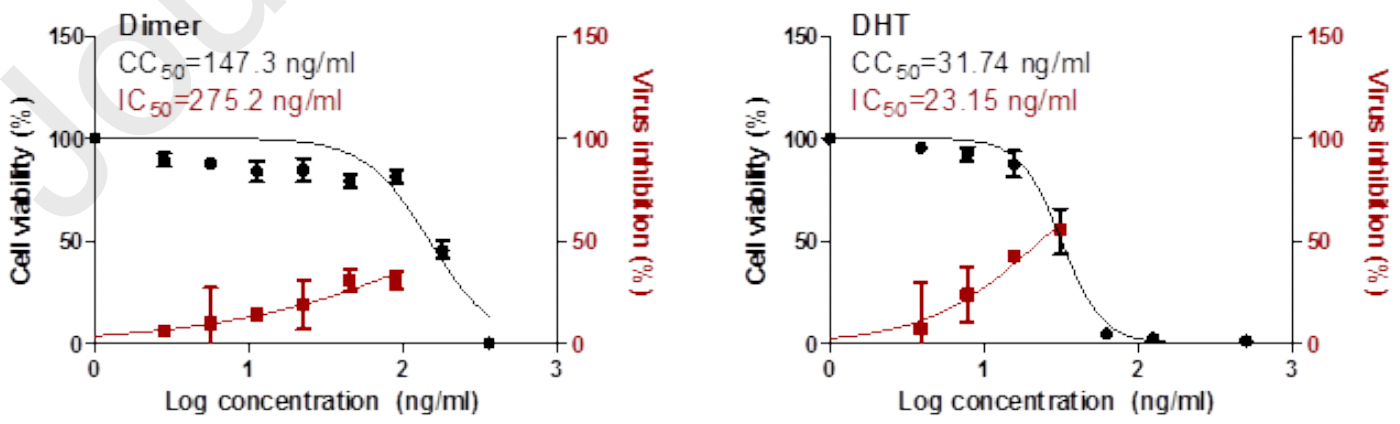
In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia
et al., Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587, Jan 2022
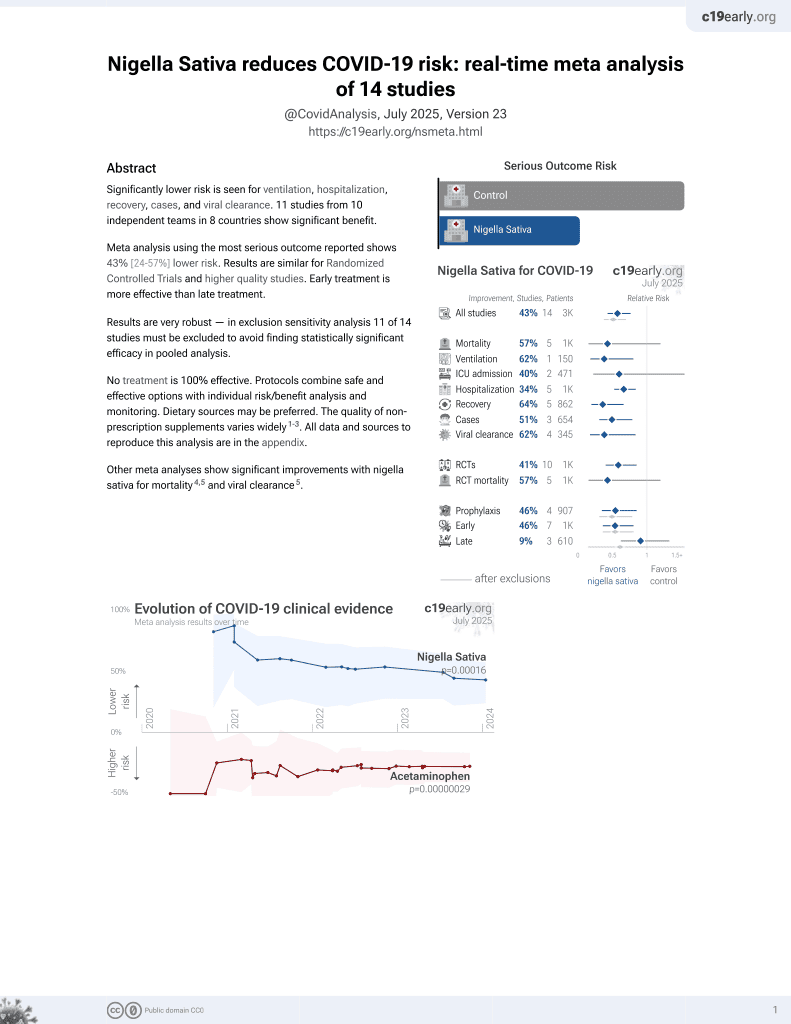
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro and in silico study of nigella sativa components, showing anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity at non-cytotoxic nanomolar concentrations for thymohydroquinone with selectivity index 1.4.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Esharkawy et al., 1 Jan 2022, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
In vitro potential antiviral SARS-CoV-19- activity of natural product thymohydroquinone and dithymoquinone from Nigella sativa
Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conclusion: The current study highlight in vitro antiviral studies on two compounds from three major compounds in Nigela Sativa depending on bioinformatic analysis, which reveals the importance of three major compounds (TQ, DTQ, and HTQ), as antiviral agents. in vitro antiviral screening on two compounds (DTQ and HTQ) showed the tested drugs exhibited a promising in vitro activity against COVID-19, and have promising antiviral activities, further investigations in clinical trials to determine actual in vivo activity in the treatment of COVID-19 have recommended.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare any conflict of interest.
Conflict of interest: The author sdeclare any conflict of interest
References
Abdallah, Markb, Potential Cytotoxic, Antifungal, and Antioxidant Activity of Dithymoquinone and Thymoquinone, Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences
Ainane, Askaoui, Elkouali, Talbi, Hammouti et al., Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oil of Nigella sativa seeds from Beni Mellal (Morocco): What is the most important part,Essential Oil or the rest of seeds?, J. Mater. Environ
Ajmal, Bhat, Dongre, Almalki, Berredjem et al., Synthesis, Biological Activity and POM/DFT/Docking Analyses of Annulated Pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives: Identification of Antibacterial and Antitumor Pharmacophore sites, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104480
Alenzi, El-Sayed El-Bolkiny&, Salem, Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil and thymoquinone against toxicity induced by the anticancer drug cyclophosphamide, British Journal of Biomedical Science, doi:10.1080/09674845.2010.11730285
Aliasgharjarrahpour, Véroniquesinou, Latour, Djouhribouktab, Brunel et al., Synthesis of New β-Lactams Bearing the Biologically Important Morpholine Ring and POM Analyses of Their Antimicrobial and Antimalarial Activities, Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research
Amel, Kamal, Abdelhady, Taibi, Hadda, Two novel flavone C-glycosides isolated from Podocarpusgracilior: POM analyses and in-vitro anticancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma, Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, doi:10.22159/ijpps.2019v11i7.33163
Ameri, Jarrahpour, Latour, Sinou, Michel Brunel et al., Synthesis and antimicrobial/antimalarial activities of novel naphthalimido trans-β-lactam derivatives, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-017-1920-z
Amirkhanov, Rauf, Hadda, Ovchynnikov, Trush et al., Pharmacophores modeling in terms of prediction of theoretical physico-chemical properties and verification by experimental correlations of Carbacylamidophosphates (CAPh) and Sulfanylamidophosphates (SAPh) Tested as New Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors, Mini Rev Med Chem, doi:10.2174/1389557519666190222172757
Badary, Hamza, Tikamdas, Thymoquinone: A Promising Natural Compound with Potential Benefits for COVID-19 Prevention and Cure, Drug Des Devel Ther, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S308863InvitropotentialAntiviralSARS-CoV-19-
Banerjee, Padhye, Azmi, Wang, Philip et al., None
Bawazeer, Khan, Rauf, Taibi, Hadda et al., POM Analysis and Computational Interactions of 8-Hydroxydiospyrin Inside Active Site of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B, BIOCELL, doi:10.32604/biocell.2021.014004
Bechlem, Aissaoui, Belhani, Rachedi, Bouacida et al., Synthesis, X-ray crystallographic study and molecular docking of new a-sulfamidophosphonates: POM analyses of their cytotoxic activity, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127990
Ben Hadda, Ahmad, Sultana, Shaheen, Bader et al., POM analyses for Antimicrobial evaluation of Thienopyrimidinones Derivatives: A Rapid Method for Drug Design, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-013-0614-4
Ben Hadda, Ali, Masand, Gharby, Fergoug et al., Tautomeric Origin of Dual Effects of N1-nicotinoyl-3-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methyl phenyl)-5-[(sub)phenyl]-2-pyrazolines on Bacterial and Viral Strains: POM Analyses as New Efficient Bioinformatics' Platform to Predict and Optimize Bioactivity of Drugs, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0143-6
Ben Hadda, Fathi, Chafchaouni, Masand, Charrouf et al., Computational POM and 3D-QSAR Evaluation of Experimental in vitro HIV-1 Integrase Inhibition of Amide-containing di-Ketoacids Medicinal Chemistry Research, doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0120-0
Ben Hadda, Fergoug, Warad, POM Theoretical Calculations and Experimental Verification of Antibacterial Potentialof 5-Hydroxy-4-(Substituted-Amino)-2(5H)-Furanones, Res Chem Intermed, doi:10.1007/s11164-012-0729-0
Ben Hadda, Genc, Masand, Nebbache, Warad et al., Computational POM and DFT Evaluation of Experimental in-vitro Cancer Inhibition of Staurosporine-Ruthenium(II) Complexes: The Power Force of Organometallics in Drug Design, Acta Chim. Slov
Ben Hadda, Oualidtalhi, Silva, Sezersenol, Ilkay Erdogan Orhan et al., Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Some semi-Rigid Spiro Heterocycles: POM Analyses and Crystalline Structure of Pharmacophore Site, Mini Rev. Med Chem, doi:10.2174/1389557517666170713114039
Ben Hadda, Rahimamouhoub, Jawarkar, Masand, Warad, POM Analyses of Antitrypanosomal Activity of 2-Iminobenzimidazoles: Favorable and Unfavorable Parameters for Drugs Optimization, Medicinal Chemistry Research, doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0238-0
Ben Hadda, Rastija, Almalki, Abderrahimtiti, Touzani et al., Petra/Osiris/Molinspiration and Molecular Docking Analyses of 3-Hydroxy-Indolin-2-one Derivatives as Potential Antiviral Agents, Current Computer-Aided Drug Design, doi:10.2174/1573409916666191226110029
Ben Hadda, Sezersenol, Ilkay Erdogan Orhan, Hsainezgou, Rauf et al., Spiro Heterocyclic Compounds as Potential Anti-Alzheimer agents (Part 2): their Metal Chelation Capacity, POM Analyses and DFTStudies, Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/1573406416666200610185654
Ben Hadda, Srivastava, Das, Salgado-Zamora, Shaheen et al., POM Analyses of Antimicrobial activity of Some 2,3-Armed 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-Benzothiophenes: Favourable and UnfavourablePhysico-chemical Parameters in Design of Antibacterial and Mycolytic Agents, Medicinal Chemistry Research, doi:10.1007/s00044-013-0707-0
Bennani, Kerbal, Baba, Daoudi, Warad et al., Synthesis, characterization, bioactivity, and POM analyses of isothiochromeno[3,4-e][1,2]oxazines, Medicinal Chemistry Research2013, doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0392-4
Boussaidi1, Alaoui, Eddiouane1, Fitri, Touimibenjelloun et al., Theoretical study of the effect of substitution with alternating donor and acceptor groups on the optoelectronic and photovoltaic properties ofsome oligomers containing thiophene and phenylene, Arabian Journal of Chemical and Environmental Research
Chander, Tang, Al-Maqtari, Jamalis, Penta et al., Synthesis and Study of Anti-HIV-1 RT Activity of 5-benzoyl-4-methyl-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-1,5-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.03.013
Cruz-Rodriguez, Barea, Tamayo, Hochwimmer, Hadda et al., ELIDAN certificate: BEHAVIOR is the key to save places from Covid-19, Journal of Bioscience & Biomedical Engineering
Cruz-Rodriguez, Batista, Hochwimmer, Hadda, Almalki et al., How to Evaluate Viral Transmission in Enclosed Areas, Medical Geology saving places from Covid-19 Journal of Bioscience & Biomedical Engineering (J. B. Bio. Engine
El-Dakhakhany, Studies on the chemical constitution of Egyptian nigella sativa l. Seeds. Ii: The essential oil, Planta Med
Elfaydy, Ounine, Rastija, Almalki, Jamalis, Abdelkader Applications of Cannabinoids Extracted from Cannabis sativa (L.): A new Route to Fight against COVID-19?, Current Pharmaceutical Design, doi:10.2174/1381612826666201202125807
Elsharkawy, None
Emam; Nabila, Kheder, Elmalki, Taibi, Hadda, Synthesis, Antiviral, and Molecular Docking Studies of Some Novel 1,2,4-Triazine Nucleosides as Potential Bioactive Compounds, Carbohydrate Research, doi:10.1016/j.carres.2021.108246
Eman, El-Sharkawy, Almalki, Ben Hadda, Rastija et al., DFT Calculations and POM Analyses of Cytotoxicity of Some Flavonoids from Aerial Parts of Cupressus sempervirens: Docking and Identification of Pharmacophore Sites, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103850
Farghaly, Abbas, Hassan, Structure Determination and Quantum Chemical Analysis of 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Nitrile Imines and New Dipolarophiles and POM Analyses of the Products as Potential Breast Cancer Inhibitors, Russ J Org Chem, doi:10.1134/S1070428020070210
Fathi, Masand, Jawarkar, Mouhoub, Ben et al., POM as Efficient Tools to Predict and Improve Both Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Aryl Aldazines, J. Comput. Method. Mol. Design
Forschung, None, Drug Research
Genc, Zuhalkaragozgenc, Suattekin, Sandal, Sirajuddin et al., Design, Synthesis, in vitro Antiproliferative Activity, Binding Modeling of 1,2,4,-Triazoles as New Anti-Breast Cancer Agents, Acta ChimicaSlovenica, doi:10.17344/acsi.2016.2428
Gharby, Harhar, Guillaume, Roudani, Boulbaroud et al., Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco, Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, doi:.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2013.12.001
Grib, Berredjem, Rachedi, Djouad, Bouacida et al., None
Hadda, Fergoug, Warad, Masand, Sheikh, POM as a quick bioinformatic platform to select flavonoids and their metabolites as potential and efficient HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, Res Chem Intermed, doi:10.1007/s11164-012-0679-6
Hakkou, Maciuk, Leblais, Elhoudabouanani, Hassanemekhfi et al., Antihypertensive and vasodilator effects of methanolic extract of Inulaviscosa: Biological evaluation and POM analysis of cynarin, chlorogenic acid as potential hypertensive, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.015
Halawani, Antibacterial Activity of Thymoquinone and Thymohydroquinone of Nigella sativa L. and Their Interaction with Some Antibiotics, Advances in Biological Research
Harjeetjuneja, Sheikh, Ingle, Taibi, Hadda, Synthesis, Antibacterial Screening and POM Analyses of Novel Bis-Isoxazolyl/Pyrazoyl-1,3-diols, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-013-0755-5
Header, Elsawy, El-Boshy, Basalamah, Mubarak et al., POM Analyses of Constituents of Rosmarinus officinalis and Their Synergistic Effect in Experimental Diabetic Rats, J Bioanal Biomed, doi:10.4172/1948-593X.1000118
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan
Ihsaneelmeskini, Daoudi, Abdelalikerbal, Diogo, Moreira et al., Is It Possible For The 2-[(4-chloro-phenyl)-(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)-methyl]-malonic acid diethyl ester To Present a Potential Candidate HIV-Integrase Inhibitor On The Basis of Its (O,N,O)-Ligand Structure, Moroccan Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, doi:10.48369/IMIST.PRSM/jmch-v18i2.16384
Jarrahpour, Fathi, Mimouni, Ben Hadda, Sheikh et al., Petra, Osiris and Molinspiration (POM) Together as a Successful Support in Drug Design: Antibacterial Activity and Biopharmaceutical Characterization of Some Azo Schiff Bases, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-011-9723-0
Joazaizulfazlijamalis, Mohamed Yusof, Chander, Abd, Wahab et al., Psoralen Derivatives: Synthetic Strategy and Pharmacological Properties, Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/1871523018666190625170802
Kadri, Ben Hadda, Belhania, Novel N-sulfonylphthalimides: Efficient synthesis, X-ray characterization, spectral investigations, POM analyses, DFT computations and antibacterial activity, Journal of Molecular Structure. Available online
Kalai, Chelfi, Benchat, Brahimhacht, Bouklah et al., New organic extractant based on pyridazinone scaffold compounds: liquid-Liquid extraction study and DFT calculations, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.033
Khadidjaotmanerachedi, Bahadi, Aissaoui, Taibi, Hadda et al., DFT Study, POM Analyses and Molecular Docking of Novel Oxazaphosphinanes: Identification of Antifungal Pharmacophore Site, Indones. J. Chem, doi:10.22146/ijc.46375
Khalife&, Lupidi, Nonenzymatic reduction of thymoquinone in physiological conditions, Free Radical Research
Khodair, El-Barbary, None
Kurupatham, Chen, Chan, Vasoo, Lye, Epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore, JAMA, doi:148810.1001/jama.2020.3204
Lakhrissi, Rbaa, Mequedade, Berkiks, Mague et al., Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Evaluation of Biologycal Activity of Novel Heterocyclic Derivative of 8-Hydroxyquinoline
Lupidi, Nonenzymatic reduction of thymoquinone in physiological conditions, Free Radical Research
Mabkhot, Alatibi, El-Sayed, Kheder, Wadood et al., Experimental-ComputationalEvaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Novel Armed Thiophene Derivatives, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules21020222
Mabkhot, Aldawsari, Al-Showiman, Barakat, Ben Hadda et al., Synthesis, bioactivity, molecular docking and POM anlysis of novel substituted thieno[2,3-b]thiophenes and related congeners, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules20021824
Mabkhot, Aldawsari, Al-Showiman, Barakat, Soliman et al., Synthesis, Molecular Structure Optimization, and Cytotoxicity Assay of a Novel 2-Acetyl-3-amino-5-[(2-oxopropyl)sulfanyl]-4-cyanothiophene, Molecules
Mahajan, Masand, Patil, Ben Hadda, Jawarkar et al., Vesna Rastija, CoMSIA and POM analyses of anti-malarial activity of synthetic prodiginines, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.05.115
Masand, Patil, Jawarkar, Ben Hadda, Youssoufi et al., Exploring interactions of 2-Amino-6-arylsulfonylbenzonitrile derivatives as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors of H IV-1 using docking studies, J. Comput. Method. Mol. Design
Meriemguerf, Berredjem, Abdeslembouzina, Ben Hadda, Marminon et al., Novel α-sulfamidophosphonates analogues of Fotemustine: Efficient synthesis using ultrasound under solvent-free conditions, MonatsheftefürChemie -Chemical Monthly, doi:10.1007/s00706-020-02711-5
Mohamed, Abdelhady, Amel, Kamal, Rauf et al., Bioassay-guided isolation and POM analyses of a new immunomodulatory polyphenolic constituent from Callistemon Viridiflorus, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2015.1045508
Mohammed Al-Maqtari, Joazaizulfazlijamalis, Ben Hadda ; Murugesan Sankaranarayanan, Chander, Noor et al., Synthesis, characterization, POM analysis and antifungal activity of novel heterocyclic chalcone derivatives containing acylated pyrazole, Res Chem Intermed, doi:10.1007/s11164-016-2737-y
Mostafa, Kandeil, Elshaier, Kutkat, Moatasim et al., FDA-Approved Drugs with Potent In Vitro Antiviral Activity against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph13120443
Moulay, Youssoufi, Pramod, Sahu, Sahu et al., POM analyses of Antimicrobial Activity of 4H-Pyrimido[2,1-b]Benzothiazole, Pyrazole and Benzylidene Derivatives of Curcumin, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-014-1297-1
Mouslimmessali, Aouad • Adeeb, Ali, NadjetRezki • Taibi Ben Hadda • BelkheirHammouti. Synthesis, characterization and POM analysis of novel bioactive imidazolium-based ionic liquids, Medicinal Chemistry Research, doi:10.1007/s00044-014-1211-x
Nasser Mabkhot, Barakat, Yousuf, Choudhary, Frey et al., Substitutedthieno[2,3-b]thiophenes and related congeners: Synthesis, <beta>-glucuronidase inhibition activity, crystal structure, and POM analyses, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.08.014
Osama, Badary, Taha, Ayman, Gamal El-Din et al., Is a Potent Superoxide Anion Scavenger, Drug and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1081/DCT-120020404
Ou, Liu, Lei, Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9
Rachedi, Ouk, Bahadir, Bouzinaa, Djouad et al., Synthesis, DFT and POM analyses of cytotoxicity activity of α-amidophosphonates derivatives: Identification of potential antiviral O,Opharmacophore site, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.07.053
Rakib, Saad, Sami, Jahan Mimi, Chowdhury et al., Immunoinformatics-guided design of an epitope-based vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndromecoronavirus spike glycoprotein, Computers in Biology and Medicine
Rauf, Uddin, Bina, Siddiqui, Khan et al., POM Analysis of Phytotoxic Agents from Pistaciaintegerrima Stewart, Current Bioactive Compounds
Rauf, Uddin, Bina, Siddiqui, Khan et al., POM Analysis of Phytotoxic Agents from Pistaciaintegerrima Stewart, Current Bioactive Compounds. Current Bioactive Compounds
Rbaa, Hichar, Dohare, El, Anouar et al., Synthesis, Characterization, Biocomputational Modeling and Antibacterial Study of Novel Pyran Based on 8-Hydroxyquinoline Arabian, Journal for Science and Engineering, doi:10.1007/s13369-020-05089-y
Rbaa, Jabli, Lakhrissi, Ouhssine, Almalki et al., Synthesis, antibacterial properties and bioinformatics computationalanalyses of novel 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e0268
Rbaa, Oubihi, Anouar, Ouhssineb, Almalki et al., Synthesis of New Heterocyclic Systems Oxazino Derivatives of 8-Hydroxyquinoline: Drug Design and POM Analyses of Substituent Effects on their Potential Antibacterial Properties, Chemical Data Collections, doi:10.1016/j.cdc.2019.100306
Sajid, Ahmad, Aslam, Ali Ashfaq, Fawad Zahoor et al., Novel armed pyrazolobenzothiazine derivatives: synthesis, X-ray crystal structure and POM analyses of biological activity against drug resistant clinical isolate of staphylococus aureus, Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, doi:10.1007/s11094-016-1417-y
Salem, Hossain, Protective effect of black seed oil from Nigella sativa against murine cytomegalovirus infection, Int J Immunopharmacol
Sarkar, Mohammad, Review on Molecular and Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone in
Sayed, Traditional medicine in health care, J Ethnopharmacol
Sheikh, Vijay Taile, Ghatole, Vishwas Ingle • Murat Genc, Sihamlahsasni et al., Antimicrobial/antioxidant activity and POM analyses of novel7-O-b-Dglucopyranosyloxy-3-(4,5-disubstitutedimidazol-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-ones, Med Chem Res, doi:10.1007/s00044-015-1326-8
Sukhdeoraodongre, Meshram, Sudhakarraoselokar, Almalki, Ben Hadda, Antibacterial activity of synthetic pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines armed with nitrile group: POM analyses and identification of pharmacophore sites of nitriles as important pro-drugs, New J. Chem, doi:10.1039/C8NJ02081G
Taibi, Hadda, Hasnabendaha, Sheikh, Ahmad et al., Computational POM Evaluation of Experimental in vitro Trypanosoma cruzi and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Inhibition of Heterocyclic-2-Carboxylic Acid (3-Cyano-1,4-di-Noxidequinoxalin-2-yl)amide Derivatives, Medicinal Chemistry Research, doi:.10.1007/s00044-013-0781-3
Tatar, Sevilşenkardeş, Sellitepe, Küçükgüzel, Şengülalpaykaraoğlu et al., Synthesis, prediction of molecular properties and antimicrobial activity of some acylhydrazones derived from N-(arylsulfonyl)methionine, Turkish Journal of Chemistry
Tesarova, Svobodova, Kokoska, Marsik, Pribylova et al., Determination of oxygen radical absorbance capacity of black cumin (nigella sativa) seed quinone compounds, Nat. Prod. Commun
Tighadouni, Smaailradi, Sirajuddin, Akkurt, Namıközdemir et al., Vitro Antifungal, Anticancer Activities and POM Analyses of a Novel Bioactive Schiff Base 4-{[(E)-furan-2-ylmethylidene]amino}p-henol: Synthesis, Characterization and Crystal Structure, J.Chem.Soc.Pak
Titi, Messali, Alqurashy, Touzani, Shiga et al., Synthesis, Characterization, X-Ray Crystal Study and Bioactivities of Pyrazole Derivatives: Identification of Antitumor, Antifungal and Antibacterial Pharmacophore Sites, Journal of Molecular Structure, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127625
Topozada, Masloum, El-Dakhakhany, The anti-bacterial properties of Nigella sativa seeds: Active principle with some clinical application, Journal of the Egyptian Medical Association
Uddin, Nasruddin, Abdur Rauf, Haroon Khan, Mamadalieva et al., Phytochemical analysis, urease inhibitory effect and antimicrobial potential of Allium humile, ZeitschriffürArznei-und Gewürzpflanzen
Uddin, Rauf, Bibi, Khan, Ben Hadda et al., Bioactive compounds andbiological activities of Alnusnitida, ZArznei-Gewurzpfla
Warad, Al-Nuri, Ali, Abu-Reidah, Barakat et al., None
Yahia, Mabkhot, Arfan, Hsainezgou, Genc et al., How to Improve Antifungal Bioactivity: POM and DFT Study of some Chiral Amides Derivatives of Diacetyl-L-tartaric Acid and Amines, Research on Chemical Intermediates, doi:10.1007/s11164-016-2578-8
Yang, Sahidul Islam, Wang, Li, Chen, Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Patients Infected with 2019-New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Review and Perspective, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.45538
Young, Ong, Kalimuddin, Low, Tan et al., None
Zarrouk, Radi, Smaail, Touzani, Elmsellem, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical, Hirschfield Surface and DFT/B3LYP Calculation of Two New Hexahydropyrimidine Heterocyclic Compounds, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Article
Zhou, Zhao, Perspectives on therapeutic neutralizing antibodies against the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.45123
Zi-Wei, Yuan, Yuen, Fung, Chan et al., Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.45472
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587",
"ISSN": [
"0045-2068"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587",
"alternative-id": [
"S0045206821009652"
],
"article-number": "105587",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esharkawy",
"given": "Eman R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Almalki",
"given": "Faisal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ben Hadda",
"given": "Taibi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Bioorganic Chemistry"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T15:33:50Z",
"timestamp": 1641051230000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-06T05:18:07Z",
"timestamp": 1641446287000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100007471",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Northern Borders University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-06T06:21:12Z",
"timestamp": 1641450072961
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0045-2068"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0045206821009652?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0045206821009652?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105587",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jssas.2013.12.001",
"article-title": "Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco",
"author": "Gharby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0005",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oil of Nigella sativa seeds from Beni Mellal (Morocco): What is the most important part, Essential Oil or the rest of seeds?J",
"author": "Ainane",
"first-page": "2017",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Mater. Environ. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0010",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "Forschung",
"first-page": "1227",
"journal-title": "Drug Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0015",
"volume": "15",
"year": "1965"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.3204",
"article-title": "Epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore",
"author": "Young",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1488",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0020",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0025",
"unstructured": "Ou, X., Liu, Y., Lei, X.et al.Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV.Nat Commun11,1620 (2020). DOI.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0030",
"unstructured": "Huang, C. et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20) 30183-5 (2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45472",
"article-title": "Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses",
"author": "Zi-Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1686",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0035",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45538",
"article-title": "Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Patients Infected with 2019-New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Review and Perspective",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0040",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45123",
"article-title": "Perspectives on therapeutic neutralizing antibodies against the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1718",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0045",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Antibacterial Activity of Thymoquinone and Thymohydroquinone of Nigella sativa L. and Their Interaction with Some Antibiotics",
"author": "Halawani",
"first-page": "148",
"issue": "5–6",
"journal-title": "Advances in Biological Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0050",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "The anti-bacterial properties of Nigella sativa seeds: Active principle with some clinical application",
"author": "Topozada",
"first-page": "187",
"journal-title": "Journal of the Egyptian Medical Association",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0055",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1965"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01635581.2010.509832",
"article-title": "Review on Molecular and Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone in Cancer",
"author": "Banerjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "938",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrition and Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0060",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1081/DCT-120020404",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0065",
"unstructured": "Osama A. Badary, Ragia A. Taha, Ayman M. Gamal El-Din & Mohamed H. Abdel- Wahab(2003)Thymoquinone Is a Potent Superoxide Anion Scavenger,Drug and Chemical Toxicology,26:2,87-98,DOI:10.1081/DCT-120020404."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09674845.2010.11730285",
"article-title": "Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil and thymoquinone against toxicity induced by the anticancer drug cyclophosphamide",
"author": "Alenzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Biomedical Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0070",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Studies on the chemical constitution of Egyptian nigella sativa l",
"author": "El-Dakhakhany",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Seeds. Ii: The essential oil. Planta Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0075",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1963"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10715760600978815",
"article-title": "Nonenzymatic reduction of thymoquinone in physiological conditions",
"author": "Khalife",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Free Radical Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0080",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0192-0561(00)00036-9",
"article-title": "Protective effect of black seed oil from Nigella sativa against murine cytomegalovirus infection",
"author": "Salem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "729",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Int J Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0085",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0378-8741(80)90023-9",
"article-title": "Traditional medicine in health care",
"author": "Sayed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0090",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"article-title": "Determination of oxygen radical absorbance capacity of black cumin (nigella sativa) seed quinone compounds",
"author": "Tesarova",
"first-page": "213",
"journal-title": "Nat. Prod. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0095",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0100",
"unstructured": "Elsharkawy R,E,. Abdallah, M, E, Abo Markb, A. Potential Cytotoxic, Antifungal, and Antioxidant Activity of Dithymoquinone and Thymoquinone, Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences, 2021,48 (9)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph13120443",
"article-title": "FDA-Approved Drugs with Potent In Vitro Antiviral Activity against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus",
"author": "Mostafa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "443",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0105",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carres.2021.108246",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0110",
"unstructured": "Ahmed Khodair*, Ahmed A. El-Barbary; Dalia R. Emam; Nabila A. Kheder; Faisal Elmalki; Taibi Ben Hadda. Synthesis, Antiviral, and Molecular Docking Studies of Some Novel 1,2,4-Triazine Nucleosides as Potential Bioactive Compounds. Carbohydrate Research. 500 (2021) 108246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2021.108246"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0115",
"unstructured": "IhsaneELMeskini, LoicToupet, Maria Daoudi, AbdelaliKerbal, Diogo R. M. Moreira, Taibi B. Hadda. Is It Possible For The 2-[(4-chloro-phenyl)-(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)-methyl]-malonic acid diethyl ester To Present a Potential Candidate HIV-Integrase Inhibitor On The Basis of Its (O,N,O)-Ligand Structure. Moroccan Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, Vol 18, No 2 (2019) 36-45. https://doi.org/10.48369/IMIST.PRSM/jmch-v18i2.16384"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0120",
"unstructured": "Cruz-Rodriguez L., Rodolfo Barea, Zayas Tamayo A.M., Hochwimmer B., Ben Hadda T., Almalki F. A., Lambert Brown D, Pelaez Figueroa Y., Sanchez Batista L. and Warad I. ELIDAN certificate: BEHAVIOR is the key to save places from Covid-19. Journal of Bioscience &Biomedical Engineering. 1(2), 2020, pp1-21. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343794128_ELIDAN_certificate_BEHAVIOR_is_the_key_to _save_places_from_Covid-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cdc.2020.100593",
"article-title": "Synthesis and antimicrobial activity evaluation of some new 7-substituted quinolin-8-ol derivatives: POM analyses, docking, and identification of antibacterial pharmacophore sites",
"author": "Faydy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100593",
"journal-title": "Chemical Data Collections",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0125",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "19, 688–705",
"author": "Hadda",
"first-page": "688",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "DOI",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0130",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1381612826666201202125807",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0135",
"unstructured": "Shah Khalid*, Faisal A. Almalki, , Taibi Ben Hadda*, , Ammar Bader, , Tareq Abu-Izneid, , Malika Berredjem, , Eman R. Elsharkawy, Ali M . Alqahtani. “Medicinal Applications of Cannabinoids Extracted from Cannabis sativa (L.): A new Route to Fight against COVID-19?” Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2020. DOI:10.2174/1381612826666201202125807."
},
{
"DOI": "10.32604/biocell.2021.014004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0140",
"unstructured": "Saud Bawazeer, Asghar Khan, Abdur Rauf, Taibi Ben Hadda, Umer Rashid, Inamullah Khan, Muhammad Asif Nawaz, Md. Sahab Uddin, Ahmed Olatunde, Mohammad Ali Shariati. POM Analysis and Computational Interactions of 8-Hydroxydiospyrin Inside Active Site of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B. BIOCELL, 2021 45(3): 751-759. doi:10.32604/biocell.2021.014004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13369-020-05089-y",
"article-title": "Synthesis, Characterization, Biocomputational Modeling and Antibacterial Study of Novel Pyran Based on 8-Hydroxyquinoline",
"author": "Rbaa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5533",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Arab J Sci Eng",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0145",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104480",
"article-title": "Synthesis, biological activity and POM/DFT/docking analyses of annulated pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives: Identification of antibacterial and antitumor pharmacophore sites",
"author": "Bhat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104480",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0150",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573409916666191226110029",
"article-title": "Petra/Osiris/Molinspiration and Molecular Docking Analyses of 3-Hydroxy-Indolin-2-one Derivatives as Potential Antiviral Agents",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "CAD",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0155",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0160",
"unstructured": "Lakhrissi Y., Rbaa M., Mequedade M., Berkiks I., Mague J., El Hessni A., Ramli Y, Almalki F., Ben Hadda T., Lakhrissi B. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Evaluation of Biologycal Activity of Novel Heterocyclic Derivative of 8-Hydroxyquinoline. Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3589130"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00706-020-02711-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0165",
"unstructured": "MeriemGuerf, Malika Berredjem, AbdeslemBouzina, Taibi Ben Hadda, Christelle Marminon, KhadidjaOtmaneRachedi, Novel α-sulfamidophosphonates analogues of Fotemustine: Efficient synthesis using ultrasound under solvent-free conditions. MonatsheftefürChemie - Chemical Monthly, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02711-5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S1070428020070210",
"article-title": "Structure Determination and Quantum Chemical Analysis of 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Nitrile Imines and New Dipolarophiles and POM Analyses of the Products as Potential Breast Cancer Inhibitors",
"author": "Farghaly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1258",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Russ J Org Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0170",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0175",
"unstructured": "Ahmed Rakib, Saad Ahmed Sami, Nusrat Jahan Mimi, Md. Mustafiz Chowdhury, TaslimaAkter Eva, FirzanNainu, Arkajyoti Paul, Asif Shahriar, Abu MontakimTareq, Nazim Uddin Emon6, Sajal Chakraborty, Sagar Shil4, Sabrina Jahan Mily, Taibi Ben Hadda*, Faisal A. Almalki, Talha Bin Emran*. Immunoinformatics-guided design of an epitope-based vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndromecoronavirus spike glycoprotein. Computers in Biology and Medicine (CBM). Accepted for publication."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0180",
"unstructured": "Cruz-Rodriguez, Sanchez Batista, Hochwimmer, Ben Hadda T., Almalki F.A., Dilsiz N., Caparros J.L., Lambert Brown D., Ziarati P., Zayas Tamayo A.M., Pelaez Figueroa Y, Herrera Sanchez M.B., Garcia Hernandez A., Bin Zhao.How to Evaluate Viral Transmission in Enclosed Areas. Medical Geology saving places from Covid-19 Journal of Bioscience & Biomedical Engineering (J. B. Bio. Engine.), 2020, 1(1):1-8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C8NJ02081G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0185",
"unstructured": "Rajendra SukhdeoraoDongre*, Jyostna S. Meshram, Rupali SudhakarraoSelokar, Faisal A. Almalki, Taibi Ben Hadda*. Antibacterial activity of synthetic pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines armed with nitrile group: POM analyses and identification of pharmacophore sites of nitriles as important pro-drugs. New J. Chem., 2018, 42, 15610-15617.DOI: 10.1039/C8NJ02081G."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128423",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0190",
"unstructured": "I. Grib, M. Berredjem, K.O. Rachedi, S.-E. Djouad, S. Bouacida, R. Bahadi, T.-S. Ouk; M. Kadri, T. Ben Hadda, B. Belhania. NovelN-sulfonylphthalimides: Efficient synthesis, X-ray characterization, spectral investigations, POM analyses, DFT computations and antibacterial activity. Journal of Molecular Structure. Available online 14 May 2020, 128423. in press."
},
{
"article-title": "103850",
"author": "Elsharkawy",
"first-page": "103850",
"journal-title": "In press",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0195",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11164-016-2737-y",
"article-title": "Synthesis, characterization, POM analysis and antifungal activity of novel heterocyclic chalcone derivatives containing acylated pyrazole",
"author": "Al-Maqtari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1893",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Res Chem Intermed",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0200",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0205",
"unstructured": "S. Boussaidi1, Y. Alaoui, A. Eddiouane1, A. Fitri, A. TouimiBenjelloun, H.Zgou, H. Chaib, M. Bouachrine, M. Hamidi and T. Ben Hadda. Theoretical study of the effect of substitution with alternating donor and acceptor groups on the optoelectronic and photovoltaic properties ofsome oligomers containing thiophene and phenylene.Arabian Journal of Chemical and Environmental Research. Vol. 3 N° 1 (2016) 51– 63."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0210",
"unstructured": "Ghias Uddin, Abdur Rauf, Sania Bibi, Haroon Khan, Taibi Ben Hadda, Mohamed Fawzy Ramadan. Bioactive compounds andbiological activities of Alnusnitida.ZArznei- Gewurzpfla | 22 (3): 121–124 | ERLING Verlag GmbH & Co. KG 2017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573406416666200610185654",
"article-title": "Spiro Heterocyclic Compounds as Potential Anti-Alzheimer Agents (Part 2): Their Metal Chelation Capacity, POM Analyses and DFT Studies",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "834",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "MC",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0215",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127990",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0220",
"unstructured": "Bechlem K, Aissaoui M, Belhani B, Rachedi KO, Bouacida S, Bahadi R, Djouad SE, Mansour RB, Bouaziz M, Almalki FA, Ben Hadda T, Berredjem, M. Synthesis, X-ray crystallographic study and molecular docking of new a-sulfamidophosphonates: POM analyses of their cytotoxic activity. Journal of Molecular Structure 2020, 1210, 127990. doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.07.053",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0225",
"unstructured": "Rachedi KT, Ouk T-S,BahadiR,BouzinaA,Djouad S-E,BechlemK,ZerroukiR,BenHaddaT,AlmalkiFA,Berredjem M. Synthesis, DFT and POM analyses of cytotoxicity activity of α-amidophosphonates derivatives: Identification of potential antiviralO,O-pharmacophore site. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2019, 1197, 196-203. doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.07.053."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02689",
"article-title": "Synthesis, antibacterial properties and bioinformatics computationalanalyses of novel 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives",
"author": "Rbaa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Heliyon 5",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0230",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22146/ijc.46375",
"article-title": "POM Analyses and Molecular Docking of Novel Oxazaphosphinanes: Identification of Antifungal Pharmacophore Site",
"author": "Rachedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "440",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Indones. J. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0235",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Synthesis, Characterization, X-Ray Crystal Study and Bioactivities of Pyrazole Derivatives: Identification of Antitumor, Antifungal and Antibacterial Pharmacophore Sites",
"author": "Titi",
"journal-title": "Journal of Molecular Structure",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0240",
"volume": "127625",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0245",
"unstructured": "Warad, Ismail; Al-Nuri, Mohammed; Ali, Oraib; Abu-Reidah, Ibrahim M.; Barakat, Assem; Ben Hadda, Taibi; Zarrouk, Abdelkader; Radi, Smaail; Touzani, Rachid; Elmsellem, Hicham.Synthesis, Physico-Chemical, Hirschfield Surface and DFT/B3LYP Calculation of Two New Hexahydropyrimidine Heterocyclic Compounds. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Article Vol. 38, No. 4, 2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Synthesis of New Heterocyclic Systems Oxazino Derivatives of 8-Hydroxyquinoline: Drug Design and POM Analyses of Substituent Effects on their Potential Antibacterial Properties, Chemical Data",
"author": "Rbaa",
"first-page": "100306",
"journal-title": "Collections",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0250",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871523018666190625170802",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0255",
"unstructured": "JoazaizulfazliJamalis, FatenSyahira Mohamed Yusof, Subhash Chander, Roswanira Abd. Wahab, Deepak P. Bhagwat, Murugesan Sankaranarayanan, Faisal Almalki, Taibi Ben Hadda. Psoralen Derivatives: Synthetic Strategy and Pharmacological Properties. Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 19, 222-239. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666190625170802."
},
{
"DOI": "10.22159/ijpps.2019v11i7.33163",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0260",
"unstructured": "Amel M. Kamal , Mohamed I. S. Abdelhady , Taibi Ben Hadda. Two novel flavone C-glycosides isolated from Podocarpusgracilior: POM analyses and in-vitro anticancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 11, Issue 7, 2019, 57-62. DOI:10.22159/ijpps.2019v11i7.33163"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389557519666190222172757",
"article-title": "Pharmacophores modeling in terms of prediction of theoretical physico-chemical properties and verification by experimental correlations of Carbacylamidophosphates (CAPh) and Sulfanylamidophosphates (SAPh) Tested as New Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors",
"author": "Amirkhanov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Mini Rev Med Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0265",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0270",
"unstructured": "Fouad El Kalai, Tarik Chelfi, Noureddine Benchat, BrahimHacht, Mohamed Bouklah, AbdelmalekElaatiaoui, Said Daoui, Mustapha Allali, Taibi Ben Hadda, Faisal Almalki. New organic extractant based on pyridazinone scaffold compounds: liquid-Liquid extraction study and DFT calculations. Journal of Molecular Structure, 119 (2019) 24-31. DOI 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.033."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0275",
"unstructured": "AliasgharJarrahpour, RoghayehHeiran, VéroniqueSinou, Christine Latour, Lamia DjouhriBouktab, Jean Michel Brunel, Javed Sheikhand Taibi Ben Hadda. Synthesis of New β-Lactams Bearing the Biologically Important Morpholine Ring and POM Analyses of Their Antimicrobial and Antimalarial Activities. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (2019), 18 (1): 34-48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389557517666170713114039",
"article-title": "Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Some semi-Rigid Spiro Heterocycles: POM Analyses and Crystalline Structure of Pharmacophore Site",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "711",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "MRMC",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0280",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-017-1920-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0285",
"unstructured": "JavadAmeriRad, AliasgharJarrahpour, ChristineLatour, VeroniqueSinou, JeanMichelBrunel, HsaineZgou, YahiaMabkhot, TaibiBenHadda, EdwardTuros. Synthesis and antimicrobial/antimalarial activities of novel naphthalimidotrans-β-lactam derivatives.Med Chem Res26 (2017),2235–2242. doi:10.1007/s00044-017-1920-z"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0290",
"unstructured": "Ghias Uddin,·Nasruddin,·Abdur Rauf,·Haroon khan, Nilufar Z. Mamadalieva, Ajmal Khan, Umar Farooq, Taibi Ben Hadda and·Mohamed Fawzy Ramadan . Phytochemical analysis, urease inhibitory effect and antimicrobial potential of Allium humile. ZeitschriffürArznei- und Gewürzpflanzen, 2018, 22 (4): 173-175."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.015",
"article-title": "Antihypertensive and vasodilator effects of methanolic extract of Inula viscosa: Biological evaluation and POM analysis of cynarin, chlorogenic acid as potential hypertensive",
"author": "Hakkou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0295",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17344/acsi.2016.2428",
"article-title": "Design, Synthesis, in vitro Antiproliferative Activity, Binding Modeling of 1,2,4,-Triazoles as New Anti-Breast Cancer Agents",
"author": "Genc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "726",
"journal-title": "ACSi",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0300",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.03.013",
"article-title": "Synthesis and Study of Anti-HIV-1 RT Activity of 5-benzoyl-4-methyl-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-1,5-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives",
"author": "Chander",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "74",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic Chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0305",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11164-016-2578-8",
"article-title": "Saud Bawazeer, and Taibi Ben Hadda. How to Improve Antifungal Bioactivity: POM and DFT Study of some Chiral Amides Derivatives of Diacetyl-L-tartaric Acid and Amines",
"author": "Mabkhot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8055",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Research on Chemical Intermediates",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0310",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573407211666151012191902",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0315",
"unstructured": "Abdur Rauf, Ghias Uddin, Bina S. Siddiqui, Haroon Khan, Mujeeb-ur-Rehman, Ismail Warad,Taibi Ben Hadda, Seema Patel, Ajmal Khan and Umar Farooq. POM Analysis of Phytotoxic Agents from Pistaciaintegerrima Stewart. Current Bioactive Compounds 11 (2015) 231-238."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules21020222",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0320",
"unstructured": "Yahia Mabkhot, Alotaibi Alatibi, Nahed El-sayed, Nabila Kheder,Abdul Wadood, Abdur Rauf, Saud Bawazeer, Salim Al-Showiman, Taibi Ben Hadda. Experimental-ComputationalEvaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Novel Armed Thiophene Derivatives. Molecules2016,21(2), 222; doi:10.3390/molecules21020222."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/kim-1509-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0325",
"unstructured": "Esra Tatar, SevilŞenkardeş, H.Erdinç Sellitepe, Ş.Güniz Küçükgüzel, ŞengülAlpayKaraoğlu, ArifBozdeveci, Erik De Clercq, Christophe Pannecouque, Taibi Ben Hadda,İlkayKüçükgüzel. Synthesis, prediction of molecular properties and antimicrobial activity of some acylhydrazones derived from N-(arylsulfonyl)methionine. Turkish Journal of Chemistry . 5/1/16, Vol. 40 Issue 3, 510-534."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0330",
"unstructured": "Said Tighadouni, SmaailRadi, Muhammad Sirajuddin*, Mehmet Akkurt, NamıkÖzdemir, Matloob Ahmad, Yahia N. Mabkhot and Taibi Ben Hadda. In Vitro Antifungal, Anticancer Activities and POM Analyses of a Novel Bioactive Schiff Base 4-{[(E)-furan-2-ylmethylidene]amino}p-henol: Synthesis, Characterization and Crystal Structure. J.Chem.Soc.Pak., (2016) 38(1):157-165."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules21020214",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0335",
"unstructured": "YahiaMabkhot, Fahad Aldawsari, Salim Al-Showiman, Assem Barakat, Saied Soliman, Mohammad Choudhary, Sammer Yousuf, Taibi Ben Hadda, Mohammad Mubarak. Synthesis, Molecular Structure Optimization, and Cytotoxicity Assay of a Novel 2-Acetyl-3-amino-5-[(2-oxopropyl)sulfanyl]-4-cyanothiophene. Molecules (2016) 21, 214;"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11094-016-1417-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0340",
"unstructured": "Zara Sajid, Matloob Ahmad*, Sana Aslam, Usman Ali Ashfaq, Ameer Fawad Zahoor, Furqan Ahmad Saddique, Masood Parvez, Abdul Hameed, Sadia Sultan, HsaineZgou and Taibi Ben Hadda. Novel armed pyrazolobenzothiazine derivatives: synthesis, X-ray crystal structure and POM analyses of biological activity against drug resistant clinical isolate of staphylococus aureus, Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, Vol. 50, No. 3, June, 2016 (Russian Original Vol. 50, No. 3, March, 2016). DOI 10.1007/s11094-016-1417-y"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573407211666151012191902",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0345",
"unstructured": "Abdur Rauf, Ghias Uddin, Bina S. Siddiqui, Haroon Khan, Mujeeb-ur-Rehman, Ismail Warad, Taibi Ben Hadda, Seema Patel, Ajmal Khan and Umar Farooq. POM Analysis of Phytotoxic Agents from Pistaciaintegerrima Stewart. Current Bioactive Compounds. Current Bioactive Compounds, 2015, 11(4): 231-238."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786419.2015.1045508",
"article-title": "Taibi Ben Hadda. Bioassay-guided isolation and POM analyses of a new immunomodulatory polyphenolic constituent from Callistemon Viridiflorus",
"author": "Abdelhady",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1131",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Natural Product Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0350",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "POM Analyses of Constituents of Rosmarinus officinalis and Their Synergistic Effect in Experimental Diabetic Rats",
"author": "Header",
"first-page": "018",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Bioanal Biomed",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0355",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17344/acsi.2015.1357",
"article-title": "Computational POM and DFT Evaluation of Experimental in-vitro Cancer Inhibition of Staurosporine-Ruthenium(II) Complexes: The Power Force of Organometallics in Drug Design",
"author": "Ben Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "Acta Chim. Slov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0360",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0365",
"unstructured": "Javed Sheikh • Vijay Taile • Ajay Ghatole • Vishwas Ingle • Murat Genc • SihamLahsasni • Taibi Ben Hadda• Kishor Hatzade. Antimicrobial/antioxidant activity and POM analyses of novel7-O-b-D-glucopyranosyloxy-3-(4,5-disubstitutedimidazol-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-ones. Med Chem Res 2015. DOI 10.1007/s00044-015-1326-8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules20021824",
"article-title": "Synthesis, bioactivity, molecular docking and POM anlysis of novel substituted thieno[2,3-b]thiophenes and related congeners",
"author": "Mabkhot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1824",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0370",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-014-1297-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0375",
"unstructured": "Moulay H. Youssoufi, Pramod K. Sahu, Praveen K. Sahu, Dau D. Agarwal, Ahmad Mushtaq, MouslimMessali, SihamLahsasni, Taibi Ben Hadda. POM analyses of Antimicrobial Activity of 4H-Pyrimido[2,1-b]Benzothiazole, Pyrazole and Benzylidene Derivatives of Curcumin. Med Chem Res (2015) 24:2381–2392. DOI 10.1007/s00044-014-1297-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2014.08.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0380",
"unstructured": "Yahia Nasser Mabkhot, Assem Barakat, Sammer Yousuf, M. Iqbal Choudhary, Wolfgang Frey, TaibiBenHadda, Mohammad S. Mubarak.Substitutedthieno[2,3-b]thiophenes and related congeners: Synthesis, <beta>-glucuronidase inhibition activity, crystal structure, and POM analyses. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2014, 22(23):6715–6725. DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.08.014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-014-1211-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0385",
"unstructured": "MouslimMessali • Mohamed R. Aouad • Adeeb A.-S. Ali, NadjetRezki • Taibi Ben Hadda • BelkheirHammouti. Synthesis, characterization and POM analysis of novel bioactive imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2014. DOI 10.1007/s00044-014-1211-x"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-012-0392-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0390",
"unstructured": "B. Bennani, A. Kerbal, B. F. Baba, M. Daoudi, I. Warad, M. Aljofan, A. M. Alafeefy, V. Masand, T. Ben Hadda. Synthesis, characterization, bioactivity, and POM analyses of isothiochromeno[3,4-e][1,2]oxazines. Medicinal Chemistry Research2013, 22(10): 4798-4809. doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0392-4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-013-0781-3",
"article-title": "Computational POM Evaluation of Experimental in vitro Trypanosoma cruzi and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Inhibition of Heterocyclic-2-Carboxylic Acid (3-Cyano-1,4-di-Noxidequinoxalin-2-yl)amide Derivatives",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1956",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Medicinal Chemistry Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0395",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-013-0755-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0400",
"unstructured": "HarjeetJuneja, DhanashriPanchbhai, Javed Sheikh, Vishwas Ingle, Taibi Ben Hadda. Synthesis, Antibacterial Screening and POM Analyses of Novel Bis-Isoxazolyl/Pyrazoyl-1,3-diols. 2013, Med Chem Res. DOI 10.1007/s00044-013-0755-5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-013-0707-0",
"article-title": "POM Analyses of Antimicrobial activity of Some 2,3-Armed 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-Benzothiophenes: Favourable and UnfavourablePhysico-chemical Parameters in Design of Antibacterial and Mycolytic Agents",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Medicinal Chemistry Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0405",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-013-0614-4",
"article-title": "POM analyses for Antimicrobial evaluation of Thienopyrimidinones Derivatives: A Rapid Method for Drug Design",
"author": "Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Med Chem Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0410",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-012-0238-0",
"article-title": "POM analyses of antitrypanosomal activity of 2-iminobenzimidazoles: favorable and unfavorable parameters for drugs optimization",
"author": "Ben Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2437",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Med Chem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0415",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-012-0143-6",
"article-title": "Tautomeric Origin of Dual Effects of N1-nicotinoyl-3-(4’-hydroxy-3’-methyl phenyl)-5-[(sub)phenyl]-2-pyrazolines on Bacterial and Viral Strains: POM Analyses as New Efficient Bioinformatics' Platform to Predict and Optimize Bioactivity of Drugs",
"author": "Ben Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1438",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Med Chem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0420",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-012-0120-0",
"article-title": "Computational POM and 3D-QSAR Evaluation of Experimental in vitro HIV-1 Integrase Inhibition of Amide-containing di-Ketoacids",
"author": "Ben Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1456",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Medicinal Chemistry Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0425",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11164-012-0679-6",
"article-title": "POM as a quick bioinformatic platform to select flavonoids and their metabolites as potential and efficient HIV-1 integrase inhibitors",
"author": "Ben Hadda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1227",
"journal-title": "Res Chem Intermed",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0430",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.05.115",
"article-title": "Vesna Rastija, CoMSIA and POM analyses of anti-malarial activity of synthetic prodiginines",
"author": "Mahajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4827",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0435",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11164-012-0729-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0440",
"unstructured": "T. Ben Hadda, T. Fergoug and I. Warad. POM Theoretical Calculations and Experimental Verification of Antibacterial Potentialof 5-Hydroxy-4-(Substituted-Amino)-2(5H)-Furanones. Res Chem Intermed (2013) 39:1963–1971. DOI: 10.1007/s11164-012-0729-0. (Impact Factor = 0.715)."
},
{
"article-title": "POM as Efficient Tools to Predict and Improve Both Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Aryl Aldazines",
"author": "Fathi",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Method. Mol. Design.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0445",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Exploring interactions of 2-Amino-6-arylsulfonylbenzonitrile derivatives as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors of H IV-1 using docking studies",
"author": "Masand",
"first-page": "39",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Method. Mol. Design",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0450",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00044-011-9723-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0455",
"unstructured": "A. Jarrahpour, J. Fathi, M. Mimouni, T. Ben Hadda, J. Sheikh, Z. H. Chohan and A. Parvez. Petra, Osiris and Molinspiration (POM) Together as a Successful Support in Drug Design: Antibacterial Activity and Biopharmaceutical Characterization of Some Azo Schiff Bases. Med Chem Res (2012) 21(8): 1984–1990. DOI 10.1007/s00044-011-9723-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S308863",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587_b0460",
"unstructured": "Badary OA, Hamza MS, Tikamdas R. Thymoquinone: A Promising Natural Compound with Potential Benefits for COVID-19 Prevention and Cure.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:1819-1833.https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S308863"
}
],
"reference-count": 92,
"references-count": 92,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Bioorganic Chemistry"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Organic Chemistry",
"Drug Discovery",
"Molecular Biology",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}