Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil thymoquinone and dexamethasone on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats
et al., Veterinary Research Forum, doi:10.30466/vrf.2024.2024154.4196, Nov 2024
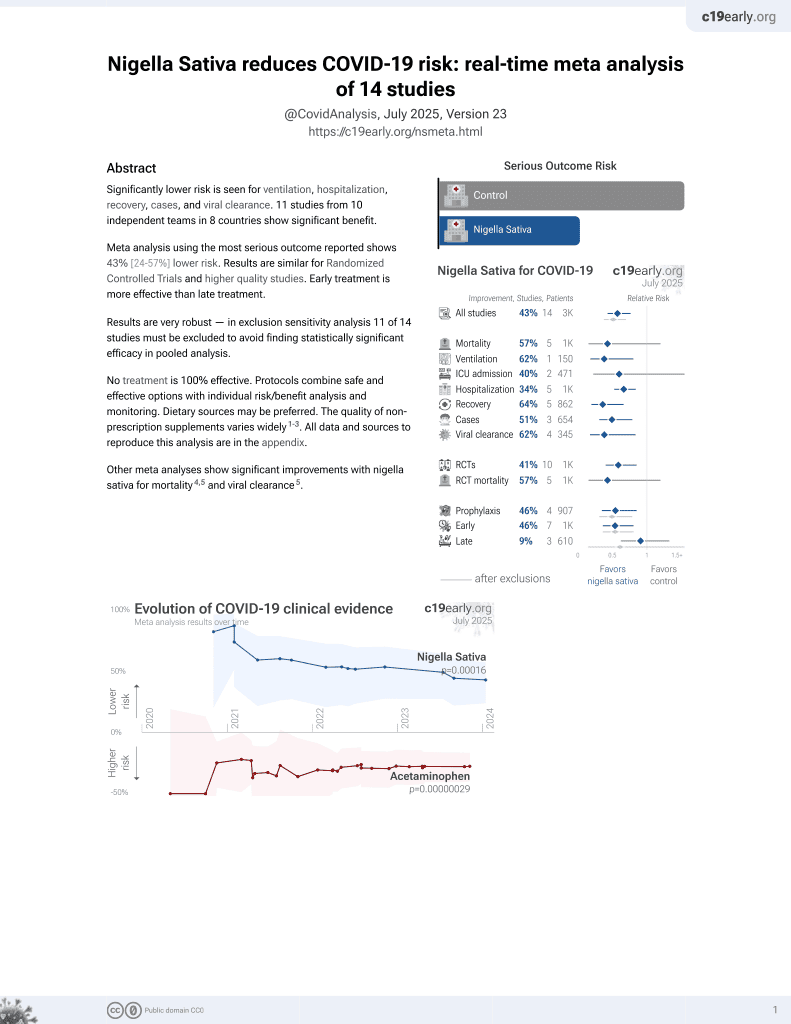
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
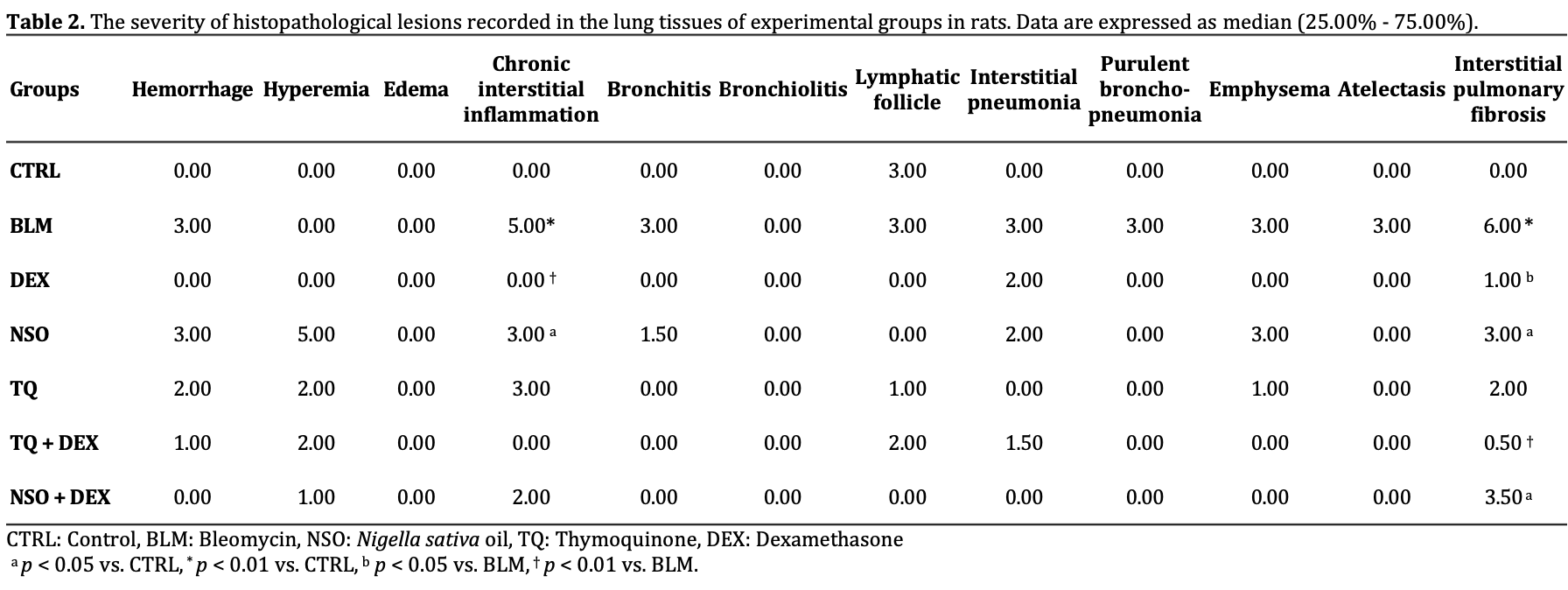
Rat study showing protective effects of nigella sativa oil (NSO), thymoquinone (TQ), and dexamethasone (DEX), alone or in combination, against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. The TQ + DEX combination significantly reduced the severity of fibrosis and inflammation compared to bleomycin alone. NSO and TQ alone also showed improvements, but to a lesser extent than the TQ + DEX combination. Authors suggest NSO and TQ, especially combined with DEX, may be potential protective agents against pulmonary fibrosis, including in COVID-19 patients.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Saghghaei et al., 30 Nov 2024, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: arasooli@ut.ac.ir.
Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil, thymoquinone and dexamethasone on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats
doi:10.30466/vrf.2024.2024154.4196
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic interstitial lung disease with a progressive damage to the air sacs and deposition of collagen fibers in the lung tissue. The study aimed to explore the effects of Nigella sativa oil (NSO) or thymoquinone (TQ), alone or in combination with dexamethasone (DEX), on the development of bleomycin (BLM)-induced PF. Forty-two male rats were divided into seven groups: Control (CTRL); BLM, received a single dose of BLM on day 0, intratracheally; all remaining groups received BLM, as well. DEX, received DEX daily, intraperitoneally, 1 day before BLM and continued for 14 days; NSO and TQ groups, received daily NSO and TQ, respectively, 7 days before BLM and continued for 35 days; DEX + TQ, received both DEX and TQ; DEX + NSO, received both DEX and NSO. At the end, lung tissues were used for histopathological and biochemical analyses. BLM significantly increased the severity of fibrosis and inflammation compared to the CTRL. Bleomycin also significantly increased the amount of hydroxyproline, however, decreased most antioxidant enzymes in the lung tissue compared to the other groups. Group TQ + DEX significantly reduced the severity of BLMinduced PF as well as alterations in biochemical parameters, lung weight and O2 saturation. Nigella sativa oil slightly reduced BLM-induced PF, however, it caused non-significant hyperemia in lung tissue. Thymoquinone potentiated the effects of DEX on most biochemical and pathological alterations of BLM-induced lung injury much better than NSO. More studies are needed to support the use of NSO and TQ as potential protective agents against PF.
Conflict of interest The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
References
Abidi, Bahri, Khamsa, Nigella sativa fixed oil, attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in a rat model
Ahmad, Alkharfy, Jan, Thymoquinone treatment modulates the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and abrogates the inflammatory response in an animal model of lung fibrosis, Exp Lung Res
Almuhayawi, Efficacy of Nigella sativa in wound healing, Indian J Pharm Sci
Alzohairy, Khan, Alsahli, Protective effects of thymoquinone, an active compound of Nigella sativa, on rats with Benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung injury through regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26113218
Amani, Noorbakhsh, Ahmadi, Evaluation of the protective effect of citral, silymarin, and thymoquinone on methotrexate-induced lung injury in rats, J Pharmacopuncture
Ayala, Torres, Vivar, Changes in the pattern of fibrosis in the rat lung with repetitive orotracheal instillations of gastric contents: evidence of persistent collagen accumulation, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Boseila, Messalam, Immunostimulant effect of different fractions of Nigella sativa L. seeds against Rabies vaccine, Nat Sci
Boskabady, Khazdair, Bargi, Thymoquinone ameliorates lung inflammation and pathological changes observed in lipopolysaccharideinduced lung injury, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2021/6681729
Darakhshan, Pour, Colagar, Thymoquinone and its therapeutic potentials, Pharmacol Res
Dik, Mcanulty, Versnel, Short course dexamethasone treatment following injury inhibits bleomycin-induced fibrosis in rats, Thorax
El-Khouly, El-Bakly, Awad, Thymoquinone blocks lung injury and fibrosis by attenuating bleomycin-induced oxidative stress and activation of nuclear factor Kappa-B in rats, Toxicology
Erboga, Erboga, Donmez, Nigella sativa attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by inhibition of inflammation, fibrosis, and inducible nitric oxide synthase, J Exp Clin Med
Gao, Tong, Li, Dexamethasone promotes regeneration of crushed inferior alveolar nerve by inhibiting NF-κB activation in adult rats, Arch Oral Biol
Houghton, Zarka, De Las Heras, Fixed oil of Nigella sativa and derived thymoquinone inhibit eicosanoid generation in leukocytes and membrane lipid peroxidation, Planta Medica
Hübner, Gitter, Mokhtari, Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples, Biotechniques
Javadi, Nooshabadi, Goudarzi, Protective effects of celery (Apium graveloens) seed extract on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, J Babol Univ Med Sci
Kalayarasan, Sriram, Sudhandiran, Diallyl sulfide attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis: critical role of iNOS, NF-kappaB, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta, Life Sci
Kalemci, Zeybek, Kargi, Can the development of lung fibrosis be prevented after COVID-19 infection?, Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol, doi:10.5114/kitp.2022.117505
Khan, Chemical composition and medicinal properties of Nigella sativa Linn, Inflammopharmacology
Khazdair, Ghafari, Sadeghi, Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19, Pharm Biol
King Te, Pardo, Selman, Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Lancet
Latta, Cecchettini, Ry, Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: from biological mechanisms to counteractions, Pharmacol Res
Li, Li, He, The influence of dexamethasone on the proliferation and apoptosis of pulmonary inflammatory cells in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, Respirology
Li, Li, Wei, Dexamethasone combined with berberine is an effective therapy for bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, Exp Ther Med
Marnett, Lipid peroxidation-DNA damage by malondialdehyde, Mutat Res
Moeller, Rodriguez-Lecompte, Wang, Models of pulmonary fibrosis, Drug Discov Today Dis Models
Oku, Shimizu, Kawabata, Antifibrotic action of pirfenidone and prednisolone: different effects on pulmonary cytokines and growth factors in bleomycininduced murine pulmonary fibrosis, Eur J Pharmacol
Park, Christman, Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in the molecular pathogenesis of inflammatory lung diseases, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Pashangzadeh, Taherian, Vafashoar, The effect of dexamethasone on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in the mouse model of systemic sclerosis [Persian], Qom Univ Med Sci J
Sadeghi, Imenshahidi, Hosseinzadeh, Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone: a review, Mol Biol Rep
Saghir, Gabri, Khafaga, Thymoquinone-PLGA-PVA nanoparticles ameliorate bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via regulation of inflammatory cytokines and iNOS signaling, Animals, doi:10.3390/ani9110951
Samareh-Fekri, Poursalehi, Mandegary, The effect of methanol extract of fennel on bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in rats [Persian], J Kerman Univ Med Sci
Shi, Jiang, Ma, Dexamethasone attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice through TGFβ, Smad3 and JAK-STAT pathway, Int J Clin Exp Med
Tashiro, Rubio, Limper, Exploring animal models that resemble idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2017.00118
Uhal, Apoptosis in lung fibrosis and repair, Chest
Vafaee, Hosseini, Hassanzadeh, The effects of Nigella sativa hydro-alcoholic extract on memory and brain tissues oxidative damage after repeated seizures in rats, Iran J Pharm Res
Zargar, Hemmati, Ghafourian, Longterm treatment with royal jelly improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, Can J Physiol Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.30466/vrf.2024.2024154.4196",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2024.2024154.4196",
"author": [
{
"family": "Saghghaei",
"given": "Farid"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6591-2404",
"family": "Rassouli",
"given": "Ali"
},
{
"family": "SadeghiHashjin",
"given": "Goudarz"
},
{
"family": "Sasani",
"given": "Farhang"
},
{
"family": "Koohi",
"given": "Mohammad Kazem"
}
],
"container-title": "Veterinary Research Forum",
"container-title-short": "Vet Res Forum",
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"journalAbbreviation": "Vet Res Forum",
"language": "eng",
"publisher": "Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Urmia University",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil thymoquinone and dexamethasone on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "15"
}