Real-world effectiveness of simnotrelvir-ritonavir versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in China: a retrospective cohort study
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9, Jul 2025
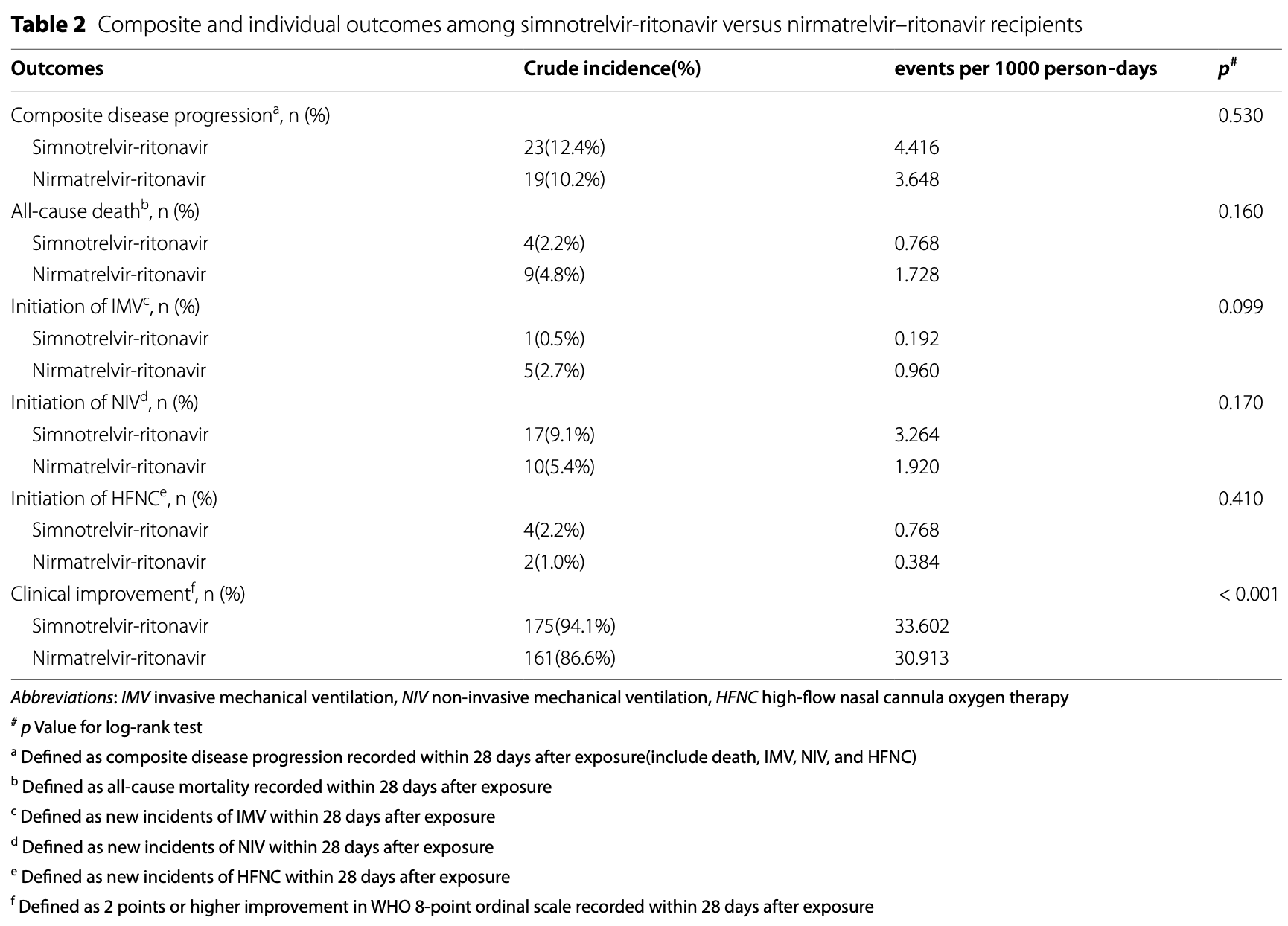
Retrospective 585 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing that xiannuoxin provided better clinical improvement than paxlovid. There were no significant differences for progression, mortality, or respiratory support.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Study covers xiannuoxin and paxlovid.
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Li et al., 1 Jul 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 17 authors, study period 20 December, 2022 - 30 November, 2023.
Contact: ydyyzjq@163.com, haopot@163.com.
Real-world effectiveness of simnotrelvir-ritonavir versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in China: a retrospective cohort study
BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9
Objective This study aims to assess the comparative clinical effectiveness of the 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro) inhibitors simnotrelvir-ritonavir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in China.
Methods The retrospective analysis of data from adult hospitalized patients with COVID-19 treated with either simnotrelvir-ritonavir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir as antiviral treatment strategies will be conducted to determine any differences in clinical outcomes between the two drugs.
Results This study involved a total of 585 participants, with 264 in the simnotrelvir group and 321 in the nirmatrelvir group. Following propensity score matching, there were 186 individuals in each group. There was no statistically significant difference in the cumulative risk of the composite disease progression, all-cause death, and respiratory support at 28 days following initiation of drug exposure between the two groups (p > 0.05). However, the simnotrelvir group exhibited more cases of clinical improvement compared to the nirmatrelvir group (33.602 events per 1000 person-days vs. 30.913 events per 1000 person-days), with a better cumulative incidence in the simnotrelvir group (p < 0.05). The multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that non-severe COVID-19 (HR 0.630, 95% CI 0.496-0.801; p < 0.001), lower C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (HR 0.993, 95% CI 0.990-0.997; p < 0.001), and treatment with simnotrelvir-ritonavir (HR 1.395, 95% CI 1.118-1.741; p = 0.003) were independently associated with a higher likelihood of clinical improvement.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s12879-025-11195-9 . Supplementary Material 1.
Authors' contributions
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all participants in this study through telephone follow-up procedures. Approval of Clinical Research by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University[(2024 L)No. 75].
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Battat, Lavie et al., Nirmatrelvir use and severe covid-19 outcomes during the omicron surge, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919
Boehm, Kronig, Neher, Eckerle, Vetter et al., Geneva Centre for Emerging Viral Diseases. Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: the pandemics within the pandemic, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022
Cao, Wang, Jian, Song, Yisimayi et al., Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3
Charlson, Carrozzino, Guidi, Patierno, Charlson Comorbidity Index: a critical review of clinimetric properties, Psychother Psychosom, doi:10.1159/000521288
Chen, Zhu, Shen, Zhou, Feng et al., Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in severe hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and in patients at high risk for progression to critial illness: a real-world study, J Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1177/08850666241c228841
Deng, Li, Sun, Zhou, Xiao et al., Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvirritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012
Eng, Dantonio, Kadar, Obach, Di et al., Disposition of nirmatrelvir, an orallybioavailable Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease, across animals and humans, Drug Metab Dispos, doi:10.1124/dmd.121.000801
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Fleishaker, Almas et al., Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2309003
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle et al., Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Han, Gao, Li, Yuan, Cui et al., Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in Beijing: a multicenter retrospective cohort study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8
Hu, Cui, Lei, Tang, Zhang et al., Comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ ritonavir and combined use in patients with COVID-19, Infect Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S433186
Iketani, Mohri, Culbertson, Hong, Duan et al., Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2
Jiang, Su, Shang, Zhou, Zhang et al., Structure-based development and preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor simnotrelvir, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-42102-y
Li, Lin, Zhou, Zhong, Zeng et al., Structural basis of the main proteases of coronavirus bound to drug candidate PF-07321332, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.02013-21
Liu, Pan, Zhang, Li, Ma et al., Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694
Ma, Li, Xie, Zhao, Yi et al., Repurposing of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105419
Selvi-Sabater, De La Rubiaortí, Urbieta-Sanz, Oral simnotrelvir for adult patients with mild-to-moderate covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2402378
Wan, Yan, Mok, Wang, Xu et al., Effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-3057
Wang, Møhlenberg, Wang, Zhou, Immune evasion of neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 omicron, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.03.006
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among communitydwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0
Xiong, Su, Zhao, Xie, Shao et al., What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: from structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design, Med Res Rev, doi:10.1002/med.21783
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2334"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9",
"alternative-id": [
"11195"
],
"article-number": "840",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "12 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2 June 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "1 July 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all participants in this study through telephone follow-up procedures. Approval of Clinical Research by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University[(2024 L)No. 75]."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Chuntao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Qingzhao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Dajin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Jiaqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Zehua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiang",
"given": "Yaling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Jinbiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Keke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Yandi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xuemei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jiashu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Yuping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Jianqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Long",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "BMC Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-01T10:29:35Z",
"timestamp": 1751365775000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-01T10:29:38Z",
"timestamp": 1751365778000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"no. 202401AYO70001-239"
],
"name": "2024 Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department-Kunming Medical University Joint Basic Research Program, China"
},
{
"award": [
"no. L2019007"
],
"name": "Medical Leaders Training Program of Yunnan Provincial Health Commission"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-02T04:10:27Z",
"timestamp": 1751429427478,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1751328000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1751328000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "11195_CR1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). Number of COVID-19 cases reported to WHO. 2024. Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"key": "11195_CR2",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). SARS-CoV-2 variant classifications anddefinitions. 2023. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"key": "11195_CR3",
"unstructured": "Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID). Phylodynamics of pandemic coronavirus across the globe. 2024. Available from: https://gisaid.org/phylodynamics/global/nextstrain. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"key": "11195_CR4",
"unstructured": "Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC). COVID-19 vaccination status. 2022. Available from: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_12208/202212/t20221225_263105.html. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"key": "11195_CR5",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-therapeutics-2023.2. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2402378",
"author": "P Selvi-Sabater",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1534",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "11195_CR6",
"unstructured": "Selvi-Sabater P, de la RubiaOrtí JE, Urbieta-Sanz E. Oral simnotrelvir for adult patients with mild-to-moderate covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(16):1534. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2402378.",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14656566.2024.2323597",
"author": "MW McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "233",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Pharmacother",
"key": "11195_CR7",
"unstructured": "McCarthy MW. Simnotrelvir as a potential treatment for COVID-19. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024;25(3):233–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2024.2323597.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21783",
"author": "M Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1965",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Med Res Rev",
"key": "11195_CR8",
"unstructured": "Xiong M, Su H, Zhao W, Xie H, Shao Q, Xu Y. What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: from structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(4):1965–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21783.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.02013-21",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0201321",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "11195_CR9",
"unstructured": "Li J, Lin C, Zhou X, Zhong F, Zeng P, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Yu B, Fan X, McCormick PJ, Fu R, Fu Y, Jiang H, Zhang J. Structural basis of the main proteases of coronavirus bound to drug candidate PF-07321332. J Virol. 2022;96(8):e0201321. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02013-21.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.121.000801",
"author": "H Eng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "576",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab Dispos",
"key": "11195_CR10",
"unstructured": "Eng H, Dantonio AL, Kadar EP, Obach RS, Di L, Lin J, Patel NC, Boras B, Walker GS, Novak JJ, Kimoto E, Singh RSP, Kalgutkar AS. Disposition of nirmatrelvir, an orallybioavailable Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease, across animals and humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2022;50(5):576–90. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.121.000801.",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "11195_CR11",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, Baniecki M, Hendrick VM, Damle B, Simón-Campos A, Pypstra R, Rusnak JM, EPIC-HR Investigators. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2118542.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "11195_CR12",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Fountaine RJ, Yunis C, Fleishaker D, Almas M, Bao W, Wisemandle W, Baniecki ML, Hendrick VM, Kalfov V, Simón-Campos JA, Pypstra R, Rusnak JM. Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(13):1186–95. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2309003.",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3057",
"author": "EYF Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "11195_CR13",
"unstructured": "Wan EYF, Yan VKC, Mok AHY, Wang B, Xu W, Cheng FWT, Lai FTT, Chui CSL, Li X, Wong CKH, Li PH, Cowling BJ, Hung IFN, Lau CS, Wong ICK, Chan EWY. Effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(4):505–14. https://doi.org/10.7326/M22-3057.",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"author": "CKH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1681",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "11195_CR14",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Au ICH, Lau KTK, Lau EHY, Cowling BJ, Leung GM. Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong’s omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22(12):1681–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100694",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "11195_CR15",
"unstructured": "Liu J, Pan X, Zhang S, Li M, Ma K, Fan C, Lv Y, Guan X, Yang Y, Ye X, Deng X, Wang Y, Qin L, Xia Z, Ge Z, Zhou Q, Zhang X, Ling Y, Qi T, Wen Z, Huang S, Zhang L, Wang T, Liu Y, Huang Y, Li W, Du H, Chen Y, Xu Y, Zhao Q, Zhao R, Annane D, Qu J, Chen D. Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023;33:100694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012",
"author": "Y Dian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e24",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "11195_CR16",
"unstructured": "Dian Y, Meng Y, Sun Y, Deng G, Zeng F. Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities. J Infect. 2023;87(2):e24–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"author": "R Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "11195_CR17",
"unstructured": "Arbel R, Wolff Sagy Y, Hoshen M, Battat E, Lavie G, Sergienko R, Friger M, Waxman JG, Dagan N, Balicer R, Ben-Shlomo Y, Peretz A, Yaron S, Serby D, Hammerman A, Netzer D. Nirmatrelvir use and severe covid-19 outcomes during the omicron surge. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(9):790–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2204919.",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2",
"author": "S Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "558",
"issue": "7944",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "11195_CR18",
"unstructured": "Iketani S, Mohri H, Culbertson B, Hong SJ, Duan Y, Luck MI, Annavajhala MK, Guo Y, Sheng Z, Uhlemann AC, Goff SP, Sabo Y, Yang H, Chavez A, Ho DD. Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir. Nature. 2023;613(7944):558–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2.",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-42102-y",
"author": "X Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6463",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "11195_CR19",
"unstructured": "Jiang X, Su H, Shang W, Zhou F, Zhang Y, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Xie H, Jiang L, Nie T, Yang F, Xiong M, Huang X, Li M, Chen P, Peng S, Xiao G, Jiang H, Tang R, Zhang L, Shen J, Xu Y. Structure-based development and preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor simnotrelvir. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6463. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42102-y.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105419",
"author": "L Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105419",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "11195_CR20",
"unstructured": "Ma L, Li Q, Xie Y, Zhao J, Yi D, Guo S, Guo F, Wang J, Yang L, Cen S. Repurposing of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. Antiviral Res. 2022;207:105419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105419.",
"volume": "207",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000521288",
"author": "ME Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Psychother Psychosom",
"key": "11195_CR21",
"unstructured": "Charlson ME, Carrozzino D, Guidi J, Patierno C. Charlson Comorbidity Index: a critical review of clinimetric properties. Psychother Psychosom. 2022;91(1):8–35. https://doi.org/10.1159/000521288.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "11195_CR22",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health (NIH). COVID-19 treatment guidelines: clinical spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 infection. 2023. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"author": "National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China (NHC)",
"first-page": "81",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Chin J Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "11195_CR23",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC). Diagnosis and treatment plan for COVID-19 (Trial Version 9). Chin J Clin Infect Dis. 2022;2(15):81–9.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC)",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Chin J Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "11195_CR24",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC). Diagnosis and treatment plan for COVID-19 (Trial Version 10). Chin J Clin Infect Dis. 2023;16(1):1–9.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "11195_CR25",
"unstructured": "National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). Simnotrelvir tablets/ritonavir tablets (co-packaged) and deuremidevir hydrobromide tablets for treating COVID-19. 2023. Available from: https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2023-01/29/c_888728.htm. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"key": "11195_CR26",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). WHO R&D Blueprint: novel coronavirus COVID-19 therapeutic trial synopsis. 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/blue-print/covid-19-therapeutic-trial-synopsis.pdf. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022",
"author": "E Boehm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect.",
"key": "11195_CR27",
"unstructured": "Boehm E, Kronig I, Neher RA, Eckerle I, Vetter P, Kaiser L, Geneva Centre for Emerging Viral Diseases. Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: the pandemics within the pandemic. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021;27(8):1109–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"author": "Y Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "657",
"issue": "7898",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "11195_CR28",
"unstructured": "Cao Y, Wang J, Jian F, Xiao T, Song W, Yisimayi A, Huang W, Li Q, Wang P, An R, Wang J, Wang Y, Niu X, Yang S, Liang H, Sun H, Li T, Yu Y, Cui Q, Liu S, Yang X, Du S, Zhang Z, Hao X, Shao F, Jin R, Wang X, Xiao J, Wang Y, Xie XS. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature. 2022;602(7898):657–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3.",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.03.001",
"author": "L Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth Factor Rev",
"key": "11195_CR29",
"unstructured": "Wang L, Møhlenberg M, Wang P, Zhou H. Immune evasion of neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 omicron. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;70:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.03.001. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Erratum in: Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024 Jun;77:117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.03.006.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "11195_CR30",
"unstructured": "Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC). National situation of novel coronavirus infection. 2023. Available from: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/. Cited 2025 May 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"author": "G Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e28756",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "11195_CR31",
"unstructured": "Deng G, Li D, Sun Y, Jin L, Zhou Q, Xiao C, Wu Q, Sun H, Dian Y, Zeng F, Pan P, Shen M. Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. J Med Virol. 2023;95(4):e28756. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.28756.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8",
"author": "X Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "11195_CR32",
"unstructured": "Han X, Gao D, Li C, Yuan X, Cui J, Zhao W, Xie F, Wang K, Liu Y, Muo G, Xi N, Zheng M, Wang R, Xiao K, Zhao D, Zhang X, Han X, Wang B, Zhang T, Xie W, Xie L. Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in Beijing: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect Dis. 2024;24(1):57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-023-08965-8.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S433186",
"author": "CY Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7797",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Infect Drug Resist",
"key": "11195_CR33",
"unstructured": "Hu CY, Cui WS, Lei Y, Tang YW, Zhang YY, Su QM, Peng F, Zeng YF, Song JL, Luo CN, Zhou Y, Li XY, Zhao ZX. Comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and combined use in patients with COVID-19. Infect Drug Resist. 2023;22(16):7797–808. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S433186.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"author": "CKH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1213",
"issue": "10359",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "11195_CR34",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Au ICH, Lau KTK, Lau EHY, Cowling BJ, Leung GM. Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study. Lancet. 2022;400(10359):1213–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0.",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/08850666241c228841",
"author": "X Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "742",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Intensive Care Med",
"key": "11195_CR35",
"unstructured": "Chen X, Zhu Y, Shen L, Zhou D, Feng N, Tong Q. Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in severe hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and in patients at high risk for progression to critial illness: a real-world study. J Intensive Care Med. 2024;39(8):742–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/08850666241c228841.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-025-11195-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of simnotrelvir-ritonavir versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in China: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "25"
}
li42