Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2
et al., Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853, Mar 2023
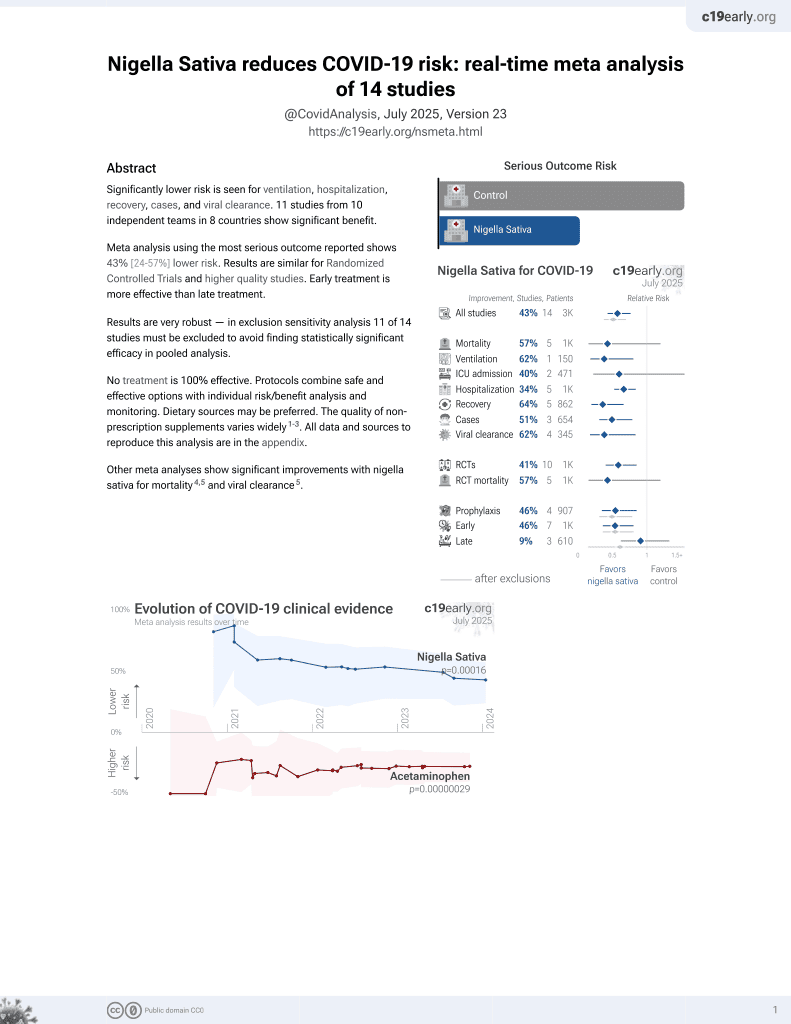
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
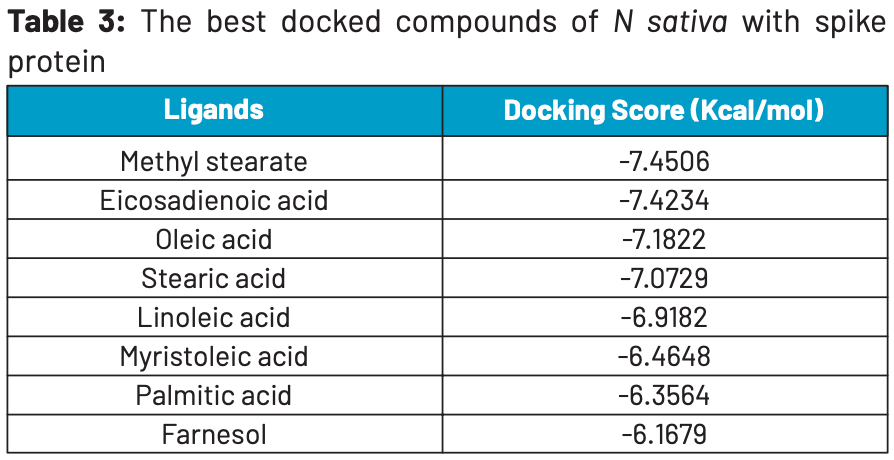
In silico study identifying multiple compounds from nigella sativa as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. Methyl stearate showed the lowest binding energy and formed a stable complex with the spike protein.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Ali et al., 31 Mar 2023, Pakistan, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: rashid.saif37@gmail.com.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2
Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853
COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which is a member of the Coronaviridae family in the Nidovirales order [1]. The virus was rst identi ed in Wuhan, China in late 2019 and has since spread globally, leading to widespread illness and death [2]. Coronaviruses are responsible for a range of diseases, including respiratory, digestive, enteric, and neurological disorders [3]. The highly transmissible nature of the virus has resulted in its spread to 216 countries worldwide [4]. As of the latest reported gures, there have been 759,408,703 con rmed cases of 866,434 deaths
C o n i c t s o f I n t e r e s t The authors declare no con ict of interest.
S o u r c e o f F u n d i n g The authors received no nancial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
References
Coutard, Valle, De Lamballerie, Canard, Seidah et al., The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade, Antiviral
Cvetković, Nikolić, Nenadić, Öcal, Noji et al., Preparedness and preventive behaviors for a pandemic disaster caused by COVID-19 in Serbia, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/erph17114124
Dias, De Azevedo, Molecular docking algorithms, Currents Drug Targets, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716
E F E R E N C E S Gorbalenya, Baker, Baric, De Groot, Drosten et al., The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2, Nature Microbiology, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
Kamble, Daulatabad, John, John, Synopsis of symptoms of COVID-19 during second wave of the pandemic in India, Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1515/hmbci-2021-0043
Ng, Li, Chua, Chaw, Zhao et al., Evaluation of the effectiveness of surveillance and containment measures for the rst 100 patients with COVID-19 in Singapore-January 2-February 29, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6911e1
Yin, Li, Ye, Ruan, Liang et al., Molecular docking and dynamic simulation of Olea europaea and Curcuma Longa compounds as potential drug agents for targeting Main-Protease of SARS-nCoV2, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2022.01
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853",
"ISSN": [
"2709-2798",
"2709-278X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853",
"abstract": "<jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 was first identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and has rapidly devastated worldwide. The lack of approved therapeutic drugs has intensified the global situation, so researchers are seeking potential treatments using regular drug agents and traditional herbs as well. Objectives: To identify new therapeutic agents from Nigella sativa against spike protein (PDB ID: 7BZ5) of SARS-CoV-2. Methods: The 46 compounds from N. sativa were docked with spike protein using Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software and compared with commercially available anti-viral drugs e.g., Arbidol, Favipiravir, Remdesivir, Nelfinavir, Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine. The Molecular Dynamic Simulation (MDS) analysis was also applied to determine ligand-protein complex stability. Furthermore, the pharmacological properties of compounds were also analyzed using AdmetSAR and SwissADME. Results: Out of its total 46 ligands, 8 compounds i.e., Methyl stearate, Eicosadienoic acid, Oleic acid, Stearic acid, Linoleic acid, Myristoleic acid, Palmitic acid, and Farnesol were selected for further analysis based on their minimum binding energy ranges from -7.45 to -7.07 kcal/mol. The docking scores of N. sativa phytocompounds were similar to drugs taken as control. Moreover, post simulation analysis of Methyl stearate complex predicted the most stable conformer. Conclusions: Further, in-vivo experiments are suggested to validate the medicinal use of Methyl stearate as potential inhibitors against spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Laraib",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saif",
"given": "Rashid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassan Raza",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osama Zafar",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zia",
"given": "Saeeda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafiq",
"given": "Mehwish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Tuba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anjum",
"given": "Iram",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pakistan BioMedical Journal",
"container-title-short": "PBMJ",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-19T11:50:20Z",
"timestamp": 1681905020000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-19T11:50:31Z",
"timestamp": 1681905031000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-20T05:56:44Z",
"timestamp": 1681970204575
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680220800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://pakistanbmj.com/journal/index.php/pbmj/article/download/853/674",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://pakistanbmj.com/journal/index.php/pbmj/article/download/853/675",
"content-type": "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://pakistanbmj.com/journal/index.php/pbmj/article/download/853/674",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "32784",
"original-title": [],
"page": "18-23",
"prefix": "10.54393",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "CrossLinks International Publishers",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref0",
"unstructured": "1. Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, de Groot RJ, Drosten C, Gulyaeva AA, et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nature Microbiology. 2020 Apr; 5(4): 536-44. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6911e1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "2. Ng Y, Li Z, Chua YX, Chaw WL, Zhao Z, Er B, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of surveillance and containment measures for the first 100 patients with COVID-19 in Singapore-January 2-February 29, 2020. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2020 Mar; 69(11): 307. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6911e1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2021-0043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "3. Kamble P, Daulatabad V, John N, John J. Synopsis of symptoms of COVID-19 during second wave of the pandemic in India. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation. 2021 Dec; 43(1): 97-104. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2021-0043."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17114124",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "4. Cvetković VM, Nikolić N, Radovanović Nenadić U, Öcal A, K. Noji E, Zečević M. Preparedness and preventive behaviors for a pandemic disaster caused by COVID-19 in Serbia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020 Jun; 17(11): 4124. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114124."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "5. Coutard B, Valle C, De Lamballerie X, Canard B, Seidah NG, Decroly E. The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade. Antiviral Research. 2020 Apr; 176: 104742. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "6. Shereen MA, Khan S, Kazmi A, Bashir N, Siddique R. COVID-19 infection: Emergence, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. Journal of Advanced Research. 2020 Jul; 24: 91-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "7. Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2020 Apr; 10(2): 102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1835726",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "8. Gyebi GA, Adegunloye AP, Ibrahim IM, Ogunyemi OM, Afolabi SO, Ogunro OB. Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry: insight from in silico interaction of drug-like alkaloids with spike glycoprotein, human ACE2, and TMPRSS2. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics. 2022 Mar; 40(5): 2121-45. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1835726."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/glycob/cwaa042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "9. Shajahan A, Supekar NT, Gleinich AS, Azadi P. Deducing the N-and O-glycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Glycobiology. 2020 Dec; 30(12): 981-8. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa042."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.95704-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "10. Li X, Luk HKH, Lau SKP, Woo PCY. Human Coronaviruses: General Features. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. 2019: B978-0-12-801238-3.95704-0. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.95704-0."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "11. Yang H and Rao Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2021 Nov; 19(11): 685-700. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21645515.2020.1788310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "12. Iqbal Yatoo M, Hamid Z, Parray OR, Wani AH, Ul Haq A, Saxena A, et al. COVID-19-Recent advancements in identifying novel vaccine candidates and current status of upcoming SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 2020 Dec; 16(12): 2891-904. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1788310."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26030727",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "13. Sytar O, Brestic M, Hajihashemi S, Skalicky M, Kubeš J, Lamilla-Tamayo L, et al. COVID-19 prophylaxis efforts based on natural antiviral plant extracts and their compounds. Molecules. 2021 Jan; 26(3): 727. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030727."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27092750",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "14. Imran M, Khan SA, Alshammari MK, Alkhaldi SM, Alshammari FN, Kamal M, et al. Nigella sativa L. and COVID-19: A glance at the anti-COVID-19 chemical constituents, clinical trials, inventions, and patent literature. Molecules. 2022 Apr; 27(9): 2750. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092750."
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "15. Bouchentouf S and Missoum N. Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study. 2020 Apr: 1-12. doi: 10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138945008786949432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "16. Dias R and de Azevedo WF Jr. Molecular docking algorithms. Currents Drug Targets. 2008 Dec; 9(12): 1040-7. doi: 10.2174/138945008786949432."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2022.01.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "17. Yin J, Li C, Ye C, Ruan Z, Liang Y, Li Y, et al. Advances in the development of therapeutic strategies against COVID-19 and perspectives in the drug design for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. 2022 Jan; 20: 824-837. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.01.026."
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.13246739.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "18. Saif R, Raza MH, Rehman T, Zafar MO, Zia S, Qureshi AR. Molecular docking and dynamic simulation of Olea europaea and Curcuma Longa compounds as potential drug agents for targeting Main-Protease of SARS-nCoV2. Biological and Medicinal Chemistry. 2021 Mar: 1-22. doi: 10.26434/chemrxiv.13246739.v2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-105301/v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "19. Saif R, Zafar MO, Raza MH, Zia S, Qureshi AR. Computational prediction of Carica papaya phytocompounds as potential drug agent against RdRp and spike protein of SARS-nCoV2 by molecular docking and dynamics simulation approaches. Research Square. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-105301/v2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026618666181025114157",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "20. Naqvi AA, Mohammad T, Hasan GM, Hassan M. Advancements in docking and molecular dynamics simulations towards ligand-receptor interactions and structure-function relationships. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 2018 Aug; 18(20): 1755-68. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666181025114157."
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://pakistanbmj.com/journal/index.php/pbmj/article/view/853"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [
"Computational Prediction of N. sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents"
],
"title": "Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article"
}