Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes
et al., iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907, Jan 2025
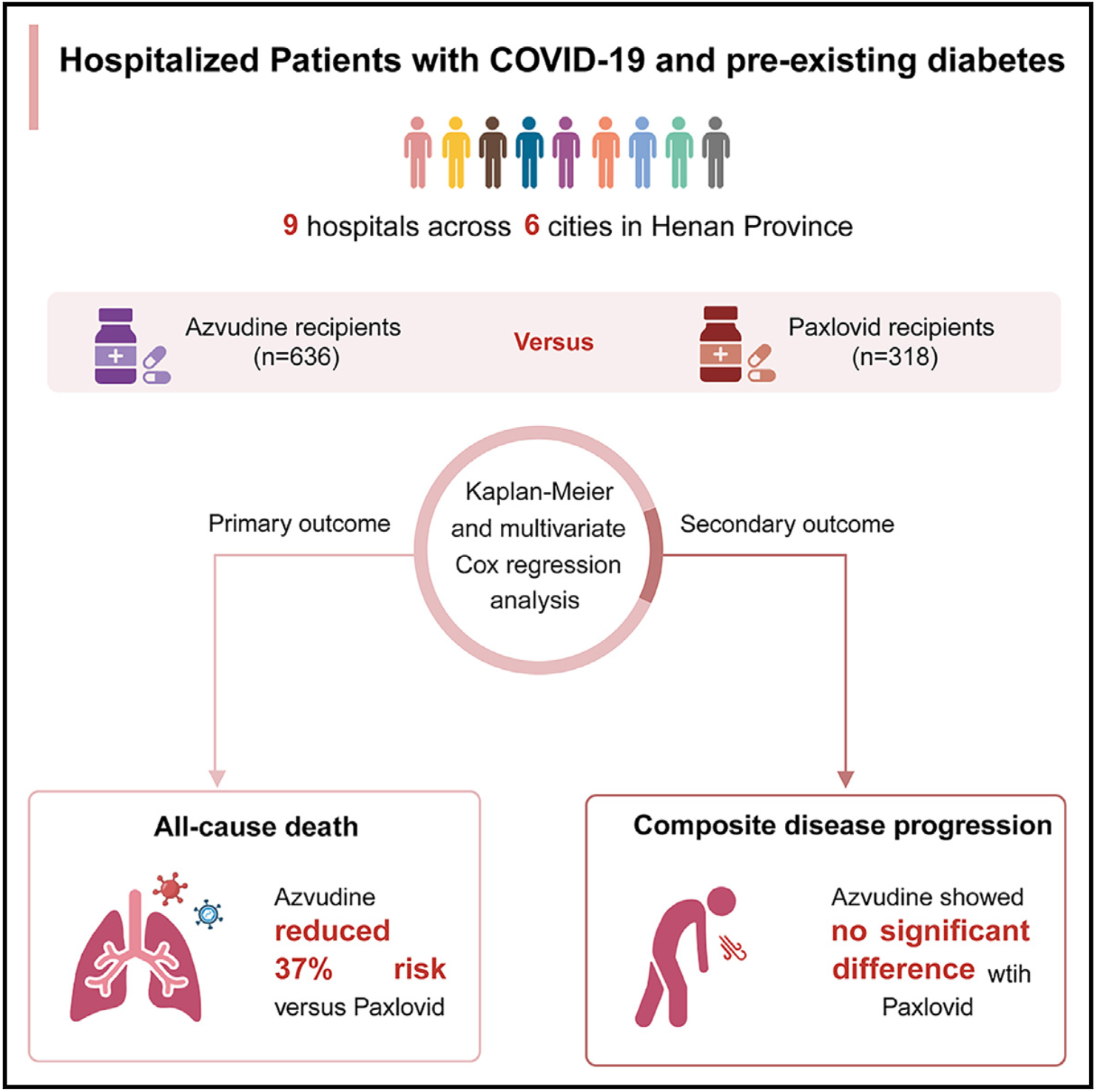
Retrospective 954 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes showing lower mortality with azvudine compared to paxlovid, but no significant difference for composite disease progression.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Study covers azvudine and paxlovid.
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Su et al., 27 Jan 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 19 authors, study period 5 December, 2022 - 31 January, 2023.
Contact: johnyuem@zzu.edu.cn (corresponding author), johnyuem@zzu.edu.cn (corresponding author), fccrenzg@zzu.edu.cn.
Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes
iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907
Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization: Z.R. and Z.Y.; resources: Z.R., Z.Y., J.X, Y.Y., H.L., S.Z., G.L., D.Z., and G.L.; data curation: G.S., M.Y., Y.Z., M.C., L.W., N.H., Z.S., G.Q., and Y.Z.; formal analysis: M.Y.; supervision: Z.R. and Z.Y.; funding acquisition: G.S., Z.R., and Z.Y.; writing-original draft: G.S., S.L., and D.Z.; writing-review and editing: G.S., S.L., and D.Z.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
STAR+METHODS Detailed methods are provided in the online version of this paper and include the following:
STAR+METHODS KEY RESOURCES TABLE EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND STUDY PARTICIPANT DETAILS
Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board from The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2023-KY-0865-001). The retrospective cohort study employing anonymized data did not require individual informed consent.
Study design and participants This is a multi-center, retrospective cohort study comparing the effectiveness and safety of azvudine with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 with pre-existing diabetes. We retrieved all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 from nine hospitals in Henan Province (e.g., the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Provincial Chest Hospital, Henan Infectious Disease Hospital, Luoyang Central Hospital, Nanyang Central Hospital, the Fifth People's Hospital of Anyang, Shangqiu..
References
Aggarwal, Molina, Beaty, Bennett, Carlson et al., Real-world use of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in outpatients with COVID-19 during the era of omicron variants including BA.4 and BA.5 in Colorado, USA: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00011-7
Andrews, Herman, Gandhi, Treatments for COVID-19, Annu. Rev. Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-052422-020316
Arbel, Wolff Sagy, Hoshen, Battat, Lavie et al., Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919
Dalva-Aydemir, Bajpai, Martinez, Adekola, Kandela et al., Targeting the metabolic plasticity of multiple myeloma with FDA-approved ritonavir and metformin, Clin. Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1088
De Souza, Cabral, Da Silva, Arruda, Cabral et al., Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916
Deng, Li, Sun, Jin, Zhou et al., Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Hardwick, Pius et al., Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1985
Gao, Luo, Ren, Duan, Han et al., Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Koelle, Martin, Antia, Lopman, Dean, The changing epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm4915
Kumar, Arora, Sharma, Anikhindi, Bansal et al., Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044
Li, Gao, You, Zhang, Pan et al., Association of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment on Upper Respiratory Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (SARS-Cov-2 RT-PCR) Negative Conversion Rates Among High-Risk Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac600
Lui, Chung, Lau, Lau, Au et al., Analysis of All-Cause Hospitalization and Death Among Nonhospitalized Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection Treated With Molnupiravir or Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir During the Omicron Wave in Hong Kong, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14393
Mazucanti, Egan, SARS-CoV-2 disease severity and diabetes: why the connection and what is to be done?, Immun. Ageing, doi:10.1186/s12979-020-00192-y
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the iScience 28, 111907, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Saha, Al-Rifai, Saha, Diabetes prevalence and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and metaregression, J. Diabetes Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00779-2
Su, Yang, Wang, Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08828-2
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981
Wei, Zeng, Wang, Gui, Zhang et al., Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott et al., Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal. Transduct. Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907",
"ISSN": [
"2589-0042"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589004225001671"
],
"article-number": "111907",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "iScience"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Guanyue",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Silin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Donghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yongjian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Yiqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qian",
"given": "Guowu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guotao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Na",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Guangming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Shixi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Mengzhao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yanyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Zhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xing",
"given": "Jiyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Zujiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0798-3444",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ren",
"given": "Zhigang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "iScience",
"container-title-short": "iScience",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-28T00:10:20Z",
"timestamp": 1738023020000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-22T00:40:29Z",
"timestamp": 1740184829000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-22T01:10:18Z",
"timestamp": 1740186618813,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1737590400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589004225001671?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589004225001671?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111907",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"article-title": "Prescott H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "782",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib1",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm4915",
"article-title": "The changing epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Koelle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1116",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib2",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12979-020-00192-y",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 disease severity and diabetes: why the connection and what is to be done?",
"author": "Mazucanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Immun. Ageing",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib3",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1985",
"article-title": "Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Docherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1985",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib4",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00779-2",
"article-title": "Diabetes prevalence and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"author": "Saha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "939",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Metab. Disord.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib5",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044",
"article-title": "Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "535",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-052422-020316",
"article-title": "Treatments for COVID-19",
"author": "Andrews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib7",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib9",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes during the Omicron Surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib10",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00011-7",
"article-title": "Real-world use of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in outpatients with COVID-19 during the era of omicron variants including BA.4 and BA.5 in Colorado, USA: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib11",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac600",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e148",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib12",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14393",
"article-title": "Analysis of All-Cause Hospitalization and Death Among Nonhospitalized Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection Treated With Molnupiravir or Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir During the Omicron Wave in Hong Kong",
"author": "Lui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib13",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment. Signal. Transduct",
"author": "Yu",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Target Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib14",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916",
"article-title": "Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients",
"author": "de Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib16",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib17",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib18",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08828-2",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib19",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Dian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e24",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib20",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib21",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib22",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294",
"article-title": "Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib23",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e158",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib24",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1088",
"article-title": "Targeting the metabolic plasticity of multiple myeloma with FDA-approved ritonavir and metformin",
"author": "Dalva-Aydemir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1161",
"journal-title": "Clin. Cancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907_bib25",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2589004225001671"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "28"
}
su6