Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study
et al., The Lancent Regional Health, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694, ChiCTR2200058477, Feb 2023
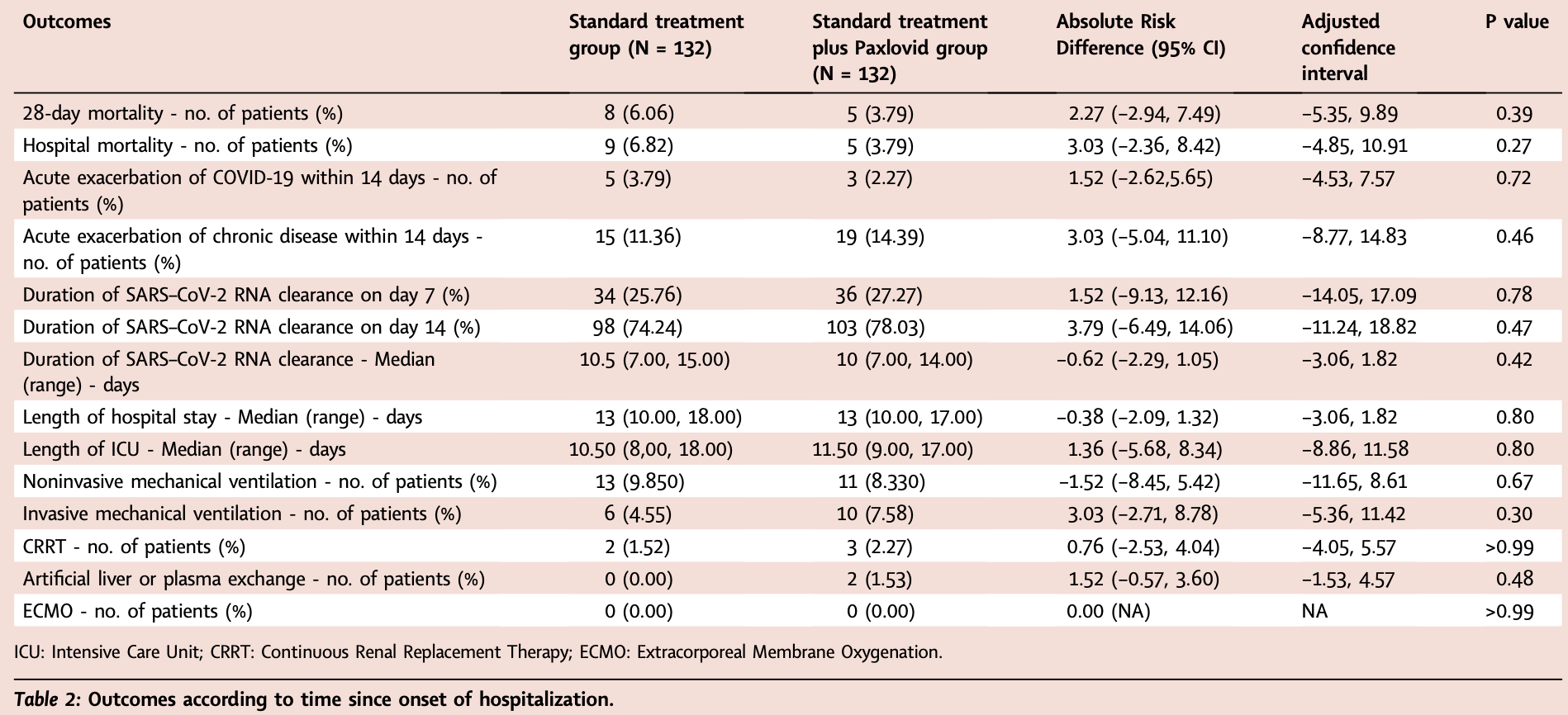
RCT 264 patients in China, showing no significant difference in outcomes with paxlovid.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death, 37.5% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.57, treatment 5 of 132 (3.8%), control 8 of 132 (6.1%), NNT 44, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 66.7% higher, RR 1.67, p = 0.44, treatment 10 of 132 (7.6%), control 6 of 132 (4.5%).
|
|
ICU time, 9.5% higher, relative time 1.10, p = 0.80, treatment 132, control 132.
|
|
risk of progression, 26.7% higher, RR 1.27, p = 0.58, treatment 19 of 132 (14.4%), control 15 of 132 (11.4%), acute exacerbation of chronic disease.
|
|
time to viral-, 4.8% lower, relative time 0.95, p = 0.42, treatment 132, control 132.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Liu et al., 5 Feb 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, 34 authors, study period 10 April, 2022 - 19 May, 2022, trial ChiCTR2200058477.
Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694
Background Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir (Paxlovid) reduced the risk of hospitalization or death by 89% in high-risk, ambulatory adults with COVID-19. We aimed at studying the efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in hospitalized adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 (Omicron BA.2.2 variant) infection and severe comorbidities.
Methods We conducted an open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled trial in which hospitalized adult patients with severe comorbidities were eligible and assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either 300 mg of nirmatrelvir plus
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data related to this article can be found at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694.
References
Bajaj, Gadi, Spihlman, Wu, Choi et al., Aging, immunity, and COVID-19: how age influences the host immune response to coronavirus infections?, Front Physiol
Bajema, Dahl, Evener, Comparative effectiveness and antibody responses to moderna and pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines among hospitalized veterans -five veterans affairs medical centers, United States, february 1, MMWR Morbidity and mortality weekly report
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chron Dis
Dai, Zhao, Wu, Effects of comorbidities on the elderly patients with COVID-19: clinical characteristics of elderly patients infected with COVID-19 from sichuan, China, J Nutr Health Aging
Dro, Rosik, Lechowicz, An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Inc, PAXLOVID nirmatrelvir and ritonavir: US fact sheet for healthcare providers
Inc, Pfizer Reports Additional Data on PAXLOVID™ Supporting Upcoming New Drug Application Submission to U
Inc, Pfizer shares top-line results from phase 2/3 EPIC-PEP study of PAXLOVID™ for post-exposure prophylactic use
Madhi, Kwatra, Myers, Population immunity and covid-19 severity with omicron variant in South Africa, N Engl J Med
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients. an official publication of the, Infectious Diseases Society of America Clin Infect Dis
Nhcotpsro, Guidelines on the Diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19
Organization, WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Perico, Benigni, Casiraghi, Ng, Renia et al., Immunity, endothelial injury and complement-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19, Nat Rev Nephrol
Pfizer, to household member(s) with a confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 infection
Radovanovic, Seifert, Urban, Validity of Charlson Comorbidity Index in patients hospitalised with acute coronary syndrome. Insights from the nationwide AMIS Plus registry 2002-2012, Heart (British Cardiac Society)
Rosenberg, Holtgrave, Dorabawila, New COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations among adults, by vaccination status -New York, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Sun, Lin, Wang, Gao, Ye, Paxlovid in patients who are immunocompromised and hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Lancet Infect Dis
Tenforde, Self, Naioti, Sustained effectiveness of pfizer-BioNTech and moderna vaccines against COVID-19 associated hospitalizations among adults -United States, march-July 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Vincent, De Mendonça, Cantraine, Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on "sepsis-related problems" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, Crit Care Med
Zeger, Liang, Albert, Models for longitudinal data: a generalized estimating equation approach, Biometrics
Zhang, Zhang, Chen, Shanghai's life-saving efforts against the current omicron wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694",
"ISSN": [
"2666-6065"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694",
"alternative-id": [
"S2666606523000123"
],
"article-number": "100694",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jiao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Xiaojun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Sheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fan",
"given": "Cunyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guan",
"given": "Xiangdong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ye",
"given": "Xiaofei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Xingqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8647-9283",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yunfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qin",
"given": "LunXiu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Zhijie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ge",
"given": "Zi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Quanhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qi",
"given": "Tangkai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wen",
"given": "Zhenliang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Sisi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Tao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yongan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yanxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Wenzhe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Du",
"given": "Hangxiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yizhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Ren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Annane",
"given": "Djillali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Jieming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1999-0211",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Dechang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-06T04:58:48Z",
"timestamp": 1675659528000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-06T15:16:05Z",
"timestamp": 1701875765000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81873944",
"82172152"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100008233",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100018920",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ruijin Hospital"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T15:59:39Z",
"timestamp": 1712073579210
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 41,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680307200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672963200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2666606523000123?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2666606523000123?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100694",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Organization WH",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drup.2021.100794",
"article-title": "An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment",
"author": "Drożdżal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist Updates",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib2",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e1",
"article-title": "New COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations among adults, by vaccination status - New York, May 3-July 25, 2021",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1150",
"issue": "34",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib3",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e2",
"article-title": "Sustained effectiveness of pfizer-BioNTech and moderna vaccines against COVID-19 associated hospitalizations among adults - United States, march-July 2021",
"author": "Tenforde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1156",
"issue": "34",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib4",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7049a2",
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness and antibody responses to moderna and pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines among hospitalized veterans - five veterans affairs medical centers, United States, february 1-September 30, 2021",
"author": "Bajema",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1700",
"issue": "49",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morbidity and mortality weekly report",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib5",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00430-3",
"article-title": "Paxlovid in patients who are immunocompromised and hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1279",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib6",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00838-8",
"article-title": "Shanghai's life-saving efforts against the current omicron wave of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2011",
"issue": "10340",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib7",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119658",
"article-title": "Population immunity and covid-19 severity with omicron variant in South Africa",
"author": "Madhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1314",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib8",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Pfizer",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"issue": "6575",
"journal-title": "Science (New York, NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib10",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Inc P",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib12",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Inc P",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib13"
},
{
"author": "Inc P",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib14",
"series-title": "Pfizer Reports Additional Data on PAXLOVID™ Supporting Upcoming New Drug Application Submission to U.S",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"first-page": "ciac443",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "China NHCotPsRo",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2531734",
"article-title": "Models for longitudinal data: a generalized estimating equation approach",
"author": "Zeger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1049",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Biometrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib17",
"volume": "44",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"author": "Commission SMH",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016",
"article-title": "Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on \"sepsis-related problems\" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine",
"author": "Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1793",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib19",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Chron Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib20",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"article-title": "Validity of Charlson Comorbidity Index in patients hospitalised with acute coronary syndrome. Insights from the nationwide AMIS Plus registry 2002-2012",
"author": "Radovanovic",
"first-page": "288",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Heart (British Cardiac Society)",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib21",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1486-1",
"article-title": "Effects of comorbidities on the elderly patients with COVID-19: clinical characteristics of elderly patients infected with COVID-19 from sichuan, China",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Health Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib22",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Aging, immunity, and COVID-19: how age influences the host immune response to coronavirus infections?",
"author": "Bajaj",
"journal-title": "Front Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib23",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-020-00357-4",
"article-title": "Immunity, endothelial injury and complement-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Nephrol",
"key": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694_bib24",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666606523000123"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Psychiatry and Mental health",
"Geriatrics and Gerontology",
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Obstetrics and Gynecology",
"Health Policy",
"Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "33"
}