In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction
et al., Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759, Aug 2024
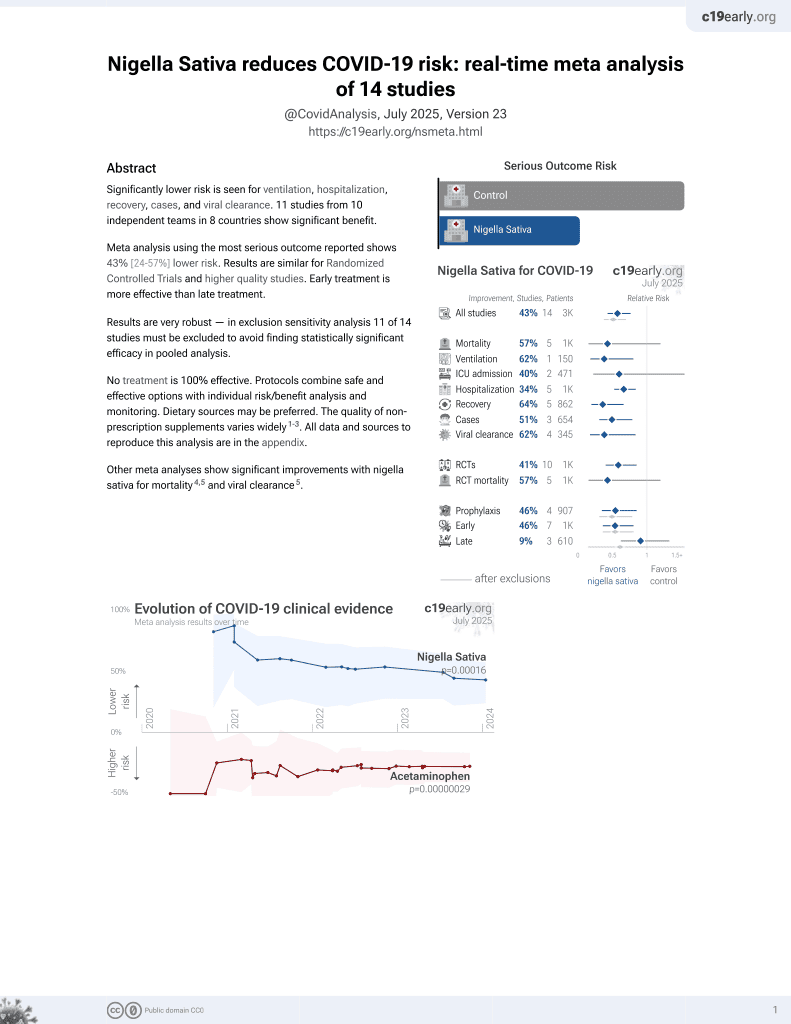
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
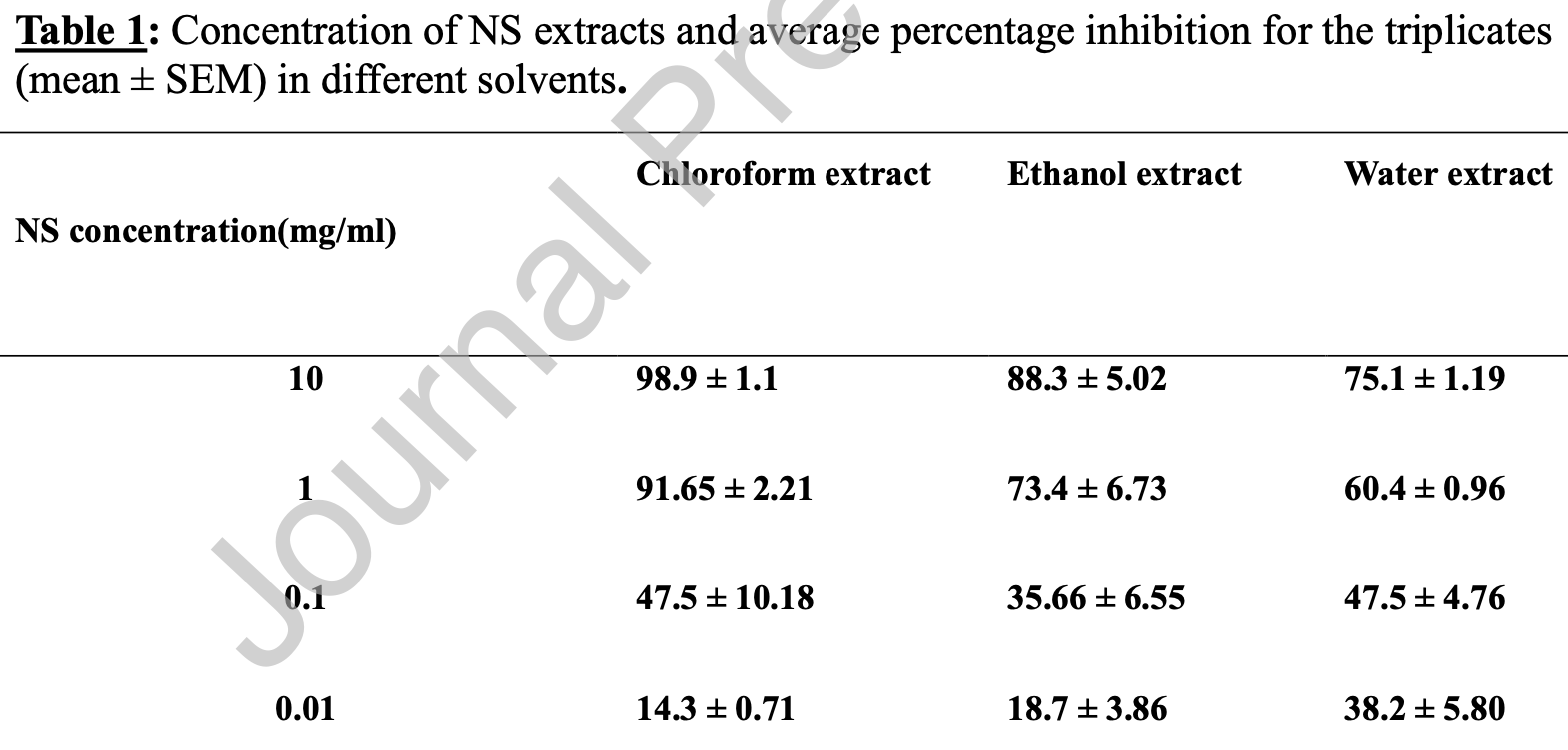
In vitro study showing nigella sativa extracts inhibit the interaction between the S1 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and ACE2 in a dose-dependent manner, with chloroform extract having the highest inhibition of 98.9% at 10 mg/ml. The higher effectiveness of the chloroform extract may be due to the presence of non-polar phytochemicals such as thymoquinone, thymohydroquinone, and nigellidine.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Ali et al., 31 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Contact: rajan.radhakrishnan@mbru.ac.ae (corresponding author).
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction.
Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759
for the authentication of NS seeds
Author contribution
Conceptualization
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
Ahmad, Abbasi, Shahid, Gul, Abbasi, Molecular docking, simulation and MM-PBSA studies of nigella sativa compounds: a computational quest to identify potential natural antiviral for COVID-19 treatment, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1775129
Ali, Vijayan, Dynamics of the ACE2-SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV spike protein interface reveal unique mechanisms, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3
Arokiaraj, Menesson, Rose and In-vitro Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike: ACE-2 Interaction, SSRN Electronic Journal, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3612898
Ashraf, Ashraf, Akmal, Ashraf, Kalsoom et al., Prophylactic potential of honey and Nigella sativa L. against hospital and community-based SARS-CoV-2 spread: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05510-3
Duru, Duru, Adegboyega, In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x
Gonfa, Temesgen, Erba, Mengesha, Sivasubramanian, Phytochemicals Analysis, In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Extracts, and Molecular Docking Studies of the Isolated Compounds from Melhania zavattarii Cufod Leaves, Journal of Tropical Medicine, doi:10.1155/2023/8820543
Imran, Khan, Abida, Alshammari, Alkhaldi et al., Nigella sativa L. and COVID-19: A Glance at The Anti-COVID-19 Chemical Constituents, Clinical Trials, Inventions, and Patent Literature, doi:10.3390/molecules27092750
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Molecular Cell Biology, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Khazdair, Ghafari, Sadeghi, Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19, Pharmaceutical Biology, doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353
Koshak, Koshak, Mobeireek, Badawi, Wali et al., Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial, Complementary Therapies in Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102769
Letko, Marzi, Munster, Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses, Nature Microbiology, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y
Li, Dietary phytochemicals against COVID-19: A focus on thymoquinone, EFood, doi:10.1002/efd2
Lin, Cherukupalli, Feng, Gao, Kang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors Targeting Virus-ACE2 or Virus-TMPRSS2 Interactions, Current Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/0929867328666210420103021
Maiti, Banerjee, Kanwar, In silico Nigellidine (N. sativa) bind to viral spike/active-sites of ACE1/2, AT1/2 to prevent COVID-19 induced vaso-tumult/vasculardamage/comorbidity, Vascular Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2021.106856
Nugraha, Ridwansyah, Ghozali, Khairani, Atik, Traditional Herbal Medicine Candidates as Complementary Treatments for COVID-19: A Review of Their Mechanisms, Pros and Cons, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2020/2560645
Tagarro, Cobos-Carrascosa, Villaverde, Sanz-Santaeufemia, Grasa et al., Clinical spectrum of COVID-19 and risk factors associated with severity in Spanish children, European Journal of Pediatrics, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04306-6
Tito, Colantuono, Pirone, Pedone, Intartaglia et al., Pomegranate Peel Extract as an Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Binding to Human ACE2 Receptor (in vitro): A Promising Source of Novel Antiviral Drugs, Frontiers in Chemistry, doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.638187
Xu, Liu, Xiao, Zhou, Ge et al., Computational and Experimental Studies Reveal That Thymoquinone Blocks the Entry of Coronaviruses Into In Vitro Cells, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00400-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759",
"ISSN": [
"0011-393X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759",
"alternative-id": [
"S0011393X24000298"
],
"article-number": "100759",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction."
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Current Therapeutic Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Najma",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cyril",
"given": "Asha Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "P",
"given": "Anagha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vazhappilly",
"given": "Cijo George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jan",
"given": "Reem Kais",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aburamadan",
"given": "Haneen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbarpoor",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shariar Islam",
"given": "S M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nessa",
"given": "Fazilatun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lozon",
"given": "Yosra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karuvantevida",
"given": "Noushad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radhakrishnan",
"given": "Rajan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Current Therapeutic Research",
"container-title-short": "Current Therapeutic Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-31T02:26:20Z",
"timestamp": 1725071180000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-04T17:42:52Z",
"timestamp": 1725471772000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-05T00:33:37Z",
"timestamp": 1725496417468
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722470400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722470400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 19,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1724112000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0011393X24000298?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0011393X24000298?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100759",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04306-6",
"article-title": "Clinical spectrum of COVID-19 and risk factors associated with severity in Spanish children",
"author": "Tagarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1105",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0001",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-71188-3",
"article-title": "Dynamics of the ACE2–SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV spike protein interface reveal unique mechanisms",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14214",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0002",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y",
"article-title": "Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses",
"author": "Letko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "562",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nature Microbiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0003",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/efd2.77",
"article-title": "Dietary phytochemicals against COVID-19: A focus on thymoquinone",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "EFood",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0004",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/2560645",
"article-title": "Traditional Herbal Medicine Candidates as Complementary Treatments for COVID-19: A Review of Their Mechanisms, Pros and Cons",
"author": "Nugraha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0005",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1775129",
"article-title": "Molecular docking, simulation and MM-PBSA studies of nigella sativa compounds: a computational quest to identify potential natural antiviral for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4225",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0006",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x",
"article-title": "In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets",
"author": "Duru",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Bulletin of the National Research Centre",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0007",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867328666210420103021",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors Targeting Virus-ACE2 or Virus-TMPRSS2 Interactions",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "682",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Current Medicinal Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0008",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vph.2021.106856",
"article-title": "In silico Nigellidine (N. sativa) bind to viral spike/active-sites of ACE1/2, AT1/2 to prevent COVID-19 induced vaso-tumult/vascular-damage/comorbidity",
"author": "Maiti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Vascular Pharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0009",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00400-2",
"article-title": "Computational and Experimental Studies Reveal That Thymoquinone Blocks the Entry of Coronaviruses Into In Vitro Cells",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "483",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0010",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05510-3",
"article-title": "Prophylactic potential of honey and Nigella sativa L. against hospital and community-based SARS-CoV-2 spread: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Ashraf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "618",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0011",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102769",
"article-title": "Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Koshak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Complementary Therapies in Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0012",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27092750",
"article-title": "Nigella sativa L. and COVID-19: A Glance at The Anti-COVID-19 Chemical Constituents, Clinical Trials, Inventions, and Patent Literature",
"author": "Imran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2750",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0013",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/8820543",
"article-title": "Phytochemicals Analysis, In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Extracts, and Molecular Docking Studies of the Isolated Compounds from Melhania zavattarii Cufod Leaves",
"author": "Gonfa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Tropical Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0014",
"volume": "2023",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0015",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353",
"article-title": "Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19",
"author": "Khazdair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "694",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutical Biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0016",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3612898",
"article-title": "Rose and In-vitro Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike: ACE-2 Interaction",
"author": "Arokiaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "SSRN Electronic Journal",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0017",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.638187",
"article-title": "Pomegranate Peel Extract as an Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Binding to Human ACE2 Receptor (in vitro): A Promising Source of Novel Antiviral Drugs",
"author": "Tito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759_bib0018",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0011393X24000298"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction.",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}