Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections
et al., Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568, Mar 2021
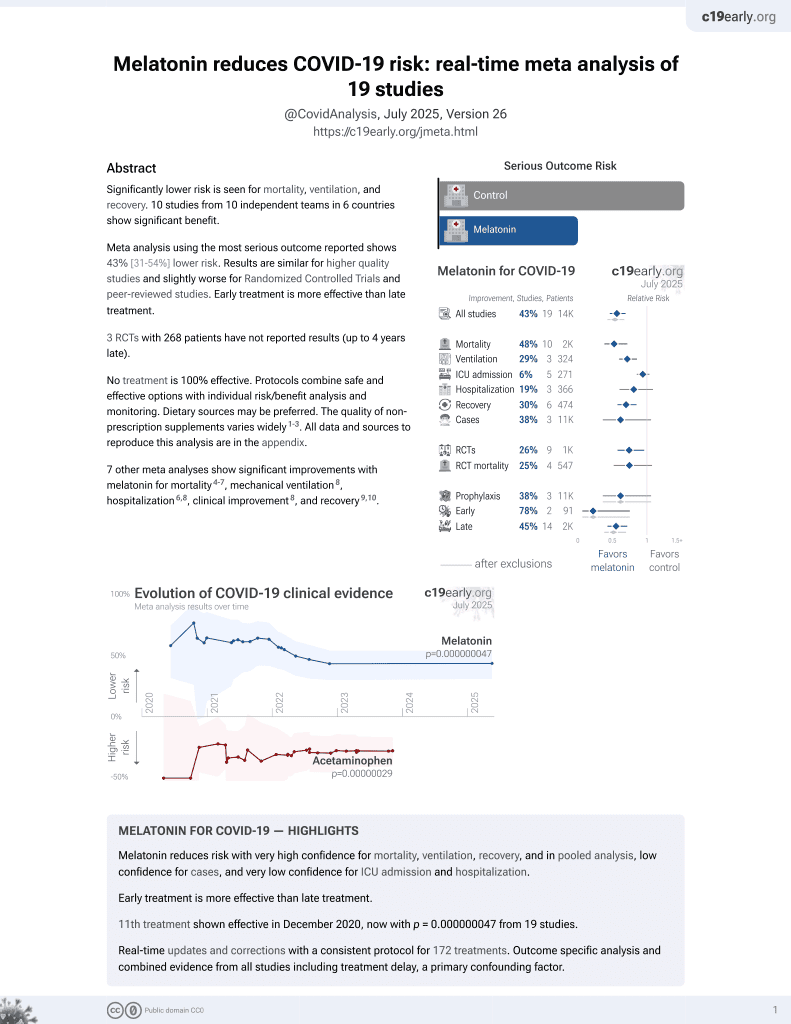
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of melatonin for COVID-19, suggesting that vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin supplementation may have general utility for the prevention and treatment of RNA virus infections, such as COVID-19 and influenza.
1.
Chen et al., Viral mitochondriopathy in COVID-19, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2025.103766.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
4.
Zhao et al., Melatonin Potentially Acts as a Widely-Acting Protective Tool in COVID-19, Medicine Research, doi:10.21127/yaoyimr20240006.
5.
Yehia et al., Melatonin: a ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration, Molecular Neurodegeneration, doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00728-6.
6.
Chacin-Bonilla et al., Melatonin and viral infections: A review focusing on therapeutic effects and SARS-CoV-2, Melatonin Research, doi:10.32794/mr112500168.
7.
Lempesis et al., A mid‑pandemic night's dream: Melatonin, from harbinger of anti‑inflammation to mitochondrial savior in acute and long COVID‑19 (Review), International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2024.5352.
8.
Alomari et al., Assessing the antiviral potential of melatonin: A comprehensive systematic review, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2499.
9.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
10.
Langen, M., Melatonin - the Hormone of Both Sun and Darkness - Protects Your Health and Can Save Your Life, Rounding The Earth, roundingtheearth.substack.com/p/melatonin-the-hormone-of-both-sun.
11.
Hosseinzadeh et al., Melatonin effect on platelets and coagulation: Implications for a prophylactic indication in COVID-19, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120866.
12.
Loh et al., Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23158122.
13.
Reiter et al., Melatonin: highlighting its use as a potential treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, doi:10.1007/s00018-021-04102-3.
14.
Tan et al., Mechanisms and clinical evidence to support melatonin's use in severe COVID-19 patients to lower mortality, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120368.
15.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
16.
Castle et al., Implications for Systemic Approaches to COVID-19: Effect Sizes of Remdesivir, Tocilizumab, Melatonin, Vitamin D3, and Meditation, Journal of Inflammation Research, doi:10.2147/JIR.S323356.
17.
Ramos et al., The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Key Emphasis on Melatonin Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10071152.
18.
Camp et al., Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps, Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546.
19.
Cross et al., Melatonin for the Early Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Possible Efficacy, Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.06.001.
20.
DiNicolantonio et al., Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568.
21.
Reiter (B) et al., Therapeutic Algorithm for Use of Melatonin in Patients With COVID-19, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00226.
22.
Charaa et al., Prophylactic Treatment Protocol against the Severity of COVID-19 Using Melatonin, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3601861.
DiNicolantonio et al., 19 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections
Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568
A recent retrospective study has provided evidence that COVID-19 infection may be notably less common in those using supplemental melatonin. It is suggested that this phenomenon may reflect the fact that, via induction of silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1), melatonin can upregulate K63 polyubiquitination of the mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein, thereby boosting virally mediated induction of type 1 interferons. Moreover, Sirt1 may enhance the antiviral efficacy of type 1 interferons by preventing hyperacetylation of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), enabling its retention in the nucleus, where it promotes transcription of interferon-inducible genes. This nuclear retention of HMGB1 may also be a mediator of the anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin therapy in COVID-19-complementing melatonin's suppression of nuclear factor kappa B activity and upregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. If these speculations are correct, a nutraceutical regimen including vitamin D, zinc and melatonin supplementation may have general utility for the prevention and treatment of RNA virus infections, such as COVID-19 and influenza.
References
Abba, Hassim, Hamzah, Antiviral activity of resveratrol against human and animal viruses, Adv Virol, doi:10.1155/2015/184241
Andersson, Ottestad, Tracey, Extracellular HMGB1: a therapeutic target in severe pulmonary inflammation including COVID-19?, Mol Med, doi:10.1186/s10020-020-00172-4
Arentz, Hunter, Yang, Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009
Aucoin, Cooley, Saunders, The effect of quercetin on the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections in humans: a rapid review, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.007
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006
Bonaldi, Talamo, Scaffidi, Monocytic cells hyperacetylate chromatin protein HMGB1 to redirect it towards secretion, Embo J, doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg516
Brice, Diamond, Antiviral activities of human host defense peptides, Curr Med Chem, doi:10.2174/0929867326666190805151654
Castillo, Quizon, Juco, Melatonin as adjuvant treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia patients requiring hospitalization (MAC-19 pro): a case series, Melatonin Res, doi:10.32794/mr11250063
Chen, Zhou, Mueller-Steiner, SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-beta toxicity through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M509329200
Chimento, Amicis, Sirianni, Progress to improve oral bioavailability and beneficial effects of resveratrol, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20061381
Costford, Bajpeyi, Pasarica, Skeletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00318.2009
De, Brasiel, The key role of zinc in elderly immunity: a possible approach in the COVID-19 crisis, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.06.003
Dinicolantonio, Barroso-Aranda, Mccarty, Azithromycin and glucosamine may amplify the type 1 interferon response to RNA viruses in a complementary fashion, Immunol Lett, doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.008
Dinicolantonio, Mccarty, Targeting casein kinase 2 with quercetin or enzymatically modified isoquercitrin as a strategy for boosting the type 1 interferon response to viruses and promoting cardiovascular health, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109800
Dinicolantonio, None, Open Heart
Early, Menon, Wyse, Circadian clock protein BMAL1 regulates IL-1β in macrophages via NRF2, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.1800431115
Ehlers, Xie, Agapov, BMAL1 links the circadian clock to viral airway pathology and asthma phenotypes, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1038/mi.2017.24
Fulco, Cen, Zhao, Glucose restriction inhibits skeletal myoblast differentiation by activating SIRT1 through AMPK-mediated regulation of NAMPT, Dev Cell, doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.004
García, Volt, Venegas, Disruption of the NF-ΰB/NLRP3 connection by melatonin requires retinoid-related orphan receptor-α and blocks the septic response in mice, Faseb J, doi:10.1096/fj.15-273656
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients2020, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hardeland, Melatonin and inflammation-Story of a double-edged blade, J Pineal Res, doi:10.1111/jpi.12525
Hong-Ji, Chen-Hui, Li-Tian, Activation of silent information regulator 1 exerts a neuroprotective effect after intracerebral hemorrhage by deacetylating NF-κB/p65, J Neurochem, doi:10.1111/jnc.15258
Huang, Li, Zhang, RIG-1 and MDA-5 signaling pathways contribute to IFN-β production and viral replication in porcine circovirus virus type 2-infected PK-15 cells in vitro, Vet Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.09.022
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.14.20152728
Jung, Kwak, The Nrf2 system as a potential target for the development of indirect antioxidants, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules15107266
Liu, Zhang, Chu, The ubiquitin E3 ligase TRIM31 promotes aggregation and activation of the signaling adaptor MAVS through Lys63-linked polyubiquitination, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/ni.3641
Mariani, Giménez, Bergam, Association between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 incidence, complications, and mortality in 46 countries: an ecological study, Health Secur, doi:10.1089/hs.2020.0137
Mclachlan, The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms, Clin Hypertens, doi:10.1186/s40885-020-00147-x
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence regarding vitamin D and risk of COVID-19 and its severity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113361
Milne, Lambert, Schenk, Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature06261
Mossink, Zinc as nutritional intervention and prevention measure for COVID-19 disease, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000095
Nogueira-Machado, De, Volpe, HMGB-1 as a target for inflammation controlling, Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, doi:10.2174/187221412802481784
Ong, Lee, Leong, Dengue virus infection mediates HMGB1 release from monocytes involving PCAF acetylase complex and induces vascular leakage in endothelial cells, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041932
Patel, Zhong, Grant, Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1-7 axis of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708
Peters, Smith, Stark, IRF-3-dependent, NFkappa B-and JNK-independent activation of the 561 and IFN-beta genes in response to double-stranded RNA, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.092133199
Prasad, Beck, Bao, Zinc supplementation decreases incidence of infections in the elderly: effect of zinc on generation of cytokines and oxidative stress, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837
Pryke, Duggan, White, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces vitamin D-1-hydroxylase activity in normal human alveolar macrophages, J Cell Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.1041420327
Saenwongsa, Nithichanon, Chittaganpitch, Metformininduced suppression of IFN-α via mTORC1 signalling following seasonal vaccination is associated with impaired antibody responses in type 2 diabetes, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-60213-0
Song, Qi, Cao, MAVS O-GlcNAcylation is essential for host antiviral immunity against lethal RNA viruses, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.085
Street, HMGB1: a possible crucial therapeutic target for COVID-19?, Horm Res Paediatr, doi:10.1159/000508291
Telcian, Zdrenghea, Edwards, Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004
Tripathi, Tecle, Verma, The human cathelicidin LL-37 inhibits influenza A viruses through a mechanism distinct from that of surfactant protein D or defensins, J Gen Virol, doi:10.1099/vir.0.045013-0
Wei, Gao, Dai, SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00119.2018
Xu, Lu, Yao, Novel role of resveratrol: suppression of high-mobility group protein box 1 nucleocytoplasmic translocation by the upregulation of sirtuin 1 in sepsis-induced liver injury, Shock, doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000000225
Zainal, Chang, Cheng, Resveratrol treatment reveals a novel role for HMGB1 in regulation of the type 1 interferon response in dengue virus infection, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep42998
Zhang, Fang, Wu, Acetylation-Dependent deubiquitinase OTUD3 controls MAVS activation in innate antiviral immunity, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.020
Zhou, Hou, Shen, A network medicine approach to investigation and population-based validation of disease manifestations and drug repurposing for COVID-19, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000970
Zhou, Zhang, Zhang, CLOCK/BMAL1 regulates circadian change of mouse hepatic insulin sensitivity by SIRT1, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.26992
Zhu, Li, Zhang, TRAF3IP3 mediates the recruitment of TRAF3 to MAVS for antiviral innate immunity, Embo J, doi:10.15252/embj.2019102075
Çelebier, İbrahim Celalettin, Could targeting HMGB1 be useful for the clinical management of COVID-19 infection?, Comb Chem High Throughput Screen, doi:10.2174/1386207323999200728114927
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568",
"ISSN": [
"2053-3624"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A recent retrospective study has provided evidence that COVID-19 infection may be notably less common in those using supplemental melatonin. It is suggested that this phenomenon may reflect the fact that, via induction of silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1), melatonin can upregulate K63 polyubiquitination of the mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein, thereby boosting virally mediated induction of type 1 interferons. Moreover, Sirt1 may enhance the antiviral efficacy of type 1 interferons by preventing hyperacetylation of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), enabling its retention in the nucleus, where it promotes transcription of interferon-inducible genes. This nuclear retention of HMGB1 may also be a mediator of the anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin therapy in COVID-19—complementing melatonin’s suppression of nuclear factor kappa B activity and upregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. If these speculations are correct, a nutraceutical regimen including vitamin D, zinc and melatonin supplementation may have general utility for the prevention and treatment of RNA virus infections, such as COVID-19 and influenza.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7888-1528",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "DiNicolantonio",
"given": "James J",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarty",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barroso-Aranda",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Heart",
"container-title-short": "Open Heart",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-19T16:17:53Z",
"timestamp": 1616170673000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-19T16:18:17Z",
"timestamp": 1616170697000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-27T02:29:26Z",
"timestamp": 1711506566345
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 18,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1616112000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e001568",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Melatonin is significantly associated with survival of intubated COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Ramlall",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.15-273656",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12525",
"article-title": "Melatonin and inflammation-Story of a double-edged blade",
"author": "Hardeland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Pineal Res",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.3",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules15107266",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000970",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40885-020-00147-x",
"article-title": "The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms",
"author": "McLachlan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Clin Hypertens",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.7",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.26992",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1800431115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.09.022",
"article-title": "RIG-1 and MDA-5 signaling pathways contribute to IFN-β production and viral replication in porcine circovirus virus type 2-infected PK-15 cells in vitro",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Vet Microbiol",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.10",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2019102075",
"article-title": "TRAF3IP3 mediates the recruitment of TRAF3 to MAVS for antiviral innate immunity",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Embo J",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.11",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.3641",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.020",
"article-title": "Acetylation-Dependent deubiquitinase OTUD3 controls MAVS activation in innate antiviral immunity",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "304",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.13",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M509329200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jnc.15258",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.15",
"unstructured": "Deng Hong‐Ji , Zhou Chen‐Hui , Huang Li‐Tian , et al . Activation of silent information regulator 1 exerts a neuroprotective effect after intracerebral hemorrhage by deacetylating NF‐κB/p65. J Neurochem 2020.doi:10.1111/jnc.15258"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.092133199",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep42998",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/mi.2017.24",
"article-title": "BMAL1 links the circadian clock to viral airway pathology and asthma phenotypes",
"author": "Ehlers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.18",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/emboj/cdg516",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0041932",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajprenal.00119.2018",
"article-title": "SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "F20",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Renal Physiol",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.21",
"volume": "316",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SHK.0000000000000225",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187221412802481784",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000508291",
"article-title": "HMGB1: a possible crucial therapeutic target for COVID-19?",
"author": "Street",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Horm Res Paediatr",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.24",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s10020-020-00172-4",
"article-title": "Extracellular HMGB1: a therapeutic target in severe pulmonary inflammation including COVID-19?",
"author": "Andersson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Mol Med",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.25",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1386207323999200728114927",
"article-title": "Could targeting HMGB1 be useful for the clinical management of COVID-19 infection?",
"author": "Çelebier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Comb Chem High Throughput Screen",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00318.2009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-60213-0",
"article-title": "Metformin-induced suppression of IFN-α via mTORC1 signalling following seasonal vaccination is associated with impaired antibody responses in type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Saenwongsa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.29",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature06261",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20061381",
"article-title": "Progress to improve oral bioavailability and beneficial effects of resveratrol",
"author": "Chimento",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.31",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/293524",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113361",
"article-title": "Evidence regarding vitamin D and risk of COVID-19 and its severity",
"author": "Mercola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.33",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/hs.2020.0137",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 incidence, complications, and mortality in 46 countries: an ecological study",
"author": "Mariani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Health Secur",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro",
"author": "Telcian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.35",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.1041420327",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.045013-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867326666190805151654",
"article-title": "Antiviral activities of human host defense peptides",
"author": "Brice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1420",
"journal-title": "Curr Med Chem",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.38",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.40",
"unstructured": "Grant WB , Lahore H , McDonnell SL , et al . Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients 2020 ;;12:988. April 2. doi:10.3390/nu12040988"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009",
"article-title": "Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review",
"author": "Arentz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Adv Integr Med",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.42",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000095",
"article-title": "Zinc as nutritional intervention and prevention measure for COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Mossink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr Prev Health",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.43",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.06.003",
"article-title": "The key role of zinc in elderly immunity: a possible approach in the COVID-19 crisis",
"author": "de Almeida Brasiel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.45",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.085",
"article-title": "MAVS O-GlcNAcylation is essential for host antiviral immunity against lethal RNA viruses",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2386",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.46",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.008",
"article-title": "Azithromycin and glucosamine may amplify the type 1 interferon response to RNA viruses in a complementary fashion",
"author": "DiNicolantonio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Immunol Lett",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.47",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109800",
"article-title": "Targeting casein kinase 2 with quercetin or enzymatically modified isoquercitrin as a strategy for boosting the type 1 interferon response to viruses and promoting cardiovascular health",
"author": "DiNicolantonio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.48",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.007",
"article-title": "The effect of quercetin on the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections in humans: a rapid review",
"author": "Aucoin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Adv Integr Med",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.49",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32794/mr11250063",
"article-title": "Melatonin as adjuvant treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia patients requiring hospitalization (MAC-19 pro): a case series",
"author": "Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Melatonin Res.",
"key": "2021031909151460000_8.1.e001568.50",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://openheart.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "8"
}