19 initiated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment, whereas those not initiated with the drug served as the control group. Data was analyzed from July 14, 2022 to December 31, 2022. Results: A total of 20,966 COVID-19 high-risk outpatients (n = 10,483 for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir group and n = 10,483 for control group) were included in the study. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment was associated with a 36% reduction (adjusted hazard ratio 0.64 [95% CI 0.43, 0.94]) in hospitalization compared with those not given the drug. There was a single ICU admission for the control group and one death each was reported in the nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and control group, respectively. Conclusions: Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment was associated with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with COVID-19 even in highly vaccinated populations.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author contributions EVL, MP, SC, KP designed the study. MZ, MZ, SB, WRK, WJL, MR and TTZ collected the data. EVL and MP acquired and analyzed the data. The data was interpreted by all authors. EVL wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript. EVL, MD, SC, and KP performed the critical revision of the manuscript for intellectual contact. All authors had full access to all data in the studies and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Data sharing statement The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request, and with protocol approved by the Medical Research and Ethics Committee, Ministry of Health Malaysia.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003 .
References
Aggarwal, Molina, Beaty, Bennett, Carlson et al., Real-world use of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in outpatients with COVID-19 during the era of omicron variants including BA.4 and BA.5 in Colorado, USA: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00011-7
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Battat, Lavie et al., Nirmatrelvir use and severe Covid-19 outcomes during the omicron surge, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919
Arumugam, Malaysia to get Covid-19 oral antivriral drug, Paxlovid, this month (NSTTV)
Baker, Bolt, Smith, Piasecki, Conner et al., The relationship of COVID-19 vaccination with mortality among 86,732 hospitalized patients: subpopulations, patient factors, and changes over time, J Gen Intern Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-022-08007-0
Ccider), Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), CCIDER-COVID
Dryden-Peterson, Kim, Kim, Caniglia, Lennes et al., Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 in a Large U.S. health system: a population-based cohort study, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-2141
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Havers, Pham, Taylor, Whitaker, Patel et al., COVID-19-associated hospitalizations among vaccinated and unvaccinated adults 18 years or older in 13 US states, January 2021 to April 2022, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.4299
Karyakarte, Das, Dudhate, Agarasen, Pillai et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases infected with omicron subvariants and the XBB recombinant variant, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.35261
Kkm Now, The latest data on the pandemic in Malaysia
Lewnard, Mclaughlin, Malden, Hong, Puzniak et al., Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4
Liu, Wei, He, Differences in case-fatality-rate of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, Public Health Pract (Oxf), doi:10.1016/j.puhip.2022.100350
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Khoury, Amar et al., Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/penalty-@Mciac443
Produk, Oleh Pyt, Pbkd, None
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Patidar, Younis et al., Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN Compr Clin Med, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4
Shah, Joyce, Plumb, Sahakian, Feldstein et al., Paxlovid associated with decreased hospitalization rate among adults with COVID-19 -United States, April-September 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7148e2
Vanderweele, Ding, Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-value, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M16-2607
Wang, Liu, Zhang, Huang, Zhao et al., Differences in incidence and fatality of COVID-19 by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant versus Delta variant in relation to vaccine coverage: a world-wide review, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28118
Wong, Lau, Leung, Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvirritonavir against BA.4 and BA.5 omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00056-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971223006884"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Real-world nirmatrelvir-ritonavir outpatient treatment in reducing hospitalization for high-risk patients with COVID-19 during Omicron BA.4, BA.5 and XBB subvariants dominance in Malaysia: A retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8596-1318",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Low",
"given": "Ee Vien",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8385-0315",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pathmanathan",
"given": "Mohan Dass",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chidambaram",
"given": "Suresh Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1912-2940",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Wee Ric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0008-4062-5829",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Wei Jia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teh",
"given": "Zhi Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Appannan",
"given": "Maheshwara Rao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zin",
"given": "Shahanizan Mohd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zin",
"given": "Faizah Muhamad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "Samha Bashirah Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Mastura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samad",
"given": "Azah Abdul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9279-3498",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Peariasamy",
"given": "Kalaiarasu M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"ijidonline.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-09T16:04:28Z",
"timestamp": 1691597068000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T14:51:11Z",
"timestamp": 1715439071000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013885",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100013885",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-19T21:54:14Z",
"timestamp": 1724104454386
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691280000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971223006884?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971223006884?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "77-83",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0001",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health Malaysia and Department of Statistics Malaysia. The latest data on the pandemic in Malaysia, https://data.moh.gov.my/covid; 2023 [accessed 23 March 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0002",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying medical conditions associated with higher risk for severe COVID-19: information for healthcare professionals, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html; 2023 [accessed 25 April 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0003",
"series-title": "National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2019 non-communicable diseases, healthcare demand, and health literacy: key Findings",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0004",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health Malaysia. Situasi terkini COVID-19 di Malaysia, https://covid-19.moh.gov.my/terkini; 2023 [accessed 20 April, 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0005",
"series-title": "Transition to endemic phase, prime minister of Malaysia",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0006",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health Malaysia and Department of Statistics Malaysia. KKM Now, The latest data on the pandemic in Malaysia, https://data.moh.gov.my/covid; 2023 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Sanyaolu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1069",
"journal-title": "SN Compr Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0007",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0008",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration. Emergency use authorizations for drugs and non-vaccine biological products, https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/emergency-use-authorizations-drugs-and-non-vaccine-biological-products; 2023 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0009",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for PaxlovidTM, https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download; 2021 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0010",
"series-title": "Annex 2e: Clinical management of confirmed COVID-19 case in adult and paediatric",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0011",
"series-title": "National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency, PRODUK S, DILULUSKAN OLEH PYT, DADAH PBK (PBKD) DALAM MESYUARAT PBKD KALI KE –370",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Arumugam",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_sbref0012",
"series-title": "Malaysia to get Covid-19 oral antivriral drug, Paxlovid, this month (NSTTV)",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0013",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00011-7",
"article-title": "Real-world use of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in outpatients with COVID-19 during the era of omicron variants including BA.4 and BA.5 in Colorado, USA: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0014",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0015",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system",
"author": "Lewnard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "806",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0016",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M16-2607",
"article-title": "Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-value",
"author": "VanderWeele",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0017",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0018",
"unstructured": "Our world in data. SARS-CoV-2 Variants in analyzed sequences, Malaysia, https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/covid-variants-area?time=2022-07-04.2023-01-02&country=∼MYS; 2023 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-022-08007-0",
"article-title": "The relationship of COVID-19 vaccination with mortality among 86,732 hospitalized patients: subpopulations, patient factors, and changes over time",
"author": "Baker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1248",
"journal-title": "J Gen Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0019",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.4299",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated hospitalizations among vaccinated and unvaccinated adults 18 years or older in 13 US states, January 2021 to April 2022",
"author": "Havers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0020",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Differences in case-fatality-rate of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Liu",
"journal-title": "Public Health Pract (Oxf)",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0021",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases infected with omicron subvariants and the XBB recombinant variant",
"author": "Karyakarte",
"first-page": "e35261",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0022",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28118",
"article-title": "Differences in incidence and fatality of COVID-19 by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant versus Delta variant in relation to vaccine coverage: a world-wide review",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28118",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0023",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir use and severe Covid-19 outcomes during the omicron surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0024",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-2141",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 in a Large U.S. health system: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Dryden-Peterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0025",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00056-7",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir against BA.4 and BA.5 omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0026",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0027",
"unstructured": "Hospital Authority Central Committee on Infectious Disease and Emergency Response (CCIDER). Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12) (Issue Date: 14 April 2022)"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0028",
"unstructured": "News.gov.hk. COVID-19 antiviral eligibility relaxed. https://www.news.gov.hk/eng/2022/07/20220729/20220729_170528_537.html; 2022 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0029",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel, Coronavirus Disease, https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/prioritization-of-therapeutics/; 2019 [accessed 20 April 2023]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7148e2",
"article-title": "Paxlovid associated with decreased hospitalization rate among adults with COVID-19 - United States, April–September 2022",
"author": "Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.08.003_bib0030",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971223006884"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world nirmatrelvir-ritonavir outpatient treatment in reducing hospitalization for high-risk patients with COVID-19 during Omicron BA.4, BA.5 and XBB subvariants dominance in Malaysia: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "135"
}