The potential of carrageenan for the drug discovery of COVID-19 via molecular docking with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2
, H., Journal of Bioinformatics and Genomics, doi:10.18454/jbg.2022.18.2.001, Nov 2022
In Silico study identifying significant binding affinity for ACE2 and Mpro with kappa-, lambda-, and iota-carrageenan.
19 preclinical studies support the efficacy of iota-carrageenan for COVID-19:
1.
Herida et al., Chemical Insights into the Antiviral Mechanisms of Marine Sulfated Polysaccharides: An In-Silico Screening and Molecular Docking Study, Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, doi:10.33263/BRIAC155.071.
2.
Krylova et al., Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26136175.
3.
Rohilla et al., Algae Polysaccharides (Carrageenan and Alginate)—A Treasure-Trove of Antiviral Compounds: An In Silico Approach to Identify Potential Candidates for Inhibition of S1-RBD Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Stresses, doi:10.3390/stresses3030039.
4.
Thet, H., The potential of carrageenan for the drug discovery of COVID-19 via molecular docking with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2, Journal of Bioinformatics and Genomics, doi:10.18454/jbg.2022.18.2.001.
5.
Alsaidi et al., Griffithsin and Carrageenan Combination Results in Antiviral Synergy against SARS-CoV-1 and 2 in a Pseudoviral Model, Marine Drugs, doi:10.3390/md19080418.
6.
Sattari et al., Repositioning Therapeutics for COVID-19: Virtual Screening of the Potent Synthetic and Natural Compounds as SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Inhibitors, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-37994/v1.
7.
Hoffmann et al., Controlling the Sulfation Density of Glycosaminoglycan Glycopolymer Mimetics Enables High Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Reduces Anticoagulant Activity, Biomacromolecules, doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.5c00576.
8.
Yathindranath et al., Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Host Cell Infection, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S448005.
9.
Setz et al., Iota-Carrageenan Inhibits Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Omicron BA.1, BA.2 and BA.5, Nutraceuticals, doi:10.3390/nutraceuticals3030025.
10.
Meister et al., Virucidal activity of nasal sprays against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, Journal of Hospital Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2021.10.019.
11.
Bovard et al., Iota-carrageenan extracted from red algae is a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 infection in reconstituted human airway epithelia, Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101187.
12.
Fröba et al., Iota-Carrageenan Inhibits Replication of SARS-CoV-2 and the Respective Variants of Concern Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms222413202.
13.
Varese et al., Iota-carrageenan prevents the replication of SARS-CoV-2 on an in vitro respiratory epithelium model, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.04.27.441512.
14.
Morokutti-Kurz et al., Iota-carrageenan neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 and inhibits viral replication in vitro, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0237480.
15.
Song et al., Inhibitory activities of marine sulfated polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2, Food & Function, doi:10.1039/D0FO02017F.
Thet et al., 22 Nov 2022, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
THE POTENTIAL OF CARRAGEENAN FOR THE DRUG DISCOVERY OF COVID-19 VIA MOLECULAR DOCKING WITH ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME 2 (ACE2) AND THE MAIN PROTEASE (MPRO) OF SAR-COV-2
doi:10.18454/jbg.2022.18.2.001
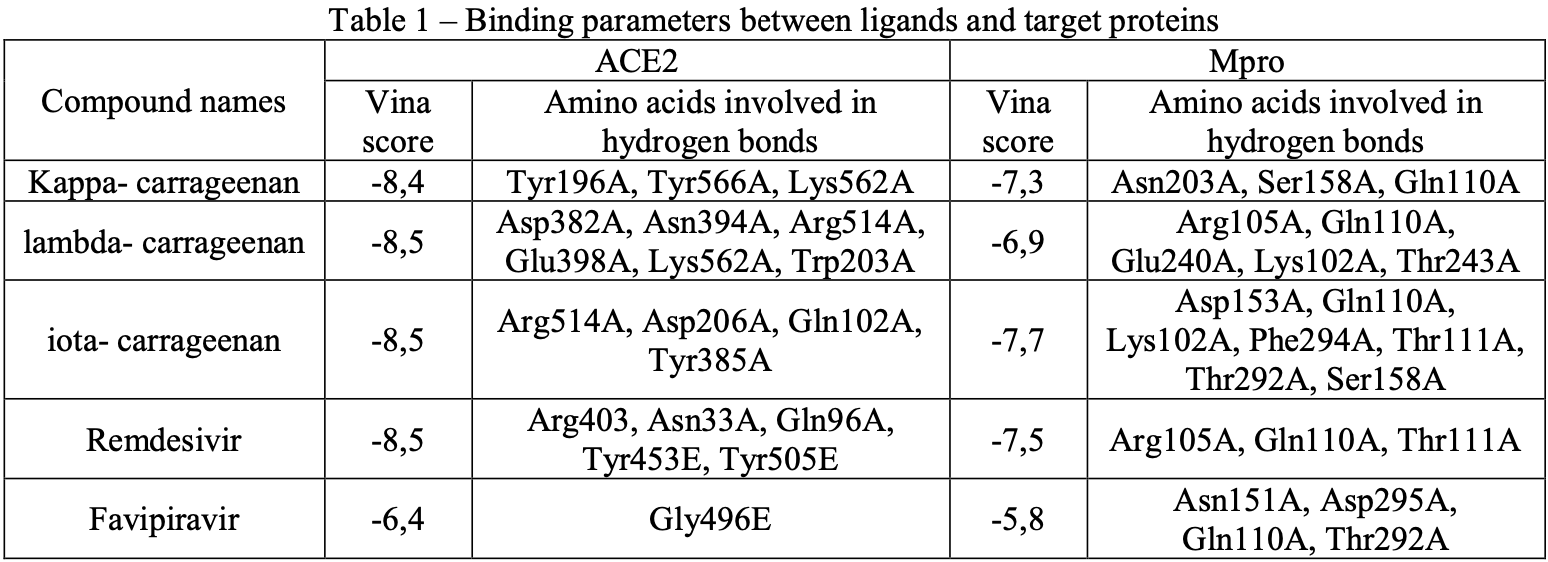
The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified COVID-19 as a pandemic infection due to the global spread of new corona virus infections. Due to this virus infection, millions of people all around the world had to die or endure severe disease. It will be crucial to find new therapeutic treatments in order to prepare for a similar viral pandemic in the future. Carrageenans have apparently been effective against 12 viruses, including SAR-COV-2. In this investigation, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and main protease (Mpro) were used as molecular targets for virtual screening of kappa-, lambda-, and iotacarrageenans. When compared to antiviral drugs, the results show that all three carrageenans have substantial binding affinity for ACE2 and Mpro. The binding affinity of iota-carrageenan is greater than that of other compounds. The binding affinity suggests that carrageenans could be utilized to produce potent antiviral drugs.
Protein-ligand interaction The best poses of the protein-ligand complex pdb file acquired from the CB-Dock web server were submitted to the The ProteinPlus web server (http://protein.plus). PoseView [7] was used to analyze the 2D interaction diagram with hydrogen and hydrophobic contacts for the protein-ligand interaction.
Results and Discussion In order to estimate the binding sites and affinities with the Autodock Vina program, carrageenans were molecularly docked with HER2 and Mpro utilizing CB-Dock, an online application. Since 2019, the CB-Dock web server, which Autodock Vina is utilized for, has seen roughly 200 entries per day posted by academics from around the world. AutoDock Vina is an open-source, free software program that quickly determines the binding affinity (Vina scores) that roughly represent the binding energy (Kcal/mol). Affinity indicates the extent of the drug's interaction with the receptor. A low vina score denotes a high binding affinity of the protein to the ligand. Drug candidates are picked from ligands that bind firmly to the target protein because the stronger the connections, the more the ligand will influence the physiological function of the target proteins. A high affinity usually results in a reduced dose requirement [8] . Lambda-and iota-carrageenan had the lowest scores for ACE2 with vina values of -8.5, followed by kappa-carrageenan (-8.4), albeit their scores are extremely close to one another. Remdesivir and Favipiravir, the..
References
Alvarez-Vinas, Alvarez-Vinas, Souto, Florez-Fernandez, Antiviral Activity of Carrageenans and Processing Implications / M, doi:10.3390/md19080437
Aung, Proximicin A-C as prospective HER2-positive and negative breast cancer drugs: Molecular docking and in silico ADME modeling, IPS Journal of Molecular Docking Simulations, doi:10.54117/ijmds.v1i1.9
Froba, Delta, Froba, Grobe, Setz, Iota-Carrageenan Inhibits Replication of SARS-CoV-2 and the Respective Variants of Concern Alpha, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms222413202
Joshi, Joshi, Joshi, Sharma, European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
Liu, Liu, Yang, Gan, CB-Dock2: improved protein-ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting, Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac394
Ni, Ni, Yang, Yang, Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in Covid 19, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0
Padmi, Padmi, Kharisma, Ansori, Macroalgae Bioactive Compounds for the potential Antiviral of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study, J Pure Appl Microbiol, doi:10.2227/JPAM.16.2.26
Pantsar, Binding Affinity via Docking: Fact and Fiction / T, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules2381899
Robinson, Why we still need drugs for COVID-19 and can't just rely on vaccines, doi:10.1111/resp.14199
Stierand, Poseview-molecular interaction patterns at a glance / Stierand and Rarey, Journal of Cheminformatics
Vicidomini, In silico investigation on the interaction of Chiral phytochemicals from Opuntia ficus-indica with SARS-CoV-2 Mpro / C. Vicidomini, doi:10.3390/sym1361041
Yadav, Chaudhary, Jain, None, doi:10.3390/cells10040821
Yadav, Role of structural and Non-structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18454/JBG.2022.18.2.001",
"URL": "https://journal-biogen.org/index.php/jbg/article/view/50",
"abstract": "The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified COVID-19 as a pandemic infection due to the global spread of new corona virus infections. Due to this virus infection, millions of people all around the world had to die or endure severe disease. It will be crucial to find new therapeutic treatments in order to prepare for a similar viral pandemic in the future. Carrageenans have apparently been effective against 12 viruses, including SAR-COV-2. In this investigation, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and main protease (Mpro) were used as molecular targets for virtual screening of kappa-, lambda-, and iota- carrageenans. When compared to antiviral drugs, the results show that all three carrageenans have substantial binding affinity for ACE2 and Mpro. The binding affinity of iota-carrageenan is greater than that of other compounds. The binding affinity suggests that carrageenans could be utilized to produce potent antiviral drugs.",
"author": [
{
"family": "Thet",
"given": "H.A."
}
],
"categories": [
"Covid-19",
"Carrageenan",
"binding affinity",
"ACE2",
"Mpro",
"каррагинан",
"связывающая аффинность"
],
"container-title": "Journal of Bioinformatics and Genomics",
"contributor": [
{
"family": "Thet",
"given": "H.A."
}
],
"copyright": "Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International",
"id": "https://doi.org/10.18454/jbg.2022.18.2.001",
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"page": "Pages 1-6",
"publisher": "Издательский дом Цифра",
"title": "THE POTENTIAL OF CARRAGEENAN FOR THE DRUG DISCOVERY OF COVID-19 VIA MOLECULAR DOCKING WITH ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME 2 (ACE2) AND THE MAIN PROTEASE (MPRO) OF SAR-COV-2",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "Выпуск 2 "
}