Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria
, S., International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940, Mar 2024
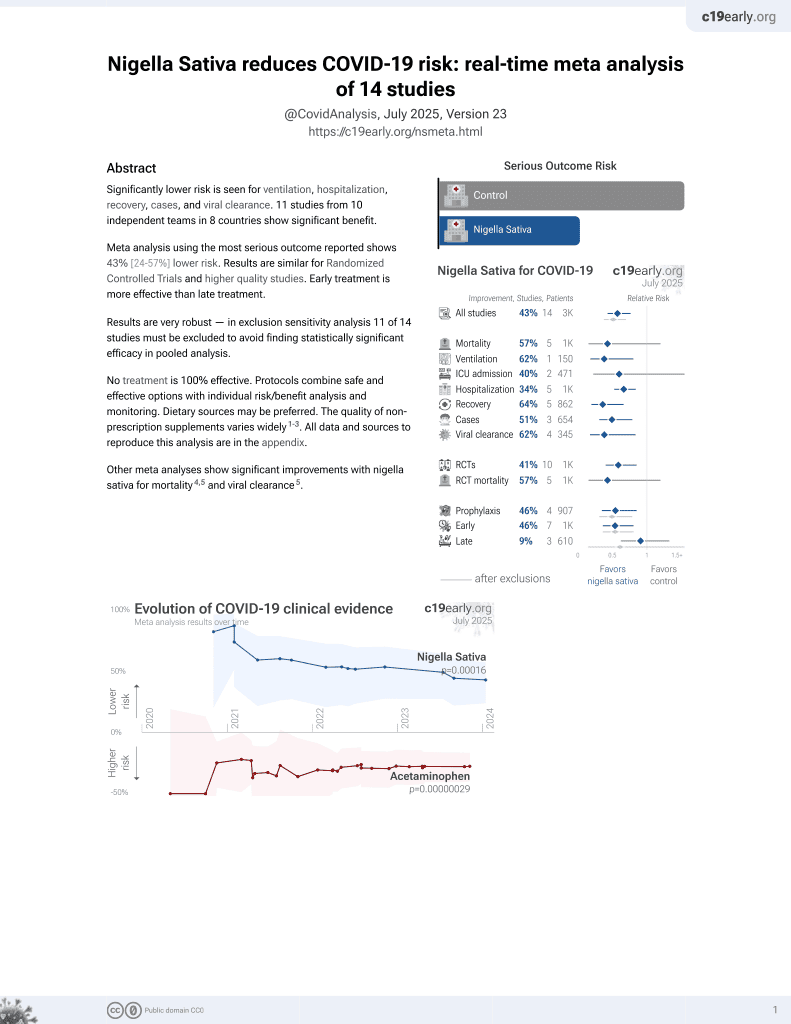
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico study showing that the phytochemicals longifolene and thymohydroquinone from nigella sativa may be suitable alternatives to hydroxychloroquine for treating COVID-19. Authors found that these compounds share binding sites with hydroxychloroquine on the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), which is essential for viral replication. Docking studies revealed conventional hydrogen bonds and alkyl/pi-alkyl interactions between the phytochemicals and key residues on Mpro, suggesting potential for stable binding.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis et al., 5 Mar 2024, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/sr24323192940
The goal of the current study is to find an alternative to hydroxychloroquine that is an antimalarial and has in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2. The crystal structure of the COVID-19 main protease in complex with an inhibitor N3 (6LU7) was used for molecular docking analysis with hydroxychloroquine and phytochemicals with medicinal properties. The novel corona virus (2019-nCoV), family Coronaviridae, genus Beta coronavirus, is thought to be one of the most dangerous pathogenic RNA viruses that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome and is thought to be a threat to humanity. Our research has led to the discovery of two useful phytochemicals that can be obtained from the annual flowering plant Nigella sativa, which is native to the Indian Subcontinent and West Asia. These phytochemicals, longifolene and thymohydroquinone, are suitable alternatives to hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of malaria and COVID-19.
References
Bolton, Dunlap, Formation and Biological Targets of Quinones: Cytotoxic versus Cytoprotective Effects, Chem Res Toxicol, doi:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00256
Colson, Rolain, Lagier, Brouqui, Raoult, Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight COVID-19, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Colson, Rolain, Raoult, Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105923
Gao, Tian, Yang, Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies, Biosci Trends, doi:10.5582/bst.2020.01047
Grover, Behl, Virmani, Sanduja, Makeen et al., Exploration of Cytotoxic Potential of Longifolene/Junipene Isolated from Chrysopogon zizanioides, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27185764
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Mahmud, Paul, Afroze, Islam, Gupt et al., Efficacy of Phytochemicals Derived from Avicennia officinalis for the Management of COVID-19: A Combined In Silico and Biochemical Study, Molecules, doi:2210.10.3390/molecules26082210
Naz, Asif, Alwutayd, Sarfaraz, Abbasi et al., Repurposing FIASMAs against Acid Sphingomyelinase for COVID-19: A Computational Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation Approach, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28072989
Rates, Plants as source of drugs, doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(00)00154-9
Srinivasan, Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) and black cumin (Nigella sativa) seeds: traditional uses, chemical constituents, and nutraceutical effects, Food Quality and Safety, doi:10.1093/fqsafe/fyx031
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Wang, Ye, Liu, A review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) based on current evidence, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Who Director, General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-11
Zhang, Gao, Hu, Wang, Zhong et al., Structure-Based Discovery and Structural Basis of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Natural Product against the Main Protease of Coronavirus, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01253-21
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21275/sr24323192940",
"ISSN": [
"2319-7064"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21275/sr24323192940",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafar Nayak Snehasis",
"given": "Sayed",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": [
"International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T09:30:14Z",
"timestamp": 1715592614000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T10:05:48Z",
"timestamp": 1715594748000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-14T00:35:47Z",
"timestamp": 1715646947696
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2319-7064"
}
],
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
}
},
"member": "8810",
"original-title": [
"Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria"
],
"page": "1571-1578",
"prefix": "10.21275",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "International Journal of Science and Research",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ijsr.net/archive/v13i3/SR24323192940.pdf"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"IJSR"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}