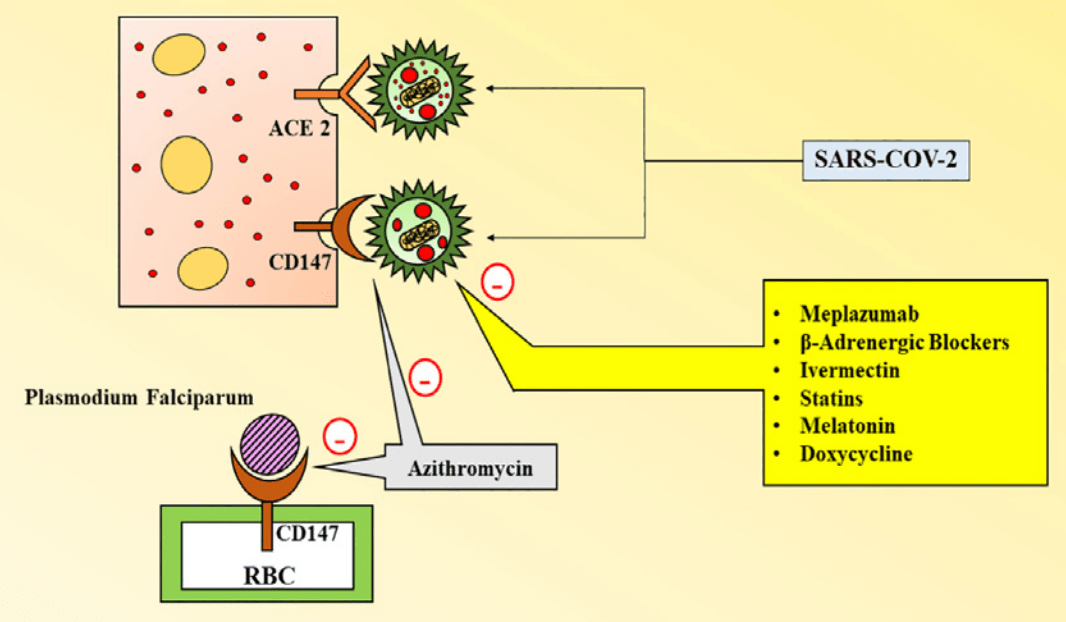
CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target
et al., Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072, Dec 2021
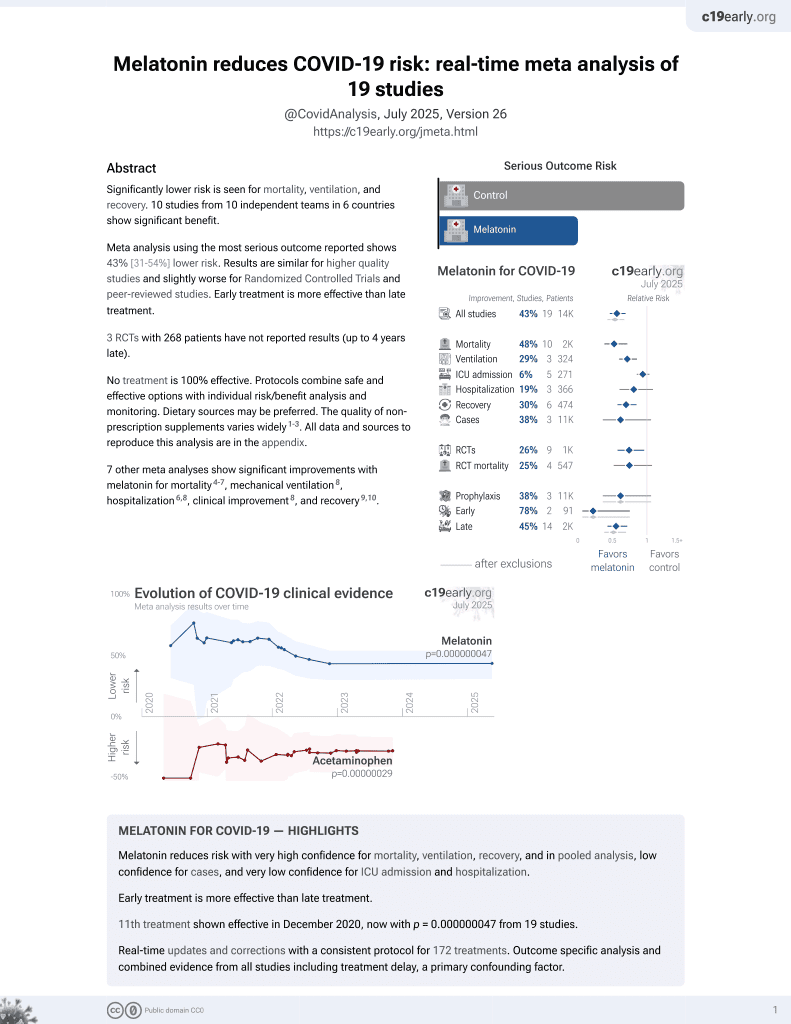
Melatonin for COVID-19
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) transmembrane protein as an entry route for SARS-CoV-2, correlation with observed characteristics of COVID-19, and relevant potential therapeutics including azithromycin, melatonin, statins, beta adrenergic blockers, ivermectin, and meplazumab.
Review covers melatonin and ivermectin.
1.
Chen et al., Viral mitochondriopathy in COVID-19, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2025.103766.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
4.
Zhao et al., Melatonin Potentially Acts as a Widely-Acting Protective Tool in COVID-19, Medicine Research, doi:10.21127/yaoyimr20240006.
5.
Yehia et al., Melatonin: a ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration, Molecular Neurodegeneration, doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00728-6.
6.
Chacin-Bonilla et al., Melatonin and viral infections: A review focusing on therapeutic effects and SARS-CoV-2, Melatonin Research, doi:10.32794/mr112500168.
7.
Lempesis et al., A mid‑pandemic night's dream: Melatonin, from harbinger of anti‑inflammation to mitochondrial savior in acute and long COVID‑19 (Review), International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2024.5352.
8.
Alomari et al., Assessing the antiviral potential of melatonin: A comprehensive systematic review, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2499.
9.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
10.
Langen, M., Melatonin - the Hormone of Both Sun and Darkness - Protects Your Health and Can Save Your Life, Rounding The Earth, roundingtheearth.substack.com/p/melatonin-the-hormone-of-both-sun.
11.
Hosseinzadeh et al., Melatonin effect on platelets and coagulation: Implications for a prophylactic indication in COVID-19, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120866.
12.
Loh et al., Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23158122.
13.
Reiter et al., Melatonin: highlighting its use as a potential treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, doi:10.1007/s00018-021-04102-3.
14.
Tan et al., Mechanisms and clinical evidence to support melatonin's use in severe COVID-19 patients to lower mortality, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120368.
15.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
16.
Castle et al., Implications for Systemic Approaches to COVID-19: Effect Sizes of Remdesivir, Tocilizumab, Melatonin, Vitamin D3, and Meditation, Journal of Inflammation Research, doi:10.2147/JIR.S323356.
17.
Ramos et al., The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Key Emphasis on Melatonin Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10071152.
18.
Camp et al., Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps, Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546.
19.
Cross et al., Melatonin for the Early Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Possible Efficacy, Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.06.001.
20.
DiNicolantonio et al., Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568.
21.
Reiter (B) et al., Therapeutic Algorithm for Use of Melatonin in Patients With COVID-19, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00226.
22.
Charaa et al., Prophylactic Treatment Protocol against the Severity of COVID-19 Using Melatonin, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3601861.
Behl et al., 1 Dec 2021, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target
Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072
The combat against the Corona virus disease of 2019 , has created a chaos among the healthcare institutions and researchers, in turn accelerating the dire need to curtail the infection spread. The already established entry mechanism, via ACE2 has not yet successfully aided in the development of a suitable and reliable therapy. Taking in account the constant progression and deterioration of the cases worldwide, a different perspective and mechanistic approach is required, which has thrown light onto the cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) transmembrane protein, as a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 entry. Despite lesser affinity towards COVID-19 virus, as compared to ACE2, this receptor provides a suitable justification behind elevated blood glucose levels in infected patients, retarded COVID-19 risk in women, enhanced susceptibility in geriatrics, greater infection susceptibility of T cells, infection prevalence in non-susceptible human cardiac pericytes and so on. The manuscript invokes the title role and distribution of CD147 in COVID-19 as an entry receptor and mediator of endocytosis-promoted entry of the virus, along with the "catch and clump" hypothesis, thereby presenting its Fundamental significance as a therapeutic target for potential candidates, such as Azithromycin, melatonin, statins, beta adrenergic blockers, ivermectin, Meplazumab etc. Thus, the authors provide a comprehensive review of a different perspective in COVID-19 infection, aiming to aid the researchers and virologists in considering all aspects of viral entry, in order to develop a sustainable and potential cure for the 2019 COVID-19 disease.
References
Adikwu, Ebinyo, Bokolo, Melatonin and alpha lipoic acid attenuate methotrexate/cisplatin-induced kidney toxicity in albino rats, J. Nephropharmacol, doi:10.15171/npj.2020.17
Aguiar, Tremblay, Mansfield, Gene expression and in situ protein profiling of candidate SARS-CoV-2 receptors in human airway epithelial cells and lung tissue, doi:10.1101/2020.04.07.030742
Ahmed, Angel, Edson, Bibby, Bivins et al., First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community, Sci. Total Environ
Ahmetaj-Shala, Vaja, Atanur, Cardiorenal tissues express SARS-CoV-2 entry genes and basigin (BSG/CD147) increases with age in endothelial cells, JACC: basic to translational
Amendola, Human cardiosphere-derived stromal cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 evolve into hyper-inflammatory/pro-fibrotic phenotype and produce infective viral particles depending on the levels of ACE2 receptor expression, Cardiovasc. Res
Arendt, Increased expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in multiple myeloma: role in regulation of myeloma cell proliferation, Leukemia
Arima, Cui, Kimura, Sonoda, Ishibashi et al., Basigin can be a therapeutic target to restore the retinal vascular barrier function in the mouse model of diabetic retinopathy, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep38445
Avanzini, Human mesenchymal stromal cells do not express ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and are not permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Stem Cells Transl. Med
Avolio, Carrabba, Milligan, The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein disrupts human cardiac pericytes function through CD147-receptor-mediated signalling: a potential non-infective mechanism of COVID-19 microvascular disease, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.12.21.423721
Bao, Min, Twigg, Monocyte CD147 is induced by advanced glycation end products and high glucose concentration: possible role in diabetic complications, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00228.2010
Barth, Blasche, Kasper, Lack of evidence for caveolin-1 and CD147 interaction before and after bleomycin-induced lung injury, Histochem. Cell Biol
Bernard, Pathogenic Neisseria meningitidis utilizes CD147 for vascular colonization, Nat. Med
Bian, Zheng, Wei, Meplazumab treats COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-labelled, concurrent controlled add-on clinical trial, doi:10.1101/2020.03.21.20040691
Bonilla, Valero, Chacin-Bonilla, Medina-Leendertz, Melatonin and viral infections, J. Pineal Res, doi:10.1046/j.1600-079x.2003.00105.x
Bourgonje, Abdulle, Timens, Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease
Bukrinsky, Extracellular cyclophilins in health and disease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.013
Cai, Suppression of coronavirus replication by inhibition of the MEK signaling pathway, J. Virol
Calma, The COVID-19 pandemic is generating tons of medical waste, The Verge
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity, Science
Cdc, and Control FAQs for COVID-19
Chan, Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 is an important surface attachment factor that facilitates entry of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol
Chen, Function of HAb18G/CD147 in invasion of host cells by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Infect. Dis
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J. Med. Virol
Chen, Peng, Lei, Nuclear envelope-distributed CD147 interacts with and inhibits the transcriptional function of RING1 and promotes melanoma cell motility, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0183689
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Cheung, Poon, Ng, Cytokine responses in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected macrophages in vitro: possible relevance to pathogenesis, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.12.7819-7826.2005
Chu, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus and bat coronavirus HKU9 both can utilize GRP78 for attachment onto host cells, J. Biol. Chem
Crosnier, Bustamante, Bartholdson, Basigin is a receptor essential for erythrocyte invasion by plasmodium falciparum, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature10606
Dai, KSHV activation of VEGF secretion and invasion for endothelial cells is mediated through viral upregulation of emmprin-induced signal transduction, Int. J. Cancer
Daly, Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Science, doi:10.1111/bph.15166
De Farias, Da Paixao, Cruz, Melatonin supplementation attenuates the pro-inflammatory adipokines expression in visceral fat from obese mice induced by a high-fat diet, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells8091041
Donoghue, Hsieh, Baronas, A novel angioten sin-converting enzymerelated carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/01.res.87.5.e1
Emingil, Atilla, Sorsa, The effect of adjunctive subantimicrobial dose doxycycline therapy on gcf emmprin levels in chronic periodontitis, J. Perinatol, doi:10.1902/jop.2008.070165
Eyster, Discovery of new cargo proteins that enter cells through clathrinindependent endocytosis, Traffic
Fadare, Okoffo, Covid-19 face masks: a potential source of microplastic fibers in the environment, Sci. Total Environ
Fehr, Channappanavar, Jankevicius, The conserved coronavirus macrodomain promotes virulence and suppresses the innate immune response during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, Published, doi:10.1128/mBio.01721-16
Fehr, Perlman, Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis, Methods Mol. Biol
Fu, Wang, A novel small-molecule compound targeting CD147 inhibits the motility and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6990
Ghasemnejad-Berenji, Pashapour, SARS-CoV-2 and the possible role of Raf/ MEK/ERK pathway in viral survival: is this a potential therapeutic strategy for COVID 19?, Pharmacology
Gorbalenya, Baker, Baric, The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classi fying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
Hamashima, Gautam, Lau, Khiong, Blenkinsop et al., Potential modes of COVID-19 transmission from human eye revealed by single-cell atlas, doi:10.1101/2020.05.09.085613
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J. Pathol
Harmer, Gilbert, Borman, Clark, Quantitative mRNA expression profling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03640-2
Harrison, Viral membrane fusion, Virology
Hoffmann, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hu, Dang, Yao, Involvement of HAb18G/CD147 in T cell activation and immunological synapse formation, J. Cell. Mol. Med, doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01012.x
Hu, Interleukin-6 drives multiple myeloma progression by up-regulating of CD147/emmprin expression, Blood
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Hui, Azhar, Madani, The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health -the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Hulswit, De Haan, Bosch, Coronavirus spike protein and tropism changes, Adv. Virus Res
Jin, Inhibition of CD147 (cluster of differentiation 147) ameliorates acute ischemic stroke in mice by reducing thromboinflammation, Stroke
Jouneau, Khorasani, Souza, EMMPRIN (CD147) regulation of MMP-9 in bronchial epithelial cells in COPD, Respirology, doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.01960.x
Kalungi, Kinyanda, Akena, Less severe cases of COVID-19 in subsaharan Africa: could co-infection or a recent history of plasmodium falciparum infection be protective? Front, Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.565625
Karamitri, Jockers, Melatonin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-018-0130-1
Kini, Kundu, Infection-GENOMICS of COVID-19: Are Some Communities Resistant?, doi:10.20944/preprints202004.0310.v1
Kirk, Wilson, Heddle, CD147 is tightly asso ciated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression, EMBO J, doi:10.1093/emboj/19.15.3896
Kong, Liao, Zhang, A regulatory loop involving miR-22, Sp1, and cmyc modulates CD147 expression in breast cancer invasion and metastasis, Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3555
Kuba, A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med
Kuba, Imai, Ohto-Nakanishi, Penninger, Tril ogy of ACE2: a peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters, Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.06.003
Kucukakin, Lykkesfeldt, Nielsen, Utility of melatonin to treat surgical stress after major vascular surgery-a safety study, J. Pineal Res, doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00545.x
Lan, Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature
Lee, Sun, Sung, Daily melatonin protects the endothelial lineage and functional integrity against the aging process, oxidative stress, and toxic environment and restores blood fow in critical limb ischemia area in mice, J. Pineal Res, doi:10.1111/jpi.12489
Lei, Li, Li, Qi, CT imaging of the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200236
Li, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect. Dis. Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x
Li, Huang, Long, CD147 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Akt/ mTOR/SREBP1c and P38/PPARalpha pathways, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.039
Li, Si, Zhu, Yang, Anderson et al., Discovery of bat coronaviruses through surveillance and probe capture-based next-generation sequencing, mSphere
Li, Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins, Annu. Rev. Virol
Li, Xie, Yi, Expression of cyclophilin a and CD147 during skin aging, Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban
Liang, Yang, Guo, Shi, Hou et al., Atorvastatin attenuates plaque vulnerability by downregulation of EMMPRIN expression via COX-2/PGE2 pathway, Exp. Ther. Med, doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4062
Liu, Brunn, Zhu, Cyclophilin a and CD147: novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of COVID-19, Med. Drug Discov
Liu, Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province, Chin. Med. J
Liu, Spike protein of SARS-CoV stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent protein kinase C pathways, FASEB J
Loh, The potential of melatonin in the prevention and attenuation of oxidative hemolysis and myocardial injury from cd147 SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding, Melatonin Res
Lu, Basolateral CD147 induces hepatocyte polarity loss by E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma progress, Hepatology
Lu, Liu, Shao, Melatonin is responsible for rice resistance to rice stripe virus infection through a nitric oxide dependent pathway, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s1298-3
Lu, Zhao, Li, Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
Maeda, Seike, Kon, Erythrocyte aggregation as a determinant of blood flow: effect of pH, temperature and osmotic pressure, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol
Magagnoli, Narendran, Pereira, Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19, doi:10.1101/2020.04.16.20065920
Mahdian, Shahhoseini, Moini, COVID-19 mediated by basigin can affect male and female fertility, IntJ Fertil Steril, doi:10.22074/ijfs.2020.134702
Mahdian, Zarrabi, Panahi, Dabbagh, Keshavarz, Repurposing FDA-approved drugs to fight COVID-19 using in silico methods: targeting SARS-CoV-2 RdRp enzyme and host cell receptors (ACE2, CD147) through virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulations, Informatics Med. Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155151
Mallapaty, How sewage could reveal true scale of coronavirus outbreak, Nature
Malleret, Xu, Mohandas, Significant biochemical, biophysical and metabolic diversity in circulating human cord blood reticulocytes, PLoS One
Manchanda, 16 -anemias: Red blood cell morphology and approach to diagnosis
Marchiq, Albrengues, Granja, Knock out of the BASIGIN/CD147 chaperone of lactate/H+ symporters dis proves its pro-tumour action via extracellular matrix metallo proteases (MMPs) induction, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4323
Mattos, Lim, Russell, Matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in asthma: effect of asthma severity, allergen challenge, and inhaled corticosteroids, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.122.5.1543
Mauvais-Jarvis, Estradiol, progesterone, immunomodulation and COVID-19 outcomes, Endocrinology, doi:10.1210/endocr/bqaa127
Miyauchi, Kanekura, Yamaoka, Basigin, a new, broadly distributed member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has strong homology with both the immunoglobulin V domain and the beta-chain of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen, J. Biochem, doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123045
Mock, Matthews, Zhu, Red blood cell (RBC) volume can be independently determined in vivo in humans using RBCs labeled at different densities of biotin, Transfusion
Moheimani, Koops, Williams, Influenza a virus infection dysregulates the expression of microRNA-22 and its targets; CD147 and HDAC4, in epithelium of asthmatics, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-018-0851-7
Moheimani, Koops, Williams, Influenza a virus infection dysregulates the expression of microRNA-22 and its targets; CD147 and HDAC4, in epithelium of asthmatics, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-018-0851-7
Mok, Ooi, Ng, A new prospective on the role of melatonin in diabetes and its complications, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1515/hmbci-2019-0036
Molina, Delaugerre, Le Goff, No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical benefit with the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection. Six of the 11 study subjects had cancer or HIV, and all but one were on oxygen at the start of the trial, Med. Mal. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.006
Muralidharan, Striepen, Teaching old drugs new tricks to stop malaria invasion in its tracks, BMC Biol, doi:10.1186/s12915-015-0185-6
Muramatsu, Basigin (CD147), a multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein with various binding partners, J. Biochem
Negrette, Bonilla, Valero, Melatonin treatment enhances the efciency of mice immunization with venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus TC-83, Neurochem. Res, doi:10.1023/a:1011645400123
Nghiem, Morgan, Donner, Short, The COVID-19 pandemic: considerations for the waste and wastewater services sector, Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng
Odièvre, Bony, Benkerrou, Modulation of erythroid adhesion receptor expression by hydroxyurea in children with sickle cell disease, Haematologica
Pan, Mu, Ren, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study
Peng, Liu, Xu, SARS-CoV-2 can be detected in urine, blood, anal swabs and oropharyngeal swabs specimens, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25936
Phan, Nguyen, Luong, Importation and human-to-human transmission of a novel coronavirus in Vietnam, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2001272
Pushkarsky, CD147 facilitates HIV-1 infection by interacting with virus associated cyclophilin a, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Pushkarsky, Zybarth, Dubrovsky, CD147 facilitates HIV-1 infection by interacting with virus-associated cyclophilin a, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Qiao, The expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and CD147, and protease TMPRSS2 in human and mouse brain cells and mouse brain tissues
Radzikowska, Ding, Tan, Zhakparov, Peng, Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors, Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1111/all.14429
Radzikowska, Ding, Tan, human tissues and immune cells in health and disease, doi:10.1101/2020.05.14.090332
Rahman, Bodrud-Doza, Griffiths, Mamun, Biomedical waste amid COVID-19: perspectives from Bangladesh
Raj, Mou, Smits, Dekkers, Müller et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC, Nature
Ramos, López-Muñoz, Gil-Martín, Egea, The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): key emphasis on melatonin safety and therapeutic efficacy, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10071152
Raony, De Figueiredo, De figueiredo CS (2020) retinal outcomes of COVID-19: possible role of CD147 and cytokine storm in infected patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108280
Rodrigues-Diez, Tejera-Muñoz, Marquez-Exposito, Statins: could an old friend help in the fight against COVID-19?, Br. J. Pharmacol
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8630
Rota, Oberste, Monroe, Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1085952
Rume, Ul Islam, Environmental effects of COVID-19 pandemic and potential strategies of sustainability, Heliyon
Saghazadeh, Rezaei, Immune-epidemiological parameters of the novel coronavirus-a perspective, Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1080/1744666X.2020.1750954
Saitoh, Rab5-regulated endocytosis plays a crucial role in apical extrusion of transformed cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Saltos, Saltos, Entry of SARS-CoV2 through the basal surface of alveolar endothelial cells-a proposed mechanism mediated by CD147 in COVID-19
Sanchez-Lopez, Ortiz, Pacheco-Moises, Efcacy of melatonin on serum pro-infammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2018.12.004
Sasidhar, Downregulation of monocytic differentiation via modulation of CD147 by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors, PLoS ONE
Savtekin, Serakinci, Erzik, Effects of circadian rhythm hormones melatonin and 5-methoxytryptophol on COXs, Raf-1 and STAT3, IntJ Pharmacol, doi:10.3923/ijp.2018.787.795
Scheim, Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-mediated Vascular Occlusion, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3636557
Scheim, Ivermectina for COVID 19 treatment clinical response at quasi-threshold doses via hypothesized alleviation of CD147 mediated vascular occlusive, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00195-y
Schmidt, Bültmann, Fischel, Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) is a novel receptor on platelets, activates platelets, and augments nuclear factor kappaB-dependent inflammation in monocytes, Circ. Res
Schoeman, Fielding, Coronavirus envelope protein: current knowledge, Virol. J
Sehirli, Sayiner, Serakinci, Role of melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19; as an adjuvant through cluster diferentiation 147 (CD147), Mol. Biol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05830-8
Sehirli, Sayiner, Serakinci, Role of melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19; as an adjuvant through cluster differentiation 147 (CD147), Mol. Biol. Rep
Sharma, Singh, Ahmad, The role of melatonin in diabetes: therapeutic implications, Arch. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1590/2359-3997000000098
Shereen, Khan, Kazmi, Bashir, Siddique, COVID-19 infection: origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses, J. Adv. Res, doi:10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005
Shilts, Crozier, Greenwood, No evidence for basigin/CD147 as a direct SARS-CoV-2 spike binding receptor, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80464-1
Shneider, Kudriavtsev, Vakhrusheva, Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?, Int. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1080/08830185.2020.1756284
Singh, Tang, Ogunseitan, Environmentally sustainable management of used personal protective equipment, Environ. Sci. Technol, doi:10.1021/acs.est.0c03022
Slomiany, Dai, Tolliver, Inhibition of functional hyaluronan-CD44 interactions in CD133-positive primary human ovarian carcinoma cells by small hyaluronan oligosaccharides, Clin. Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2317
Slonska, Cymerys, Banbura, Mechanisms of endocytosis utilized by viruses during infection, Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. (Online
Somani, Srivastava, Gummadivalli, Sharma, Indirect implications of COVID-19 towards sustainable environment: an investigation in Indian context, Biores. Technol. Rep
Song, Whitcomb, Kim, The role of melatonin in the onset and progression of type 3 diabetes, Mol. Brain, doi:10.1186/s13041-017-0315-x
Sparrow, Healey, Patton, Red blood cell age determines the impact of storage and leukocyte burden on cell adhesion molecules, glycophorin a and the release of annexin V, Transfus. Apher. Sci
Srivastava, Kumar, Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14515
Su, Li, Chen, Melatonin attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through the CyPA/CD147 signaling pathway, Mol. Cell Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-016-2808-9
Su, Wan, Wang, Expression of CD147 and cyclophilin a in kidneys of patients with COVID-19, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol, doi:10.2215/CJN.09440620
Telen, Red blood cell surface adhesion molecules: their possible roles in normal human physiology and disease, Semin. Hematol
Toole, The CD147-hyaluronan axis in cancer, Anat. Rec, doi:10.1002/ar.24147
Tseng, Wang, Huang, Self-assembly of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus membrane protein, J. Biol. Chem
Ulrich, Pillat, CD147 as a target for COVID-19 treatment: suggested efects of azithromycin and stem cell engagement, Stem Cell Rev. Rep, doi:10.1007/s12015-020-09976-7
Ungern-Sternberg, Zernecke, Seizer, Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in cardiovascular disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Van Boheemen, De Graaf, Lauber, Bestebroer, Raj et al., Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans, MBio
Vasanthakumar, Beta-adrenergic blockers as a potential treatment for COVID-19 patients, BioEssays, doi:10.1002/bies.202000094
Wan, Shang, Graham, Baric, Li, Receptor recognition by novel coronavirus from Wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00127-20
Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Lian et al., CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells, Signal Transduct. Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x
Wang, Chen, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 invades host cells via a novel route: CD147-spike protein, doi:10.1101/2020.03.14.988345
Wang, Dai, Wang, Expression of CD147 (EMMPRIN) on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis enhances chemotaxis, matrix metalloproteinase production and invasive ness of synoviocytes, J. Cell Mol. Med, doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01084.x
Wang, Shi, Jiang, Zhang, Wang et al., Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor doxycycline and CD147 antagonist peptide-9 on gallbladder carcinoma cell lines, Tumor Biol, doi:10.1177/1010428317718192
Watanabe, CD147/EMMPRIN acts as a functional entry receptor for measles virus on epithelial cells, J. Virol
Watanabe, Yoneda, Ikeda, Terao-Muto, Sato et al., CD147/ EMMPRIN acts as a functional entry receptor for measles virus on epithelial cells, J. Virol
Who, Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection When Novel Coronavirus (nCoV) Infection Is Suspected: Interim Guidance
Wilson, Goodman, Sleebs, Macrolides rapidly inhibit red blood cell invasion by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, BMC Biol, doi:10.1186/s12915-015-0162-0
Wrobel, SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol
Wu, Peng, Huang, Ding, Wang et al., Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001
Xiong, Edwards 3rd, Zhou, The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms151017411
Xiong, Edwards, Zhou, The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms151017411
Yan, Zhang, Li, 2 by full-length human ACE2, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Yong, Overlooked receptors in Covid-19: what ACE2 alone cannot explain
Yu, Yang, Chen, Chen, CD147 increases mucus secretion induced by cigarette smoke in COPD, BMC Pulm. Med, doi:10.1186/s12890-019-0791-0
Yurchenko, Constant, Bukrinsky, Dealing with the family: CD147 interactions with cyclophilins, Immunology
Yurchenko, O'connor, Dai, CD147 is a signaling receptor for cyclophilin B, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5847
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: an evidence-based clinical review article, J. Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00430-5
Zambrano-Monserrate, Ruanob, Sanchez-Alcalde, Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment, Sci. Total Environ
Zenonos, Basigin is a druggable target for host-oriented antimalarial interventions, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20150032
Zhai, Wu, Li, CD147 promotes IKK/Ikap paB/NF-kappaB pathway to resist TNF-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fbroblasts, J. Mol. Med. (Berl), doi:10.1007/s00109-015-1334-7
Zhang, Disrupting CD147-RAP2 interaction abrogates erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum, Blood
Zhang, Fan, Xie, Elevated serum cyclophilin B levels are associated with the prevalence and severity of metabolic syndrome, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2017.00360
Zhang, Penninger, Li, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target, Intensiv. Care Med
Zhang, Wang, Ni, COVID-19: melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583
Zhao, HAb18G/CD147 promotes cell motility by regulating annexin IIactivated RhoA and Rac1 signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Hepatology
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zhu, Song, Zhang, Nanda, Li, CD147: a novel modulator of inflammatory and immune disorders, Curr. Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/0929867321666131227163352
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072",
"ISSN": [
"0048-9697"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072",
"alternative-id": [
"S0048969721071485"
],
"article-number": "152072",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Science of The Total Environment"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Behl",
"given": "Tapan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "Ishnoor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aleya",
"given": "Lotfi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sehgal",
"given": "Aayush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Sukhbir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Neelam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhatia",
"given": "Saurabh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Harrasi",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bungau",
"given": "Simona",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Science of The Total Environment"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T15:52:46Z",
"timestamp": 1638373966000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-07T11:38:55Z",
"timestamp": 1638877135000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-08T05:55:51Z",
"timestamp": 1638942951529
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0048-9697"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643673600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0048969721071485?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0048969721071485?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "152072",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Melatonin and alpha lipoic acid attenuate methotrexate/cisplatin-induced kidney toxicity in albino rats",
"author": "Adikwu",
"journal-title": "J. Nephropharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0005",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection: origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses",
"author": "Adnan Shereen",
"journal-title": "J. Adv. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0010",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Gene expression and in situ protein profiling of candidate SARS-CoV-2 receptors in human airway epithelial cells and lung tissue",
"author": "Aguiar",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0015",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764",
"article-title": "First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0020",
"volume": "728",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Cardiorenal tissues express SARS-CoV-2 entry genes and basigin (BSG/CD147) increases with age in endothelial cells. JACC: basic to translational",
"author": "Ahmetaj-Shala",
"first-page": "1111",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0025",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvab082",
"article-title": "Human cardiosphere-derived stromal cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 evolve into hyper-inflammatory/pro-fibrotic phenotype and produce infective viral particles depending on the levels of ACE2 receptor expression",
"author": "Amendola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1557",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0030",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/leu.2012.91",
"article-title": "Increased expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in multiple myeloma: role in regulation of myeloma cell proliferation",
"author": "Arendt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2286",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Leukemia",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0035",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep38445",
"article-title": "Basigin can be a therapeutic target to restore the retinal vascular barrier function in the mouse model of diabetic retinopathy",
"author": "Arima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38445",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0040",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sctm.20-0385",
"article-title": "Human mesenchymal stromal cells do not express ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and are not permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Avanzini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "636",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Stem Cells Transl. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0045",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein disrupts human cardiac pericytes function through CD147-receptor-mediated signalling: a potential non-infective mechanism of COVID-19 microvascular disease",
"author": "Avolio",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0050",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.00228.2010",
"article-title": "Monocyte CD147 is induced by advanced glycation end products and high glucose concentration: possible role in diabetic complications",
"author": "Bao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0055",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00418-006-0192-3",
"article-title": "Lack of evidence for caveolin-1 and CD147 interaction before and after bleomycin-induced lung injury",
"author": "Barth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Histochem. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0060",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3563",
"article-title": "Pathogenic Neisseria meningitidis utilizes CD147 for vascular colonization",
"author": "Bernard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "725",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0065",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Meplazumab treats COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-labelled, concurrent controlled add-on clinical trial",
"author": "Bian",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0070",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1600-079X.2003.00105.x",
"article-title": "Melatonin and viral infections",
"author": "Bonilla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0075",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.5471",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Bourgonje",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0080",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.013",
"article-title": "Extracellular cyclophilins in health and disease",
"author": "Bukrinsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2087",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0085",
"volume": "1850",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01705-06",
"article-title": "Suppression of coronavirus replication by inhibition of the MEK signaling pathway",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "446",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0090",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"author": "Calma",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0095"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd2985",
"article-title": "Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity",
"author": "Cantuti-Castelvetri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0100",
"volume": "6518",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0105"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01133-16",
"article-title": "Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 is an important surface attachment factor that facilitates entry of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9114",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0110",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/427811",
"article-title": "Function of HAb18G/CD147 in invasion of host cells by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0115",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Nuclear envelope-distributed CD147 interacts with and inhibits the transcriptional function of RING1 and promotes melanoma cell motility",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0120",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0125",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25681",
"article-title": "Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0130",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.12.7819-7826.2005",
"article-title": "Cytokine responses in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected macrophages in vitro: possible relevance to pathogenesis",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7819",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0135",
"volume": "679",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA118.001897",
"article-title": "Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus and bat coronavirus HKU9 both can utilize GRP78 for attachment onto host cells",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11709",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0140",
"volume": "293",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0145",
"series-title": "Singapore: Bentham Science Publishers",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature10606",
"article-title": "Basigin is a receptor essential for erythrocyte invasion by plasmodium falciparum",
"author": "Crosnier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "534",
"issue": "7378",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0150",
"volume": "480",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.26428",
"article-title": "KSHV activation of VEGF secretion and invasion for endothelial cells is mediated through viral upregulation of emmprin-induced signal transduction",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "834",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0155",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd3072",
"article-title": "Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Daly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0160",
"volume": "6518",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells8091041",
"article-title": "Melatonin supplementation attenuates the pro-inflammatory adipokines expression in visceral fat from obese mice induced by a high-fat diet",
"author": "de Farias",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1041",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0165",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.87.5.e1",
"article-title": "A novel angioten sin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9",
"author": "Donoghue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E1",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0170",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of adjunctive subantimicrobial dose doxycycline therapy on gcf emmprin levels in chronic periodontitis",
"author": "Emingil",
"journal-title": "J. Perinatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0175",
"volume": "2008",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00894.x",
"article-title": "Discovery of new cargo proteins that enter cells through clathrin-independent endocytosis",
"author": "Eyster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "590",
"journal-title": "Traffic",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0180",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140279",
"article-title": "Covid-19 face masks: a potential source of microplastic fibers in the environment",
"author": "Fadare",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0185",
"volume": "737",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1",
"article-title": "Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis",
"author": "Fehr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0190",
"volume": "1282",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01721-16",
"article-title": "The conserved coronavirus macrodomain promotes virulence and suppresses the innate immune response during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection",
"author": "Fehr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0195",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.6990",
"article-title": "A novel small-molecule compound targeting CD147 inhibits the motility and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0200",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and the possible role of Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in viral survival: is this a potential therapeutic strategy for COVID 19?",
"author": "Ghasemnejad-Berenji",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0205",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z",
"article-title": "The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classi fying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gorbalenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "536",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0210",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential modes of COVID-19 transmission from human eye revealed by single-cell atlas",
"author": "Hamashima",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0225",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03640-2",
"article-title": "Quantitative mRNA expression profling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme",
"author": "Harmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0230",
"volume": "532",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.043",
"article-title": "Viral membrane fusion",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0235",
"volume": "479–480",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0240",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01012.x",
"article-title": "Involvement of HAb18G/CD147 in T cell activation and immunological synapse formation",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2132",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Mol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0245",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.V128.22.5632.5632",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 drives multiple myeloma progression by up-regulating of CD147/emmprin expression",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5632",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0250",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0255",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009",
"article-title": "The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health - the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0260",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.08.004",
"article-title": "Coronavirus spike protein and tropism changes",
"author": "Hulswit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Adv. Virus Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0265",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018839",
"article-title": "Inhibition of CD147 (cluster of differentiation 147) ameliorates acute ischemic stroke in mice by reducing thromboinflammation",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3356",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Stroke",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0270",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.01960.x",
"article-title": "EMMPRIN (CD147) regulation of MMP-9 in bronchial epithelial cells in COPD",
"author": "Jouneau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "705",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0275",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.565625",
"article-title": "Less severe cases of COVID-19 in sub-saharan Africa: could co-infection or a recent history of plasmodium falciparum infection be protective?",
"author": "Kalungi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0280",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Melatonin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity",
"author": "Karamitri",
"issue": "105–125",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0285",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "Kini",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb1040",
"series-title": "Infection-GENOMICS of COVID-19: Are Some Communities Resistant?",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/emboj/19.15.3896",
"article-title": "CD147 is tightly asso ciated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression",
"author": "Kirk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3896",
"journal-title": "EMBO J",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0290",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3555",
"article-title": "A regulatory loop involving miR-22, Sp1, and c-myc modulates CD147 expression in breast cancer invasion and metastasis",
"author": "Kong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0295",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"article-title": "A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0300",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.06.003",
"article-title": "Tril ogy of ACE2: a peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0305",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00545.x",
"article-title": "Utility of melatonin to treat surgical stress after major vascular surgery—a safety study",
"author": "Kucukakin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "426",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0310",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0315",
"volume": "7807",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12489",
"article-title": "Daily melatonin protects the endothelial lineage and functional integrity against the aging process, oxidative stress, and toxic environment and restores blood fow in critical limb ischemia area in mice",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0320",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "CT imaging of the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia",
"author": "Lei",
"journal-title": "Radiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0325",
"volume": "200236",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-110615-042301",
"article-title": "Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0330",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Expression of cyclophilin a and CD147 during skin aging",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0335",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.039",
"article-title": "CD147 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Akt/ mTOR/SREBP1c and P38/PPARalpha pathways",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1378",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0340",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00807-19",
"article-title": "Discovery of bat coronaviruses through surveillance and probe capture-based next-generation sequencing",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "mSphere",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0345",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"article-title": "Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Poverty",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb1005",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2017.4062",
"article-title": "Atorvastatin attenuates plaque vulnerability by downregulation of EMMPRIN expression via COX-2/PGE2 pathway",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "835",
"journal-title": "Exp. Ther. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0350",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.06-6589com",
"article-title": "Spike protein of SARS-CoV stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent protein kinase C pathways",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0355",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100056",
"article-title": "Cyclophilin a and CD147: novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0360",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000744",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0365",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32794/mr11250069",
"article-title": "The potential of melatonin in the prevention and attenuation of oxidative hemolysis and myocardial injury from cd147 SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding",
"author": "Loh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "380",
"journal-title": "Melatonin Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0375",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.29798",
"article-title": "Basolateral CD147 induces hepatocyte polarity loss by E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma progress",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0380",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-019-1228-3",
"article-title": "Melatonin is responsible for rice resistance to rice stripe virus infection through a nitric oxide dependent pathway",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0385",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0390",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4615-9510-6_68",
"article-title": "Erythrocyte aggregation as a determinant of blood flow: effect of pH, temperature and osmotic pressure",
"author": "Maeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0395",
"volume": "222",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"article-title": "Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Magagnoli",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0400",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 mediated by basigin can affect male and female fertility",
"author": "Mahdian",
"first-page": "262",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "IntJ Fertil Steril.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0405",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2021.100541",
"article-title": "Repurposing FDA-approved drugs to fight COVID-19 using in silico methods: targeting SARS-CoV-2 RdRp enzyme and host cell receptors (ACE2, CD147) through virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulations",
"author": "Mahdian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Informatics Med. Unlocked",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0410",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155151",
"article-title": "COVID 19 cytokine storm: the anger of inflammation",
"author": "Mahmudpour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0415",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201208172",
"article-title": "Microtubuledependent endosomal sorting of clathrin-independent cargo by Hook1",
"author": "Maldonado-Baez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0420",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-020-00973-x",
"article-title": "How sewage could reveal true scale of coronavirus outbreak",
"author": "Mallapaty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "176",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0425",
"volume": "580",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0076062",
"article-title": "Significant biochemical, biophysical and metabolic diversity in circulating human cord blood reticulocytes",
"author": "Malleret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0430",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "16 - anemias: Red blood cell morphology and approach to diagnosis",
"author": "Manchanda",
"first-page": "251",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0435",
"series-title": "Rodak's Hematology",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Knock out of the BASIGIN/CD147 chaperone of lactate/H+ symporters dis proves its pro-tumour action via extracellular matrix metallo proteases (MMPs) induction",
"author": "Marchiq",
"issue": "24636–24648",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0440",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.122.5.1543",
"article-title": "Matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in asthma: effect of asthma severity, allergen challenge, and inhaled corticosteroids",
"author": "Mattos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0445",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endocr/bqaa127",
"article-title": "Estradiol, progesterone, immunomodulation and COVID-19 outcomes",
"author": "Mauvais-Jarvis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb1045",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123045",
"article-title": "Basigin, a new, broadly distributed member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has strong homology with both the immunoglobulin V domain and the beta-chain of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen",
"author": "Miyauchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "316",
"journal-title": "J. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0450",
"volume": "107",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1537-2995.2010.02770.x",
"article-title": "Red blood cell (RBC) volume can be independently determined in vivo in humans using RBCs labeled at different densities of biotin",
"author": "Mock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0455",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Influenza a virus infection dysregulates the expression of microRNA-22 and its targets; CD147 and HDAC4, in epithelium of asthmatics",
"author": "Moheimani",
"journal-title": "Respir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0460",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-018-0851-7",
"article-title": "Influenza a virus infection dysregulates the expression of microRNA-22 and its targets; CD147 and HDAC4, in epithelium of asthmatics",
"author": "Moheimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Respir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0465",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2019-0036",
"article-title": "A new prospective on the role of melatonin in diabetes and its complications",
"author": "Mok",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0470",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.006",
"author": "Molina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Med. Mal. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0475",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12915-015-0185-6",
"article-title": "Teaching old drugs new tricks to stop malaria invasion in its tracks",
"author": "Muralidharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "BMC Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0480",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jb/mvv127",
"article-title": "Basigin (CD147), a multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein with various binding partners",
"author": "Muramatsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "481",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0485",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1011645400123",
"article-title": "Melatonin treatment enhances the efciency of mice immunization with venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus TC-83",
"author": "Negrette",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "767",
"journal-title": "Neurochem. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0490",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cscee.2020.100006",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 pandemic: considerations for the waste and wastewater services sector",
"author": "Nghiem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0495",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3324/haematol.12070",
"article-title": "Modulation of erythroid adhesion receptor expression by hydroxyurea in children with sickle cell disease",
"author": "Odièvre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "502",
"journal-title": "Haematologica",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0500",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"author": "Pan",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0505"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25936",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 can be detected in urine, blood, anal swabs and oropharyngeal swabs specimens",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1676",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0510",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001272",
"article-title": "Importation and human-to-human transmission of a novel coronavirus in Vietnam",
"author": "Phan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0515",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.111583198",
"article-title": "CD147 facilitates HIV-1 infection by interacting with virus associated cyclophilin a",
"author": "Pushkarsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6360",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0520",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.111583198",
"article-title": "CD147 facilitates HIV-1 infection by interacting with virus-associated cyclophilin a",
"author": "Pushkarsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6360",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0525",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"author": "Qiao",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0535",
"series-title": "The expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and CD147, and protease TMPRSS2 in human and mouse brain cells and mouse brain tissues",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Distribution of ACE2, CD147, cyclophilins, CD26 and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in human tissues and immune cells in health and disease",
"author": "Radzikowska",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0540",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14429",
"article-title": "Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors",
"author": "Radzikowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0545",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Rahman",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0550",
"series-title": "Biomedical waste amid COVID-19: perspectives from Bangladesh",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12005",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC",
"author": "Raj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "251",
"issue": "7440",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0555",
"volume": "495",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10071152",
"article-title": "The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): key emphasis on melatonin safety and therapeutic efficacy",
"author": "Ramos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1152",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0560",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108280",
"article-title": "De figueiredo CS (2020) retinal outcomes of COVID-19: possible role of CD147 and cytokine storm in infected patients with diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Raony",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0565",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15166",
"article-title": "Statins: could an old friend help in the fight against COVID-19?",
"author": "Rodrigues-Diez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "P4873",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0575",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2493",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0580",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085952",
"article-title": "Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Rota",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1394",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0585",
"volume": "300",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04965",
"article-title": "Environmental effects of COVID-19 pandemic and potential strategies of sustainability",
"author": "Rume",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0590",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2020.1750954",
"article-title": "Immune-epidemiological parameters of the novel coronavirus—a perspective",
"author": "Saghazadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0595",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1602349114",
"article-title": "Rab5-regulated endocytosis plays a crucial role in apical extrusion of transformed cells",
"author": "Saitoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E2327",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0600",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "Saltos",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0605"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2018.12.004",
"article-title": "Efcacy of melatonin on serum pro-infammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Sanchez-Lopez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Arch. Med. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0610",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0189701",
"article-title": "Downregulation of monocytic differentiation via modulation of CD147 by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors",
"author": "Sasidhar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0615",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of circadian rhythm hormones melatonin and 5-methoxytryptophol on COXs, Raf-1 and STAT3",
"author": "Savtekin",
"issue": "787–795",
"journal-title": "IntJ Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0620",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Scheim",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0625",
"series-title": "Ivermectin for COVID-19 Treatment: Clinical Response at Quasi-threshold Doses Via Hypothesized Alleviation of CD147-mediated Vascular Occlusion",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectina for COVID 19 treatment clinical response at quasi-threshold doses via hypothesized alleviation of CD147 mediated vascular occlusive",
"author": "Scheim",
"first-page": "736",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0630",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.157990",
"article-title": "Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) is a novel receptor on platelets, activates platelets, and augments nuclear factor kappaB-dependent inflammation in monocytes",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "302",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0635",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-019-1182-0",
"article-title": "Coronavirus envelope protein: current knowledge",
"author": "Schoeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0640",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-020-05830-8",
"article-title": "Role of melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19; as an adjuvant through cluster diferentiation 147 (CD147)",
"author": "Sehirli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0645",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-020-05830-8",
"article-title": "Role of melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19; as an adjuvant through cluster differentiation 147 (CD147)",
"author": "Sehirli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8229",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0650",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/2359-3997000000098",
"article-title": "The role of melatonin in diabetes: therapeutic implications",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Arch. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0655",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80464-1",
"article-title": "No evidence for basigin/CD147 as a direct SARS-CoV-2 spike binding receptor",
"author": "Shilts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0660",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08830185.2020.1756284",
"article-title": "Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Shneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Int. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0665",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.est.0c03022",
"article-title": "Environmentally sustainable management of used personal protective equipment",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8500",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Technol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0670",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2317",
"article-title": "Inhibition of functional hyaluronan-CD44 interactions in CD133-positive primary human ovarian carcinoma cells by small hyaluronan oligosaccharides",
"author": "Slomiany",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7593",
"journal-title": "Clin. Cancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0675",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5604/17322693.1203721",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of endocytosis utilized by viruses during infection",
"author": "Slonska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "572",
"journal-title": "Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. (Online)",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0680",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Indirect implications of COVID-19 towards sustainable environment: an investigation in Indian context",
"author": "Somani",
"journal-title": "Biores. Technol. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0685",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13041-017-0315-x",
"article-title": "The role of melatonin in the onset and progression of type 3 diabetes",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Mol. Brain",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0690",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2005.09.006",
"article-title": "Red blood cell age determines the impact of storage and leukocyte burden on cell adhesion molecules, glycophorin a and the release of annexin V",
"author": "Sparrow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transfus. Apher. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0695",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Srivastava",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0700",
"volume": "00",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-016-2808-9",
"article-title": "Melatonin attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through the CyPA/CD147 signaling pathway",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0705",
"volume": "422",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2215/CJN.09440620",
"article-title": "Expression of CD147 and cyclophilin a in kidneys of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "618",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0710",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0037-1963(00)90038-6",
"article-title": "Red blood cell surface adhesion molecules: their possible roles in normal human physiology and disease",
"author": "Telen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Semin. Hematol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0715",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "The CD147-hyaluronan axis in cancer",
"author": "Toole",
"journal-title": "Anat. Rec.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0725",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M109.030270",
"article-title": "Self-assembly of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus membrane protein",
"author": "Tseng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12862",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0730",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12015-020-09976-7",
"article-title": "CD147 as a target for COVID-19 treatment: suggested efects of azithromycin and stem cell engagement",
"author": "Ulrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "434",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Rev. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0735",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00473-12",
"article-title": "Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans",
"author": "Van Boheemen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0745",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bies.202000094",
"article-title": "Beta-adrenergic blockers as a potential treatment for COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Vasanthakumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BioEssays",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0750",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19020507",
"article-title": "Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Von Ungern-Sternberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0755",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00127-20",
"article-title": "Receptor recognition by novel coronavirus from Wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0760",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01084.x",
"article-title": "Expression of CD147 (EMMPRIN) on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis enhances chemotaxis, matrix metalloproteinase production and invasive ness of synoviocytes",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "850",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Mol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0765",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cr.2013.92",
"article-title": "Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "986",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0770",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor doxycycline and CD147 antagonist peptide-9 on gallbladder carcinoma cell lines",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "Tumor Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0775",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 invades host cells via a novel route: CD147-spike protein",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0790",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"article-title": "CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb1015",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02168-09",
"article-title": "CD147/EMMPRIN acts as a functional entry receptor for measles virus on epithelial cells",
"author": "Watanabe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4183",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0800",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02168-09",
"article-title": "CD147/EMMPRIN acts as a functional entry receptor for measles virus on epithelial cells",
"author": "Watanabe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4183",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0805",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0810"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12915-015-0162-0",
"article-title": "Macrolides rapidly inhibit red blood cell invasion by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum",
"author": "Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "BMC Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0815",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-0468-7",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects",
"author": "Wrobel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "763",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0820",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001",
"article-title": "Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0830",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms151017411",
"article-title": "The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17411",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0835",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms151017411",
"article-title": "The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17411",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0840",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0845",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Overlooked receptors in Covid-19: what ACE2 alone cannot explain",
"author": "Yong",
"journal-title": "Microbial Instincts. https://medium.com/microbial-instincts/overlooked-receptors-could-explain-quirks-of-covid-19-that-ace2-alone-cannot-9470817f59d0",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0850",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12890-019-0791-0",
"article-title": "CD147 increases mucus secretion induced by cigarette smoke in COPD",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0855",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/bbrc.2001.5847",
"article-title": "CD147 is a signaling receptor for cyclophilin B",
"author": "Yurchenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "786",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0860",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02316.x",
"article-title": "Dealing with the family: CD147 interactions with cyclophilins",
"author": "Yurchenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "301",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0865",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2: an evidence-based clinical review article",
"author": "Zaidi",
"journal-title": "J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0870",
"volume": "1–13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138813",
"article-title": "Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment",
"author": "Zambrano-Monserrate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0875",
"volume": "728",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20150032",
"article-title": "Basigin is a druggable target for host-oriented antimalarial interventions",
"author": "Zenonos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1145",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0880",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109-015-1334-7",
"article-title": "CD147 promotes IKK/Ikap paB/NF-kappaB pathway to resist TNF-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fbroblasts",
"author": "Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Med. (Berl)",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0885",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2017.00360",
"article-title": "Elevated serum cyclophilin B levels are associated with the prevalence and severity of metabolic syndrome",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0890",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2017-08-802918",
"article-title": "Disrupting CD147-RAP2 interaction abrogates erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1111",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0895",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05985-9",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "586",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Intensiv. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0900",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583",
"article-title": "COVID-19: melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0905",
"volume": "250",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.24592",
"article-title": "HAb18G/CD147 promotes cell motility by regulating annexin IIactivated RhoA and Rac1 signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2012",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0910",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"issue": "1054–1062",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0915",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867321666131227163352",
"article-title": "CD147: a novel modulator of inflammatory and immune disorders",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072_bb0920",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 178,
"references-count": 178,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Science of The Total Environment"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pollution",
"Waste Management and Disposal",
"Environmental Chemistry",
"Environmental Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "808"
}