Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771, Feb 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
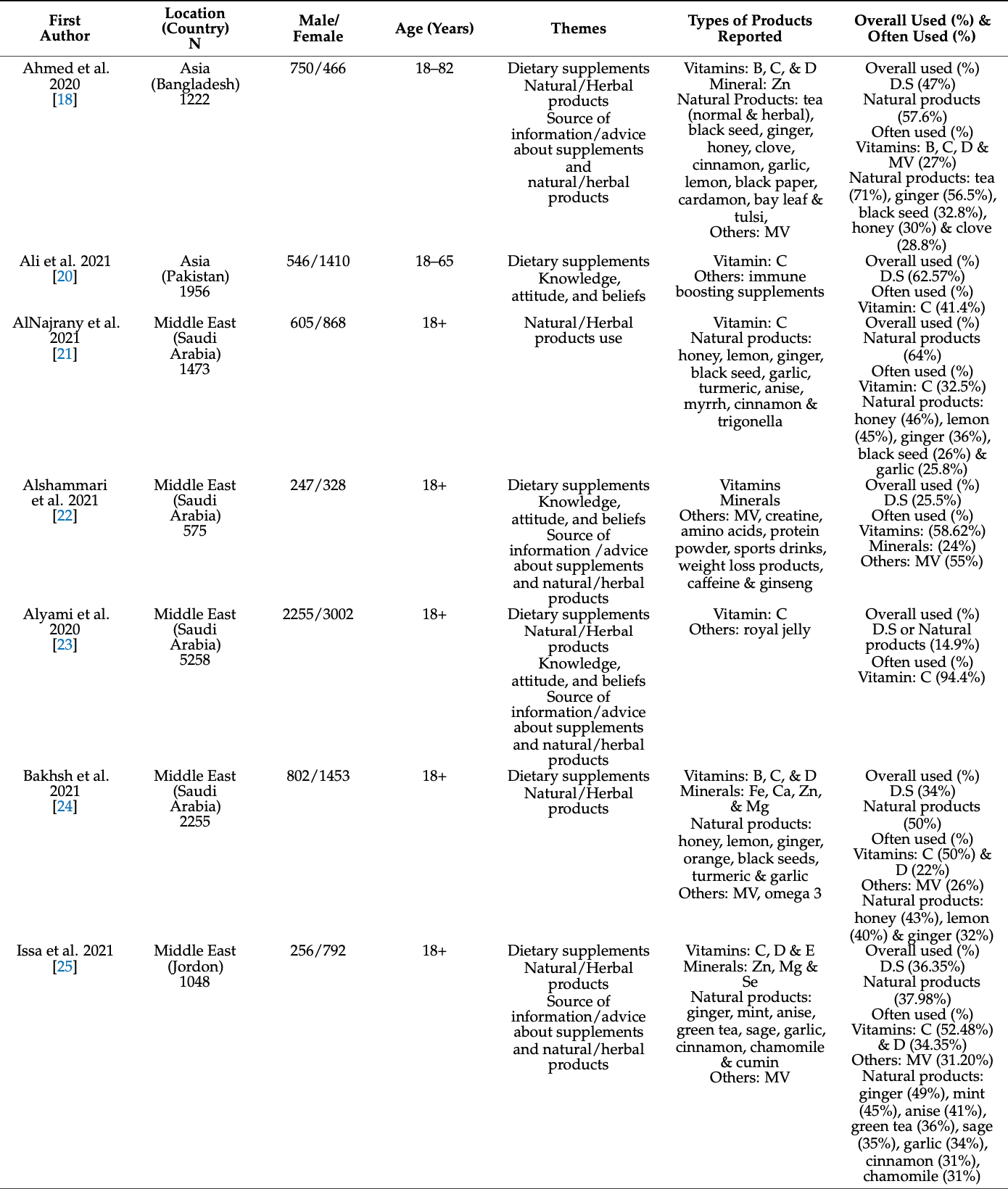
Review of 14 global studies showing that the most frequently used dietary supplements during COVID-19 were vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and multivitamins. The most common reason was for improved immune system functioning or reduced COVID-19 risk. Authors note that participants who have attained higher education levels were more likely to use supplements during COVID-19.
Currently there are 135 vitamin D treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 39% lower mortality [32‑45%], 17% lower ventilation [-5‑35%], 45% lower ICU admission [28‑57%], 22% lower hospitalization [13‑30%], and 17% fewer cases [9‑25%].
Currently there are 42 zinc treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 33% lower mortality [15‑47%], 40% lower ventilation [-1‑65%], 28% lower ICU admission [-8‑51%], 23% lower hospitalization [6‑38%], and 22% fewer cases [-10‑45%].
Currently there are 73 vitamin C for COVID-19 studies, showing 18% lower mortality [9‑27%], 9% lower ventilation [-12‑27%], 23% lower ICU admission [10‑34%], 19% lower hospitalization [7‑30%], and 3% fewer cases [-16‑19%].
1.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
4.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
5.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
6.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
7.
Hemilä et al., Rebound effect explains the divergence in survival after 5 days in a controlled trial on vitamin C for COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1391346.
8.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
9.
Yamasaki et al., Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397.
10.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
11.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
12.
Hemilä (B) et al., Bias against Vitamin C in Mainstream Medicine: Examples from Trials of Vitamin C for Infections, Life, doi:10.3390/life12010062.
13.
May et al., Therapeutic potential of megadose vitamin C to reverse organ dysfunction in sepsis and COVID-19, British Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bph.15579.
15.
Holford et al., Vitamin C—An Adjunctive Therapy for Respiratory Infection, Sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123760.
Arora et al., 2 Feb 2023, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: rahel.mathews@msstate.edu (corresponding author).
Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771
During the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the lack of cure and the intensity of the global spread raised a common awareness of health. The aim of this scoping review is to summarize dietary supplement use globally during first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. A systematic search was conducted in December 2021 following PRISMA guidelines. PubMed, ERIC, and Scopus databases were searched, and 956 results were screened for eligibility. Fourteen cross-sectional studies from 11 countries and 3 continents were examined. All studies were large population surveys investigating healthy eating and supplement use during COVID-19. Vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc and multivitamins were the most widely reported, as well as natural/herbal products such as ginger and honey. The most common reason cited for supplements use was to strengthen immune system and to prevent infection of COVID-19. These studies reported that populations are relying on healthcare providers, family, friends, and social media to learn about supplement use. Future studies on the treatment of COVID-19 should include more evidence for supplement use.
References
Ahmed, Hasan, Akter, Sarkar, Rahman et al., Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0243706
Aldahish, Almanasef, Al-Saad, Asiri, Vasudevan et al., Attitudes and belief among the population in Saudi Arabia about the consumption of herbal products for the prevention of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional study, Indian J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.36468/pharmaceutical-sciences.spl.406
Alfawaz, Khan, Aljumah, Hussain, Al-Daghri, Dietary intake and supplement use among Saudi residents during COVID-19 lockdown, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18126435
Ali, Sohaib, Iqbal, Hayat, Khan et al., Evaluation of COVID-19 disease awareness and its relation to mental health, dietary habits, and physical activity: A cross-sectional study from Pakistan, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-1451
Alnajrany, Asiri, Sales, Alruthia, The commonly utilized natural products during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional online survey, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18094688
Alshammari, Alwakeel, Alghtani, Alsabbagh, Effect of COVID-19 on awareness and consumption of dietary supplements in Saudi Arabia, J. Nat. Sci. Med
Alyami, Orabi, Aldhabbah, Alturki, Aburas et al., Knowledge about COVID-19 and beliefs about and use of herbal products during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study in Saudi Arabia, Saudi Pharm. J, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.023
Bailey, Gahche, Miller, Thomas, Dwyer, Why US adults use dietary supplements, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.2299
Bakhsh, Khawandanah, Naaman, Alashmali, The impact of COVID-19 quarantine on dietary habits and physical activity in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11540-y
Barnes, Ball, Desbrow, Alsharairi, Ahmed, Consumption and reasons for use of dietary supplements in an Australian university population, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2015.10.022
Bin Zarah, Enriquez-Marulanda, Andrade, Relationship between dietary habits, food attitudes and food security status among adults living within the United States three months post-mandated quarantine: A cross-sectional study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113468
Bogan-Brown, Nkrumah-Elie, Ishtiaq, Redpath, Shao, Potential efficacy of nutrient supplements for treatment or trevention of COVID-19, J. Diet. Suppl, doi:10.1080/19390211.2021.1881686
Błaszczyk-Bebenek, Jagielski, Bolesławska, Jagielska, Nitsch-Osuch et al., Nutrition behaviors in Polish adults before and during COVID-19 lockdown, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12103084
Dehghan, Ghanbari, Heidari, Shahrbabaki, Zakeri, Use of complementary and alternative medicine in general population during COVID-19 outbreak: A survey in Iran, J. Integr. Med, doi:10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.004
Fan, Gu, Alemi, Research group for evidence-based Chinese Medicine. Chinese herbal medicine for COVID-19: Current evidence with systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Integr. Med, doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.07.008
Gupta, Sharma, Medicinal properties of Zingiber officinale Roscoe-A review, IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci
Insightslice, Global Immune Health Supplements Market-Global Market Share, Trends, Analysis and Forecasts
Issa, Albals, Yehya, Shriedh, Assessment of lifestyle, herbs, dietary and pharmacological preventive measures used among the public in Jordan to boost immunity during COVID-19 pandemic, Trop. J. Pharm. Res, doi:10.4314/tjpr.v20i9.25
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015
Karbownik, Dobielska, Paul, Kowalczyk, Kowalczyk, Health-, medication-and dietary supplement-related behaviors and beliefs relatively unchanged during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown, Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.11.015
Khadka, Dhamala, Li, Aryal, Magar et al., The use of medicinal plants to prevent COVID-19 in Nepal, J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine, doi:10.1186/s13002-021-00449-w
Khan, Nasir, Nasir, Maha, Rehman, Vitamin D and COVID-19: Is there a role?, J. Diabetes Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00775-6
Kumar, Kumar, Bedi, Gupta, Kumar et al., Role of vitamins and minerals as immunity boosters in COVID-19, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00826-7
Kuropatnicki, Kłósek, Kucharzewski, Honey as medicine: Historical perspectives, J. Apic. Res
Lam, Koon, Chung, Cheung, A public survey of traditional, complementary and integrative medicine use during the COVID-19 outbreak in Hong Kong, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0253890
Lange, Nakamura, Lifestyle factors in the prevention of COVID-19, GHJ, doi:10.1016/j.glohj.2020.11.002
López-Alcalde, Yan, Witt, Barth, Current state of research about Chinese Herbal Medicines (CHM) for the treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A scoping review, J. Altern. Complement. Med, doi:10.1089/acm.2020.0189
López-Moreno, López, Miguel, Garcés-Rimón, Physical and psychological effects related to food habits and lifestyle changes derived from COVID-19 home confinement in the Spanish population, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113445
Mohsen, Yazbeck, Al-Jawaldeh, Chahine, Hamieh et al., Knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to dietary supplementation, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: Findings from a cross-sectional survey in the Lebanese population, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18168856
Nccih, Dietary and Herbal Supplements
Ogundijo, Tas, Onarinde, Exploring the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on eating and purchasing behaviours of people living in England, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051499
Ozenoglu, Cevik, Colak, Altıntas, Alakus, Changes in nutrition and lifestyle habits during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey and the effects of healthy eating attitudes, Med. J. Nutr. Metab, doi:10.3233/MNM-210562
Panagiotakos, Kosti, Pitsavos, How will the way we live look different in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic? A nutrition survey in Greece, Nutr. Health, doi:10.1177/02601060211009033
Puścion-Jakubik, Bielecka, Grabia, Mielech, Markiewicz-Zukowska et al., Consumption of food supplements during the three COVID-19 waves in Poland-Focus on zinc and vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103361
Pérez-Rodrigo, Citores, Bárbara, Ruiz-Litago, Sáenz et al., Patterns of change in dietary habits and physical activity during lockdown in Spain due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020300
Samad, Sodunke, Abubakar, Jahan, Sharma et al., The implications of zinc therapy in combating the COVID-19 global pandemic, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S295377
Speakman, Michienzi, Badowski, Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence, Drugs Context, doi:10.7573/dic.2021-6-2
Subedi, Tchen, Gaire, Hu, Hu, Adjunctive nutraceutical therapies for COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22041963
Zhao, Li, Ke, Huo, Ma et al., Dietary diversity among Chinese residents during the COVID-19 outbreak and its associated factors, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061699
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15030771",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15030771",
"abstract": "<jats:p>During the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the lack of cure and the intensity of the global spread raised a common awareness of health. The aim of this scoping review is to summarize dietary supplement use globally during first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. A systematic search was conducted in December 2021 following PRISMA guidelines. PubMed, ERIC, and Scopus databases were searched, and 956 results were screened for eligibility. Fourteen cross-sectional studies from 11 countries and 3 continents were examined. All studies were large population surveys investigating healthy eating and supplement use during COVID-19. Vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc and multivitamins were the most widely reported, as well as natural/herbal products such as ginger and honey. The most common reason cited for supplements use was to strengthen immune system and to prevent infection of COVID-19. These studies reported that populations are relying on healthcare providers, family, friends, and social media to learn about supplement use. Future studies on the treatment of COVID-19 should include more evidence for supplement use.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15030771"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food Science, Nutrition and Health Promotion, Mississippi State University, Starkville, MS 39762, USA"
}
],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "Ishaan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food Science, Nutrition and Health Promotion, Mississippi State University, Starkville, MS 39762, USA"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Shecoya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food Science, Nutrition and Health Promotion, Mississippi State University, Starkville, MS 39762, USA"
}
],
"family": "Mathews",
"given": "Rahel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-03T08:36:57Z",
"timestamp": 1675413417000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-03T09:27:01Z",
"timestamp": 1675416421000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"609330"
],
"name": "National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-04T05:29:49Z",
"timestamp": 1675488589803
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675296000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/771/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "771",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Office of Dietary Supplements (2022, April 12). Dietary Supplements in the Time of COVID-19, Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/COVID19-HealthProfessional/."
},
{
"article-title": "Lifestyle factors in the prevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Lange",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "GHJ",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2022, April 12). FDA 101: Dietary Supplements, Available online: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/fda-101-dietary-supplements."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.2299",
"article-title": "Why US adults use dietary supplements",
"author": "Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2015.10.022",
"article-title": "Consumption and reasons for use of dietary supplements in an Australian university population",
"author": "Barnes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "524",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-021-00826-7",
"article-title": "Role of vitamins and minerals as immunity boosters in COVID-19",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1001",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential efficacy of nutrient supplements for treatment or trevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Ishtiaq",
"first-page": "336",
"journal-title": "J. Diet. Suppl.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7573/dic.2021-6-2",
"article-title": "Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence",
"author": "Speakman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2021-6-2",
"journal-title": "Drugs Context",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22041963",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Subedi, L., Tchen, S., Gaire, B.P., Hu, B., and Hu, K. (2021). Adjunctive nutraceutical therapies for COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22."
},
{
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "insightSLICE (2022, April 12). Global Immune Health Supplements Market—Global Market Share, Trends, Analysis and Forecasts, 2023—2032. Available online: https://www.insightslice.com/immune-health-supplements-market."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18126435",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Alfawaz, H.A., Khan, N., Aljumah, G.A., Hussain, S.D., and Al-Daghri, N.M. (2021). Dietary intake and supplement use among Saudi residents during COVID-19 lockdown. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.004",
"article-title": "Use of complementary and alternative medicine in general population during COVID-19 outbreak: A survey in Iran",
"author": "Dehghan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "J. Integr. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/02601060211009033",
"article-title": "How will the way we live look different in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic? A nutrition survey in Greece",
"author": "Panagiotakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "677",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Health",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113468",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Bin Zarah, A., Enriquez-Marulanda, J., and Andrade, J.M. (2020). Relationship between dietary habits, food attitudes and food security status among adults living within the United States three months post-mandated quarantine: A cross-sectional study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12103084",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Błaszczyk-Bebenek, E., Jagielski, P., Bolesławska, I., Jagielska, A., Nitsch-Osuch, A., and Kawalec, P. (2020). Nutrition behaviors in Polish adults before and during COVID-19 lockdown. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.11.015",
"article-title": "Health-, medication- and dietary supplement-related behaviors and beliefs relatively unchanged during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown",
"author": "Karbownik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1501",
"journal-title": "Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113445",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "López-Moreno, M., López, M.T.I., Miguel, M., and Garcés-Rimón, M. (2020). Physical and psychological effects related to food habits and lifestyle changes derived from COVID-19 home confinement in the Spanish population. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.15.20175513",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Ahmed, I., Hasan, M., Akter, R., Sarkar, B.K., Rahman, M., Sarker, M.S., and Samad, M.A. (2020). Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103361",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Puścion-Jakubik, A., Bielecka, J., Grabia, M., Mielech, A., Markiewicz-Zukowska, R., Mielcarek, K., Moskwa, J., Naliwajko, S.K., Soroczynska, J., and Gromkowska-Kepka, K.J. (2021). Consumption of food supplements during the three COVID-19 waves in Poland—Focus on zinc and vitamin D. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-1451",
"article-title": "Evaluation of COVID-19 disease awareness and its relation to mental health, dietary habits, and physical activity: A cross-sectional study from Pakistan",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1687",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18094688",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "AlNajrany, S.M., Asiri, Y., Sales, I., and AlRuthia, Y. (2021). The commonly utilized natural products during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional online survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 18."
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of COVID-19 on awareness and consumption of dietary supplements in Saudi Arabia",
"author": "Alshammari",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "J. Nat. Sci. Med.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.023",
"article-title": "Knowledge about COVID-19 and beliefs about and use of herbal products during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study in Saudi Arabia",
"author": "Alyami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1326",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharm. J.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-021-11540-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Bakhsh, M.A., Khawandanah, J., Naaman, R.K., and Alashmali, S. (2021). The impact of COVID-19 quarantine on dietary habits and physical activity in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4314/tjpr.v20i9.25",
"article-title": "Assessment of lifestyle, herbs, dietary and pharmacological preventive measures used among the public in Jordan to boost immunity during COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Issa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1969",
"journal-title": "Trop. J. Pharm. Res.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0253890",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Lam, C.S., Koon, H.K., Chung, V.C.-H., and Cheung, Y.T. (2021). A public survey of traditional, complementary and integrative medicine use during the COVID-19 outbreak in Hong Kong. PLoS ONE, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18168856",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Mohsen, H., Yazbeck, N., Al-Jawaldeh, A., Chahine, N.B., Hamieh, H., Mourad, Y., Skaiki, F., Salame, H., Salameh, P., and Hoteit, M. (2021). Knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to dietary supplementation, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: Findings from a cross-sectional survey in the Lebanese population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13051499",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Ogundijo, D.A., Tas, A.A., and Onarinde, B.A. (2021). Exploring the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on eating and purchasing behaviours of people living in England. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/MNM-210562",
"article-title": "Changes in nutrition and lifestyle habits during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey and the effects of healthy eating attitudes",
"author": "Ozenoglu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Med. J. Nutr. Metab.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020300",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Pérez-Rodrigo, C., Citores, M.G., Bárbara, G.H., Ruiz-Litago, F., Sáenz, L.C., Arija, V., López-Sobaler, A.M., Victoria, E.M., Ortega, R.M., and Partearroyo, T. (2021). Patterns of change in dietary habits and physical activity during lockdown in Spain due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061699",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Zhao, A., Li, Z., Ke, Y., Huo, S., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., and Ren, Z. (2020). Dietary diversity among Chinese residents during the COVID-19 outbreak and its associated factors. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "NCCIH (2022, December 09). Dietary and Herbal Supplements, Available online: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/dietary-and-herbal-supplements."
},
{
"article-title": "Medicinal properties of Zingiber officinale Roscoe—A review",
"author": "Gupta",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00218839.2017.1411182",
"article-title": "Honey as medicine: Historical perspectives",
"author": "Kuropatnicki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "J. Apic. Res.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Attitudes and belief among the population in Saudi Arabia about the consumption of herbal products for the prevention of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional study",
"author": "Aldahish",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13002-021-00449-w",
"article-title": "The use of medicinal plants to prevent COVID-19 in Nepal",
"author": "Khadka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-021-00775-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19: Is there a role?",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Metab. Disord.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S295377",
"article-title": "The implications of zinc therapy in combating the COVID-19 global pandemic",
"author": "Samad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "527",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joim.2020.07.008",
"article-title": "Chinese herbal medicine for COVID-19: Current evidence with systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "J. Integr. Med.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "The Connexion (2023, January 06). Leading French Experts Advise Vitamin D to Counter COVID-19. Available online: https://www.connexionfrance.com/article/French-news/Leading-French-experts-advise-vitamin-D-to-counter-Covid-19."
},
{
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "European Food Safety Authority (2023, January 19). Food Supplements. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/food-supplements."
},
{
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "(2023, January 19). Food and Food Supplements Regulatory Services in UAE. Available online: https://foodsupplements.freyrsolutions.com/food-supplements-regulatory-services-in-uae."
},
{
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Aesan—Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition (2023, January 19). Decálogo para un Consumo Responsable de los Complementos Alimenticios. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/AECOSAN/web/para_el_consumidor/ampliacion/decalogo_consumo_responsable.htm."
},
{
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (2023, January 19). Available online: http://mohfw.gov.bd/."
},
{
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2023, January 10). WHO Expert Meeting on Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/who-expert-meeting-on-evaluation-of-traditional-chinese-medicine-in-the-treatment-of-COVID-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/acm.2020.0189",
"article-title": "Current state of research about Chinese Herbal Medicines (CHM) for the treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A scoping review",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "557",
"journal-title": "J. Altern. Complement. Med.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/771"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
arora2
