Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397, Feb 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
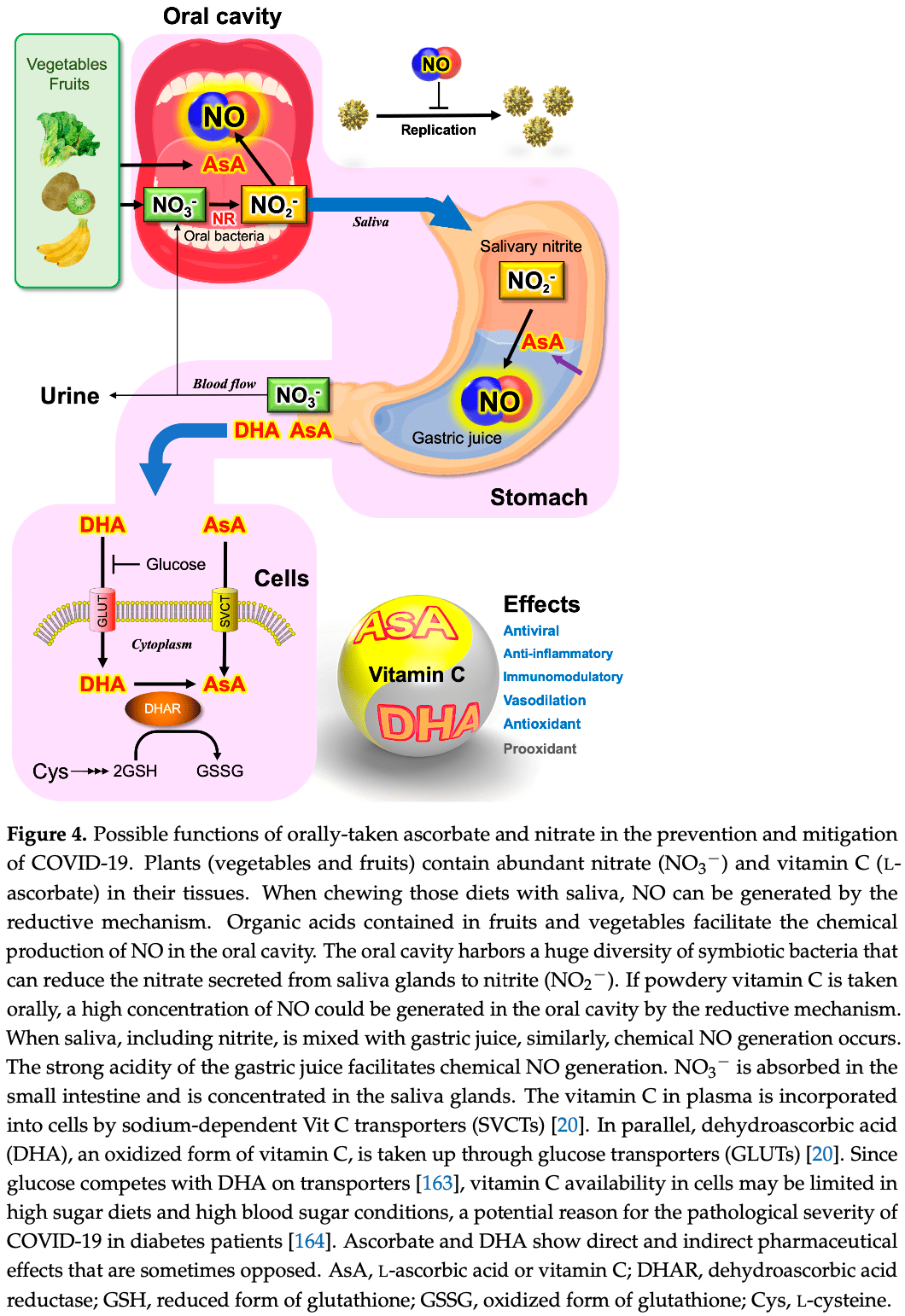
Extensive review of vitamin C and nitric oxide focusing on the potential antiviral activity of vitamin C for SARS-CoV-2 via the production of nitric oxide. Authors note that vegetables are a major dietary source of nitrate, and that dietary vitamin C from fruits and vegetables can reduce nitrite to produce nitric oxide in the oral cavity when chewing foods.
Authors conclude that intermittent bursts of nitric oxide, for example as generated by the combination of nitrite and vitamin C, is a potential therapeutic treatment to prevent and mitigate COVID-19.
Authors also note that nitric oxide may be related to the observed lower than expected risks seen with asthma and smoking. Elevated levels of nitric oxide in the breath are used for diagnosing asthma, and smoking involves bursts of concentrated nitric oxide in cigarette smoke.
Study covers nitric oxide and vitamin C.
1.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
4.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
5.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
6.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
7.
Hemilä et al., Rebound effect explains the divergence in survival after 5 days in a controlled trial on vitamin C for COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1391346.
8.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
9.
Yamasaki et al., Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397.
10.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
11.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
12.
Hemilä (B) et al., Bias against Vitamin C in Mainstream Medicine: Examples from Trials of Vitamin C for Infections, Life, doi:10.3390/life12010062.
13.
May et al., Therapeutic potential of megadose vitamin C to reverse organ dysfunction in sepsis and COVID-19, British Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bph.15579.
15.
Holford et al., Vitamin C—An Adjunctive Therapy for Respiratory Infection, Sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123760.
Yamasaki et al., 3 Feb 2023, Japan, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: yamasaki@sci.u-ryukyu.ac.jp (corresponding author).
Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397
Linus Pauling, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, suggested that a high dose of vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) might work as a prevention or treatment for the common cold. Vitamin C therapy was tested in clinical trials, but clear evidence was not found at that time. Although Pauling's proposal has been strongly criticized for a long time, vitamin C therapy has continued to be tested as a treatment for a variety of diseases, including coronavirus infectious disease 2019 . The pathogen of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, belongs to the β-coronavirus lineage, which includes human coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This review intends to shed new light on vitamin C antiviral activity that may prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection through the chemical production of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a gaseous free radical that is largely produced by the enzyme NO synthase (NOS) in cells. NO produced by upper epidermal cells contributes to the inactivation of viruses and bacteria contained in air or aerosols. In addition to enzymatic production, NO can be generated by the chemical reduction of inorganic nitrite (NO 2 − ), an alternative mechanism for NO production in living organisms. Dietary vitamin C, largely contained in fruits and vegetables, can reduce the nitrite in saliva to produce NO in the oral cavity when chewing foods. In the stomach, salivary nitrite can also be reduced to NO by vitamin C secreted from the epidermal cells of the stomach. The strong acidic pH of gastric juice facilitates the chemical reduction of salivary nitrite to produce NO. Vitamin C contributes in multiple ways to the host innate immune system as a first-line defense mechanism against pathogens. Highlighting chemical NO production by vitamin C, we suggest that controversies on the therapeutic effects of vitamin C in previous clinical trials may partly be due to less appreciation of the pleiotropic functions of vitamin C as a universal bioreductant.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Adebayo, Varzideh, Wilson, Gambardella, Eacobacci et al., L-Arginine and COVID-19: An update, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113951
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Luni, Hedenstierna et al., Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734
Akaike, Fujii, Kato, Yoshitake, Miyamoto et al., Viral mutation accelerated by nitric oxide production during infectionin vivo, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fasebj.14.10.1447
Akaike, Ida, Wei, Nishida, Kumagai et al., Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase governs cysteine polysulfidation and mitochondrial bioenergetics, Nat. Commun
Akaike, Maeda, Nitric oxide and virus infection, Immunology, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00142.x
Akaike, Noguchi, Ijiri, Setoguchi, Suga et al., Pathogenesis of influenza virus-induced pneumonia: Involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals
Akaike, Okamoto, Sawa, Yoshitake, Tamura et al., 8-nitroguanosine formation in viral pneumonia and its implication for pathogenesis, doi:10.1073/pnas.0235623100
Akerstrom, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007
Akerstrom, Mousavi-Jazi, Klingstrom, Leijon, Lundkvist et al., Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005
Al Sulaiman, Korayem, Altebainawi, Al Harbi, Alissa et al., Evaluation of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment for moderate-to-severe ARDS in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter cohort study, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y
Al-Sehemi, Pannipara, Parulekar, Patil, Choudhari et al., Potential of NO donor furoxan as SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)) inhibitors: In silico analysis, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn
Albert, Ruíz, Pemán, Salavert, Domingo-Calap, Lack of evidence for infectious SARS-CoV-2 in feces and sewage, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol, doi:10.1007/s10096-021-04304-4
Alqahtani, Aldhahir, Al Ghamdi, Albahrani, Aldraiwiesh et al., Inhaled nitric oxide for clinical management of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph191912803
Asada, Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions, Plant Physiol
Asada, The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: Scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol, doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.601
Badejo, Wada, Gao, Maruta, Sawa et al., Translocation and the alternative D-galacturonate pathway contribute to increasing the ascorbate level in ripening tomato fruits together with the D-mannose/L-galactose pathway, J. Exp. Bot, doi:10.1093/jxb/err275
Bagate, Tuffet, Masi, Perier, Razazi et al., Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00769-2
Bahadoran, Mirmiran, Kashfi, Ghasemi, Lost-in-translation of metabolic effects of inorganic nitrate in type 2 diabetes: Is ascorbic acid the answer?, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22094735
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-Final report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bender, Schwarz, Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide synthesis by molybdenum enzymes, FEBS Lett
Benito, Lopez, Saiz, Buxaderas, Sanchez et al., A flavonoid-rich diet increases nitric oxide production in rat aorta, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704534
Benjamin, O'driscoll, Dougall, Duncan, Smith et al., Stomach NO synthesis, Nature, doi:10.1038/368502a0
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bhowmik, Barek, Aziz, Islam, Impact of high-dose vitamin C on the mortality, severity, and duration of hospital stay in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Health Sci. Rep, doi:10.1002/hsr2.762
Bondonno, Croft, Ward, Considine, Hodgson, Dietary flavonoids and nitrate: Effects on nitric oxide and vascular function, Nutr. Rev, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuu014
Boretti, Banik, Intravenous vitamin C for reduction of cytokines storm in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Pharmanutrition, doi:10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100190
Bryan, Calvert, Gundewar, Lefer, Dietary nitrite restores NO homeostasis and is cardioprotective in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.040
Capra, The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern Mysticism
Carlsson, Wiklund, Engstrand, Weitzberg, Lundberg, Effects of pH, nitrite, and ascorbic acid on nonenzymatic nitric oxide generation and bacterial growth in urine, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1006/niox.2001.0371
Cegolon, Mirandola, Salaris, Salvati, Mastrangelo et al., Hypothiocyanite and hypothiocyanite/lactoferrin mixture exhibit virucidal activity in vitro against SARS-CoV-2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10020233
Chan, Poon, Cheng, Guan, Hung et al., Detection of SARS coronavirus in patients with suspected SARS, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid1002.030610
Chen, Liu, Gao, Sun, Chao et al., Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: A rescue trial in Beijing, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1086/425357
Cheng, Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?, Med. Drug Disc
Cheung, Hung, Chan, Lung, Tso et al., Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.065
Clausen, The influence of nutrition upon resistance to infection, Physiol. Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.1934.14.3.309
Cohen, Lamattina, Yamasaki, Nitric oxide signaling by plant-associated bacteria
Cohen, Mazzola, Yamasaki, Nitric oxide research in agriculture
Cohen, Yamasaki, Mazzola, Brassica napus seed meal soil amendment modifies microbial community structure, nitric oxide production and incidence of Rhizoctonia root rot, Soil Biol. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.11.027
Colasanti, Persichini, Venturini, Ascenzi, S-nitrosylation of viral proteins: Molecular bases for antiviral effect of nitric oxide, IUBMB Life, doi:10.1080/713803459
Colla, Kim, Kyriacou, Rouphael, Nitrate in fruits and vegetables, Sci. Hortic-Amst, doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2018.04.016
Comly, Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water, J. Am. Med. Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.1945.02860360014004
Corpe, Eck, Wang, Al-Hasani, Levine, Intestinal dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) transport mediated by the facilitative sugar transporters, GLUT2 and GLUT8, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.436790
Cortese-Krott, Koning, Kuhnle, Nagy, Bianco et al., The reactive rpecies Iinteractome: Evolutionary emergence, biological significance, and opportunities for redox metabolomics and personalized medicine, Antioxid. Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7083
Cully, A tale of two antiviral targets-And the COVID-19 drugs that bind them, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/d41573-021-00202-8
Dai, Tan, Ren, Shao, Tao et al., COVID-19 risk appears to vary across different alcoholic beverages, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.772700
Dancer, Li, Hart, Tang, Jones, What is the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 from the use of public toilets?, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148341
Das, Reddy, Chadchan, Patil, Biradar et al., Nickel and oxidative stress: Cell signaling mechanisms and protective role of vitamin C, Endocr. Metab. Immune, doi:10.2174/1871530319666191205122249
Daxon, Lark, Matzek, Fields, Haselton, Nebulized nitroglycerin for coronavirus disease 2019-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A case report, A A Pract, doi:10.1213/XAA.0000000000001376
Dedon, Tannenbaum, Reactive nitrogen species in the chemical biology of inflammation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2003.12.017
Degroote, Fang, Antimicrobial properties of nitric oxide
Demartino, Kim-Shapiro, Patel, Gladwin, Nitrite and nitrate chemical biology and signalling, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.14484
Deo, Deshmukh, Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals, J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol, doi:10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_304_18
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Dominguez, Cuenca, Mate-Munoz, Garcia-Fernandez, Serra-Paya et al., Effects of beetroot juice supplementation on cardiorespiratory endurance in athletes. a systematic review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9010043
Dresen, Lee, Hill, Notz, Patel et al., History of scurvy and use of vitamin C in critical illness: A narrative review, Nutr. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1002/ncp.10914
Duncan, Dougall, Johnston, Green, Brogan et al., Chemical generation of nitric oxide in the mouth from the enterosalivary circulation of dietary nitrate, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm0695-546
Eaton, Hemoglobin S polymerization and sickle cell disease: A retrospective on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of Pauling's Science paper, Am. J. Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.25687
Ellis, Anderson, Chirkov, Morris-Thurgood, Jackson et al., Acute effects of vitamin c on platelet responsiveness to nitric oxide donors and endothelial function in patients with chronic heart failure, J. Cardiovasc. Pharm, doi:10.1097/00005344-200105000-00008
Elsaba, Khan, Galal, Lakshmanadoss, Bolkini, Infantile free sialic acid storage disease presenting as non-immune hydrops fetalis, J. Pediat. Neon. Individ. Med
Evans, Causation and disease: The Henle-Koch postulates revisited, Yale J. Biol. Med
Farsalinos, Barbouni, Poulas, Polosa, Caponnetto et al., Current smoking, former smoking, and adverse outcome among hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis, doi:10.1177/2040622320935765
Fenech, Amaya, Valpuesta, Botella, Vitamin C content in fruits: Biosynthesis and regulation, Front. Plant Sci, doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.02006
Fernandez-Hernando, Fukata, Bernatchez, Fukata, Lin et al., Identification of Golgilocalized acyl transferases that palmitoylate and regulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase, J. Cell Biol
Filipovic, Zivanovic, Alvarez, Banerjee, Chemical biology of H 2 S signaling through persulfidation, Chem. Rev, doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00205
Fiorentino, Coppola, Izzo, Annunziata, Bernardo et al., Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis, Eclinicalmedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125
Forstermann, Sessa, Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
Fortenberry, Inhaled nitric oxide for pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: Another brick in the wall?, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000003394
Foyer, Halliwell, The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: A proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism, Planta, doi:10.1007/BF00386001
Fukuto, Perez-Ternero, Zarenkiewicz, Lin, Hobbs et al., Hydropersulfides (RSSH) and nitric oxide (NO) signaling: Possible effects on S-nitrosothiols (RS-NO), Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11010169
Gago, Lundberg, Barbosa, Laranjinha, Red wine-dependent reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide in the stomach, Free Radic. Bio. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.06.007
Garcia-Diaz, Lopez-Legarrea, Quintero, Martinez, Vitamin C in the treatment and/or prevention of obesity, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol, doi:10.3177/jnsv.60.367
Ginestra, Mitchell, Anesi, Christie, COVID-19 critical illness: A data-driven review, Annu. Rev. Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042420-110629
Gladwin, Raat, Shiva, Dezfulian, Hogg et al., Nitrite as a vascular endocrine nitric oxide reservoir that contributes to hypoxic signaling, cytoprotection, and vasodilation, Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Green, COVID-19 accelerates endothelial dysfunction and nitric oxide deficiency, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.006
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19-Preliminary report, N. Engl. J. Med
Guns, Vanherle, Hendriks, Bogie, Protein lipidation by palmitate controls macrophage function, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11030565
Guo, Tao, Flavell, Zhu, Potential intestinal infection and faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00416-6
Gupta, Ghosh, Singh, Misra, Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002
Hassimotto, Genovese, Lajolo, Antioxidant activity of dietary fruits, vegetables, and commercial frozen fruit pulps, J. Agric. Food Chem, doi:10.1021/jf047894h
Hedenstierna, Chen, Hedenstierna, Lieberman, Fine, Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect against COVID 19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005
Hemilä, Bias against vitamin C in mainstream medicine: Examples from trials of vitamin C for infections, Life, doi:10.3390/life12010062
Hess, Diet, nutrition and infection, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM193210132071501
Horie, Mcnicholas, Rezoagli, Pham, Curley et al., Emerging pharmacological therapies for ARDS: COVID-19 and beyond, Intensive Care Med
Hsu, Arcot, Alice Lee, Nitrate and nitrite quantification from cured meat and vegetables and their estimated dietary intake in Australians, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.081
Huang, Huang, Mashimo, Bloch, Moskowitz et al., Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase, Nature, doi:10.1038/377239a0
Huizing, Hackbarth, Adams, Wasserstein, Patterson et al., Free sialic acid storage disorder: Progress and promise, Neurosci. Lett, doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135896
Ichinose, Roberts, Jr, Zapol, Inhaled nitric oxide: A selective pulmonary vasodilator: Current uses and therapeutic potential, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62
Ignarro, Inhaled nitric oxide and COVID-19, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.15085
Inoue, Japanese strategy to COVID-19: How does it work?, Glob. Health Med, doi:10.35772/ghm.2020.01043
Iwasaki, Grubaugh, Why does Japan have so few cases of COVID-19?, EMBO Mol. Med, doi:10.15252/emmm.202012481
Jalil, Concentrations of thiocyanate and hypothiocyanite in the saliva of young adults, J. Nihon Univ. Sch. Dent
Jendrny, Schulz, Twele, Meller, Von Kockritz-Blickwede et al., Scent dog identification of samples from COVID-19 patients-A pilot study, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-020-05281-3
Kamenshchikov, Berra, Carroll, Therapeutic effects of inhaled nitric oxide therapy in COVID-19 patients, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020369
Kashiouris, ; L'heureux, Cable, Fisher, Leichtle et al., The emerging role of vitamin C as a treatment for sepsis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12020292
Kelly, Ohlsson, Shah, Sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension in neonates, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005494.pub4
Keyaerts, Vijgen, Chen, Maes, Hedenstierna et al., Inhibition of SARS-coronavirus infection in vitro by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, a nitric oxide donor compound, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012
Kim, Lee, Yang, Lee, Effenberger et al., Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19, Theranostics, doi:10.7150/thno.49713
Kinoshita, Sato, Vellingiri, Green, Tanaka, Inverse association between hypertension treatment and COVID-19 prevalence in Japan, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.071
Kleinert, Art, Pautz, Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase
Klingstrom, Akerstrom, Hardestam, Stoltz, Simon et al., Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite have different antiviral effects against hantavirus replication and free mature virions, Eur. J. Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.200535587
Kopic, Corradini, Sidani, Murek, Vardanyan et al., Ethanol inhibits gastric acid secretion in rats through increased AMP-kinase activity, Cell. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1159/000276553
Kopic, Geibel, Update on the mechanisms of gastric acid secretion, Curr. Gastro. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11894-010-0137-9
Krammer, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2798-3
Lee, The SARS epidemic in Hong Kong, J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health, doi:10.1136/jech.57.9.652
Li, Liu, Lu, Gao, Zhang, Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is critical for S-mediated syncytia formation and virus entry, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27339
Li, Meng, Zhu, Li, Research progress of betalain in response to adverse stresses and evolutionary relationship compared with anthocyanin, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules24173078
Li, Yuan, Li, Wang, Spike protein mediated membrane fusion during SARS-CoV-2 infection, J. Med. Virol
Liu, Liu, Zhou, Dong, Jiang et al., Rampant C-to-U deamination accounts for the intrinsically high mutation rate in SARS-CoV-2 spike gene, RNA
Lombardi, Gani, Berti, Comberiati, Peroni et al., Asthma and COVID-19: A dangerous liaison?, Asthma Res. Pract, doi:10.1186/s40733-021-00075-z
Lorente, Gomez-Bernal, Martin, Navarro-Gonzalvez, Argueso et al., High serum nitrates levels in non-survivor COVID-19 patients, Med. Intensiv
Lorusso, Combes, Lo Coco, De Piero, Belohlavek et al., ECMO for COVID-19 patients in Europe and Israel, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06272-3
Lu, Glutathione synthesis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.09.008
Lundberg, Carlström, Weitzberg, Metabolic effects of dietary nitrate in health and disease, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.06.007
Lundberg, Weitzberg, Gladwin, The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/nrd2466
Lundberg, Weitzberg, Lundberg, Alving, Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: Measurements in expelled air, Gut, doi:10.1136/gut.35.11.1543
Ma, Hu, Feng, Wang, Nitrate and nitrite in health and disease, Aging Dis, doi:10.14336/AD.2017.1207
Magalhaes, Singh, Passos, None
Main, Fuller, Protein S-palmitoylation: Advances and challenges in studying a therapeutically important lipid modification, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15781
Mario, Roberto, Marta, Teresa, Laura, Hypothesis of COVID-19 therapy with sildenafil, Int. J. Prev. Med, doi:10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_258_20
Martel, Ko, Young, Ojcius, Could nasal nitric oxide help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19?, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002
May, How does ascorbic acid prevent endothelial dysfunction? Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00269-0
Mcfadyen, Garfield, Mancio, Ridge, Semple et al., Use of sildenafil in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonitis, Br. J. Anaesth, doi:10.1016/j.bja.2022.04.004
Mcknight, Smith, Drummond, Duncan, Golden et al., Chemical synthesis of nitric oxide in the stomach from dietary nitrate in humans, Gut, doi:10.1136/gut.40.2.211
Miguel, Betalains in some species of the Amaranthaceae family: A review, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox7040053
Mitchell, Shonle, Grindley, The origin of the ntirate in the urine, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)87531-7
Miyara, Tubach, Pourcher, Morelot-Panzini, Pernet et al., Low rate of daily active tobacco smoking in patients with symptomatic COVID-19, WPP19W, doi:10.32388/wpp19w.4
Morais-Almeida, Aguiar, Martin, Ansotegui, Ebisawa et al., COVID-19, asthma, and biologic therapies: What we need to know, World Allergy Organ. J
Morina, Takahama, Yamauchi, Hirota, Veljovic-Jovanovic, Quercetin 7-O-glucoside suppresses nitrite-induced formation of dinitrosocatechins and their quinones in catechin/nitrite systems under stomach simulating conditions, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/C4FO00695J
Mussa, Mohd Idris, Ahmed, Ahmad, Murtadha et al., High-Dose Vitamin C for Cancer Therapy, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15060711
Nag, Kathpalia, Gorla, Wadhwa, Localization of nitro-tyrosine immunoreactivity in human retina, Ann. Anat, doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2019.01.006
Nemzer, Pietrzkowski, Hunter, Robinson, Fink, Betalain-rich dietary supplement, but not PETN, increases vasodilation and nitric oxide: A comparative, single-dose, randomized, placebo-controlled, blinded, crossover pilot study, J. Food Res, doi:10.5539/jfr.v10n1p26
Nijveldt, Van Nood, Van Hoorn, Boelens, Van Norren et al., Flavonoids: A review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/74.4.418
Ochoa-Brust, Fernandez, Villanueva-Ruiz, Velasco, Trujillo-Hernandez et al., Daily intake of 100 mg ascorbic acid as urinary tract infection prophylactic agent during pregnancy, Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand
Oda, Akaike, Hamamoto, Suzuki, Hirano et al., Oxygen radicals in influenza-induced pathogenesis and treatment with pyran polymer-conjugated SOD, Science, doi:10.1126/science.2543070
Olczak-Pruc, Swieczkowski, Ladny, Pruc, Juarez-Vela et al., Vitamin C supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14194217
Oldfield, Loomba, Monteith, Crowley, Medel et al., Safety and pharmacokinetics of sodium nitrite in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: A phase IIa study, J. Neurosurg
Ortis, Lenhart, Becker, Schwamback, Tovo et al., Drug-induced liver injury and COVID-19: A review for clinical practice, World J. Hepatol, doi:10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1143
Otaki, Nakasone, Nakamura, Nonself mutations in the spike protein suggest an increase in the antigenicity and a decrease in the virulence of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, COVID, doi:10.3390/covid2030029
Otaki, Nakasone, Nakamura, Self and nonself short constituent sequences of amino acids in the SARS-CoV-2 proteome for vaccine development, COVID, doi:10.3390/covid1030047
Oza, Kashfi, Utility of NO and H2S donating platforms in managing COVID-19: Rationale and promise, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2022.08.003
Padayatty, Sun, Wang, Riordan, Hewitt et al., Vitamin C pharmacokinetics: Implications for oral and intravenous use, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010
Pannala, Mani, Spencer, Skinner, Bruckdorfer et al., The effect of dietary nitrate on salivary, plasma, and urinary nitrate metabolism in humans, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01353-9
Patel, Mcandrew, Sellak, White, Jo et al., Biological aspects of reactive nitrogen species, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(99)00028-6
Pauling, Ascorbic acid and the common cold, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/24.11.1294
Pauling, How to Live Longer and Feel Better
Pauling, Itano, Singer, Wells, Sickle cell anemia, a molecular disease, Science, doi:10.1126/science.110.2865.543
Pauling, Orthomolecular psychiatry, Science, doi:10.1126/science.160.3825.265
Pauling, The significance of the evidence about ascorbic acid and the common cold
Pauling, Vitamin C and the Common Cold
Perkins, Ji, Connolly, Couper, Lall et al., Effect of noninvasive respiratory dtrategies on intubation or mortality among patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and COVID-19: The RECOVERY-RS randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0028
Perrone, Belser, Wadford, Katz, Tumpey, Inducible nitric oxide contributes to viral pathogenesis following highly pathogenic influenza virus infection in mice, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jit062
Peterson, Mackowiak, Barnett, Marling-Cason, Haley, The human gastric bactericidal barrier: Mechanisms of action, relative antibacterial activity, and dietary influences, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/159.5.979
Pignatelli, Fabietti, Ricci, Piattelli, Curia, How periodontal disease and presence of nitric oxide reducing oral bacteria can affect blood pressure, Int. J Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21207538
Popov, Human exhaled breath analysis, Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.anai.2011.02.016
Qin, Liu, Sun, Fan, Xia et al., Sialin (SLC17A5) functions as a nitrate transporter in the plasma membrane, doi:10.1073/pnas.1116633109
Rathbone, Johnson, Wyatt, Kelleher, Heatley et al., Ascorbic acid: A factor concentrated in human gastric juice, Clin. Sci, doi:10.1042/cs0760237
Roberts, Fineman, Morin, Shaul, Rimar et al., Inhaled nitric oxide and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM199702273360902
Robertson, The vitamins and resistance to infection, Medicine, doi:10.1097/00005792-193405000-00001
Rocha, Gago, Barbosa, Laranjinha, Dietary polyphenols generate nitric oxide from nitrite in the stomach and induce smooth muscle relaxation, Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.tox.2009.09.008
Rocha, Laranjinha, Nitrate from diet might fuel gut microbiota metabolism: Minding the gap between redox signaling and inter-kingdom communication, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.001
Roychoudhury, Basu, Ascorbate-glutathione and plant tolerance to various abiotic stresses
Ruddell, Blendis, Walters, Nitrite and thiocyanate in the fasting and secreting stomach and in saliva, Gut, doi:10.1136/gut.18.1.73
Rusznyak, Szent-Györgyi, Vitamin, Flavonols as vitamins, Nature, doi:10.1038/138027a0
Sachs, Carlsson, Lindberg, Wallmark, Gastric, K-ATPase as therapeutic target, Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol
Sakihama, Cohen, Grace, Yamasaki, Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: Phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants, Toxicology, doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00196-8
Sakihama, Mano, Sano, Asada, Yamasaki, Reduction of phenoxyl radicals mediated by monodehydroascorbate reductase, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.4053
Sakihama, Tamaki, Shimoji, Ichiba, Fukushi et al., Enzymatic nitration of phytophenolics: Evidence for peroxynitrite-independent nitration of plant secondary metabolites, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01059-7
Sakihama, Yamasaki, Phytochemical antioxidants: Past, present and future
Sanchez, Ibargoyen, Mastrogiovanni, Radi, Keszenman et al., Fast and biphasic 8-nitroguanine production from guanine and peroxynitrite, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.317
Sandrini, Taylor, Thomas, Yates, Fractional exhaled nitric oxide in asthma: An update, Respirology
Santamarina, Beddings, Lomakin, Boisier Riscal, Gutierrez Claveria et al., Sildenafil for treating patients with COVID-19 and perfusion mismatch: A pilot randomized trial, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03885-y
Saura, Zaragoza, Mcmillan, Quick, Hohenadl et al., An antiviral mechanism of nitric oxide: Inhibition of a viral protease, Immunity, doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80003-5
Shei, Baranauskas, More questions than answers for the use of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2022.05.001
Sobala, Schorah, Sanderson, Dixon, Tompkins et al., Ascorbic acid in the human stomach, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1016/0016-5085(89)90071-1
Sobko, Marcus, Govoni, Kamiya, Dietary nitrate in Japanese traditional foods lowers diastolic blood pressure in healthy volunteers, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2009.10.007
Sorbo, Michaelsen, Ali, Wang, Ribeiro et al., High doses of inhaled nitric oxide as an innovative antimicrobial strategy for lung infections, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10071525
Steudel, Hurford, Zapol, Inhaled nitric oxide: Basic biology and clinical applications, Anesthesiology, doi:10.1097/00000542-199910000-00030
Stuehr, Marletta, Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: Mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738
Sun, Zhang, Broderick, Fein, Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by using Griess reaction assay, Sensors, doi:10.3390/s30800276
Sundqvist, Larsen, Carlstrom, Bottai, Pernow et al., A randomized clinical trial of the effects of leafy green vegetables and inorganic nitrate on blood pressure, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Sunjaya, Allida, Di Tanna, Jenkins, Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2021.1888116
Svirbely, Szent-Györgyi, The chemical nature of vitamin C, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/bj0260865
Szabo, Multiple pathways of peroxynitrite cytotoxicity, Toxicol. Lett, doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00507-6
Takahashi, Tamashiro, Sakihama, Yamamoto, Kawamitsu et al., High-susceptibility of photosynthesis to photoinhibition in the tropical plant Ficus microcarpa L. f. cv. Golden Leaves, BMC Plant Biol, doi:10.1186/1471-2229-2-2
Tan, Yip, Hans Selye, Founder of the stress theory, Singap. Med. J, doi:10.11622/smedj.2018043
Tang, Paonessa, Zhang, Ambrosone, Mccann, Total isothiocyanate yield from raw cruciferous vegetables commonly consumed in the United States, J. Funct. Foods, doi:10.1016/j.jff.2013.07.011
Tao, Tzou, Nouhin, Gupta, De Oliveira et al., The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nat. Rev. Genet, doi:10.1038/s41576-021-00408-x
Terrett, Bell, Brown, Ellis, Sildenafil (VIAGRA(TM)), a potent and selective inhibitor of type 5 cGMP phosphodiesterase with utility for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett, doi:10.1016/0960-894X(96)00323-X
Toda, Ayajiki, Okamura, Control of systemic and pulmonary blood pressure by nitric oxide formed through neuronal nitric oxide synthase, J. Hypertens, doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832e8ddf
Torrens, Feelisch, How to beet hypertension in pregnancy: Is there more to beetroot juice than nitrate?, J. Physiol
Traber, Stevens, Vitamins, Beneficial effects from a mechanistic perspective, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.017
Trevejo-Nunez, Kolls, De Wit, Alcohol use as a risk factor in infections and healing: A clinician's perspective, Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev
Tun, Gleeson, Al-Joudeh, Dube, Immune-mediated hepatitis with the Moderna vaccine, no longer a coincidence but confirmed, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.031
Tuo, Yan, Ge, Ou, Zhao, Ascorbic acid secretion in the human stomach and the effect of gastrin, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.704
Usman, Siddiqi, Khan, Patel, Shahid et al., Is there a smoker's paradox in COVID-19?, BMJ Evidence-Based Med, doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111492
Vabret, Britton, Gruber, Hegde, Kim et al., Immunology of COVID-19: Current state of the science, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002
Valsecchi, Winterton, Safaee Fakhr, Collier, Nozari et al., High-dose inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of spontaneously breathing pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia, Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847
Villacorta, Gao, Schopfer, Freeman, Chen, Nitro-fatty acids in cardiovascular regulation and diseases: Characteristics and molecular mechanisms, Front. Biosci, doi:10.2741/4425
Vitrone, Mele, Durante-Mangoni, Zampino, Drugs and liver injury: A not to be overlooked binomial in COVID-19, J. Chemother, doi:10.1080/1120009X.2021.1988203
Wagner, Erkenbrack, Love, Stress-induced evolutionary innovation: A mechanism for the origin of cell types, Bioessays, doi:10.1002/bies.201800188
Waring, Drake, Schorah, White, Lynch et al., Ascorbic acid and total vitamin C concentrations in plasma, gastric juice, and gastrointestinal mucosa: Effects of gastritis and oral supplementation, Gut, doi:10.1136/gut.38.2.171
Watanabe, Yamasaki, Dynamics of nitrite content in fresh spinach leaves: Evidence for nitrite formation caused by microbial nitrate reductase activity, J. Nutrit. Food Sci, doi:10.4172/2155-9600.1000572
Weitzberg, Lundberg, Nonenzymatic nitric oxide production in humans, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1006/niox.1997.0162
Weitzberg, Lundberg, Novel aspects of dietary nitrate and human health, Annu. Rev. Nutrit, doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161159
Wong, Saier, Jr, The SARS-coronavirus infection cycle: A survey of viral membraneproteins, their functional interactions and pathogenesis, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22031308
Wu, Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002
Yamasaki, A function of colour, Trend. Plant Sci, doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(97)82730-6
Yamasaki, Cohen, Biological consilience of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in plants: Gases of primordial earth linking plant, microbial and animal physiologies, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2016.04.002
Yamasaki, Cohen, NO signal at the crossroads: Polyamine-induced nitric oxide synthesis in plants? Trend, Plant Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2006.09.009
Yamasaki, Grace, EPR detection of phytophenoxyl radicals stabilized by zinc ions: Evidence for the redox coupling of plant phenolics with ascorbate in the H 2 O 2 peroxidase system, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00048-9
Yamasaki, Nitric oxide research in plant biology: Its past and future, Nitric Oxide Signaling in Higher Plants
Yamasaki, Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide production pathway: Implications for involvement of active nitrogen species in photoinhibition in vivo, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci, doi:10.1098/rstb.2000.0708
Yamasaki, Sakihama, Takahashi, An alternative pathway for nitric oxide production in plants: New features of an old enzyme, Trend. Plant Sci, doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(99)01393-X
Yamasaki, The NO world for plants: Achieving balance in an open system, Plant Cell Environ, doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01297.x
Yamasaki, Uefuji, Sakihama, Bleaching of the red anthocyanin induced by superoxide radical, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1006/abbi.1996.0331
Yamasaki, Watanabe, Fukuto, Cohen, Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide production pathway: Diversity of NO production systems
Yamasaki, Watanabe, Sakihama, Cohen, An overview of methods in plant nitric oxide (NO) research: Why do we always need to use multiple methods? In Plant Nitric Oxide: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology
Yun, Mullarky, Lu, Bosch, Kavalier et al., Vitamin C selectively kills KRAS and BRAF mutant colorectal cancer cells by targeting GAPDH, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aaa5004
Zhai, Li, Wang, Wu, Drug-induced liver disturbance during the treatment of COVID-19, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.719308
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Yuan, Yang et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
Zhen, Leigh, Nitrate accumulation by wheat (Triticum aestivum) in relation to growth and tissue N concentrations, Plant Soil, doi:10.1007/BF00009253
Zhou, Li, Zhao, Chu, Wang et al., Human intestinal tract serves as an alternative infection route for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Sci. Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.aao4966
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11020397",
"ISSN": [
"2076-2607"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020397",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Linus Pauling, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, suggested that a high dose of vitamin C (l-ascorbic acid) might work as a prevention or treatment for the common cold. Vitamin C therapy was tested in clinical trials, but clear evidence was not found at that time. Although Pauling’s proposal has been strongly criticized for a long time, vitamin C therapy has continued to be tested as a treatment for a variety of diseases, including coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19). The pathogen of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, belongs to the β-coronavirus lineage, which includes human coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This review intends to shed new light on vitamin C antiviral activity that may prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection through the chemical production of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a gaseous free radical that is largely produced by the enzyme NO synthase (NOS) in cells. NO produced by upper epidermal cells contributes to the inactivation of viruses and bacteria contained in air or aerosols. In addition to enzymatic production, NO can be generated by the chemical reduction of inorganic nitrite (NO2−), an alternative mechanism for NO production in living organisms. Dietary vitamin C, largely contained in fruits and vegetables, can reduce the nitrite in saliva to produce NO in the oral cavity when chewing foods. In the stomach, salivary nitrite can also be reduced to NO by vitamin C secreted from the epidermal cells of the stomach. The strong acidic pH of gastric juice facilitates the chemical reduction of salivary nitrite to produce NO. Vitamin C contributes in multiple ways to the host innate immune system as a first-line defense mechanism against pathogens. Highlighting chemical NO production by vitamin C, we suggest that controversies on the therapeutic effects of vitamin C in previous clinical trials may partly be due to less appreciation of the pleiotropic functions of vitamin C as a universal bioreductant.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"microorganisms11020397"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Science, University of the Ryukyus, Nishihara 903-0213, Okinawa, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Yamasaki",
"given": "Hideo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3793-1146",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Science, University of the Ryukyus, Nishihara 903-0213, Okinawa, Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Imai",
"given": "Hideyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8277-1188",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Science, University of the Ryukyus, Nishihara 903-0213, Okinawa, Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tanaka",
"given": "Atsuko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3425-7085",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Science, University of the Ryukyus, Nishihara 903-0213, Okinawa, Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Otaki",
"given": "Joji M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microorganisms",
"container-title-short": "Microorganisms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-06T09:08:07Z",
"timestamp": 1675674487000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-16T06:12:51Z",
"timestamp": 1676527971000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-17T05:36:16Z",
"timestamp": 1676612176610
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675382400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/2/397/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "397",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome",
"author": "Devaux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/thno.49713",
"article-title": "Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "316",
"journal-title": "Theranostics",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.0028",
"article-title": "Effect of noninvasive respiratory dtrategies on intubation or mortality among patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and COVID-19: The RECOVERY-RS randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Perkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "546",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042420-110629",
"article-title": "COVID-19 critical illness: A data-driven review",
"author": "Ginestra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10020369",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Kamenshchikov, N.O., Berra, L., and Carroll, R.W. (2022). Therapeutic effects of inhaled nitric oxide therapy in COVID-19 patients. Biomedicines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06272-3",
"article-title": "ECMO for COVID-19 patients in Europe and Israel",
"author": "Lorusso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1261/rna.079160.122",
"article-title": "Rampant C-to-U deamination accounts for the intrinsically high mutation rate in SARS-CoV-2 spike gene",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "917",
"journal-title": "RNA",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41576-021-00408-x",
"article-title": "The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Tao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Genet.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/covid2030029",
"article-title": "Nonself mutations in the spike protein suggest an increase in the antigenicity and a decrease in the virulence of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Otaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"journal-title": "COVID",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—Final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41573-021-00202-8",
"article-title": "A tale of two antiviral targets—And the COVID-19 drugs that bind them",
"author": "Cully",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2798-3",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development",
"author": "Krammer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "516",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "586",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/covid1030047",
"article-title": "Self and nonself short constituent sequences of amino acids in the SARS-CoV-2 proteome for vaccine development",
"author": "Otaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "555",
"journal-title": "COVID",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19—Preliminary report",
"author": "Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028",
"article-title": "Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100028",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Disc.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.762",
"article-title": "Impact of high-dose vitamin C on the mortality, severity, and duration of hospital stay in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Bhowmik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e762",
"journal-title": "Health Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14194217",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Olczak-Pruc, M., Swieczkowski, D., Ladny, J.R., Pruc, M., Juarez-Vela, R., Rafique, Z., Peacock, F.W., and Szarpak, L. (2022). Vitamin C supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100190",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C for reduction of cytokines storm in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Boretti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100190",
"journal-title": "Pharmanutrition",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12020292",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Kashiouris, M.G., L’Heureux, M., Cable, C.A., Fisher, B.J., Leichtle, S.W., and Fowler, A.A. (2020). The emerging role of vitamin C as a treatment for sepsis. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph191912803",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Alqahtani, J.S., Aldhahir, A.M., Al Ghamdi, S.S., AlBahrani, S., AlDraiwiesh, I.A., Alqarni, A.A., Latief, K., Raya, R.P., and Oyelade, T. (2022). Inhaled nitric oxide for clinical management of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide: A selective pulmonary vasodilator: Current uses and therapeutic potential",
"author": "Ichinose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3106",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00000542-199910000-00030",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide: Basic biology and clinical applications",
"author": "Steudel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1090",
"journal-title": "Anesthesiology",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15085",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide and COVID-19",
"author": "Ignarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3848",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000003394",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide for pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: Another brick in the wall?",
"author": "Fortenberry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1879",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199702273360902",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn",
"author": "Roberts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "605",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "336",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/425357",
"article-title": "Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: A rescue trial in Beijing",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "Could nasal nitric oxide help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Martel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847",
"article-title": "High-dose inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of spontaneously breathing pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia",
"author": "Valsecchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Obstet. Gynecol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y",
"article-title": "Evaluation of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment for moderate-to-severe ARDS in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Korayem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "304",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2022.05.001",
"article-title": "More questions than answers for the use of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19",
"author": "Shei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00769-2",
"article-title": "Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Bagate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function",
"author": "Forstermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "829",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125",
"article-title": "Effects of adding l-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis",
"author": "Fiorentino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101125",
"journal-title": "Eclinicalmedicine",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13113951",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Adebayo, A., Varzideh, F., Wilson, S., Gambardella, J., Eacobacci, M., Jankauskas, S.S., Donkor, K., Kansakar, U., Trimarco, V., and Mone, P. (2021). L-Arginine and COVID-19: An update. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06141-z",
"article-title": "Emerging pharmacological therapies for ARDS: COVID-19 and beyond",
"author": "Horie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2265",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/XAA.0000000000001376",
"article-title": "Nebulized nitroglycerin for coronavirus disease 2019-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A case report",
"author": "Daxon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01376",
"journal-title": "A A Pract.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-coronavirus infection in vitro by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, a nitric oxide donor compound",
"author": "Keyaerts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005344-200105000-00008",
"article-title": "Acute effects of vitamin c on platelet responsiveness to nitric oxide donors and endothelial function in patients with chronic heart failure",
"author": "Ellis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "J. Cardiovasc. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1790038",
"article-title": "Potential of NO donor furoxan as SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)) inhibitors: In silico analysis",
"author": "Pannipara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5804",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0960-894X(96)00323-X",
"article-title": "Sildenafil (VIAGRA(TM)), a potent and selective inhibitor of type 5 cGMP phosphodiesterase with utility for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction",
"author": "Terrett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1819",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"article-title": "Sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension in neonates",
"author": "Kelly",
"first-page": "CD005494",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_258_20",
"article-title": "Hypothesis of COVID-19 therapy with sildenafil",
"author": "Mario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Prev. Med.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03885-y",
"article-title": "Sildenafil for treating patients with COVID-19 and perfusion mismatch: A pilot randomized trial",
"author": "Santamarina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bja.2022.04.004",
"article-title": "Use of sildenafil in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonitis",
"author": "McFadyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e18",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Anaesth.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40733-021-00075-z",
"article-title": "Asthma and COVID-19: A dangerous liaison?",
"author": "Lombardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Asthma Res. Pract.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02770903.2021.1888116",
"article-title": "Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Sunjaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "866",
"journal-title": "J. Asthma",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100126",
"article-title": "COVID-19, asthma, and biologic therapies: What we need to know",
"author": "Aguiar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100126",
"journal-title": "World Allergy Organ. J.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01616.x",
"article-title": "Fractional exhaled nitric oxide in asthma: An update",
"author": "Sandrini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2040622320935765",
"article-title": "Current smoking, former smoking, and adverse outcome among hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Farsalinos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2040622320935765",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32388/WPP19W.4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Miyara, M., Tubach, F., Pourcher, V., Morelot-Panzini, C., Pernet, J., Haroche, J., Lebbah, S., Morawiec, E., Gorochov, G., and Caumes, E. (2020). Low rate of daily active tobacco smoking in patients with symptomatic COVID-19. Qeios, WPP19W.4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111492",
"article-title": "Is there a smoker’s paradox in COVID-19?",
"author": "Usman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "BMJ Evidence-Based Med.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect against COVID 19",
"author": "Hedenstierna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00142.x",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide and virus infection",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/b111485",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Fang, F.C. (2002). Nitric Oxide and Infection, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2017.7083",
"article-title": "The reactive rpecies Iinteractome: Evolutionary emergence, biological significance, and opportunities for redox metabolomics and personalized medicine",
"author": "Koning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "684",
"journal-title": "Antioxid. Redox Signal.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0005-2728(99)00028-6",
"article-title": "Biological aspects of reactive nitrogen species",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "1411",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aanat.2019.01.006",
"article-title": "Localization of nitro-tyrosine immunoreactivity in human retina",
"author": "Nag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann. Anat.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0235623100",
"article-title": "8-nitroguanosine formation in viral pneumonia and its implication for pathogenesis",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "685",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2741/4425",
"article-title": "Nitro-fatty acids in cardiovascular regulation and diseases: Characteristics and molecular mechanisms",
"author": "Villacorta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "873",
"journal-title": "Front. Biosci.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01059-7",
"article-title": "Enzymatic nitration of phytophenolics: Evidence for peroxynitrite-independent nitration of plant secondary metabolites",
"author": "Sakihama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "553",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11010169",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Fukuto, J.M., Perez-Ternero, C., Zarenkiewicz, J., Lin, J., Hobbs, A.J., and Toscano, J.P. (2022). Hydropersulfides (RSSH) and nitric oxide (NO) signaling: Possible effects on S-nitrosothiols (RS-NO). Antioxidants, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2003.12.017",
"article-title": "Reactive nitrogen species in the chemical biology of inflammation",
"author": "Dedon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "423",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rstb.2000.0708",
"article-title": "Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide production pathway: Implications for involvement of active nitrogen species in photoinhibition in vivo",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1477",
"journal-title": "Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "355",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832e8ddf",
"article-title": "Control of systemic and pulmonary blood pressure by nitric oxide formed through neuronal nitric oxide synthase",
"author": "Toda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1929",
"journal-title": "J. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00507-6",
"article-title": "Multiple pathways of peroxynitrite cytotoxicity",
"author": "Szabo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "Toxicol. Lett.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "140-141",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.317",
"article-title": "Fast and biphasic 8-nitroguanine production from guanine and peroxynitrite",
"author": "Sanchez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "474",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fasebj.14.10.1447",
"article-title": "Viral mutation accelerated by nitric oxide production during infectionin vivo",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1447",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2022.08.003",
"article-title": "Utility of NO and H2S donating platforms in managing COVID-19: Rationale and promise",
"author": "Oza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.200535587",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite have different antiviral effects against hantavirus replication and free mature virions",
"author": "Klingstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2649",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80003-5",
"article-title": "An antiviral mechanism of nitric oxide: Inhibition of a viral protease",
"author": "Saura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/713803459",
"article-title": "S-nitrosylation of viral proteins: Molecular bases for antiviral effect of nitric oxide",
"author": "Colasanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "IUBMB Life",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Akerstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1966",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"article-title": "Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro",
"author": "Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101734",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11030565",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_76",
"unstructured": "Guns, J., Vanherle, S., Hendriks, J.J.A., and Bogie, J.F.J. (2022). Protein lipidation by palmitate controls macrophage function. Cells, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected",
"author": "Akerstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22031308",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_78",
"unstructured": "Wong, N.A., and Saier, M.H. (2021). The SARS-coronavirus infection cycle: A survey of viral membraneproteins, their functional interactions and pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27339",
"article-title": "Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is critical for S-mediated syncytia formation and virus entry",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15781",
"article-title": "Protein S-palmitoylation: Advances and challenges in studying a therapeutically important lipid modification",
"author": "Main",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.200601051",
"article-title": "Identification of Golgi-localized acyl transferases that palmitoylate and regulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase",
"author": "Fukata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Spike protein mediated membrane fusion during SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "e28212",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1873-3468.13089",
"article-title": "Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide synthesis by molybdenum enzymes",
"author": "Bender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2126",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "592",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00407.2006",
"article-title": "Nitrite as a vascular endocrine nitric oxide reservoir that contributes to hypoxic signaling, cytoprotection, and vasodilation",
"author": "Gladwin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H2026",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161159",
"article-title": "Novel aspects of dietary nitrate and human health",
"author": "Weitzberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Nutrit.",
"key": "ref_86",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2018.06.007",
"article-title": "Metabolic effects of dietary nitrate in health and disease",
"author": "Lundberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd2466",
"article-title": "The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics",
"author": "Lundberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "156",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.040",
"article-title": "Dietary nitrite restores NO homeostasis and is cardioprotective in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice",
"author": "Bryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "468",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-0679-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_90",
"unstructured": "Tsukahara, H., and Kaneko, K. (2014). Studies on Pediatric Disorders, Springer. Oxidative Stress in Applied Basic Research and Clinical Practice."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01297.x",
"article-title": "The NO world for plants: Achieving balance in an open system",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "78",
"journal-title": "Plant Cell Environ.",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.14484",
"article-title": "Nitrite and nitrate chemical biology and signalling",
"author": "DeMartino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/377239a0",
"article-title": "Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "377",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"key": "ref_94",
"unstructured": "Kleinert, H., Art, J., and Pautz, A. (2010). Nitric Oxide, Elsevier."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/s30800276",
"article-title": "Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by using Griess reaction assay",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Sensors",
"key": "ref_95",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738",
"article-title": "Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: Mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide",
"author": "Stuehr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7738",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "82",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-3600-7_1",
"article-title": "An overview of methods in plant nitric oxide (NO) research: Why do we always need to use multiple methods?",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Plant Nitric Oxide: Methods and Protocols",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "Volume 1424",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.40.2.211",
"article-title": "Chemical synthesis of nitric oxide in the stomach from dietary nitrate in humans",
"author": "McKnight",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/368502a0",
"article-title": "Stomach NO synthesis",
"author": "Benjamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "502",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "368",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(18)87531-7",
"article-title": "The origin of the ntirate in the urine",
"author": "Mitchell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "461",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_100",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1916"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01353-9",
"article-title": "The effect of dietary nitrate on salivary, plasma, and urinary nitrate metabolism in humans",
"author": "Pannala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "576",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_101",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm0695-546",
"article-title": "Chemical generation of nitric oxide in the mouth from the enterosalivary circulation of dietary nitrate",
"author": "Duncan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "546",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_102",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1116633109",
"article-title": "Sialin (SLC17A5) functions as a nitrate transporter in the plasma membrane",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13434",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_103",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Infantile free sialic acid storage disease presenting as non-immune hydrops fetalis",
"author": "Elsaba",
"first-page": "e080114",
"journal-title": "J. Pediat. Neon. Individ. Med.",
"key": "ref_104",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135896",
"article-title": "Free sialic acid storage disorder: Progress and promise",
"author": "Huizing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135896",
"journal-title": "Neurosci. Lett.",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "755",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21207538",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_106",
"unstructured": "Pignatelli, P., Fabietti, G., Ricci, A., Piattelli, A., and Curia, M.C. (2020). How periodontal disease and presence of nitric oxide reducing oral bacteria can affect blood pressure. Int. J Mol. Sci., 21."
},
{
"article-title": "Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals",
"author": "Deo",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_107",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14336/AD.2017.1207",
"article-title": "Nitrate and nitrite in health and disease",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "938",
"journal-title": "Aging Dis.",
"key": "ref_108",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.35.11.1543",
"article-title": "Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: Measurements in expelled air",
"author": "Lundberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1543",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_109",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00016340701273189",
"article-title": "Daily intake of 100 mg ascorbic acid as urinary tract infection prophylactic agent during pregnancy",
"author": "Fernandez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "783",
"journal-title": "Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand.",
"key": "ref_110",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpls.2018.02006",
"article-title": "Vitamin C content in fruits: Biosynthesis and regulation",
"author": "Fenech",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2006",
"journal-title": "Front. Plant Sci.",
"key": "ref_111",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/niox.1997.0162",
"article-title": "Nonenzymatic nitric oxide production in humans",
"author": "Weitzberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_112",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/bbrc.2000.4053",
"article-title": "Reduction of phenoxyl radicals mediated by monodehydroascorbate reductase",
"author": "Sakihama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "949",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "ref_113",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/niox.2001.0371",
"article-title": "Effects of pH, nitrite, and ascorbic acid on nonenzymatic nitric oxide generation and bacterial growth in urine",
"author": "Carlsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "580",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_114",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/cs0760237",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid: A factor concentrated in human gastric juice",
"author": "Rathbone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Clin. Sci.",
"key": "ref_115",
"volume": "76",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.38.2.171",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid and total vitamin C concentrations in plasma, gastric juice, and gastrointestinal mucosa: Effects of gastritis and oral supplementation",
"author": "Waring",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_116",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0016-5085(89)90071-1",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid in the human stomach",
"author": "Sobala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "357",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_117",
"volume": "97",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.704",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid secretion in the human stomach and the effect of gastrin",
"author": "Tuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "704",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_118",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22094735",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_119",
"unstructured": "Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Kashfi, K., and Ghasemi, A. (2021). Lost-in-translation of metabolic effects of inorganic nitrate in type 2 diabetes: Is ascorbic acid the answer?. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00009253",
"article-title": "Nitrate accumulation by wheat (Triticum aestivum) in relation to growth and tissue N concentrations",
"author": "Zhen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Plant Soil",
"key": "ref_120",
"volume": "124",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scienta.2018.04.016",
"article-title": "Nitrate in fruits and vegetables",
"author": "Colla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Sci. Hortic-Amst.",
"key": "ref_121",
"volume": "237",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.081",
"article-title": "Nitrate and nitrite quantification from cured meat and vegetables and their estimated dietary intake in Australians",
"author": "Hsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "334",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_122",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf047894h",
"article-title": "Antioxidant activity of dietary fruits, vegetables, and commercial frozen fruit pulps",
"author": "Hassimotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2928",
"journal-title": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_123",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Dynamics of nitrite content in fresh spinach leaves: Evidence for nitrite formation caused by microbial nitrate reductase activity",
"author": "Watanabe",
"first-page": "572",
"journal-title": "J. Nutrit. Food Sci.",
"key": "ref_124",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/1-4020-4389-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_125",
"unstructured": "Rai, K., and Takabe, T. (2006). Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants, Springer."
},
{
"key": "ref_126",
"unstructured": "Hyat, S., Miri, M., Pichel, J., and Ahmad, A. (2010). Nitric Oxide in Plant Physiology, Wiley-VCH."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2016.04.002",
"article-title": "Biological consilience of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in plants: Gases of primordial earth linking plant, microbial and animal physiologies",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_127",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00196-8",
"article-title": "Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: Phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants",
"author": "Sakihama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Toxicology",
"key": "ref_128",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1360-1385(99)01393-X",
"article-title": "An alternative pathway for nitric oxide production in plants: New features of an old enzyme",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Trend. Plant Sci.",
"key": "ref_129",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tplants.2006.09.009",
"article-title": "NO signal at the crossroads: Polyamine-induced nitric oxide synthesis in plants?",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "Trend. Plant Sci.",
"key": "ref_130",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.160.3825.265",
"article-title": "Orthomolecular psychiatry",
"author": "Pauling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_131",
"volume": "160",
"year": "1968"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.601",
"article-title": "The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: Scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons",
"author": "Asada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_132",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jxb/err275",
"article-title": "Translocation and the alternative D-galacturonate pathway contribute to increasing the ascorbate level in ripening tomato fruits together with the D-mannose/L-galactose pathway",
"author": "Badejo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Bot.",
"key": "ref_133",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00386001",
"article-title": "The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: A proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism",
"author": "Foyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Planta",
"key": "ref_134",
"volume": "133",
"year": "1976"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1104/pp.106.082040",
"article-title": "Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions",
"author": "Asada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Plant Physiol.",
"key": "ref_135",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2229-2-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_136",
"unstructured": "Takahashi, S., Tamashiro, A., Sakihama, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Kawamitsu, Y., and Yamasaki, H. (2002). High-susceptibility of photosynthesis to photoinhibition in the tropical plant Ficus microcarpa L. f. cv. Golden Leaves. BMC Plant Biol., 2."
},
{
"key": "ref_137",
"unstructured": "Umar, S., and Naser, A.A. (2012). Oxidative Stress in Plants: Causes, Consequences and Tolerance, IK International Publishers."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/138027a0",
"article-title": "Vitamin P: Flavonols as vitamins",
"author": "Rusznyak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_138",
"volume": "138",
"year": "1936"
},
{
"key": "ref_139",
"unstructured": "Waisundara, V. (2021). Antioxidants, IntechOpen Limited."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/74.4.418",
"article-title": "Flavonoids: A review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications",
"author": "Nijveldt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_140",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuu014",
"article-title": "Dietary flavonoids and nitrate: Effects on nitric oxide and vascular function",
"author": "Bondonno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_141",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0704534",
"article-title": "A flavonoid-rich diet increases nitric oxide production in rat aorta",
"author": "Benito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "910",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_142",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1360-1385(97)82730-6",
"article-title": "A function of colour",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Trend. Plant Sci.",
"key": "ref_143",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/abbi.1996.0331",
"article-title": "Bleaching of the red anthocyanin induced by superoxide radical",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_144",
"volume": "332",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.06.007",
"article-title": "Red wine-dependent reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide in the stomach",
"author": "Gago",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Bio. Med.",
"key": "ref_145",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tox.2009.09.008",
"article-title": "Dietary polyphenols generate nitric oxide from nitrite in the stomach and induce smooth muscle relaxation",
"author": "Rocha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Toxicology",
"key": "ref_146",
"volume": "265",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00048-9",
"article-title": "EPR detection of phytophenoxyl radicals stabilized by zinc ions: Evidence for the redox coupling of plant phenolics with ascorbate in the H2O2 peroxidase system",
"author": "Yamasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett.",
"key": "ref_147",
"volume": "422",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C4FO00695J",
"article-title": "Quercetin 7-O-glucoside suppresses nitrite-induced formation of dinitrosocatechins and their quinones in catechin/nitrite systems under stomach simulating conditions",
"author": "Morina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Food Funct.",
"key": "ref_148",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox7040053",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_149",
"unstructured": "Miguel, M.G. (2018). Betalains in some species of the Amaranthaceae family: A review. Antioxidants, 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules24173078",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_150",
"unstructured": "Li, G., Meng, X., Zhu, M., and Li, Z. (2019). Research progress of betalain in response to adverse stresses and evolutionary relationship compared with anthocyanin. Molecules, 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9010043",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_151",
"unstructured": "Dominguez, R., Cuenca, E., Mate-Munoz, J.L., Garcia-Fernandez, P., Serra-Paya, N., Estevan, M.C., Herreros, P.V., and Garnacho-Castano, M.V. (2017). Effects of beetroot juice supplementation on cardiorespiratory endurance in athletes. a systematic review. Nutrients, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5539/jfr.v10n1p26",
"article-title": "Betalain-rich dietary supplement, but not PETN, increases vasodilation and nitric oxide: A comparative, single-dose, randomized, placebo-controlled, blinded, crossover pilot study",
"author": "Nemzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "J. Food Res.",
"key": "ref_152",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1113/JP280091",
"article-title": "How to beet hypertension in pregnancy: Is there more to beetroot juice than nitrate?",
"author": "Torrens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3823",
"journal-title": "J. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_153",
"volume": "598",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1945.02860360014004",
"article-title": "Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water",
"author": "Comly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "ref_154",
"volume": "129",
"year": "1945"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3171/2013.3.JNS13266",
"article-title": "Safety and pharmacokinetics of sodium nitrite in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: A phase IIa study",
"author": "Oldfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "634",
"journal-title": "J. Neurosurg.",
"key": "ref_155",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-021-00416-6",
"article-title": "Potential intestinal infection and faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_156",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "Immunology of COVID-19: Current state of the science",
"author": "Vabret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "910",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "ref_157",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.065",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_158",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid1002.030610",
"article-title": "Detection of SARS coronavirus in patients with suspected SARS",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_159",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jech.57.9.652",
"article-title": "The SARS epidemic in Hong Kong",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health",
"key": "ref_160",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-021-04304-4",
"article-title": "Lack of evidence for infectious SARS-CoV-2 in feces and sewage",
"author": "Albert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2665",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_161",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148341",
"article-title": "What is the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 from the use of public toilets?",
"author": "Dancer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148341",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "ref_162",
"volume": "792",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M112.436790",
"article-title": "Intestinal dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) transport mediated by the facilitative sugar transporters, GLUT2 and GLUT8",
"author": "Corpe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9092",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_163",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002",
"article-title": "Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_164",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/159.5.979",
"article-title": "The human gastric bactericidal barrier: Mechanisms of action, relative antibacterial activity, and dietary influences",
"author": "Peterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "979",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_165",
"volume": "159",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000276553",
"article-title": "Ethanol inhibits gastric acid secretion in rats through increased AMP-kinase activity",
"author": "Kopic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Cell. Physiol. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_166",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.001413",
"article-title": "Gastric H, K-ATPase as therapeutic target",
"author": "Sachs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_167",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11894-010-0137-9",
"article-title": "Update on the mechanisms of gastric acid secretion",
"author": "Kopic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "458",
"journal-title": "Curr. Gastro. Rep.",
"key": "ref_168",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.aao4966",
"article-title": "Human intestinal tract serves as an alternative infection route for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eaao4966",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_169",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Alcohol use as a risk factor in infections and healing: A clinician’s perspective",
"author": "Kolls",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev.",
"key": "ref_170",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.772700",
"article-title": "COVID-19 risk appears to vary across different alcoholic beverages",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "772700",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_171",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bies.201800188",
"article-title": "Stress-induced evolutionary innovation: A mechanism for the origin of cell types",
"author": "Wagner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1800188",
"journal-title": "Bioessays",
"key": "ref_172",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11622/smedj.2018043",
"article-title": "Hans Selye (1907–1982): Founder of the stress theory",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "Singap. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_173",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.6.2448",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis of influenza virus-induced pneumonia: Involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2448",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_174",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.2543070",
"article-title": "Oxygen radicals in influenza-induced pathogenesis and treatment with pyran polymer-conjugated SOD",
"author": "Oda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "974",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_175",
"volume": "244",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jit062",
"article-title": "Inducible nitric oxide contributes to viral pathogenesis following highly pathogenic influenza virus infection in mice",
"author": "Perrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1576",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_176",
"volume": "207",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002",
"article-title": "Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_177",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15060711",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_178",
"unstructured": "Mussa, A., Mohd Idris, R.A., Ahmed, N., Ahmad, S., Murtadha, A.H., Tengku Din, T., Yean, C.Y., Wan Abdul Rahman, W.F., Mat Lazim, N., and Uskokovic, V. (2022). High-Dose Vitamin C for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceuticals, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3177/jnsv.60.367",
"article-title": "Vitamin C in the treatment and/or prevention of obesity",
"author": "Quintero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol.",
"key": "ref_179",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010",
"article-title": "Vitamin C pharmacokinetics: Implications for oral and intravenous use",
"author": "Padayatty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_180",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012481",
"article-title": "Why does Japan have so few cases of COVID-19?",
"author": "Iwasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12481",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_181",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.35772/ghm.2020.01043",
"article-title": "Japanese strategy to COVID-19: How does it work?",
"author": "Inoue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "131",
"journal-title": "Glob. Health Med.",
"key": "ref_182",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2009.10.007",
"article-title": "Dietary nitrate in Japanese traditional foods lowers diastolic blood pressure in healthy volunteers",
"author": "Sobko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "136",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_183",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa024",
"article-title": "A randomized clinical trial of the effects of leafy green vegetables and inorganic nitrate on blood pressure",
"author": "Sundqvist",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_184",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medin.2020.10.003",
"article-title": "High serum nitrates levels in non-survivor COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Lorente",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "Med. Intensiv.",
"key": "ref_185",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj0260865",
"article-title": "The chemical nature of vitamin C",
"author": "Svirbely",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "865",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "ref_186",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1932"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM193210132071501",
"article-title": "Diet, nutrition and infection",
"author": "Hess",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "637",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_187",
"volume": "207",
"year": "1932"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.1934.14.3.309",
"article-title": "The influence of nutrition upon resistance to infection",
"author": "Clausen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "309",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_188",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1934"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005792-193405000-00001",
"article-title": "The vitamins and resistance to infection",
"author": "Robertson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "ref_189",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1934"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.68.11.2678",
"article-title": "The significance of the evidence about ascorbic acid and the common cold",
"author": "Pauling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2678",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_190",
"volume": "68",
"year": "1971"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/24.11.1294",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid and the common cold",
"author": "Pauling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1294",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_191",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1971"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1971.03180280086025",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_192",
"unstructured": "Pauling, L. (1970). Vitamin C and the Common Cold, Freeman."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life12010062",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_193",
"unstructured": "Hemilä, H. (2022). Bias against vitamin C in mainstream medicine: Examples from trials of vitamin C for infections. Life, 12."
},
{
"key": "ref_194",
"unstructured": "Pauling, L. (1986). How to Live Longer and Feel Better, Freeman."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.719308",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver disturbance during the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Zhai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "719308",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_195",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1143",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury and COVID-19: A review for clinical practice",
"author": "Ortis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1143",
"journal-title": "World J. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_196",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1120009X.2021.1988203",
"article-title": "Drugs and liver injury: A not to be overlooked binomial in COVID-19",
"author": "Vitrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "207",
"journal-title": "J. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_197",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.031",
"article-title": "Immune-mediated hepatitis with the Moderna vaccine, no longer a coincidence but confirmed",
"author": "Tun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_198",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.017",
"article-title": "Vitamins C and E: Beneficial effects from a mechanistic perspective",
"author": "Traber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1000",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_199",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Nickel and oxidative stress: Cell signaling mechanisms and protective role of vitamin C",
"author": "Das",
"first-page": "1024",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Metab. Immune",
"key": "ref_200",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00269-0",
"article-title": "How does ascorbic acid prevent endothelial dysfunction?",
"author": "May",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1421",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_201",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "History of scurvy and use of vitamin C in critical illness: A narrative review",
"author": "Dresen",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_202",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.110.2865.543",
"article-title": "Sickle cell anemia, a molecular disease",
"author": "Pauling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "543",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_203",
"volume": "110",
"year": "1949"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25687",
"article-title": "Hemoglobin S polymerization and sickle cell disease: A retrospective on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of Pauling’s Science paper",
"author": "Eaton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hematol.",
"key": "ref_204",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Causation and disease: The Henle-Koch postulates revisited",
"author": "Evans",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Yale J. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_205",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1976"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aaa5004",
"article-title": "Vitamin C selectively kills KRAS and BRAF mutant colorectal cancer cells by targeting GAPDH",
"author": "Yun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1391",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_206",
"volume": "350",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.09.008",
"article-title": "Glutathione synthesis",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3143",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta.",
"key": "ref_207",
"volume": "1830",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "ref_208",
"unstructured": "Capra, F. (1975). The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern Mysticism, Shambhala."
},
{
"key": "ref_209",
"unstructured": "Magalhaes, J.R., Singh, R.P., and Passos, L.P. (2004). Nitric Oxide Signaling in Higher Plants, Studium Press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00205",
"article-title": "Chemical biology of H2S signaling through persulfidation",
"author": "Filipovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1253",
"journal-title": "Chem. Rev.",
"key": "ref_210",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-01311-y",
"article-title": "Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase governs cysteine polysulfidation and mitochondrial bioenergetics",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1177",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_211",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2334/josnusd1959.36.254",
"article-title": "Concentrations of thiocyanate and hypothiocyanite in the saliva of young adults",
"author": "Jalil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "254",
"journal-title": "J. Nihon Univ. Sch. Dent.",
"key": "ref_212",
"volume": "36",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10020233",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_213",
"unstructured": "Cegolon, L., Mirandola, M., Salaris, C., Salvati, M.V., Mastrangelo, G., and Salata, C. (2021). Hypothiocyanite and hypothiocyanite/lactoferrin mixture exhibit virucidal activity in vitro against SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.18.1.73",
"article-title": "Nitrite and thiocyanate in the fasting and secreting stomach and in saliva",
"author": "Ruddell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_214",
"volume": "18",
"year": "1977"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2013.07.011",
"article-title": "Total isothiocyanate yield from raw cruciferous vegetables commonly consumed in the United States",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1996",
"journal-title": "J. Funct. Foods",
"key": "ref_215",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10071525",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_216",
"unstructured": "Sorbo, L.D., Michaelsen, V.S., Ali, A., Wang, A., Ribeiro, R.V.P., and Cypel, M. (2022). High doses of inhaled nitric oxide as an innovative antimicrobial strategy for lung infections. Biomedicines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.006",
"article-title": "COVID-19 accelerates endothelial dysfunction and nitric oxide deficiency",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_217",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.071",
"article-title": "Inverse association between hypertension treatment and COVID-19 prevalence in Japan",
"author": "Kinoshita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_218",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.001",
"article-title": "Nitrate from diet might fuel gut microbiota metabolism: Minding the gap between redox signaling and inter-kingdom communication",
"author": "Rocha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_219",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.11.027",
"article-title": "Brassica napus seed meal soil amendment modifies microbial community structure, nitric oxide production and incidence of Rhizoctonia root rot",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1215",
"journal-title": "Soil Biol. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_220",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-020-05281-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_221",
"unstructured": "Jendrny, P., Schulz, C., Twele, F., Meller, S., von Kockritz-Blickwede, M., Osterhaus, A., Ebbers, J., Pilchova, V., Pink, I., and Welte, T. (2020). Scent dog identification of samples from COVID-19 patients—A pilot study. BMC Infect. Dis., 20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.anai.2011.02.016",
"article-title": "Human exhaled breath analysis",
"author": "Popov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol.",
"key": "ref_222",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2011"
}
],
"reference-count": 222,
"references-count": 222,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/2/397"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
