Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps
et al., Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546, Jul 2021
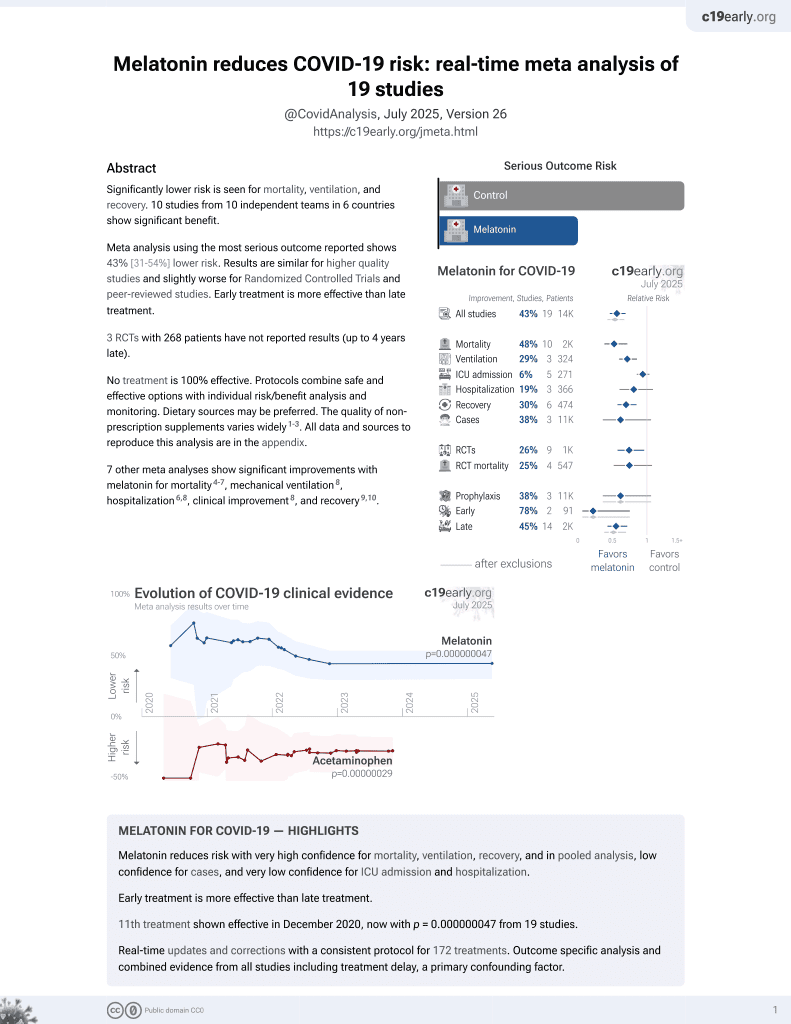
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000015 from 18 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review discussing how melatonin may improve COVID-19 prognosis by acting to reduce oxygen deficiency and hypoxia, vitamin B12 deficiency, NO deficiency, oxidative stress, and sleep disturbance.
1.
Chen et al., Viral mitochondriopathy in COVID-19, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2025.103766.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
4.
Zhao et al., Melatonin Potentially Acts as a Widely-Acting Protective Tool in COVID-19, Medicine Research, doi:10.21127/yaoyimr20240006.
5.
Yehia et al., Melatonin: a ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration, Molecular Neurodegeneration, doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00728-6.
6.
Chacin-Bonilla et al., Melatonin and viral infections: A review focusing on therapeutic effects and SARS-CoV-2, Melatonin Research, doi:10.32794/mr112500168.
7.
Lempesis et al., A mid‑pandemic night's dream: Melatonin, from harbinger of anti‑inflammation to mitochondrial savior in acute and long COVID‑19 (Review), International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2024.5352.
8.
Alomari et al., Assessing the antiviral potential of melatonin: A comprehensive systematic review, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2499.
9.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
10.
Langen, M., Melatonin - the Hormone of Both Sun and Darkness - Protects Your Health and Can Save Your Life, Rounding The Earth, roundingtheearth.substack.com/p/melatonin-the-hormone-of-both-sun.
11.
Hosseinzadeh et al., Melatonin effect on platelets and coagulation: Implications for a prophylactic indication in COVID-19, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120866.
12.
Loh et al., Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23158122.
13.
Reiter et al., Melatonin: highlighting its use as a potential treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, doi:10.1007/s00018-021-04102-3.
14.
Tan et al., Mechanisms and clinical evidence to support melatonin's use in severe COVID-19 patients to lower mortality, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120368.
15.
Behl et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Science of The Total Environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072.
16.
Castle et al., Implications for Systemic Approaches to COVID-19: Effect Sizes of Remdesivir, Tocilizumab, Melatonin, Vitamin D3, and Meditation, Journal of Inflammation Research, doi:10.2147/JIR.S323356.
17.
Ramos et al., The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Key Emphasis on Melatonin Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10071152.
18.
Camp et al., Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps, Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546.
19.
Cross et al., Melatonin for the Early Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Possible Efficacy, Endocrine Practice, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.06.001.
20.
DiNicolantonio et al., Melatonin may decrease risk for and aid treatment of COVID-19 and other RNA viral infections, Open Heart, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2020-001568.
21.
Reiter (B) et al., Therapeutic Algorithm for Use of Melatonin in Patients With COVID-19, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00226.
22.
Charaa et al., Prophylactic Treatment Protocol against the Severity of COVID-19 Using Melatonin, SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3601861.
Camp et al., 17 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546
Recent studies have shown a correlation between COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and the distinct, exaggerated immune response titled "cytokine storm". This immune response leads to excessive production and accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause clinical signs characteristic of COVID-19 such as decreased oxygen saturation, alteration of hemoglobin properties, decreased nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, vasoconstriction, elevated cytokines, cardiac and/or renal injury, enhanced D-dimer, leukocytosis, and an increased neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio. Particularly, neutrophil myeloperoxidase (MPO) is thought to be especially abundant and, as a result, contributes substantially to oxidative stress and the pathophysiology of COVID-19. Conversely, melatonin, a potent MPO inhibitor, has been noted for its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic, and neuroprotective actions. Melatonin has been proposed as a safe therapeutic agent for COVID-19 recently, having been given with a US Food and Drug Administration emergency authorized cocktail, REGEN-COV2, for management of COVID-19 progression. This review distinctly highlights both how the destructive interactions of HOCl with tetrapyrrole rings may contribute to oxygen deficiency and hypoxia, vitamin B12 deficiency, NO deficiency, increased oxidative stress, and sleep disturbance, as well as how melatonin acts to prevent these events, thereby improving COVID-19 prognosis.
References
Abu-Soud, Hazen, None, Biochemistry
Abu-Soud, Hazen, None, J. Biol. Chem
Abu-Soud, Maitra, Byun, Souza, Banerjee et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Abu-Soud, Maitra, Shaeib, Khan, Byun et al., None, J. Inorg. Biochem
Ali, Khan, Chatzicharalampous, Bai, Abu-Soud, None, J. Inorg. Biochem
Andersen, Gogenur, Rosenberg, Reiter, None, Clin. Drug Investig
Anderson, Reiter, None, Rev. Med. Virol
Arroyo, Garcia-Martinez, Salvatella, None, J. Hepatol
Banerjee, Maitra, Diamond, Abu-Soud, None, J. Pineal Res
Banerjee, Ragsdale, None, Annu. Rev. Biochem
Beckman, Chen, Ischiropoulos, Crow, None, Methods Enzymol
Bjornsdottir, Welin, Michaelsson, Osla, Berg et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Bonini, Siraki, Atanassov, Mason, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Bonnefont-Rousselot, Collin, None, Toxicology
Burner, Furtmuller, Kettle, Koppenol, Obinger, None, J. Biol. Chem
Cardinali, Brown, Pandi-Perumal, None, Diseases
Carrillo-Vico, Guerrero, Lardone, Reiter, None, Endocrine
Collin, None, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Davies, Hawkins, Pattison, Rees, None, Antioxid. Redox Signal
De Pinho, Da Silva, De Castro Cortes, Da Silva Vasconcelos, Sousa et al., None, Exp. Parasitol
Dondorp, Hayat, Aryal, Beane, Schultz, None, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg
Fang, Jiang, Su, Shu, Liu et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Floris, Wever, None, Eur. J. Biochem
Forstermann, Sessa, None, Eur. Heart J
Franchina, Dostert, Brenner, None, Trends Immunol
Furtmuller, Burner, Jantschko, Regelsberger, Obinger, None, Redox Rep
Galano, Tan, Reiter, None, J. Pineal Res
Galijasevic, Abdulhamid, Abu-Soud, None, Biochemistry
Galijasevic, Abdulhamid, Abu-Soud, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Gebicka, Banasiak, None, Toxicol. in Vitro
Gomez, Raba, Cerutti, Silva, None, J. Pineal Res
Goud, Bai, Abu-Soud, None, Int. J. Biol. Sci
Grisham, Jefferson, Thomas, None, J. Biol. Chem
Gulcin, Buyukokuroglu, Kufrevioglu, None, J. Pineal Res
Hallingback, Gabdoulline, Wade, None, Biochemistry
Halliwell, None, Br. J. Exp. Pathol
Hardeland, None, J. Pineal Res
Hawkins, Brown, Davies, None, Arch. Biochem. Biophys
Ikeda, Asai, Moriya, Sagara, Inoue et al., None, Brain Res
Jacob, None, Clin. Immunol
Jeelani, Maitra, Chatzicharalampous, Najeemuddin, Morris et al., None, J. Pineal Res
Johnson, Fatemi, Winlow, None, Front. Cardiovasc. Med
Jomova, Valko, None, Toxicology
Jovic, Ali, Ibrahim, Jessop, Tarassoli et al., None, Nutrients
Kettle, Albrett, Chapman, Dickerhof, Forbes et al., None, Biochim. Biophys. Acta
Khomich, Kochetkov, Bartosch, Ivanov, None, Viruses
Klinger, Abman, Gladwin, None, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med
Kohgo, Ikuta, Ohtake, Torimoto, Kato, None, Int. J. Hematol
Koyuncu, Budayeva, Miteva, Ricci, Silhavy et al., None, mBio
Li, Raman, Glaser, Blasko, Young et al., None, J. Biol. Chem
Liu, Zhou, Yang, None, Cell. Mol. Immunol
Lu, Galijasevic, Abdulhamid, Abu-Soud, None, Br. J. Pharmacol
Maitra, Abdulhamid, Diamond, Saed, Abu-Soud, None, J. Pineal Res
Maitra, Ali, Abdulridha, Shaeib, Khan et al., None, PLoS One
Maitra, Byun, Andreana, Abdulhamid, Diamond et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Maitra, Byun, Andreana, Abdulhamid, Saed et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Maitra, Shaeib, Abdulhamid, Abdulridha, Saed et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Miller, Pandi-Perumal, Esquifino, Cardinali, Maestroni, None, Int. J. Exp. Pathol
Minigh, XPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference
Molteni, Principi, Esposito, None, Free Radic. Res
Nybo, Davies, Rogowska-Wrzesinska, None, Redox Biol
O'leary, Samman, None, Nutrients
Ogino, Than, Hosako, Ozaki, Omori et al., None, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol
Ong, Halliwell, None, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci
Parker, Winterbourn, None, Front. Immunol
Pattison, Davies, None, Chem. Res. Toxicol
Pedrosa, Weinlich, Mognol, Robbs, Viola et al., None, J. Immunol
Pennathur, Maitra, Byun, Sliskovic, Abdulhamid et al., None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Pieretti, Rubilar, Weller, Tortella, Seabra, None, Virus Res
Podrez, Abu-Soud, Hazen, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Pullar, Vissers, Winterbourn, None, IUBMB Life
Qin, Li, Zhu, Gao, Fan et al., None, Aging
Ramlall, Zucker, Tatonetti, None, medRxiv
Reiter, Abreu-Gonzalez, Marik, Dominguez-Rodriguez, None, Front. Med
Reiter, Korkmaz, Ma, Rosales-Corral, Tan, None, Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res
Reiter, Mayo, Tan, Sainz, Alatorre-Jimenez et al., None, J. Pineal Res
Rudra, Pal, Maiti, Reiter, Swarnakar, None, J. Pineal Res
Schonrich, Raftery, Samstag, None, Adv. Biol. Regul
Sethuram, Bai, Abu-Soud, Potential role of zinc in the COVID-19 disease process and its probable impact on reproduction, Reprod. Sci, doi:10.1007/s43032-020-00400-6
Seyoum, Enawgaw, Melku, None, Thromb. J
Shaeib, Banerjee, Maitra, Diamond, Abu-Soud, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Shaeib, Khan, Ali, Najafi, Maitra et al., None, PLoS One
Shahbaz, Xu, Osman, Sligl, Shields et al., None, Stem Cell Reports
Shakoor, Feehan, Mikkelsen, Al Dhaheri, Ali et al., None, Maturitas
Shang, Xu, Wu, Jiang, Wu et al., None, Chin. Med. J
Siwik, Colucci, None, Heart Fail. Rev
Sliskovic, Abdulhamid, Sharma, Abu-Soud, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Solun, Shoenfeld, None, Med. Drug Discov
Souza, Maitra, Saed, Diamond, Moura et al., None, PLoS One
Stocker, Keaney, None, Physiol. Rev
Stover, None, Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care
Summers, Morgan, Davies, Hawkins, None, Chem. Res. Toxicol
Sun, Lee, Kao, Chiang, Sung et al., None, J. Pineal Res
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cherng, Teh et al., None, Nutrition
Tay, Poh, Renia, Macary, Ng, None, Nat. Rev. Immunol
Trinder, Fox, Vautier, Olynyk, None, Gut
Ueland, Holter, Holten, Muller, Lind et al., None, J. Inf. Secur
Ulfig, Bader, Varatnitskaya, Lupilov, Winklhofer et al., None, Redox Biol
Ulfig, Leichert, None, Cell. Mol. Life Sci
Vissers, Stern, Kuypers, Van Den Berg, Winterbourn, None, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Wade, Ford, Crawford, Mcconnachie, Nir et al., None, BMC Med
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., None, Nature
Ximenes, Silva, Rodrigues, Catalani, Maghzal et al., None, J. Biol. Chem
Zavodnik, Lapshina, Zavodnik, Soszynski, Bartosz et al., None, Bioelectrochemistry
Zhang, He, Chen, Su, Yan et al., None, Aging
Zhang, Tecson, Mccullough, None, Rev. Cardiovasc. Med
Zhang, Wang, Ni, Di, Ma et al., None, Life Sci
Zhou, Hou, Shen, Mehra, Kallianpur et al., None, PLoS Biol
Zou, Shi, Cohen, None, J. Clin. Invest
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546",
"ISSN": [
"0162-0134"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546",
"alternative-id": [
"S0162013421001938"
],
"article-number": "111546",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camp",
"given": "Olivia G.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bai",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonullu",
"given": "Damla C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nayak",
"given": "Neha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abu-Soud",
"given": "Husam M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-17T06:23:06Z",
"timestamp": 1626502986000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-28T15:46:29Z",
"timestamp": 1630165589000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-18T22:00:13Z",
"timestamp": 1639864813644
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0162-0134"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0162013421001938?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0162013421001938?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111546",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.51811",
"author": "Goud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0005",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0283",
"author": "Dondorp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1191",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0010",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Parker",
"first-page": "424",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0015",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.10.398",
"author": "Bjornsdottir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1024",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0020",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00229-X",
"author": "Podrez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1717",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0025",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2007.1927",
"author": "Davies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"journal-title": "Antioxid. Redox Signal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0030",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15216540051080958",
"author": "Pullar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "IUBMB Life",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0035",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0110595",
"author": "Maitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0040",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.07.004",
"author": "Kettle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0045",
"volume": "1840",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-020-03591-y",
"author": "Ulfig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0050",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.11.019",
"author": "Bonini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "530",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0055",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.011",
"author": "Maitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "374",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0060",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.03.040",
"author": "Maitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "364",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0065",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.10.496",
"author": "Abu-Soud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0070",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"author": "Souza",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0075",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI0214442",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "817",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0080",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0076-6879(94)33026-3",
"author": "Beckman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "Methods Enzymol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0085",
"volume": "233",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"author": "Halliwell",
"first-page": "737",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Exp. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0090",
"volume": "70",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"author": "Zhou",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0095",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00226",
"author": "Reiter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0100",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117583",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0105",
"volume": "250",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Ramlall",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0110",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi702016q",
"author": "Galijasevic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2668",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0115",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/bjp.2008.173",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1308",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0120",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diseases8040044",
"author": "Cardinali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0125",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tox.2010.04.008",
"author": "Bonnefont-Rousselot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Toxicology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0130",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00916.x",
"author": "Galano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0135",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12360",
"author": "Reiter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "253",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0140",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1741-7015-8-51",
"author": "Wade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "BMC Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0145",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-015-0368-5",
"author": "Andersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "169",
"journal-title": "Clin. Drug Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0150",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential role of zinc in the COVID-19 disease process and its probable impact on reproduction",
"author": "Sethuram",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Reprod. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0155",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.12.007",
"author": "Shaeib",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0160",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20102407",
"author": "Collin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0165",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.275.48.37524",
"author": "Abu-Soud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37524",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0170",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M000181200",
"author": "Burner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20597",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0175",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/tx8001719",
"author": "Summers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1832",
"journal-title": "Chem. Res. Toxicol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0180",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00047.2003",
"author": "Stocker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1381",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0185",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.04.009",
"author": "Maitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0190",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0195",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v10080392",
"author": "Khomich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0200",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cmi.2015.74",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0205",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17097.x",
"author": "Floris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0210",
"volume": "207",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/tx0155451",
"author": "Pattison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1453",
"journal-title": "Chem. Res. Toxicol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0215",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1179/135100000101535717",
"author": "Furtmuller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Redox Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0220",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2019.101236",
"author": "Nybo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101236",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0225",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.04.001",
"author": "Shahbaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1165",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0230",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm.2020.03.126",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "Rev. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0235",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/abbi.2001.2581",
"author": "Hawkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0240",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0891-5849(94)90185-6",
"author": "Vissers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "703",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0245",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1567-5394(01)00126-8",
"author": "Zavodnik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "Bioelectrochemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0250",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(17)39793-4",
"author": "Grisham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6757",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0255",
"volume": "259",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.00988.x",
"author": "Maitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0260",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0120737",
"author": "Shaeib",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0265",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12463",
"author": "Jeelani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0270",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.06.018",
"author": "Abu-Soud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "J. Inorg. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0275",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.101981",
"author": "Ulfig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101981",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0280",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.00153",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Front. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0285",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.012",
"author": "Arroyo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "396",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0290",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tiv.2012.04.010",
"author": "Gebicka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "Toxicol. in Vitro",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0295",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304",
"author": "Forstermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "829",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0300",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201304-0686PP",
"author": "Klinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0305",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.008",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0310",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198202",
"author": "Pieretti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198202",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0315",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110706",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110706",
"journal-title": "J. Inorg. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0320",
"volume": "197",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1196/annals.1306.005",
"author": "Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0325",
"volume": "1012",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.51.2.290",
"author": "Trinder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0330",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12185-008-0120-5",
"author": "Kohgo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Hematol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0335",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092550",
"author": "Jovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0340",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007",
"author": "Shakoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0345",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Tan",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0350",
"volume": "79–80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu2030299",
"author": "O'Leary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "299",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0355",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0360",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Minigh",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0365",
"series-title": "XPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161828",
"author": "Banerjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "209",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0370",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.003",
"author": "Pennathur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0375",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Ueland",
"first-page": "e41",
"journal-title": "J. Inf. Secur.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0380",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/B:HREV.0000011393.40674.13",
"author": "Siwik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Heart Fail. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0385",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exppara.2014.09.003",
"author": "de Pinho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "Exp. Parasitol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0390",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.102537",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11391",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0395",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.102472",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10499",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0400",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.274.30.21276",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21276",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0405",
"volume": "274",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001",
"author": "Jomova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Toxicology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0410",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100741",
"author": "Schonrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Adv. Biol. Regul.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0415",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.01.003",
"author": "Galijasevic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1570",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0420",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M506384200",
"author": "Ximenes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38160",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0425",
"volume": "280",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi051510e",
"author": "Hallingback",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2940",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0430",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12959-018-0170-8",
"author": "Seyoum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Thromb. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0435",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/10715762.2014.945443",
"author": "Molteni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1163",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0440",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2018.01.005",
"author": "Franchina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "489",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0445",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108591",
"author": "Jacob",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108591",
"journal-title": "Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0450",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.12.002",
"author": "Reiter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0455",
"volume": "751",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00949.x",
"author": "Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "349",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0460",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1385/ENDO:27:2:189",
"author": "Carrillo-Vico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0465",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1600-079X.2003.00042.x",
"author": "Gulcin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0470",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.00977.x",
"author": "Banerjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0475",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_47",
"author": "Ogino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0480",
"volume": "643",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12034",
"author": "Rudra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "398",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0485",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100052",
"author": "Solun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0490",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12199",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0495",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0b013e328333d157",
"author": "Stover",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0500",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00262-5",
"author": "Ikeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "98",
"journal-title": "Brain Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0505",
"volume": "795",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12525",
"author": "Hardeland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Pineal Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0510",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2109",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0515",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02249-14",
"author": "Koyuncu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0520",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0902961",
"author": "Pedrosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3487",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0525",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Shang",
"first-page": "1388",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0530",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0959-9673.2006.00474.x",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Exp. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0535",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi010478v",
"author": "Abu-Soud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10747",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0540",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.007",
"author": "Sliskovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1005",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546_bb0545",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2009"
}
],
"reference-count": 109,
"references-count": 109,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Inorganic Chemistry",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "223"
}