Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect against Covid 19
et al., Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005, Jun 2020
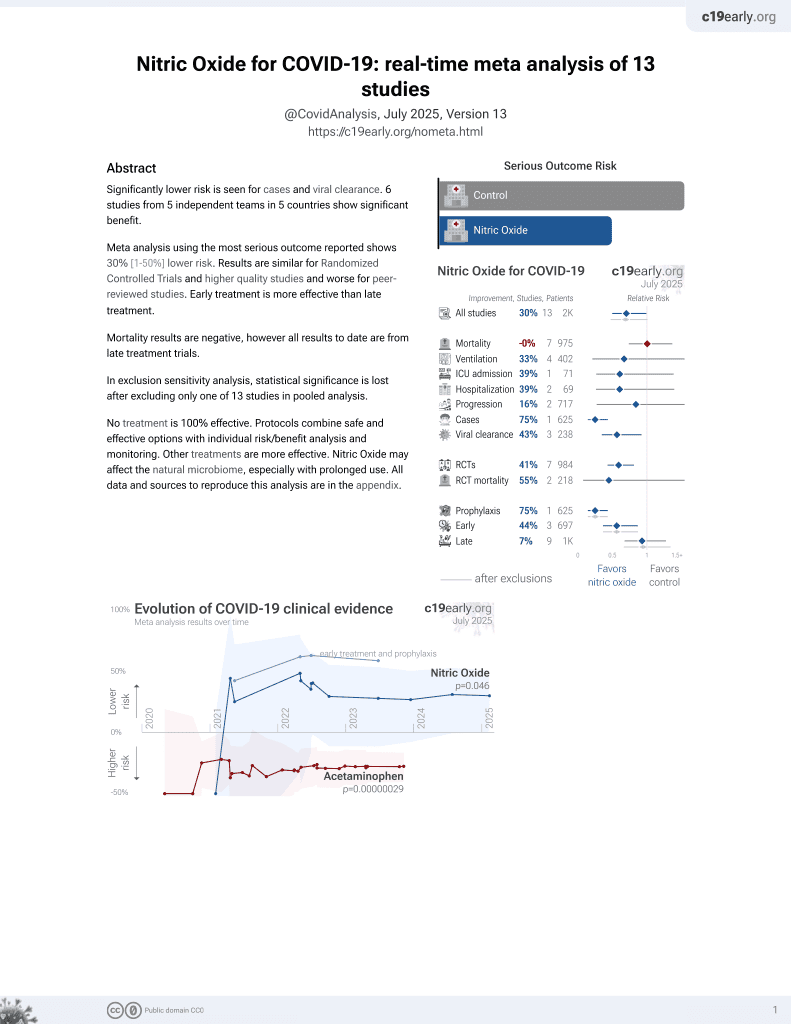
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Hypothesis that reduced incidence of COVID-19 cases for smokers in some studies is due to bursts of high concentrations of nitric oxide during smoking.
1.
Wright et al., Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID‐19: Nasal Sprays, Inhalants and Nanoparticles, Biochemistry Research International, doi:10.1155/bri/8846903.
2.
Zhang et al., Saying No to SARS-CoV-2: the potential of nitric oxide in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia, Medical Gas Research, doi:10.4103/2045-9912.385414.
3.
Zhao et al., Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases?, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552.
4.
Yamasaki et al., Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397.
Hedenstierna et al., 23 Jun 2020, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: goran.hedenstierna@medsci.uu.se.
Abstract: Nitric Oxide 103 (2020) 1–3
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Nitric Oxide
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yniox
Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect
against Covid 19
€ran Hedenstierna a, *, Luni Chen b, Magnus Hedenstierna c, Robert Lieberman d, David H. Fine e
Go
a
Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Department of MTC, Karolinska Institute, Solna, Sweden
c
Department of Infectious Diseases, Danderyd Hospital, Danderyd, Sweden
d
Contello Consulting LLC, New Jersey, USA
e
Pieto LLC, Florida, USA
b
A R T I C L E I N F O
A B S T R A C T
Keywords:
Nitric oxide
Smoking
Viral suppression
Covid-19
It has long been suggested that NO may inhibit an early stage in viral replication. Furthermore, in vitro tests have
shown that NO inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Despite smoking
being listed as a risk factor to contract Covid-19, only a low proportion of the smokers suffered from SARS-corona
infection in China 2003, and from Covid-19 in China, Europe and the US. We hypothesize, that the intermittent
bursts of high NO concentration in cigarette smoke may be a mechanism in protecting against the virus.
Mainstream smoke from cigarettes contains NO at peak concentrations of between about 250 ppm and 1350 ppm
in each puff as compared to medicinal use of no more than 80 to a maximum of 160 ppm. The diffusion of NO
through the cell wall to reach the virus should be significantly more effective at the very high NO concentration
in the smoke, according to classic laws of physics. The only oxide of nitrogen in the mainstream smoke is NO, and
the NO2 concentration that is inhaled is very low or undetectable, and methemoglobin levels are lower in
smokers than non-smokers, reasonably explained by the breaths of air in between the puffs that wash out the NO.
Specialized iNO machines can now be developed to provide the drug intermittently in short bursts at high
concentration dose, which would then provide both a preventative drug for those at high risk, as well as an
effective treatment, without the health hazards associated with smoking.
In this commentary we present a hypothesis that inhaled nitric oxide,
iNO, delivered in short bursts at a high concentration, has a protective
effect against Covid-19.
It has long been suggested that NO may inhibit an early stage in viral
replication and thus prevent viral spread, promoting viral clearance and
recovery of the host [1]. In a recent letter, Ignarro assumed this to apply
also to inhalation of NO (iNO) [2], supported by findings in a previous
SARS-corona epidemic. One of the authors of this commentary treated
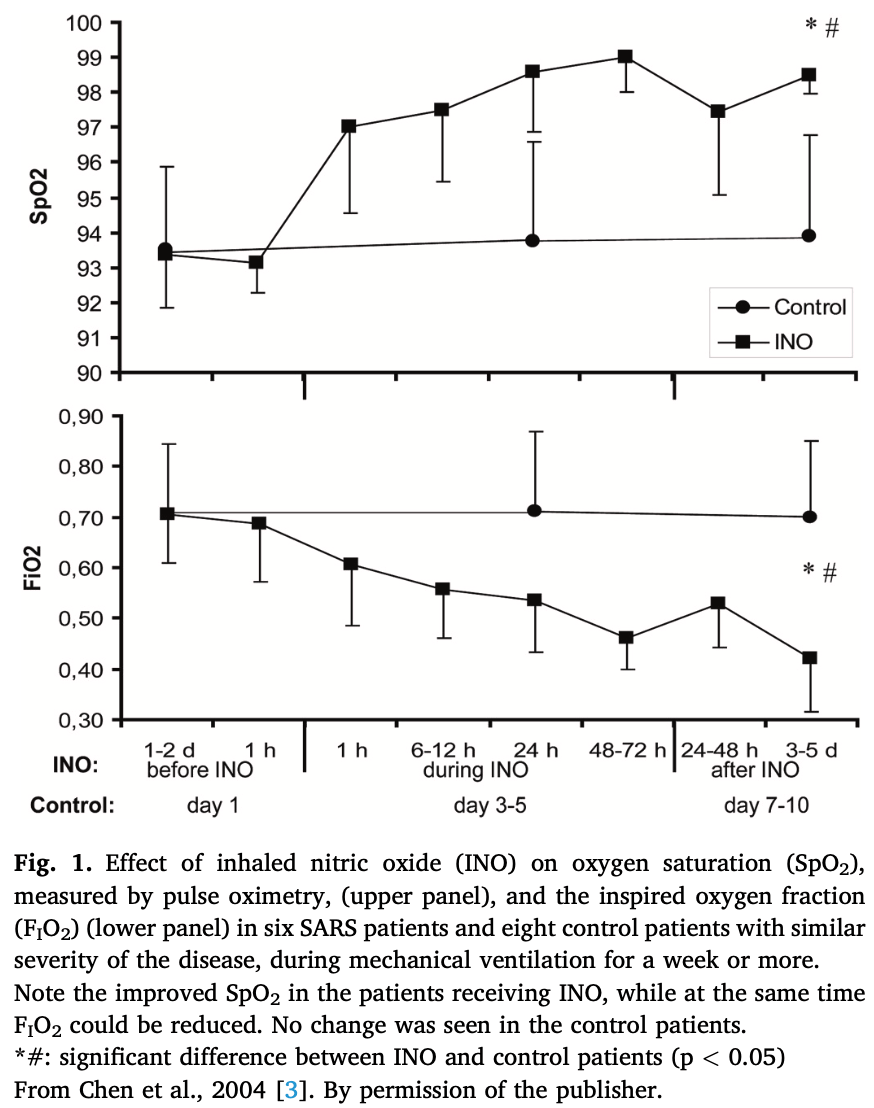
SARS patients in Beijing with iNO in a limited number of patients [3].
iNO dramatically improved arterial oxygenation, expressed as arterial
oxygen tension, PaO2, divided by the inspired oxygen fraction, FIO2,
within 2–3 days. The PaO2/FIO2 ratio increased from a mean of 97–260
mmHg and, as shown in Fig. 1, the transcutaneous O2 saturation
increased and respiratory support was at the same time reduced or
discontinued. The 270% increase in the PaO2/FIO2 ratio is many times
larger than commonly seen when treating ARDS patients with iNO,
where an improvement by 20% is considered significant [4]. A similar
low PaO2/FIO2 ratio (110 mmHg) was also reported in another study
with a larger number of patients [5]. This suggests that the SARS pa
tients benefitted more by iNO with..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005",
"ISSN": [
"1089-8603"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005",
"alternative-id": [
"S1089860320301610"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect against Covid 19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nitric Oxide"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hedenstierna",
"given": "Göran",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Luni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8539-9820",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hedenstierna",
"given": "Magnus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lieberman",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fine",
"given": "David H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"container-title-short": "Nitric Oxide",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-24T01:11:40Z",
"timestamp": 1592961100000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-17T11:30:32Z",
"timestamp": 1597663832000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-07T14:26:32Z",
"timestamp": 1678199192431
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 37,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1592870400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1089860320301610?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1089860320301610?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-3",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.72.6.4547-4551.1998",
"article-title": "Does nitric oxide play a critical role in viral infections?",
"author": "Reiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4547",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib1",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"author": "Ignarro",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/425357",
"article-title": "Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib3",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s001340050982",
"article-title": "Inhalation of nitric oxide in acute lung injury: results of a European multicentre study. The European Study Group of Inhaled Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Lundin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "911",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib4",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13412-5",
"article-title": "HKU/UCH SARS Study Group : clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study",
"author": "Peiris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1767",
"issue": "9371",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib5",
"volume": "361",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Akerstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1966",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib6",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-coronavirus infection in vitro by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, a nitric oxide donor compound",
"author": "Keyaerts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid0909.030362",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome: clinical outcome and prognostic correlates",
"author": "Tsui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1064",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ntr/ntaa059",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and smoking",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nicotine Tob. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/tlcr.2019.03.12",
"article-title": "Tobacco and the lung cancer epidemic in China",
"author": "Parascandola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S21",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Transl. Lung Cancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib11",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "Miyara",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2010419",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of covid-19 in New York city",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2372",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib13",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Smoking prevalence in low in symptomatic patients admitted for COVID-19",
"author": "Gaibazzi",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ntr/ntaa082",
"article-title": "Smoking is associated with COVID-19 progression: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Patanavanich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nicotine Tob. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30239-3",
"article-title": "Tobacco smoking and COVID-19 infection",
"author": "van Zyl-Smit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18332/tid/119324",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and smoking: a systematic review of the evidence",
"author": "Vardavas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Tob. Induc. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib17",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Uk Department of Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib18",
"series-title": "Nitric Oxide Yields of Cigarettes. Results for Cigarettes Sampled in 1996. Commissioned by Smoking Policy Unit, 135 Waterloo Road, London SE 1 BUG June",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/tx050220w",
"article-title": "Quantitative puff-by-puff-resolved characterization of selected toxic compounds in cigarette mainstream smoke",
"author": "Adam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Chem. Res. Toxicol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib19",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of some nitrogenous Blen on components NO/NOx and HCN levels in Mainstream and sidestream smoke",
"author": "Norman",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Beitrage zur Tabakforschung Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thx.2005.056093",
"article-title": "Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: clinical application and interpretation",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "817",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib21",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.06.00113705",
"article-title": "Effect of smoking on exhaled nitric oxide and flow-independent nitric oxide exchange parameters",
"author": "Malinovschi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "339",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib22",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00039896.1985.10545943",
"article-title": "Methemoglobin levels in smokers and non-smokers",
"author": "Borland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "330",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Arch. Environ. Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib23",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2016.06.001",
"article-title": "Nitrogen dioxide reducing ascorbic acid technologies in the ventilator circuit leads to uniform NO concentration during inspiration",
"author": "Pezone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib24",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpregu.00099.2018",
"article-title": "Nicotine and the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Oakes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R895",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib25",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00688-2020",
"article-title": "ACE-2 expression in the small airway epithelia of smokers and COPD patients: implications for COVID-19",
"author": "Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.005_bib26",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1089860320301610"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cancer Research",
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Physiology",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nitric oxide dosed in short bursts at high concentrations may protect against Covid 19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "103"
}
hedenstierna