Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919, Jun 2022 (preprint)
Retrospective 109,254 patients in Israel, 3,902 treated with nirmatrelvir, showing lower mortality and hospitalization with treatment for the subgroup of patients >65. Authors only provide subgroup results.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 55.8% lower, HR 0.44, p = 0.37, treatment 3,902, control 105,352, adjusted per study, both age groups combined.
|
|
risk of death, 79.0% lower, HR 0.21, p = 0.03, treatment 2 of 2,484 (0.1%), control 158 of 40,337 (0.4%), NNT 321, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, age 65+.
|
|
risk of death, 32.0% higher, HR 1.32, p = 0.81, treatment 1 of 1,418 (0.1%), control 16 of 65,015 (0.0%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, age 40-64.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 56.5% lower, HR 0.43, p = 0.10, treatment 3,902, control 105,352, adjusted per study, both age groups combined.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 73.0% lower, HR 0.27, p < 0.001, treatment 2 of 2,484 (0.1%), control 151 of 40,337 (0.4%), NNT 340, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, age 65+.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 26.0% lower, HR 0.74, p = 0.44, treatment 1 of 1,418 (0.1%), control 13 of 65,015 (0.0%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, age 40-64.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Arbel et al., 1 Jun 2022, retrospective, Israel, peer-reviewed, mean age 60.0, 16 authors.
Contact: ronen.arbel@gmail.com.
Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge
New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2204919
BACKGROUND The oral protease inhibitor nirmatrelvir has shown substantial efficacy in highrisk, unvaccinated patients infected with the B.1.617.2 (delta) variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Data regarding the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir in preventing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outcomes from the B.1.1.529 (omicron) variant are limited.
METHODS We obtained data for all members of Clalit Health Services who were 40 years of age or older at the start of the study period and were assessed as being eligible to receive nirmatrelvir therapy during the omicron surge. A Cox proportional-hazards regression model with time-dependent covariates was used to estimate the association of nirmatrelvir treatment with hospitalization and death due to Covid-19, with adjustment for sociodemographic factors, coexisting conditions, and previous SARS-CoV-2 immunity status.
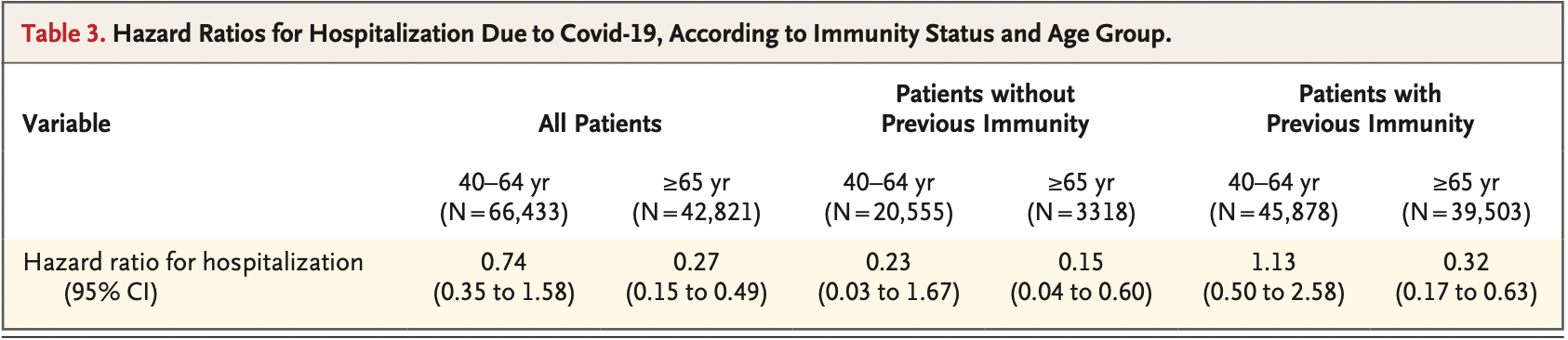
RESULTS A total of 109,254 patients met the eligibility criteria, of whom 3902 (4%) received nirmatrelvir during the study period. Among patients 65 years of age or older, the rate of hospitalization due to Covid-19 was 14.7 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients as compared with 58.9 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.27; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.49). The adjusted hazard ratio for death due to Covid-19 was 0.21 (95% CI, 0.05 to 0.82). Among patients 40 to 64 years of age, the rate of hospitalization due to Covid-19 was 15.2 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients and 15.8 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.35 to 1.58). The adjusted hazard ratio for death due to Covid-19 was 1.32 (95% CI, 0.16 to 10.75).
CONCLUSIONS Among patients 65 years of age or older, the rates of hospitalization and death due to Covid-19 were significantly lower among those who received nirmatrelvir than among those who did not. No evidence of benefit was found in younger adults.
References
Arbel, Hammerman, Sergienko, BNT162b2 vaccine booster and mortality due to Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Arbel, Sergienko, Friger, Effectiveness of a second BNT162b2 booster vaccine against hospitalization and death from COVID-19 in adults aged over 60 years
Callaway, Ledford, How bad is omicron? What scientists know so far, Nature
Dagan, Barda, Kepten, BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass vaccination setting, N Engl J Med
Dryden-Peterson, Kim, Kim, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 and hospitalization in a large US health system, doi:10.1101/2022.06.14.22276393v2
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for highrisk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Li, Wang, Lavrijsen, SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination, Cell Res
Lévesque, Hanley, Kezouh, Suissa, Problem of immortal time bias in cohort studies: example using statins for preventing progression of diabetes, BMJ
Rubin, Baden, Morrissey, Audio interview: understanding the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, N Engl J Med
Rubin, Baden, The potential of intentional drug development, N Engl J Med
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Covid-19 omicron variant, N Engl J Med
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2, N Engl J Med
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2204919",
"ISSN": [
"0028-4793",
"1533-4406"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1056/NEJMoa2204919"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6058-8665",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Arbel",
"given": "Ronen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Wolff Sagy",
"given": "Yael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Hoshen",
"given": "Moshe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Battat",
"given": "Erez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Lavie",
"given": "Gil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Sergienko",
"given": "Ruslan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Friger",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Waxman",
"given": "Jacob G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8811-7825",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dagan",
"given": "Noa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Balicer",
"given": "Ran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Ben-Shlomo",
"given": "Yatir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Peretz",
"given": "Alon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Yaron",
"given": "Shlomit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Serby",
"given": "Danielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4396-5246",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hammerman",
"given": "Ariel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Division of Community Medical Services (R.A., A.P., S.Y., D.S., A.H., D.N.), the Branch of Planning and Strategy (Y.W.S., M.H., E.B., G.L.), and the Clalit Research Institute, Division of Innovation (J.G.W., N.D., R.B., Y.B.-S.), Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, the Maximizing Health Outcomes Research Lab, Sapir College, Sderot (R.A.), the Department of Bioinformatics, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem (M.H.), the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel Institute..."
}
],
"family": "Netzer",
"given": "Doron",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "N Engl J Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T21:00:10Z",
"timestamp": 1661374810000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T21:00:12Z",
"timestamp": 1661374812000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-24T21:41:53Z",
"timestamp": 1661377313466
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "150",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1056",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Massachusetts Medical Society",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2202699",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2202160",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2101765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2115624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.b5087",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01832-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00618-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03614-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r16"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2204919"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge",
"type": "journal-article"
}