Viral kinetics in adults with Covid-19 treated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir: a population-based, observational cohort study
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2, Jan 2026
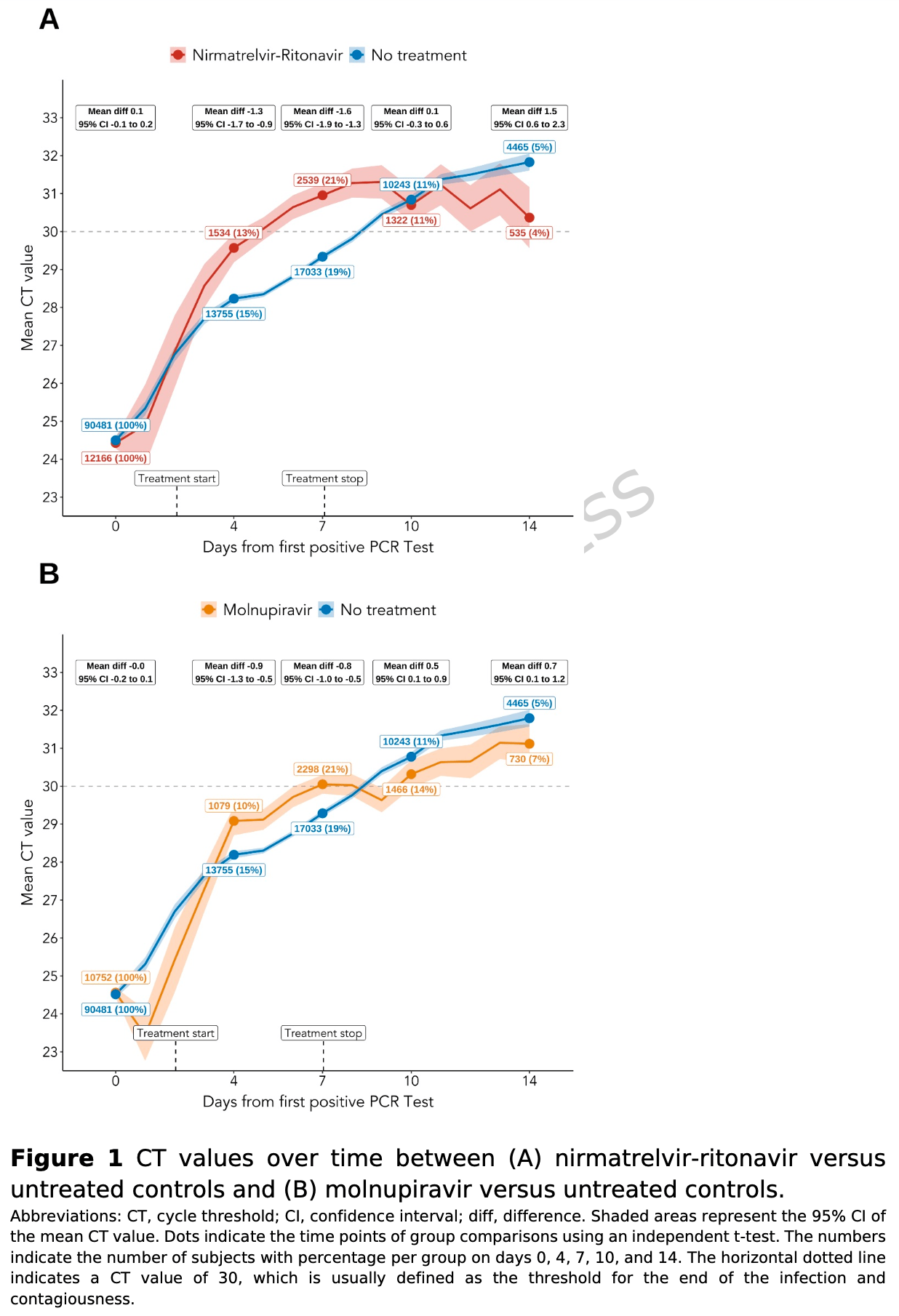
Observational cohort study of 113,399 COVID-19 outpatients in Vienna showing viral kinetics patterns with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir treatment. Both antivirals showed improved viral clearance at 7 days, but worse viral clearance at 14 days, suggesting viral rebound.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
relative Ct improvement, 21.7% worse, RR 1.22, p < 0.001, treatment mean 6.0 (±7.08) n=12,166, control mean 7.3 (±14.48) n=90,481, relative differences, day 14.
|
|
relative Ct improvement, 27.3% better, RR 0.73, p < 0.001, treatment mean 6.6 (±6.82) n=12,166, control mean 4.8 (±14.55) n=90,481, relative differences, day 7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Prager et al., 10 Jan 2026, retrospective, Austria, peer-reviewed, 17 authors.
Contact: markus.zeitlinger@meduniwien.ac.at.
Abstract: Virology Journal
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2
Article in Press
Viral kinetics in adults with Covid-19 treated
with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir: a
population-based, observational cohort study
Received: 11 November 2025
Accepted: 21 December 2025
Cite this article as: Prager M., Ensle D.,
Eser H. et al. Viral kinetics in adults with
Covid-19 treated with nirmatrelvirritonavir or molnupiravir: a populationbased, observational cohort study.
Virol J (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/
s12985-025-03057-2
A
Marlene Prager, Dominik Ensle, Hubert Eser, Florentin Glötzl, Benjamin Riedl,
Marton Szell, Arschang Valipour, Alexander Zoufaly, Christoph Wenisch, Doris Haider,
Heinz Burgmann, Florian Thalhammer, Florian Götzinger, Bernd Jilma, Ursula
Karnthaler, Markus Zeitlinger & Anselm Jorda
E
R
P
S
S
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its
findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please
note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers
apply.
IN
If this paper is publishing under a Transparent Peer Review model then Peer
Review reports will publish with the final article.
I
T
R
E
L
C
© The Author(s) 2025. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit
to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do
not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this
article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the
article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain
permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
ACCEPTED
ARTICLE IN
MANUSCRIPT
PRESS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
Viral kinetics in adults with Covid-19 treated with
nirmatrelvir-ritonavir
or
molnupiravir:
a
population-based, observational cohort study
Running Title: Viral kinetics after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir
Marlene Prager1, Dominik Ensle2, Hubert Eser3, Florentin Glötzl4, Benjamin Riedl5,
Marton Szell6, Arschang Valipour7, Alexander Zoufaly8, Christoph Wenisch8, Doris
Haider9, Heinz Burgmann10, Florian Thalhammer11, Florian Götzinger12, Bernd
Jilma1, Ursula Karnthaler2, Markus Zeitlinger1*, Anselm Jorda1
1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
²Municipal Department for Public Health Services of the City of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
3Municipal Department for Information Technology of the City of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
4Institute
for Ecological Economics, Department for Socioeconomics, Vienna University of Economics and Business,
Vienna, Austria
5Department of Research, Vienna Healthcare Group, Vienna, Austria
6Department of Internal Medicine 2, Emergency Department, Klinik Donaustadt, Vienna,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2",
"ISSN": [
"1743-422X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2",
"alternative-id": [
"3057"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 November 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "21 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 January 2026"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Ethical approval for this study was given from the Ethics Committee of the City of Vienna (ID: EK23-146-VK)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prager",
"given": "Marlene",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ensle",
"given": "Dominik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eser",
"given": "Hubert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glötzl",
"given": "Florentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riedl",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szell",
"given": "Marton",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valipour",
"given": "Arschang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zoufaly",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wenisch",
"given": "Christoph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haider",
"given": "Doris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgmann",
"given": "Heinz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thalhammer",
"given": "Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Götzinger",
"given": "Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jilma",
"given": "Bernd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karnthaler",
"given": "Ursula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeitlinger",
"given": "Markus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jorda",
"given": "Anselm",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Virology Journal",
"container-title-short": "Virol J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:53:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768006380000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:53:04Z",
"timestamp": 1768006384000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T06:04:13Z",
"timestamp": 1768025053413,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768003200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768003200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "3057_CR1",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. [Internet]. 2024 Feb. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7251a2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3057_CR2",
"unstructured": "Harrington PR, Cong J, Troy SB, Rawson JMO, Julian;, O’rear J et al. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Rebound After Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment in Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials-United States and International Sites, 2021–2022 [Internet]. Vol. 22. 2023. Available from: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2023/217188Orig1s000ltr.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac481",
"author": "N Ranganath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E537",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "3057_CR3",
"unstructured": "Ranganath N, O’Horo JC, Challener DW, Tulledge-Scheitel SM, Pike ML, O’Brien M, et al. Rebound phenomenon after Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in High-Risk persons. Clin Infect Dis. 2023;76(3):E537–9.",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.45086",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3057_CR4",
"unstructured": "Wong GLH, Yip TCF, Lai MSM, Wong VWS, Hui DSC, Lui GCY. Incidence of viral rebound after treatment with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and molnupiravir. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(12):e2245086."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2206449",
"author": "ME Charness",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1045",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "3057_CR5",
"unstructured": "Charness ME, Gupta K, Stack G, Strymish J, Adams E, Lindy DC, et al. Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 infection after Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir treatment. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(11):1045–7.",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1765",
"author": "Z Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E241765",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "3057_CR6",
"unstructured": "Yang Z, Xu Y, Zheng R, Ye L, Lv G, Cao Z, et al. COVID-19 rebound after VV116 vs Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir treatment: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):E241765.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08835-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3057_CR7",
"unstructured": "Schilling WHK, Jittamala P, Watson JA, Boyd S, et al; PLATCOV Collaborative Group. Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024;24(1):36–45."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-49458-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3057_CR8",
"unstructured": "Esmaeili S, Owens K, Wagoner J, Polyak SJ, White JM, Schiffer JT. A unifying model to explain frequent SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir treatment and limited prophylactic efficacy. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):5478."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01623-24",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3057_CR9",
"unstructured": "Phan T, Ribeiro RM, Edelstein GE, Boucau J, Uddin R, Marino C, et al. Modeling suggests SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment is driven by target cell preservation coupled with incomplete viral clearance. J Virol. 2025;99(3):e0162324."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2024.10.026",
"author": "A Jorda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "3057_CR10",
"unstructured": "Jorda A, Ensle D, Eser H, Glötzl F, Riedl B, Szell M, et al. Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir in non-hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a population-based, retrospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2025;31(3):451–8.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa619",
"author": "MR Tom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2252",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "3057_CR11",
"unstructured": "Tom MR, Mina MJ, Oxford University Press. To interpret the SARS-CoV-2 test, consider the cycle threshold value. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2252–4.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "3057_CR12",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1186/s12985-025-03057-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Viral kinetics in adults with Covid-19 treated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir: a population-based, observational cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}
prager