Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study
et al., International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306, Feb 2023
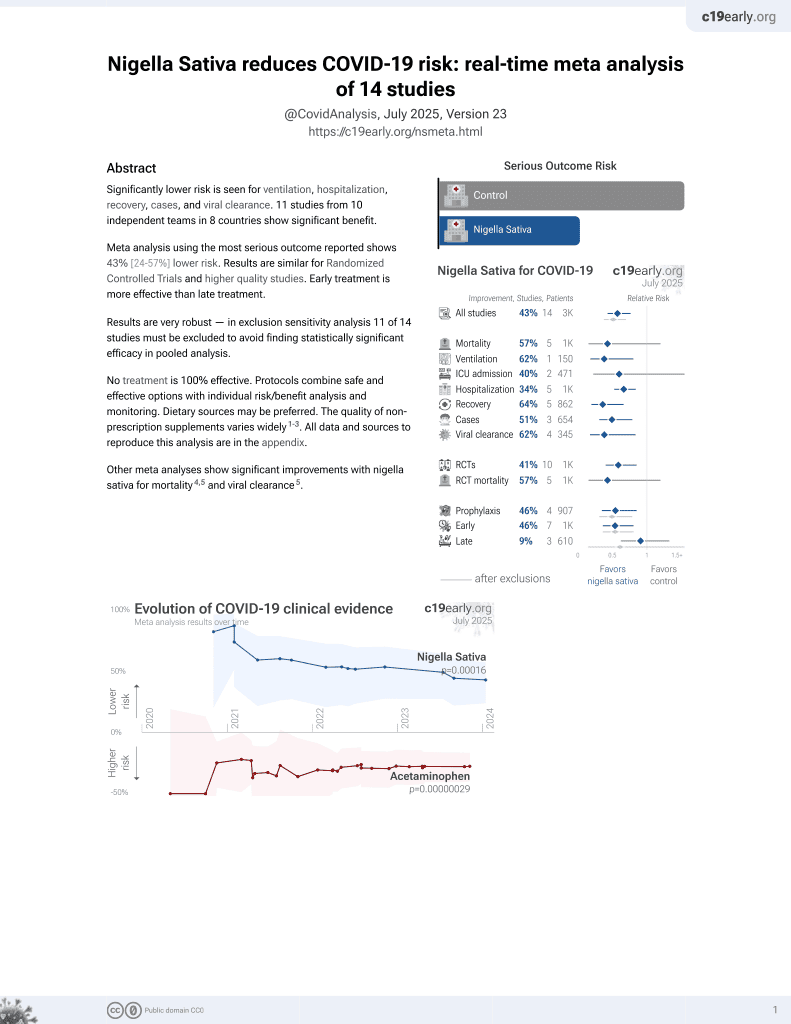
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
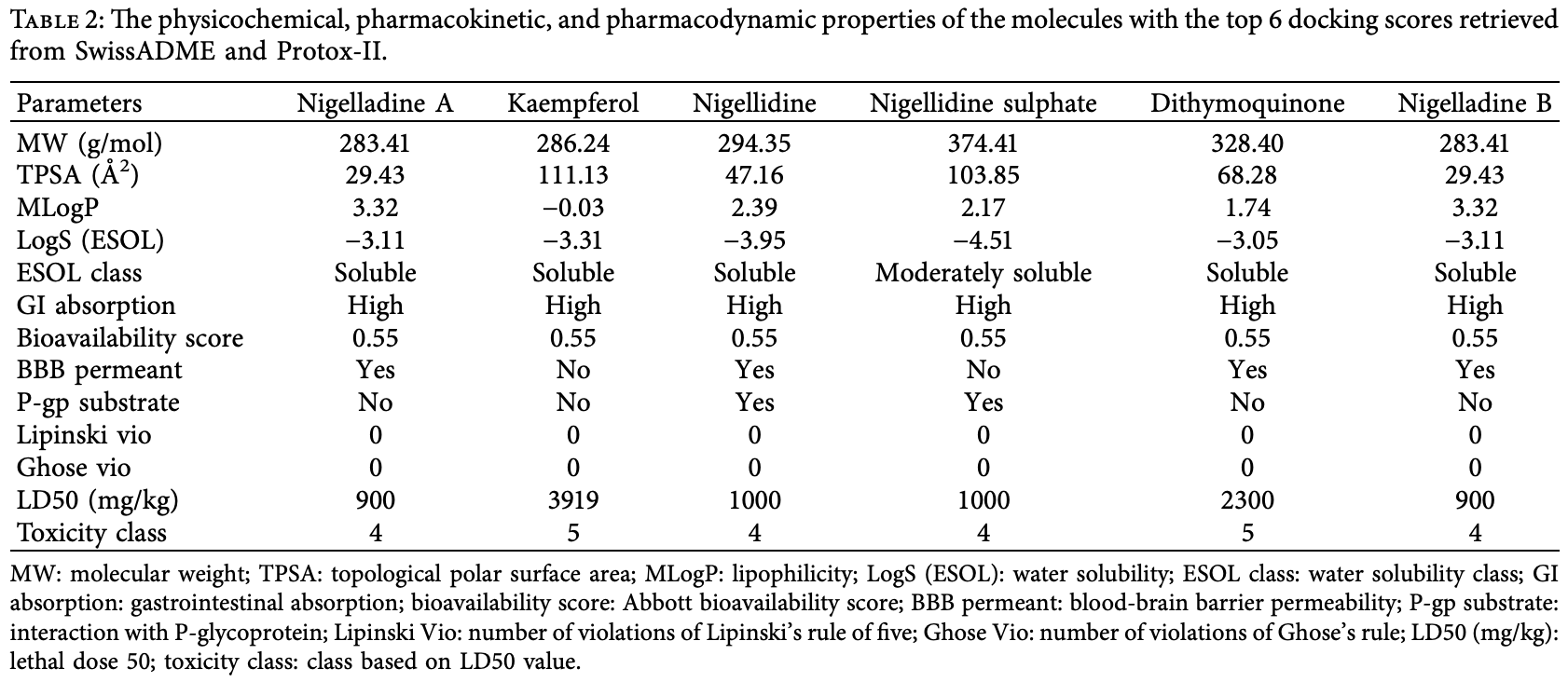
In silico study of 96 phytochemical compounds of nigella sativa, identifying Nigelladine A as the most promising compound for SARS-CoV-2 inhibition with the highest docking scores for the spike protein and Mpro. Dithymoquinone, kaempferol, Nigelladine B, Nigellidine, and Nigellidine sulphate also showed high docking scores.
22 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nigella sativa for COVID-19:
1.
Rahman et al., In Silico Screening of Potential Drug Candidate against Chain a of Coronavirus Binding Protein from Major Nigella Bioactive Compounds, Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, doi:10.9734/ajarr/2024/v18i7697.
2.
Zafar Nayak Snehasis, S., Molecular Docking to Discover Potential Bio-Extract Substitutes for Hydroxychloroquine against COVID-19 and Malaria, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), doi:10.21275/SR24323192940.
3.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
4.
Ali et al., Computational Prediction of Nigella sativa Compounds as Potential Drug Agents for Targeting Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Pakistan BioMedical Journal, doi:10.54393/pbmj.v6i3.853.
5.
Miraz et al., Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306.
6.
Sherwani et al., Pharmacological Profile of Nigella sativa Seeds in Combating COVID-19 through In-Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr10071346.
7.
Khan et al., Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. An in-silico study, Brazilian Journal of Biology, doi:10.1590/1519-6984.25066.
8.
Esharkawy et al., In vitro Potential Antiviral SARS-CoV-19- Activity of Natural Product Thymohydroquinone and Dithymoquinone from Nigela sativia, Bioorganic Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105587.
9.
Banerjee et al., Nigellidine (Nigella sativa, black-cumin seed) docking to SARS CoV-2 nsp3 and host inflammatory proteins may inhibit viral replication/transcription, Natural Product Research, doi:10.1080/14786419.2021.2018430.
10.
Rizvi et al., Identifying the Most Potent Dual-Targeting Compound(s) against 3CLprotease and NSP15exonuclease of SARS-CoV-2 from Nigella sativa: Virtual Screening via Physicochemical Properties, Docking and Dynamic Simulation Analysis, Processes, doi:10.3390/pr9101814.
11.
Mir et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors from the major phytochemicals of Nigella sativa: An in silico approach, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.002.
12.
Hardianto et al., Exploring the Potency of Nigella sativa Seed in Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.22146/ijc.65951.
13.
Maiti et al., Active-site Molecular docking of Nigellidine to nucleocapsid/Nsp2/Nsp3/MPro of COVID-19 and to human IL1R and TNFR1/2 may stop viral-growth/cytokine-flood, and the drug source Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds show potent antioxidant role in experimental rats, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-26464/v1.
14.
Duru et al., In silico identification of compounds from Nigella sativa seed oil as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets, Bulletin of the National Research Centre, doi:10.1186/s42269-021-00517-x.
15.
Bouchentouf et al., Identification of Compounds from Nigella Sativa as New Potential Inhibitors of 2019 Novel Coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular Docking Study, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12055716.v1.
16.
Ali (B) et al., In vitro inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa L. extracts on SARS-COV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interaction, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100759.
17.
Bostancıklıoğlu et al., Nigella sativa, Anthemis hyaline and Citrus sinensis extracts reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by fluctuating Rho GTPase, PI3K-AKT, and MAPK/ERK pathways in HeLa-CEACAM1a cells, Gene, doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148366.
Miraz et al., 20 Feb 2023, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Contact: skkbd415@juniv.edu.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study
International Journal of Clinical Practice, doi:10.1155/2023/9917306
COVID-19 has been a threat to the entire world for more than two years since its outbreak in December 2019 in Wuhan city of China. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent, had been reported to mutate over time exposing new variants. To date, no impeccable cure for the disease has been unveiled. Tis study outlines an extensive in silico approach to scrutinize certain phytochemical compounds of Nigella sativa (mainly the black cumin seeds) targeting the spike protein and the main protease (M pro ) enzyme of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Te objective of this study is to investigate the extracted compounds with a view to developing a potential inhibitor against the concerned SARS-CoV-2 variant. Te investigation contemplates drug-likeness analysis, molecular docking study, ADME and toxicity prediction, and molecular dynamics simulation which have been executed to elucidate diferent phytochemical and pharmacological properties of the tested compounds. Based on drug-likeness parameters, a total of 96 phytochemical compounds from N. sativa have been screened in the study. Interestingly, Nigelladine A among the compounds exhibited the highest docking score with both the targets with the same binding afnity which is −7.8 kcal/mol. However, dithymoquinone, kaempferol, Nigelladine B, Nigellidine, and Nigellidine sulphate showed mentionable docking scores. Molecular dynamics up to 100 nanoseconds were simulated under GROMOS96 43a1 force feld for the protein-ligand complexes exhibiting the top-docking score. Te root mean square deviations (RMSD), root mean square fuctuations (RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), solvent accessible surface area (SASA), and the number of hydrogen bonds have been evaluated during the simulation. From the fndings, the present study suggests that Nigelladine A showed the most promising results among the selected molecules. Tis framework, however, interprets only a group of computational analyses on selected phytochemicals. Further investigations are required to validate the compound as a promising drug against the selected variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Conflicts of Interest Te authors declare that they have no conficts of interest.
Supplementary Materials Te supplementary materials include the data of Lipinski's Rule of Five and Ghose's Rules Data and Docking scores. (Supplementary Materials)
References
Ahmad, Abbasi, Shahid, Gul, Abbasi, Molecular docking, simulation and MM-PBSA studies of nigella sativa compounds: a computational quest to identify potential natural antiviral for COVID-19 treatment, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Ahmad, Husain, Mujeeb, A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: a miracle herb, Asian Pacifc Journal of Tropical Biomedicine
Amadei, Linssen, Berendsen, Essential dynamics of proteins, Proteins
Banerjee, Eckert, Schrey, Preissner, ProTox-II: a webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals, Nucleic Acids Research
Daina, Michielin, Zoete, SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules, Scientifc Reports
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B. 1.1. 529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell
Ghose, Viswanadhan, Wendoloski, A knowledge-based approach in designing combinatorial or medicinal chemistry libraries for drug discovery. 1. A qualitative and quantitative characterization of known drug databases, Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, New England Journal of Medicine
Guex, Peitsch, SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-Pdb Viewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling, Electrophoresis
Hitchcock, Pennington, Structure− brain exposure relationships, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Huang, Yang, Xu, Xu, Liu, Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
Jassim, Naji, Novel antiviral agents: a medicinal plant perspective, Journal of Applied Microbiology
Kim, Tiessen, Bolton, PubChem substance and compound databases, Nucleic Acids Research
Koshak, Koshak, Nigella sativa L as a potential phytotherapy for coronavirus disease 2019: a mini review of in silico studies, Current Terapeutic Research
Li, Wu, Nie, Te impact of mutations in SARS-CoV-2 spike on viral infectivity and antigenicity, Cell
Lill, Danielson, Computer-aided drug design platform using PyMOL, Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design
Lipinski, Lombardo, Dominy, Feeney, Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews
Liu, Yang, Gan, Chen, Xiao et al., CB-Dock2: improved protein-ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template ftting, Nucleic Acids Research
Lobanov, Bogatyreva, Galzitskaya, Radius of gyration as an indicator of protein structure compactness, Molecular Biology
Macalino, Gosu, Hong, Choi, Role of computer-aided drug design in modern drug discovery, Archives of Pharmacal Research
Mengist, Dilnessa, Jin, Structural basis of potential inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Frontiers of Chemistry
Mohanraj, Karthikeyan, Vivek-Ananth, IMPPAT: a curated database of Indian medicinal plants, phytochemistry and therapeutics, Scientifc Reports
Nadkarni, Crocus sativus, Nigella sativa
Pace, Fu, Fryar, Contribution of hydrogen bonds to protein stability, Protein Science
Pajouhesh, Lenz, Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs, NeuroRx
Rose, Prlić, Altunkaya, Te RCSB protein data bank: integrative view of protein, gene and 3D structural information, Nucleic Acids Research
Schüttelkopf, Van Aalten, PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes, Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography
Shang, Wan, Luo, Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Tang, Bidon, Jaimes, Whittaker, Daniel, Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism ofers a potential target for antiviral development, Antiviral Research
Tiel, Herold, Schelle, Siddell, Viral replicase gene products sufce for coronavirus discontinuous transcription, Journal of Virology
Van Der, Spoel, Lindahl, Hess, Groenhof et al., GROMACS: fast, fexible, and free, Journal of Computational Chemistry
Xia, Zhu, Liu, Fusion mechanism of 2019-nCoV and fusion inhibitors targeting HR1 domain in spike protein, Cellular and Molecular Immunology
Yang, Yang, Ding, Te crystal structures of severe acute respiratory syndrome virus main protease and its complex with an inhibitor, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, New England Journal of Medicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/9917306",
"ISSN": [
"1742-1241",
"1368-5031"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2023/9917306",
"abstract": "<jats:p>COVID-19 has been a threat to the entire world for more than two years since its outbreak in December 2019 in Wuhan city of China. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent, had been reported to mutate over time exposing new variants. To date, no impeccable cure for the disease has been unveiled. This study outlines an extensive in silico approach to scrutinize certain phytochemical compounds of Nigella sativa (mainly the black cumin seeds) targeting the spike protein and the main protease (Mpro) enzyme of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The objective of this study is to investigate the extracted compounds with a view to developing a potential inhibitor against the concerned SARS-CoV-2 variant. The investigation contemplates drug-likeness analysis, molecular docking study, ADME and toxicity prediction, and molecular dynamics simulation which have been executed to elucidate different phytochemical and pharmacological properties of the tested compounds. Based on drug-likeness parameters, a total of 96 phytochemical compounds from N. sativa have been screened in the study. Interestingly, Nigelladine A among the compounds exhibited the highest docking score with both the targets with the same binding affinity which is −7.8 kcal/mol. However, dithymoquinone, kaempferol, Nigelladine B, Nigellidine, and Nigellidine sulphate showed mentionable docking scores. Molecular dynamics up to 100 nanoseconds were simulated under GROMOS96 43a1 force field for the protein-ligand complexes exhibiting the top-docking score. The root mean square deviations (RMSD), root mean square fluctuations (RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), solvent accessible surface area (SASA), and the number of hydrogen bonds have been evaluated during the simulation. From the findings, the present study suggests that Nigelladine A showed the most promising results among the selected molecules. This framework, however, interprets only a group of computational analyses on selected phytochemicals. Further investigations are required to validate the compound as a promising drug against the selected variant of SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"9917306",
"9917306"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1566-2272",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Miraz",
"given": "Md Mehedy Hasan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Ullah",
"given": "Md Afif",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Nayem",
"given": "Abdullah Al",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Chakrobortty",
"given": "Brototi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Deb",
"given": "Sanjoy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Laskar",
"given": "Anee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Tithi",
"given": "Nishita Umaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Saha",
"given": "Nilay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7956-169X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jagannath University, Dhaka 1100, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Anita Rani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Alam",
"given": "K. M. Khairul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Wahed",
"given": "Tania Binte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7131-1752",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Preventive Dentistry Department, Orthodontic Division, College of Dentistry, Jouf University, Sakaka 72345, Saudi Arabia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Dental Research Cell, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Chennai, India"
},
{
"name": "Department of Public Health, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Khursheed Alam",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5130-7163",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Jahangirnagar University, Savar, Dhaka 1342, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Kundu",
"given": "Sukalyan Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Clinical Practice",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Clinical Practice",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-20T13:35:21Z",
"timestamp": 1676900121000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-20T13:35:24Z",
"timestamp": 1676900124000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sainaghi",
"given": "Pier P.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-21T05:37:06Z",
"timestamp": 1676957826632
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1676851200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ijclp/2023/9917306.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ijclp/2023/9917306.xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ijclp/2023/9917306.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "98",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-14",
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Hindawi Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "W. J. Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "World Health organization",
"author": "Who Coronavirus (Covid-19) Dashboard",
"key": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3"
},
{
"article-title": "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104792",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0374-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.75.14.6676-6681.2001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1835675100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.622898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.02026.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "13"
},
{
"article-title": "WHO establishes the global centre for traditional medicine in India",
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Crocus sativus, Nigella sativa",
"author": "K. Nadkarni",
"first-page": "386",
"key": "15",
"volume-title": "Indian Materia Medica",
"year": "1976"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2221-1691(13)60075-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.curtheres.2020.100602",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1775129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12272-015-0640-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0169-409x(96)00423-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/cc9800071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv951",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-22631-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "24"
},
{
"article-title": "The RCSB protein data bank: integrative view of protein, gene and 3D structural information",
"author": "P. W. Rose",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"key": "25",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10822-010-9395-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/elps.1150181505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep42717",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gky318",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20291",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/s0907444904011679",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1602/neurorx.2.4.541",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm060642i",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.340170408",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/s0026893308040195",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pro.2449",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "37"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijclp/2023/9917306/"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nigelladine A among Selected Compounds from Nigella sativa Exhibits Propitious Interaction with Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2023"
}