Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1, May 2021
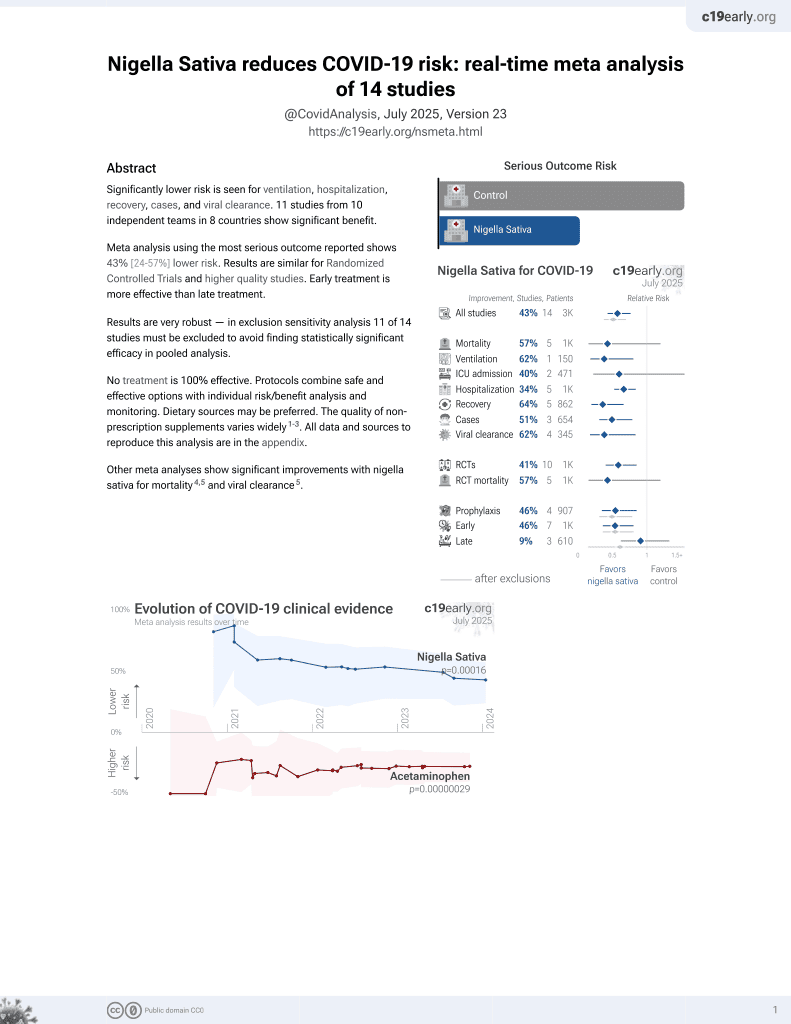
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico and animal study of nigella sativa and component nigellidine, showing nigellidine binding activity for several important SARS-CoV-2 proteins and for relevant host receptors; and that black cumin seed extract was antioxidative, hepato- and reno-protective in rats.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Maiti et al., 5 May 2021, preprint, 5 authors.
Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats.
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1
The recent outbreak of SARS CoV-2 has changed the global scenario of human lives and economy. In this pandemic-outbreak the ratio of infected person is much higher than the death encountered. Most of the dead patients were observed with dysfunction/failure of cardiac and renal systems. Beside this a 'cytokine storm' namely TNF-α/IL1 receptors i.e. TNFR1/TNFR2/IL1R over-functioning was reported in the infected-persons. Here, nigellidine, an indazole-alkaloid and key-component of Nigella Sativa L. (NS); black-cumin-seed, has been analyzed for COVID-19 different protein and TNFα receptors TNFR1/TNFR2 and IL1R inhibition through molecular-docking study and biochemical-study of cuminseed extract exposure to experimental-rat. The NMR, X-ray-crystallographic or Electron-microscopic structures of COVID-19 Main-protease(6LU7), Spike-glycoprotein(6vsb), NSP2(QHD43415_2), Nterminus-protenase (QHD43415_3), Nucleocapsid(QHD43423) and Human IL1R (1itb), TNFR1 (1ncf), TNFR2 (3alq) from PDB were retrieved/analyzed for receptor-ligand interaction in normal condition. Then those structures were docked with nigellidine using Autodock-software and Patchdock-server. Where nigellidine showed highest binding-energy of -7.61 (kcal/mol) and ligand-efficiency value of (-0.35) forming bonds with amino acids THR943/LYS945/MET1556/ALA1557/PRO1558/ILE1559. Highest ACE-value of -356.72 was also observed for nigellidine N-terminal-protease interaction. Nigellidine also showed strong interaction with NSP2 (-6.28) and Mpro/3CLpro_Q (-6.38s). Nigellidine showed affinity to TNFR1 (-6.81), IL1R (-6.23) and TNFR2 (-5.16). In rat experiment 2-groups (vehicle and NS treated) of female Wistar-rats were taken for experiments. The NS treated tissue showed marked decline in ALP/SGPT/ SGOT/MDA level then the basal-levels. From the Western-blot or activity analysis it was observed that Nigellidine, the sulfuryl-group containing drug showed no impact on Phenol-catalyzing ASTIV or Steroid-catalyzing EST expressions/activities and thus have no influence in sulfation-mediated adverse metabolic-processes. Current-results concluded that Nigellidine has hepato/reno-protective; immunomodulatory/anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities as well as it inhibits important proteins of COVID-19. With steps to further validation/checking nigellidine can be used in COVID-19 infection.
Conflict Of Interest
References
Ajebli, Eddouks, Phytotherapy of hypertension: An updated overview
Amizadeh, Rashtchizadeh, Khabbazi, Effect of Nigella sativa oil extracts on inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in Behcet's disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Avicenna J Phytomed
Babar, Jaswir, Tareq, In vivo anxiolytic and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of water-soluble extract (WSE) of Nigella sativa (L.) seeds
Banerjee Amrita, Santra, Maiti, Energetics based epitope screening in SARS CoV-2 (COVID 19) spike glycoprotein by Immuno-informatic analysis aiming to a suitable vaccine development, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.02.021725
Benvenuto, Bianchi, Giovanetti, Pascarella, Ciccozzi, The role of the nsp2 and nsp3 in its pathogenesis
Bouchentouf, Missoum, Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1
Eladl, Arafat, El-Shafei, Farag, Saleh et al., Comparative immune response and pathogenicity of the H9N2 avian influenza virus after administration of Immulant ® , based on Echinacea and Nigella sativa, in stressed chickens, Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.cimid.2019.05.017
Hamdan, Idrus, Mokhtar, Effects of Nigella Sativa on Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph16244911
Khurshid, Syed, Simjee, Beg, Ahmed, Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of proteins from black seeds (Nigella sativa) on human breast MCF-7 cancer cell line, BMC Complement Med Ther, doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2804-1
Luo, Ye, Sun, In vitro biochemical and thermodynamic characterization of nucleocapsid protein of SARS, Biophys Chem, doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2004.06.008
Mahboubi, Natural therapeutic approach of Nigella sativa (Black seed) fixed oil in management of Sinusitis, Integrative Medicine Research, doi:10.1016/j.imr.2018.01.005
Maiti, Banerjee, Epigallocatechin-Gallate and Theaflavin-Gallate Interaction in SARS CoV-2 Spike-Protein Central-Channel with Reference to the Hydroxychloroquine Interaction: Bioinformatics and Molecular Docking Study, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202004.0247.v1
Maiti, Chen, Ethanol up-regulates phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1) and hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (SULT2A1) in rat liver and intestine, Arch Physiol Biochem, doi:10.3109/13813455.2014.992440
Maiti, Dutta, Baker, In vivo and in vitro oxidative regulation of rat aryl sulfotransferase IV (AST IV), J Biochem Mol Toxicol, doi:10.1002/jbt.20064
Maiti, Zhang, Chen, Redox regulation of human estrogen sulfotransferase (hSULT1E1), Biochem Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.12.026
Majdalawieh, Fayyad, Nasrallah, Anti-cancer properties and mechanisms of action of thymoquinone, the major active ingredient of Nigella sativa, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2016.127797
Mda, Bicudo, Sicherle, Rodello, Gallego, Lipid peroxidation and generation of hydrogen peroxide in frozen-thawed ram semen cryopreserved in extenders with antioxidants, Anim Reprod Sci, doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.08.004
Mohebbati, Abbasnezhad, Effects of Nigella sativa on endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: A review, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112585
Mokhtari-Zaer, Norouzi, Askari, The protective effect of Nigella sativa extract on lung inflammation and oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112653
Morris, Huey, Lindstrom, AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, J Comput Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Nazmeen, Chen, Ghosh, Maiti, Breast cancer pathogenesis is linked to the intra-tumoral estrogen sulfotransferase (hSULT1E1) expressions regulated by cellular redox dependent Nrf-2/NFκβ interplay, Cancer Cell Int, doi:10.1186/s12935-020-1153-y
Nazmeen, Maiti, Oxidant stress induction and signalling in xenografted (human breast cancer-tissues) plus estradiol treated or N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea treated female rats via altered estrogen sulfotransferase (rSULT1E1) expressions and SOD1/catalase regulations, Mol Biol Rep, doi:10.1007/s11033-018-4425-z
Onifade, Jewell, Adedeji, Nigella sativa concoction induced sustained seroreversion in HIV patient, Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med
Otnick, Xue, Bar, Distribution of primary and specialized metabolites in Nigella sativa seeds, a spice with vast traditional and historical uses, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules170910159
Razin, Osman, Ali, Bahgat, Maghraby, Immune responses to killed reassorted influenza virus supplemented with natural adjuvants, Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung, doi:10.1556/030.64.2017.011
Razmpoosh, Safi, Abdollahi, The effect of Nigella sativa on the measures of liver and kidney parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Schneidman-Duhovny, Inbar, Nussinov, Wolfson, PatchDock and SymmDock: servers for rigid and symmetric docking, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gki481
Shakeri, Gholamnezhad, Mégarbane, Rezaee, Boskabady, Gastrointestinal effects of Nigella sativa and its main constituent, thymoquinone: a review, Avicenna J Phytomed
Shirazi, Khodakarami, Feizabad, Ghaemi, The effects of nigella sativa on anthropometric and biochemical indices in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome [published online ahead of print, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02265-w
Szerlauth, Muráth, Viski, Szilagyi, Radical scavenging activity of plant extracts from improved processing, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02763
Tabassum, Ahmad, Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation Analysis of Thymoquinone and Thymol Compounds from Nigella sativa L. that Inhibits Cag A and Vac A Oncoprotein of Helicobacter pylori: Probable Treatment of H. pylori Infections
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The recent outbreak of SARS CoV-2 has changed the global scenario of human lives and economy. In this pandemic-outbreak the ratio of infected person is much higher than the death encountered. Most of the dead patients were observed with dysfunction/failure of cardiac and renal systems. Beside this a ‘cytokine storm’ namely TNF-α/IL1 receptors i.e. TNFR1/TNFR2/IL1R over-functioning was reported in the infected-persons. Here, nigellidine, an indazole-alkaloid and key-component of <jats:italic>Nigella Sativa L</jats:italic>. (NS); black-cumin-seed, has been analyzed for COVID-19 different protein and TNFα receptors TNFR1/TNFR2 and IL1R inhibition through molecular-docking study and biochemical-study of cumin-seed extract exposure to experimental-rat. The NMR, X-ray-crystallographic or Electron-microscopic structures of COVID-19 Main-protease(6LU7), Spike-glycoprotein(6vsb), NSP2(QHD43415_2), N-terminus-protenase (QHD43415_3), Nucleocapsid(QHD43423) and Human IL1R (1itb), TNFR1 (1ncf), TNFR2 (3alq) from PDB were retrieved/analyzed for receptor-ligand interaction in normal condition. Then those structures were docked with nigellidine using Autodock-software and Patchdock-server. Where nigellidine showed highest binding-energy of -7.61 (kcal/mol) and ligand-efficiency value of (-0.35) forming bonds with amino acids THR943/LYS945/MET1556/ALA1557/PRO1558/ILE1559. Highest ACE-value of -356.72 was also observed for nigellidine N-terminal-protease interaction. Nigellidine also showed strong interaction with NSP2 (-6.28) and Mpro/3CLpro_Q (-6.38s). Nigellidine showed affinity to TNFR1 (-6.81), IL1R (-6.23) and TNFR2 (-5.16). In rat experiment 2-groups (vehicle and NS treated) of female Wistar-rats were taken for experiments. The NS treated tissue showed marked decline in ALP/SGPT/ SGOT/MDA level then the basal-levels. From the Western-blot or activity analysis<jats:italic> </jats:italic>it was observed that Nigellidine, the sulfuryl-group containing drug showed no impact on Phenol-catalyzing ASTIV or Steroid-catalyzing EST expressions/activities and thus have no influence in sulfation-mediated adverse metabolic-processes. Current-results concluded that Nigellidine has hepato/reno-protective; immunomodulatory/anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities as well as it inhibits important proteins of COVID-19. With steps to further validation/checking nigellidine can be used in COVID-19 infection.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
2
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1354-1303",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Midnapore, India"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Maiti",
"given": "Smarajit",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Midnapore, India"
}
],
"family": "Banerjee",
"given": "Amrita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Midnapore, India"
}
],
"family": "Nazmeen",
"given": "Aarifa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Midnapore, India"
}
],
"family": "Kanwar",
"given": "Mehak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Midnapore, India"
}
],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Shilpa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-05T20:59:00Z",
"timestamp": 1588712340000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-03T21:43:42Z",
"timestamp": 1599169422000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-15T14:59:31Z",
"timestamp": 1684162771854
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
5
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1588636800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-26464/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-26464/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
5
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-26464/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats.",
"type": "posted-content"
}