Clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and active tuberculosis co-infection in Beijing China: A retrospective single-center descriptive study
et al., Infectious Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169, Feb 2025
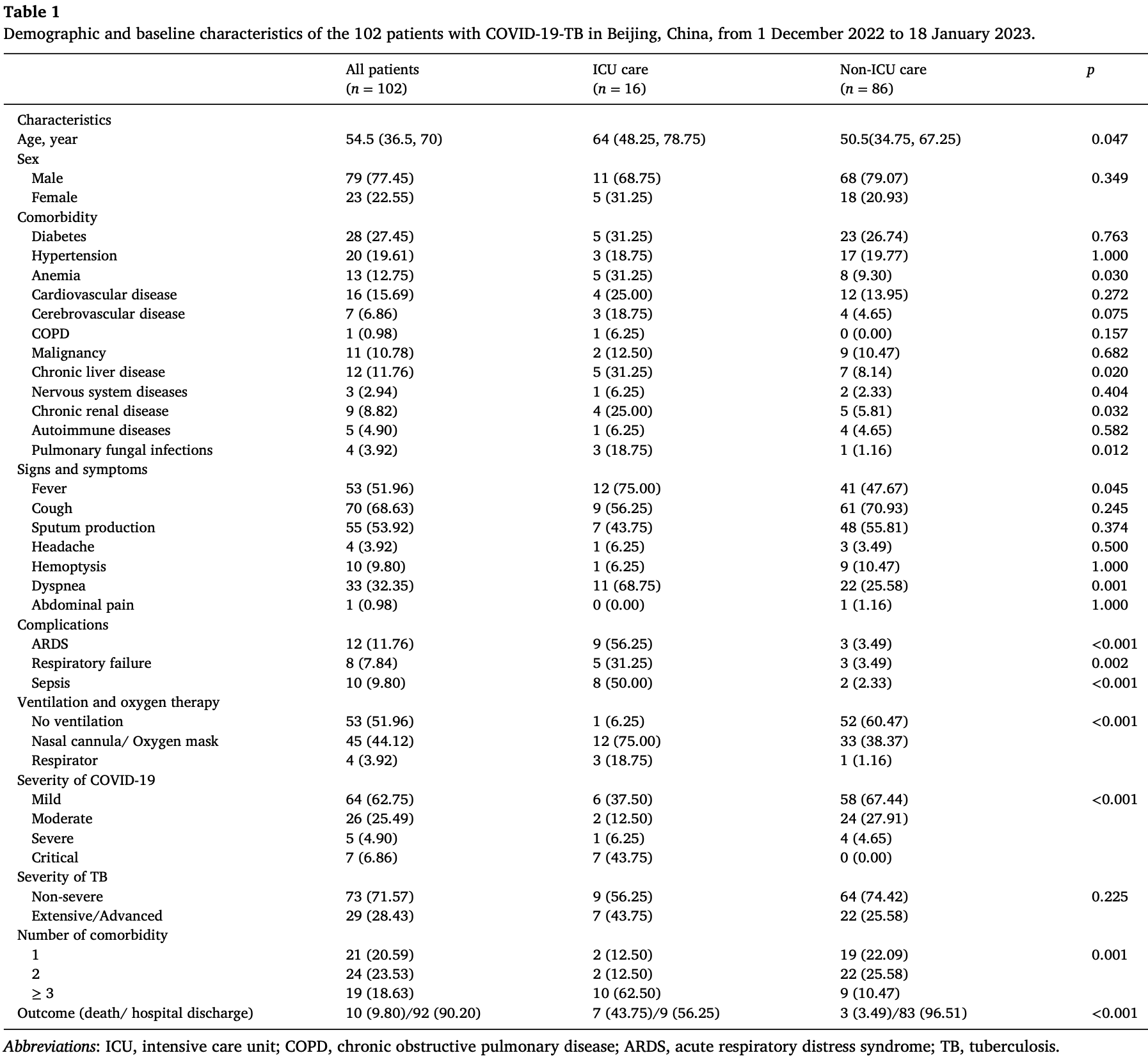
Retrospective 102 COVID-19 patients with active tuberculosis co-infection showing a mortality rate of 9.8%, compared with 0.03% for patients with COVID-19 alone. Paxlovid was used for 19 patients due limited availability but resulted in higher mortality in unadjusted results.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details; substantial unadjusted confounding by indication possible.
|
risk of death, 336.8% higher, RR 4.37, p = 0.02, treatment 5 of 19 (26.3%), control 5 of 83 (6.0%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Yang et al., 18 Feb 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 54.5, 21 authors, study period 1 December, 2022 - 18 January, 2023.
Contact: yl-14t@163.com, laurence.luu@uts.edu.au, panjunhua999@sina.com, wildwolf0101@163.com, wangguirong1230@ccmu.edu.cn.
Clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and active tuberculosis co-infection in Beijing China: A retrospective single-center descriptive study
Infectious Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and tuberculosis (TB) co-infection (COVID-19-TB) has the potential to exacerbate lung damage; however, information about the clinical features of COVID-19-TB is limited. This study aims to clarify the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with COVID-19-TB. Methods: In this single-center retrospective study, the clinical features and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 with active TB who were admitted to Beijing Chest Hospital, Beijing, China, from 1 December 2022 to 18 January 2023 were collected. The severity of COVID-19 and TB was graded according to guidelines from the World Health Organization. The relationships of demographic and clinical variables with intensive care unit (ICU) admission were evaluated using univariable and multivariable logistic regression models. Results: Overall, 102 patients with COVID-19-TB were enrolled. The mean age was 54.5 years (range 36.5-70 years). The most common clinical manifestations were cough (68.63%), sputum production (53.92%), fever (51.96%), and ground-glass opacities (35.29%). Complications included acute respiratory distress syndrome (11.76%), sepsis (9.8%), and respiratory failure (7.84%). Patients with COVID-19-TB had high concentrations of various proinflammatory cytokines, including interferon-𝛾, interleukin-1 𝛽, interferon-𝛾-inducible protein 10 kD, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Sixteen of the 102 patients with COVID-19-TB (15.69%) were admitted to the ICU, and 10 (9.80%) died during hospitalization. The significant risk factors for ICU admission were respiratory failure, pulmonary fungal infection, and ventilation and oxygen therapy. Conclusions: The mortality rate of COVID-19-TB was 9.80%. Several demographic and clinical characteristics were associated with adverse outcomes, indicating the importance of early recognition and treatment.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.imj. 2025.100169 .
References
Adzic-Vukicevic, Stosic, Antonijevic, Tuberculosis and COVID-19 co-infection in Serbia: pandemic challenge in a low-burden country, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.971008
Aggarwal, Agarwal, Dhooria, Active pulmonary tuberculosis and coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0259006
Alkhatip, Kamel, Hamza, The diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Expert Rev Mol Diagn, doi:10.1080/14737159.2021.1915773
Anonymous, Who, Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis: Module 4: Treatment -Tuberculosis Care and Support. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee
Daneshvar, Hajikhani, Sameni, COVID-19 and tuberculosis coinfection: an overview of case reports/case series and meta-analysis of prevalence studies, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13637
Deng, Han, Liu, The risks of death and hospitalizations associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron declined after lifting testing and quarantining measures, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.033
Deng, Liu, Lv, Sex disparities of the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality among patients living with tuberculosis in the United States, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1413604
Dheda, Perumal, Moultrie, The intersecting pandemics of tuberculosis and COVID-19: population-level and patient-level impact, clinical presentation, and corrective interventions, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00092-3
Gao, Liu, Chen, Association between tuberculosis and COVID-19 severity and mortality: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26311
Group, Tuberculosis and COVID-19 co-infection: description of the global cohort, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02538-2021
Gräb, Suárez, Van Gumpel, Corticosteroids inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced necrotic host cell death by abrogating mitochondrial membrane permeability transition, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08405-9
Guo, Li, Ma, Single-cell analysis of two severe COVID-19 patients reveals a monocyte-associated and tocilizumab-responding cytokine storm, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17834-w
Gupta, Harrison, Ho, Development and validation of the ISARIC 4C deterioration model for adults hospitalised with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30559-2
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jennings, Lembani, Hesseling, A decline in tuberculosis diagnosis, treatment initiation and success during the COVID-19 pandemic, using routine health data in Cape Town, South Africa, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0310383
Khayat, Fan, Vali, COVID-19 promoting the development of active tuberculosis in a patient with latent tuberculosis infection: a case report, Respir Med Case Rep, doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101344
Kishore, Khine, Thottacherry, COVID-19 and tuberculosis coinfection: outcomes depend on severity of COVID-19 and comorbid conditions, Infez Med, doi:10.53854/liim-3101-18
Koupaei, Naimi, Moafi, Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, treatment, and mortality rate of TB/COVID-19 coinfectetd patients: a systematic review, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.740593
Lee, Methods for testing statistical differences between groups in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee, Life Cycle, doi:10.54724/lc.2022.e1
Leung, Lau, Wong, Estimating the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BF.7 in Beijing after adjustment of the zero-COVID policy in November-December 2022, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02212-y
Motta, Centis, Ambrosio, Tuberculosis, COVID-19 and migrants: preliminary analysis of deaths occurring in 69 patients from two cohorts, Pulmonology, doi:10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.05.002
Mwananyanda, Gill, Macleod, Covid-19 deaths in Africa: prospective systematic postmortem surveillance study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.\penalty-\@Mn334
Najafi-Fard, Aiello, Navarra, Characterization of the immune impairment of patients with tuberculosis and COVID-19 coinfection, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.03.021
Nasir, Muhammed, Tamiru, Assessing the impact of COVID-19 on tuberculosis detection and treatment in healthcare facilities across Addis Ababa , Ethiopia: a comprehensive mixed-method, multi-center study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0311408
Nasiri, Haddadi, Tahvildari, COVID-19 clinical characteristics, and sexspecific risk of mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00459
Nuwagira, Mpagama, Katusiime, Coinfection of COVID-19 and tuberculosis in Uganda, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.22-0738
Nyberg, Ferguson, Nash, Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: a cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7
Oh, Song, Impact of coronavirus disease-2019 on chronic respiratory disease in South Korea: an NHIS COVID-19 database cohort study, BMC Pulm Med, doi:10.1186/s12890-020-01387-1
Pan, Wang, Feng, Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Beijing during 2022: an epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00129-0
Pang, Dong, Tan, Rapid diagnosis of MDR and XDR tuberculosis with the MeltPro TB assay in China, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/\penalty-\@Msrep25330
Parolina, Pshenichnaya, Vasilyeva, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in patients with tuberculosis and factors associated with the disease severity, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.04.041
Patton, Orihuela, Harrod, COVID-19 bacteremic co-infection is a major risk factor for mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-023-04312-0
Petrone, Petruccioli, Vanini, Coinfection of tuberculosis and COVID-19 limits the ability to in vitro respond to SARS-CoV-2, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.090
Pinheiro, Pessoa, Lima, Tuberculosis and coronavirus disease 2019 coinfection, Rev Soc Bras Med Trop, doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0671-2020
Reisinger, Hermann, Vagena, Tuberculosis sepsis after tocilizumab treatment, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.030
Sarkar, Khanna, Singh, Impact of COVID-19 in patients with concurrent coinfections: a systematic review and meta-analyses, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26740
Selvaraj, Damadarosamy, Kiruthiga, Critical clinical evaluation of COVID-19 patients with tuberculosis in the Indian Sub-Continent, Curr Drug Saf, doi:10.2174/1574886317666220518092819
Sereda, Korotych, Klimuk, Tuberculosis Co-infection is common in patients requiring hospitalization for COVID-19 in Belarus: mixed-methods study, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19074370
Siranart, Sowalertrat, Sukonpatip, First case series and literature review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) associated pulmonary tuberculosis in Southeast Asia: challenges and opportunities, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.11.029
Stochino, Villa, Zucchi, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 and active tuberculosis co-infection in an Italian reference hospital, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01708-2020
Tadolini, Codecasa, García-García, Active tuberculosis, sequelae and COVID-19 co-infection: first cohort of 49 cases, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01398-2020
Wang, Wang, Luu, Single-cell transcriptomic atlas reveals distinct immunological responses between COVID-19 vaccine and natural SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28012
Wang, Yu, Yu, Clinical features and outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Shanghai, China, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.001
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
Yao, Chen, Wang, Three patients with COVID-19 and pulmonary tuberculosis, Wuhan, China, January-February 2020, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2611.201536
Zhou, Fu, Zheng, Pathogenic T-cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storms in severe COVID-19 patients, Natl Sci Rev, doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa041
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169",
"ISSN": [
"2772-431X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169",
"alternative-id": [
"S2772431X25000085"
],
"article-number": "100169",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and active tuberculosis co-infection in Beijing China: A retrospective single-center descriptive study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Infectious Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Xinting",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Chaohong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xue",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Maike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Long",
"given": "Sibo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Xinlei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Tiantian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ju",
"given": "Wenfu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Mengqiu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luu",
"given": "Laurence Don Wai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Junhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Guirong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Infectious Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-19T00:29:47Z",
"timestamp": 1739924987000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-13T08:17:13Z",
"timestamp": 1741853833000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-14T04:12:53Z",
"timestamp": 1741925573892,
"version": "3.38.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740787200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740787200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1739491200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772431X25000085?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772431X25000085?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100169",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00129-0",
"article-title": "Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Beijing during 2022: an epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "664",
"issue": "10377",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0001",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7",
"article-title": "Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: a cohort study",
"author": "Nyberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1303",
"issue": "10332",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0002",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-023-02212-y",
"article-title": "Estimating the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BF.7 in Beijing after adjustment of the zero-COVID policy in November–December 2022",
"author": "Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "579",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0003",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-023-04312-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19 bacteremic co-infection is a major risk factor for mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation",
"author": "Patton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "34",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0004",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00459",
"article-title": "COVID-19 clinical characteristics, and sex-specific risk of mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nasiri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0005",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 promoting the development of active tuberculosis in a patient with latent tuberculosis infection: a case report",
"author": "Khayat",
"journal-title": "Respir Med Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0006",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2611.201536",
"article-title": "Three patients with COVID-19 and pulmonary tuberculosis, Wuhan, China, January-February 2020",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2755",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0007",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/0037-8682-0671-2020",
"article-title": "Tuberculosis and coronavirus disease 2019 coinfection",
"author": "Pinheiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev Soc Bras Med Trop",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0008",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.04.041",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in patients with tuberculosis and factors associated with the disease severity",
"author": "Parolina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S82",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0009",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1574886317666220518092819",
"article-title": "Critical clinical evaluation of COVID-19 patients with tuberculosis in the Indian Sub-Continent",
"author": "Selvaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Drug Saf",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0010",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01398-2020",
"article-title": "Active tuberculosis, sequelae and COVID-19 co-infection: first cohort of 49 cases",
"author": "Tadolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0011",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Tuberculosis and COVID-19 co-infection: description of the global cohort",
"author": "Group",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0012",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.971008",
"article-title": "Tuberculosis and COVID-19 co-infection in Serbia: pandemic challenge in a low-burden country",
"author": "Adzic-Vukicevic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0013",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0014",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Living guidance for clinical management of COVID-19. (https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/349321/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2021.2-eng.pdf, accessed August 10, 2022)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep25330",
"article-title": "Rapid diagnosis of MDR and XDR tuberculosis with the MeltPro TB assay in China",
"author": "Pang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25330",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0015",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0016",
"series-title": "Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis: Module 4: Treatment – Tuberculosis Care and Support. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.54724/lc.2022.e1",
"article-title": "Methods for testing statistical differences between groups in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1",
"journal-title": "Life Cycle",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0017",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13637",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and tuberculosis coinfection: an overview of case reports/case series and meta-analysis of prevalence studies",
"author": "Daneshvar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13637",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0018",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.033",
"article-title": "The risks of death and hospitalizations associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron declined after lifting testing and quarantining measures",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e123",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0019",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00092-3",
"article-title": "The intersecting pandemics of tuberculosis and COVID-19: population-level and patient-level impact, clinical presentation, and corrective interventions",
"author": "Dheda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0020",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0311408",
"article-title": "Assessing the impact of COVID-19 on tuberculosis detection and treatment in healthcare facilities across Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a comprehensive mixed-method, multi-center study",
"author": "Nasir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0021",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0310383",
"article-title": "A decline in tuberculosis diagnosis, treatment initiation and success during the COVID-19 pandemic, using routine health data in Cape Town, South Africa",
"author": "Jennings",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0022",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Long-term outcomes of the global tuberculosis and COVID-19 co-infection cohort",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0023",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19074370",
"article-title": "Tuberculosis Co-infection is common in patients requiring hospitalization for COVID-19 in Belarus: mixed-methods study",
"author": "Sereda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4370",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0024",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2022.11.029",
"article-title": "First case series and literature review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) associated pulmonary tuberculosis in Southeast Asia: challenges and opportunities",
"author": "Siranart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0025",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.001",
"article-title": "Clinical features and outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0026",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.740593",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, treatment, and mortality rate of TB/COVID-19 coinfectetd patients: a systematic review",
"author": "Koupaei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0027",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n334",
"article-title": "Covid-19 deaths in Africa: prospective systematic postmortem surveillance study",
"author": "Mwananyanda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n334",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0028",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0259006",
"article-title": "Active pulmonary tuberculosis and coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0029",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26740",
"article-title": "Impact of COVID-19 in patients with concurrent co-infections: a systematic review and meta-analyses",
"author": "Sarkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2385",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0030",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "Tuberculosis, COVID-19 and migrants: preliminary analysis of deaths occurring in 69 patients from two cohorts",
"author": "Motta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pulmonology",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0031",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01708-2020",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 and active tuberculosis co-infection in an Italian reference hospital",
"author": "Stochino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0032",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26311",
"article-title": "Association between tuberculosis and COVID-19 severity and mortality: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0033",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12890-020-01387-1",
"article-title": "Impact of coronavirus disease-2019 on chronic respiratory disease in South Korea: an NHIS COVID-19 database cohort study",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0034",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.03.021",
"article-title": "Characterization of the immune impairment of patients with tuberculosis and COVID-19 coinfection",
"author": "Najafi-Fard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S34",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0035",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2024.1413604",
"article-title": "Sex disparities of the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality among patients living with tuberculosis in the United States",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0036",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.090",
"article-title": "Coinfection of tuberculosis and COVID-19 limits the ability to in vitro respond to SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Petrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S82",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0037",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nsr/nwaa041",
"article-title": "Pathogenic T-cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storms in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "998",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Natl Sci Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0038",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0039",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-08405-9",
"article-title": "Corticosteroids inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced necrotic host cell death by abrogating mitochondrial membrane permeability transition",
"author": "Gräb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "688",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0040",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17834-w",
"article-title": "Single-cell analysis of two severe COVID-19 patients reveals a monocyte-associated and tocilizumab-responding cytokine storm",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3924",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0041",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28012",
"article-title": "Single-cell transcriptomic atlas reveals distinct immunological responses between COVID-19 vaccine and natural SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5304",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0042",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0043",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.030",
"article-title": "Tuberculosis sepsis after tocilizumab treatment",
"author": "Reisinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1493",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0044",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14737159.2021.1915773",
"article-title": "The diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Alkhatip",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Mol Diagn",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0045",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30559-2",
"article-title": "Development and validation of the ISARIC 4C deterioration model for adults hospitalised with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "349",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0046",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and tuberculosis coinfection: outcomes depend on severity of COVID-19 and comorbid conditions",
"author": "Kishore",
"first-page": "127",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infez Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0047",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.22-0738",
"article-title": "Coinfection of COVID-19 and tuberculosis in Uganda",
"author": "Nuwagira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1240",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.imj.2025.100169_bib0048",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2772431X25000085"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and active tuberculosis co-infection in Beijing China: A retrospective single-center descriptive study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "4"
}