Quercetin: A Functional Food-Flavonoid Incredibly Attenuates Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections through Immunomodulatory Actions
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28030938, Jan 2023
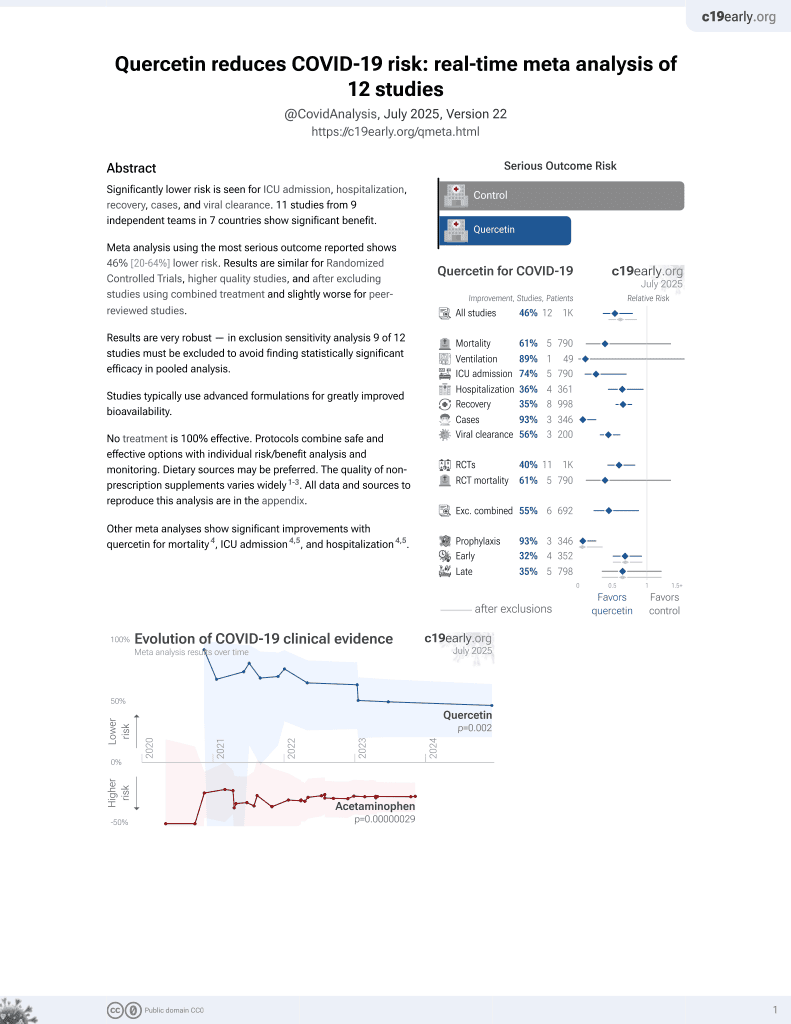
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the antiviral properties of quercetin and derivatives, and potential mechanisms of action.
1.
Ricke, D., Mast cells and histamine receptor-targeted adjunctive treatments for COVID-19: A literature review, Innovative Medicines & Omics, doi:10.36922/IMO025440058.
2.
Shokri-Afra et al., Targeting SIRT1: A Potential Strategy for Combating Severe COVID‐19, BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/bmri/9507417.
3.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
4.
Duan et al., Bioactive compounds,quercetin, curcumin and β-glucan,regulate innate immunity via the gut-liver-brain axis, Trends in Food Science & Technology, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104864.
5.
Beşler et al., Investigation of potential effects of quercetin on COVID-19 treatment: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials, Clinical Science of Nutrition, doi:10.62210/ClinSciNutr.2024.86.
6.
Ho et al., Therapeutic Implications of Quercetin and its Derived-products in COVID-19 Protection and Prophylactic, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30080.
7.
Vajdi et al., Effect of polyphenols against complications of COVID-19: current evidence and potential efficacy, Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-024-00585-6.
8.
Chen et al., Effect and mechanism of quercetin or quercetin‐containing formulas against COVID‐19: From bench to bedside, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.8175.
9.
Yong et al., Natural Products-Based Inhaled Formulations for Treating Pulmonary Diseases, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/ijn.s451206.
10.
Agrawal et al., Antiviral Significance of Isoquercetin (Quercetin-3-O-Glucoside) With Special Reference to its Anti-Coronaviral Potential, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231219560.
11.
Matías-Pérez et al., Relationship of quercetin intake and oxidative stress in persistent Covid, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1278039.
12.
Georgiou et al., Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248141.
13.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
14.
Dinda et al., Anti-SARS-CoV-2, antioxidant and immunomodulatory potential of dietary flavonol quercetin: Focus on molecular targets and clinical efficacy, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports, doi:10.1016/j.ejmcr.2023.100125.
15.
Mirza et al., Quercetin as a Therapeutic Product: Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Action and Clinical Applications—A Review, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16111631.
16.
Massimo Magro et al., Use of Quercetin for Therapeutic Purposes in COVID-19 Infections: The Opinion of the Geriatrician Doctor, Journal of Modern Biology and Drug Discovery, doi:10.53964/jmbdd.2023004.
17.
Shorobi et al., Quercetin: A Functional Food-Flavonoid Incredibly Attenuates Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections through Immunomodulatory Actions, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28030938.
18.
Gasmi et al., Quercetin in the Prevention and Treatment of Coronavirus Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15091049.
19.
Rizky et al., The pharmacological mechanism of quercetin as adjuvant therapy of COVID-19, Life Research, doi:10.53388/life2022-0205-302.
20.
Imran et al., The Therapeutic and Prophylactic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19: An Outlook on the Clinical Studies, Inventive Compositions, and Patent Literature, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11050876.
Shorobi et al., 17 Jan 2023, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: atiar@cu.ac.bd (corresponding author).
Quercetin: A Functional Food-Flavonoid Incredibly Attenuates Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections through Immunomodulatory Actions
Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28030938
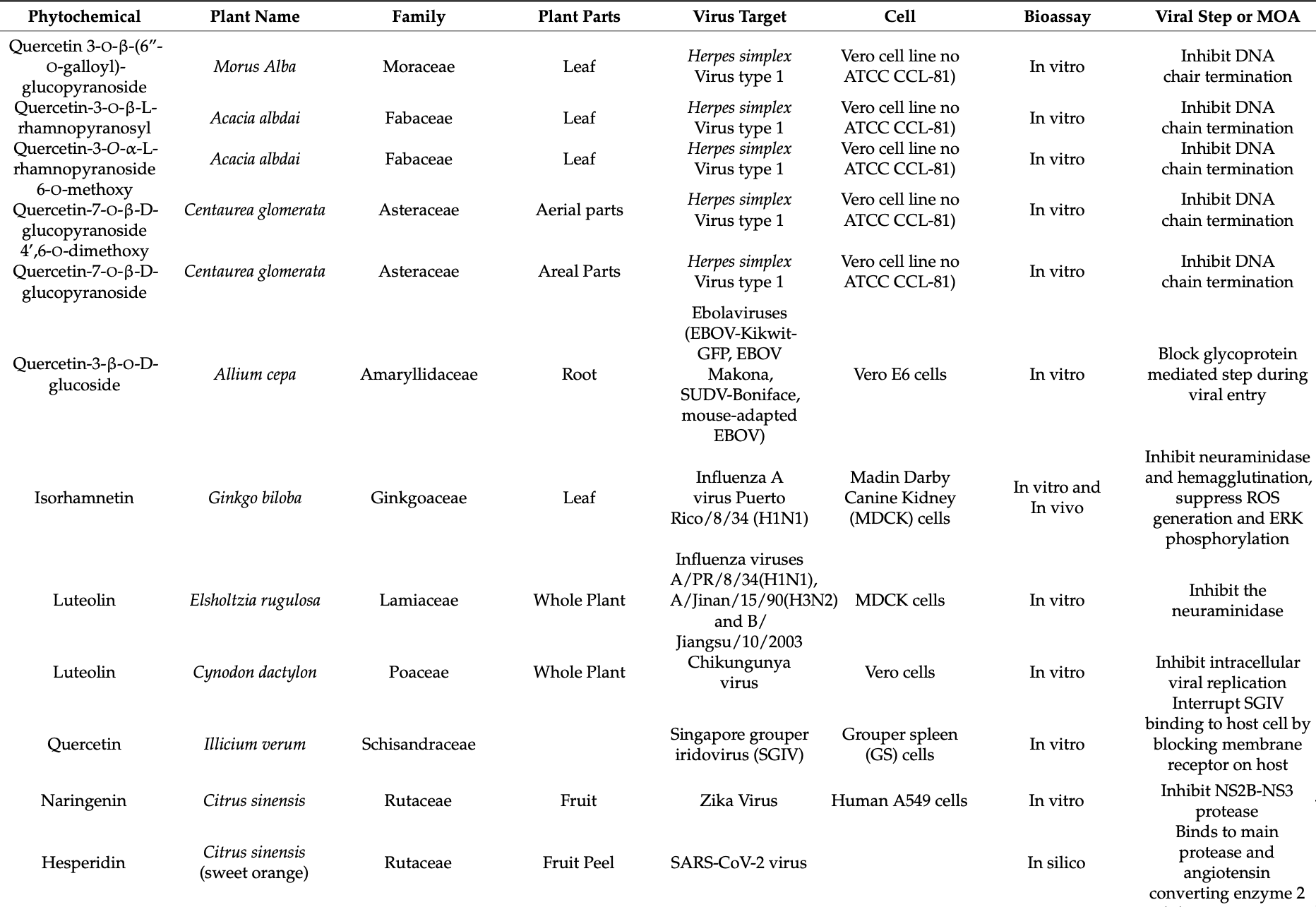
Many of the medicinally active molecules in the flavonoid class of phytochemicals are being researched for their potential antiviral activity against various DNA and RNA viruses. Quercetin is a flavonoid that can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits and vegetables. It has been reported to be effective against a variety of viruses. This review, therefore, deciphered the mechanistic of how Quercetin works against some of the deadliest viruses, such as influenza A, Hepatitis C, Dengue type 2 and Ebola virus, which cause frequent outbreaks worldwide and result in significant morbidity and mortality in humans through epidemics or pandemics. All those have an alarming impact on both human health and the global and national economies. The review extended computing the Quercetin-contained natural recourse and its modes of action in different experimental approaches leading to antiviral actions. The gap in effective treatment emphasizes the necessity of a search for new effective antiviral compounds. Quercetin shows potential antiviral activity and inhibits it by targeting viral infections at multiple stages. The suppression of viral neuraminidase, proteases and DNA/RNA polymerases and the alteration of many viral proteins as well as their immunomodulation are the main molecular mechanisms of Quercetin's antiviral activities. Nonetheless, the huge potential of Quercetin and its extensive use is inadequately approached as a therapeutic for emerging and re-emerging viral infections. Therefore, this review enumerated the food-functioned Quercetin source, the modes of action of Quercetin for antiviral effects and made insights on the mechanism-based antiviral action of Quercetin.
References
Afdhal, Reddy, Nelson, Lawitz, Gordon et al., Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Previously Treated HCV Genotype 1 Infection, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1316366
Afdhal, Zeuzem, Kwo, Chojkier, Gitlin et al., Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Untreated HCV Genotype 1 Infection, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1402454
Ahmed, Fahim, Ahmed, Almuzafar, Ahmed et al., The Preventive Effects and the Mechanisms of Action of Navel Orange Peel Hydroethanolic Extract, Naringin, and Naringenin in N-Acetyl-p-aminophenol-Induced Liver Injury in Wistar Rats, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2019/2745352
Al-Ashaal, El-Sheltawy, Antioxidant capacity of hesperidin from Citrus peel using electron spin resonance and cytotoxic activity against human carcinoma cell lines, Pharm. Biol, doi:10.3109/13880209.2010.509734
Almeida, Borge, Piskula, Tudose, Tudoreanu et al., Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf, doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12342
Ashour, Laurent-Rolle, Shi, García-Sastre, NS5 of Dengue Virus Mediates STAT2 Binding and Degradation, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02188-08
Atashpour, Fouladdel, Movahhed, Barzegar, Ghahremani et al., Quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in CD133+ cancer stem cells of human colorectal HT29 cancer cell line and enhances anticancer effects of doxorubicin, Iran J. Basic Med. Sci, doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2015.4643
Bachar, Mazumder, Bachar, Aktar, Al Mahtab, A Review of Medicinal Plants with Antiviral Activity Available in Bangladesh and Mechanistic Insight Into Their Bioactive Metabolites on SARS-CoV-2, HIV and HBV, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.732891
Bachmetov, Gal-Tanamy, Shapira, Vorobeychik, Giterman-Galam et al., Suppression of hepatitis C virus by the flavonoid quercetin is mediated by inhibition of NS3 protease activity, J. Viral. Hepat, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01507.x
Badshah, Faisal, Muhammad, Poulson, Emwas et al., Antiviral activities of flavonoids, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111596
Baseler, Chertow, Johnson, Feldmann, Morens, The Pathogenesis of Ebola Virus Disease, Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis, doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-052016-100506
Batiha, Beshbishy, Ikram, Mulla, El-Hack et al., The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods9030374
Bellavite, Donzelli, Hesperidin and SARS-CoV-2: New Light on the Healthy Function of Citrus Fruits, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9080742
Bhattacharya, Ansari, Mehle, Striker, Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Intracellular Assay for the Conformation of Hepatitis C Virus Drug Target NS5A, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00645-12
Bose, Kamra, Mullick, Bhattacharya, Das et al., Identification of a flavonoid isolated from plum (Prunus domestica) as a potent inhibitor of Hepatitis C virus entry, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04358-5
Bouvier, Palese, The biology of influenza viruses, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.039
Burstow, Mohamed, Gomaa, Sonderup, Cook et al., Hepatitis C treatment: Where are we now?, Int. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S127689
Campos, De Arruda, Da Fonseca, Special Issue "Viral Infections in Developing Countries, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14020405
Cao, Wei, Ito, Preparative Isolation of Isorhamnetin from Stigma Maydis using High Speed Countercurrent Chromatography, J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol, doi:10.1080/10826070802603369
Casaschi, Wang, Richards, Theriault, Intestinal apolipoprotein B secretion is inhibited by the flavonoid quercetin: Potential role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and diacylglycerol acyltransferase, Lipids, doi:10.1007/s11745-002-0945-8
Cataneo, Kuczera, Koishi, Zanluca, Silveira et al., The citrus flavonoid naringenin impairs the in vitro infection of human cells by Zika virus, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-52626-3
Chhatwal, He, Lopez-Olivo, Systematic Review of Modelling Approaches for the Cost Effectiveness of Hepatitis C Treatment with Direct-Acting Antivirals, Pharmacoeconomics, doi:10.1007/s40273-015-0373-9
Chiow, Phoon, Putti, Tan, Chow, Evaluation of antiviral activities of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. extract, quercetin, quercetrin and cinanserin on murine coronavirus and dengue virus infection, Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med, doi:10.1016/j.apjtm.2015.12.002
Chirumbolo, The Role of Quercetin, Flavonols and Flavones in Modulating Inflammatory Cell Function, Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/187152810793358741
Choi, Kim, Kim, Chung, Antiviral activity of ethanol extract of Geranii Herba and its components against influenza viruses via neuraminidase inhibition, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48430-8
Choi, Song, Park, Kwon, Inhibitory effects of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on influenza A virus replication, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2009.03.002
Chun, Chung, Claycombe, Song, Serum C-Reactive Protein Concentrations Are Inversely Associated with Dietary Flavonoid Intake in U.S. Adults, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/138.4.753
D'andrea, Quercetin: A flavonol with multifaceted therapeutic applications?, Fitoterapia, doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2015.09.018
Dajas, Life or death: Neuroprotective and anticancer effects of quercetin, J. Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.005
Dapiaggi, Pieraccini, Potenza, Vasile, Podlipnik, Designing Antiviral Substances Targeting the Ebola Virus Viral Protein 24, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-814966-9.00009-3
David, Arulmoli, Parasuraman, Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid, Pharmacogn. Rev, doi:10.4103/0973-7847.194044
Dayem, Choi, Kim, Cho, Antiviral Effect of Methylated Flavonol Isorhamnetin against Influenza, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0121610
Delgado, Fernandes, González-Manzano, De Freitas, Mateus et al., Anti-proliferative effects of quercetin and catechin metabolites, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/c3fo60441a
Di Petrillo, Fais, Pintus, Santos-Buelga, González-Paramás et al., Broad-range potential of Asphodelus microcarpus leaves extract for drug development, BMC Microbiol
Di Petrillo, Orrù, Fais, Fantini, Quercetin and its derivates as antiviral potentials: A comprehensive review, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7309
Di Pierro, Derosa, Maffioli, Bertuccioli, Togni et al., Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early-Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study, Int. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S318720
Dos Santos, Kuster, Yamamoto, Salles, Campos et al., Quercetin and quercetin 3-O-glycosides from Bauhinia longifolia (Bong.) Steud. show anti-Mayaro virus activity, Parasit Vectors, doi:10.1186/1756-3305-7-130
Dou, Zhou, Ren, Xu, Apigenin, flavonoid component isolated from Gentiana veitchiorum flower suppresses the oxidative stress through LDLR-LCAT signaling pathway, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110298
Du, Lin, Yang, Zhang, Wu et al., Dietary quercetin combining intratumoral doxorubicin injection synergistically induces rejection of established breast cancer in mice, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.018
El-Toumy, Salib, El Kashak, Marty, Bedoux et al., Antiviral effect of polyphenol rich plant extracts on herpes simplex virus type 1, Food Sci. Hum. Wellness, doi:10.1016/j.fshw.2018.01.001
Endale, Park, Kim, Kim, Yang et al., Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κBinduced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells, Immunobiology, doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019
Estrada-Jiménez, Peña, Flores-Mendoza, Sedeño-Monge, Santos-López et al., Upregulation of the Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling 1 and 3 Is Associated with Arrest of Phosphorylated-STAT1 Nuclear Importation and Reduced Innate Response in Denguevirus-Infected Macrophages, Viral Immunol, doi:10.1089/vim.2014.0136
Falck-Ytter, Kale, Mullen, Sarbah, Sorescu et al., Surprisingly small effect of antiviral treatment in patients with hepatitis C, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-136-4-200202190-00008
Fan, Hashem, Chen, Li, Doyle et al., Targeting the HA2 subunit of influenza A virus hemagglutinin via CD40L provides universal protection against diverse subtypes, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1038/mi.2014.59
Fanunza, Frau, Corona, Tramontano, Antiviral Agents Against Ebola Virus Infection: Repositioning Old Drugs and Finding Novel Small Molecules, Annu. Rep. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/bs.armc.2018.08.004
Fanunza, Iampietro, Distinto, Corona, Quartu et al., Quercetin Blocks Ebola Virus Infection by Counteracting the VP24 Interferon-Inhibitory Function, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00530-20
Fatima, Mathew, Suhail, Ali, Damanhouri et al., Docking studies of Pakistani HCV NS3 helicase: A possible antiviral drug target, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106339
Flores-Mendoza, Estrada-Jiménez, Sedeño-Monge, Moreno, Manjarrez et al., IL-10 and socs3 Are Predictive Biomarkers of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Mediat. Inflamm
Formica, Regelson, Review of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids, Food Chem. Toxicol
Frabasile, Koishi, Kuczera, Silveira, Verri et al., The citrus flavanone naringenin impairs dengue virus replication in human cells, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep41864
Fried, Gibbons, Kalayanarooj, Thomas, Srikiatkhachorn et al., Serotype-Specific Differences in the Risk of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: An Analysis of Data Collected in Bangkok, Thailand from 1994 to 2006, PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000617
Galochkina, Anikin, Babkin, Ostrouhova, Zarubaev, Virus-inhibiting activity of dihydroquercetin, a flavonoid from Larix sibirica, against coxsackievirus B4 in a model of viral pancreatitis, Arch. Virol
Gansukh, Kazibwe, Pandurangan, Judy, Kim, Probing the impact of quercetin-7-O-glucoside on influenza virus replication influence, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2016.06.001
Gansukh, Muthu, Paul, Ethiraj, Chun et al., Nature nominee quercetin's anti-influenza combat strategy-Demonstrations and remonstrations, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1930
Gansukh, Nile, Kim, Oh, Nile, New insights into antiviral and cytotoxic potential of quercetin and its derivatives-A biochemical perspective, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127508
Geraets, Moonen, Brauers, Wouters, Bast et al., Dietary Flavones and Flavonoles Are Inhibitors of Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/137.10.2190
Gibellini, Pinti, Nasi, Montagna, De Biasi et al., Quercetin and Cancer Chemoprevention, Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.1093/ecam/neq053
Gisondi, Piaserico, Bordin, Alaibac, Girolomoni et al., Cutaneous manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A clinical update, J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16774
Gnoni, Paglialonga, Siculella, Quercetin inhibits fatty acid and triacylglycerol synthesis in rat-liver cells, Eur. J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02167.x
Gonzalez, Fontanes, Raychaudhuri, Loo, Loo et al., The heat shock protein inhibitor Quercetin attenuates hepatitis C virus production, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.23232
Green, Rothman, Immunopathological mechanisms in dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever, Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1097/01.qco.0000244047.31135.fa
Guo, Bruno, Endogenous and exogenous mediators of quercetin bioavailability, J. Nutr. Biochem
Haleagrahara, Hodgson, Miranda-Hernandez, Hughes, Kulur et al., Flavonoid quercetin-methotrexate combination inhibits inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinase expression, providing protection to joints in collageninduced arthritis, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-018-0464-2
Herker, Harris, Hernandez, Carpentier, Kaehlcke et al., Efficient hepatitis C virus particle formation requires diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm.2238
Herrmann, Flavonols and flavones in food plants: A review, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1976.tb00743.x
Hoofnagle, Course and outcome of hepatitis C, Hepatology, doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.36227
Huang, Yu, Cheng, Ouyang, Fu et al., Immunosuppressive Effect of Quercetin on Dendritic Cell Activation and Function, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903991
Hung, Ho, Lee, Chang, Kao et al., Houttuynia cordata Targets the Beginning Stage of Herpes Simplex Virus Infection, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115475
Igbe, Shen, Jiao, Qiang, Deng et al., Dietary quercetin potentiates the antiproliferative effect of interferon-α in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activation of JAK/STAT pathway signaling by inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.22556
Ismail, Jusoh, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies to Predict Flavonoid Binding on the Surface of DENV2 E Protein, Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s12539-016-0157-8
Jasso-Miranda, Herrera-Camacho, Flores-Mendoza, Dominguez, Vallejo-Ruiz et al., Antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polyphenols on macrophages infected with dengue virus serotypes 2 and 3 enhanced or not with antibodies, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S210890
Jeong, Ryu, Park, Kim, Kwon et al., Neuraminidase inhibitory activities of flavonols isolated from Rhodiola rosea roots and their in vitro anti-influenza viral activities, Bioorganic Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2009.08.036
Karki, Sharma, Tuladhar, Williams, Zalduondo et al., Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025
Kawabata, Mukai, Ishisaka, Quercetin and related polyphenols: New insights and implications for their bioactivity and bioavailability, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/C4FO01178C
Khachatoorian, Arumugaswami, Raychaudhuri, Yeh, Maloney et al., Divergent antiviral effects of bioflavonoids on the hepatitis C virus life cycle, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2012.08.029
Kim, Narayanan, Chang, Inhibition of influenza virus replication by plant-derived isoquercetin, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.08.016
Kuhn, Becker, Ebihara, Geisbert, Johnson et al., Proposal for a revised taxonomy of the family Filoviridae: Classification, names of taxa and viruses, and virus abbreviations, Arch. Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-010-0814-x
Lani, Hassandarvish, Chiam, Moghaddam, Chu et al., Antiviral activity of silymarin against chikungunya virus, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep11421
Lee, Son, Ryu, Shin, Kim et al., Quercetin-induced apoptosis prevents EBV infection, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3687
Li, Xu, Quercetin in a lotus leaves extract may be responsible for antibacterial activity, Arch. Pharmacal Res, doi:10.1007/s12272-001-1206-5
Li, Yao, Han, Yang, Chaudhry et al., Inflammation and Immunity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8030167
Lin, Leu, Al-Suwayeh, Ku, Hwang et al., Anti-inflammatory activity and percutaneous absorption of quercetin and its polymethoxylated compound and glycosides: The relationships to chemical structures, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2012.04.024
Liu, Liu, Qin, Lee, Wang et al., Anti-Influenza Virus Activities of Flavonoids from the Medicinal Plant Elsholtzia rugulosa, Planta Med, doi:10.1055/s-2008-1074558
Liu, Zhao, Li, Shen, Huang et al., Computational screen and experimental validation of anti-influenza effects of quercetin and chlorogenic acid from traditional Chinese medicine, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep19095
Low, Ooi, Vasudevan, Current Status of Dengue Therapeutics Research and Development, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiw423
Lu, Crespi, Liu, Vu, Ahmadieh et al., A Phase I Dose Escalation Study Demonstrates Quercetin Safety and Explores Potential for Bioflavonoid Antivirals in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.5518
Lulu, Thabitha, Vino, Priya, Rout, Naringenin and quercetin-potential anti-HCV agents for NS2 protease targets, Nat. Prod. Res, doi:10.1080/14786419.2015.1020490
Martina, Koraka, Osterhaus, Dengue Virus Pathogenesis: An Integrated View, Clin. Microbiol. Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00035-09
Masood, Jamil, Rahim, Islam, Farhan et al., Role of TNF α, IL-6 and CXCL10 in Dengue disease severity, Iran. J. Microbiol
Mehrbod, Abdalla, Fotouhi, Heidarzadeh, Aro et al., Immunomodulatory properties of quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside from Rapanea melanophloeos against influenza a virus, BMC Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.1186/s12906-018-2246-1
Mehrbod, Ebrahimi, Fotouhi, Eskandari, Eloff et al., Experimental validation and computational modeling of anti-influenza effects of quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside from indigenous south African medicinal plant Rapanea melanophloeos, BMC Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2774-3
Mehrbod, Hudy, Shyntum, Markowski, Łos et al., Quercetin as a Natural Therapeutic Candidate for the Treatment of Influenza Virus, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11010010
Mlcek, Jurikova, Skrovankova, Sochor, Quercetin and Its Anti-Allergic Immune Response, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules21050623
Moon, Nakata, Oshima, Inakuma, Terao, Accumulation of quercetin conjugates in blood plasma after the short-term ingestion of onion by women, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.2000.279.2.R461
Mukhopadhyay, Kuhn, Rossmann, A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro1067
Murali, Sivasubramanian, Vincent, Murugan, Giridaran et al., Anti-Chikungunya activity of luteolin and apigenin rich fraction from Cynodon dactylon, Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med, doi:10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60343-6
Nahmias, Goldwasser, Casali, Van Poll, Wakita et al., Apolipoprotein B-dependent hepatitis C virus secretion is inhibited by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.22197
Nair, Saiyed, Gandhi, Ramchand, The Flavonoid, Quercetin, Inhibits HIV-1 Infection in Normal Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, Am. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3844/ajidsp.2009.135.141
Nanbo, Watanabe, Halfmann, Kawaoka, The spatio-temporal distribution dynamics of Ebola virus proteins and RNA in infected cells, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep01206
Nieman, Henson, Maxwell, Williams, Mcanulty et al., Effects of Quercetin and EGCG on Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Immunity, Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc, doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318199491f
Nile, Kim, Nile, Park, Gansukh et al., Probing the effect of quercetin 3-glucoside from Dianthus superbus L against influenza virus infection-In vitro and in silico biochemical and toxicological screening, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.110985
Ninfali, Mea, Giorgini, Rocchi, Bacchiocca, Antioxidant capacity of vegetables, spices and dressings relevant to nutrition, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1079/BJN20041327
Ortega, Suárez, Serrano, Baptista, Pujol et al., The role of the glycosyl moiety of myricetin derivatives in anti-HIV-1 activity in vitro, AIDS Res. Ther, doi:10.1186/s12981-017-0183-6
Pal, Berhanu, Desalegn, Kandi, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.7423
Palma-Ocampo, Flores-Alonso, Vallejo-Ruiz, Reyes-Leyva, Flores-Mendoza et al., Interferon lambda inhibits dengue virus replication in epithelial cells, Virol. J
Paredes, Alzuru, Mendez, Rodríguez-Ortega, Anti-Sindbis Activity of Flavanones Hesperetin and Naringenin, Biol. Pharm. Bull, doi:10.1248/bpb.26.108
Parvez, Rehman, Alam, Al-Dosari, Alqasoumi et al., Plant-derived antiviral drugs as novel hepatitis B virus inhibitors: Cell culture and molecular docking study, Saudi Pharm. J, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2018.12.008
Prussia, Thepchatri, Snyder, Plemper, Systematic Approaches towards the Development of Host-Directed Antiviral Therapeutics, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms12064027
Qamar, Mumtaz, Naseem, Ali, Fatima et al., Molecular Docking Based Screening of Plant Flavonoids as Dengue NS1 Inhibitors, Bioinformation, doi:10.6026/97320630010460
Qi, Zhang, Chi, Biological characteristics of dengue virus and potential targets for drug design, Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin, doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00382.x
Qian, Fan, Qian, Zhang, Wei et al., Apigenin Restricts FMDV Infection and Inhibits Viral IRES Driven Translational Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v7041613
Qiu, Kroeker, He, Kozak, Audet et al., Prophylactic Efficacy of Quercetin 3-β-O-d-Glucoside against Ebola Virus Infection, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00307-16
Quecan, Santos, Rivera, Hassimotto, Almeida et al., Effect of Quercetin Rich Onion Extracts on Bacterial Quorum Sensing, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.00867
Rahman, Shorobi, Uddin, Saha, Hossain, Quercetin attenuates viral infections by interacting with target proteins and linked genes in chemicobiological models, Silico Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s40203-022-00132-2
Rajapakse, Rodrigo, Rajapakse, Treatment of dengue fever, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S22613
Reed, Rice, Overview of hepatitis C virus genome structure, polyprotein processing, and protein properties, Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-59605-6_4
Rizky, Jihwaprani, Kindi, Ansori, Mushtaq, The pharmacological mechanism of quercetin as adjuvant therapy of COVID-19, Life Res, doi:10.53388/life2022-0205-302
Rodenhuis-Zybert, Wilschut, Smit, Dengue virus life cycle: Viral and host factors modulating infectivity, Cell Mol. Life Sci. CMLS, doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0357-z
Rojas, Del Campo, Clement, Lemasson, García-Valdecasas et al., Effect of Quercetin on Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle: From Viral to Host Targets, Sci. Rep
Sakai-Kashiwabara, Asano, Inhibitory Action of Quercetin on Eosinophil Activation In Vitro, Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.1155/2013/127105
Saraswathi, Saravanan, Santhakumar, Isolation of quercetin from the methanolic extract of Lagerstroemia speciosa by HPLC technique, its cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells and photocatalytic activity, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol
Sati, Dhyani, Bhatt, Pandey, Ginkgo biloba flavonoid glycosides in antimicrobial perspective with reference to extraction method, J. Tradit. Complement. Med, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.10.003
Senthilvel, Lavanya, Kumar, Swetha, Anitha et al., Flavonoid from Carica papaya inhibits NS2B-NS3 protease and prevents Dengue 2 viral assembly, Bioinformation, doi:10.6026/97320630009889
Shakya, Correspondence, Medicinal plants: Future source of new drugs, Int. J. Herb. Med, doi:10.13140/RG.2.1.1395.6085
Si-Si, Liao, Ling, Yun-Xia, Inhibition of TNF-α/IFN-γ induced RANTES expression in HaCaT cell by naringin, Pharm. Biol, doi:10.3109/13880209.2010.550054
Smith, Bukh, Kuiken, Muerhoff, Rice et al., Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource, Hepatology
Sousa, Wu, Nebo, Fernandes, Das et al., Flavonoids as noncompetitive inhibitors of Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease: Inhibition kinetics and docking studies, Bioorg. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.12.015
Souto, Zarpelon, Staurengo-Ferrari, Fattori, Casagrande et al., Quercetin Reduces Neutrophil Recruitment Induced by CXCL8, LTB 4 , and fMLP: Inhibition of Actin Polymerization, J. Nat. Prod, doi:10.1021/np1003017
Sun, Dodd, Moser, Sharma, Braciale, CD4+ T cell help and innate-derived IL-27 induce Blimp-1-dependent IL-10 production by antiviral CTLs, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/ni.1996
Tanaka, Kasahara, Miyamoto, Takumi, Kasai et al., Development of oligonucleotide-based antagonists of Ebola virus protein 24 inhibiting its interaction with karyopherin alpha 1, Org. Biomol. Chem, doi:10.1039/C8OB00706C
Thomas, Thio, Martin, Qi, Ge et al., Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature08463
Trujillo-Correa, Quintero-Gil, Diaz-Castillo, Quiñones, Robledo et al., In vitro and in silico anti-dengue activity of compounds obtained from Psidium guajava through bioprospecting, BMC Complement. Altern. Med, doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2695-1
Tsague, Kenmogne, Tchienou, Parra, Ngassoum, Sequential extraction of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside from Piliostigma thonningii Schum. leaves using microwave technology, SN Appl. Sci, doi:10.1007/s42452-020-3031-6
Ubol, Phuklia, Kalayanarooj, Modhiran, Mechanisms of Immune Evasion Induced by a Complex of Dengue Virus and Preexisting Enhancing Antibodies, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1086/651018
Ulusoy, Sanlier, A minireview of quercetin: From its metabolism to possible mechanisms of its biological activities, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2019.1683810
Velthuis, Fodor, Influenza virus RNA polymerase: Insights into the mechanisms of viral RNA synthesis, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.87
Verma, Sahu, Saha, Bahadur, Bhardwaj, Review on quercetin and their beneficial properties, World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.20959/wjpps20188-12151
Whitehorn, Yacoub, Anders, Macareo, Cassetti et al., Dengue Therapeutics, Chemoprophylaxis, and Allied Tools: State of the Art and Future Directions, PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis
Wianowska, Application of Sea Sand Disruption Method for HPLC Determination of Quercetin in Plants, J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol, doi:10.1080/10826076.2015.1012520
Wianowska, Dawidowicz, Bernacik, Typek, Determining the true content of quercetin and its derivatives in plants employing SSDM and LC-MS analysis, Eur. Food Res. Technol, doi:10.1007/s00217-016-2719-8
Wiejak, Dunlop, Mackay, Yarwood, Flavanoids induce expression of the suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS3) gene and suppress IL-6-activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in vascular endothelial cells, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/BJ20130481
Wilson, Von Itzstein, Recent Strategies in the Search for New Anti-Influenza Therapies, Curr. Drug Targets
Wu, Li, Li, He, Jiang et al., Quercetin as an Antiviral Agent Inhibits Influenza A Virus (IAV) Entry, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v8010006
Yan, Ma, Wang, Wu, Huang et al., Luteolin decreases the yield of influenza A virus in vitro by interfering with the coat protein I complex expression, J. Nat. Med, doi:10.1007/s11418-019-01287-7
Yang, Zhu, Ji, Deng, Lu et al., Quercetin synergistically reactivates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 latency by activating nuclear factor-κB, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.8188
Ying, Liu, Yu, Wang, Zang et al., Dietary quercetin ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by a high-fat diet in gerbils, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.10.030
Younossi, Park, Saab, Ahmed, Dieterich et al., Cost-effectiveness of all-oral ledipasvir/sofosbuvir regimens in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.13081
Zahoor, Shah, Naz, Ullah, Bari et al., Isolation of Quercetin from fruticosus, Their Concentration through NF/RO Membranes, and Recovery through Carbon Nanocomposite. A Pilot Plant Study, BioMed. Res. Int, doi:10.1155/2020/8216435
Zandi, Teoh, Sam, Wong, Mustafa et al., Antiviral activity of four types of bioflavonoid against dengue virus type-2, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-8-560
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules28030938",
"ISSN": [
"1420-3049"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030938",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Many of the medicinally active molecules in the flavonoid class of phytochemicals are being researched for their potential antiviral activity against various DNA and RNA viruses. Quercetin is a flavonoid that can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits and vegetables. It has been reported to be effective against a variety of viruses. This review, therefore, deciphered the mechanistic of how Quercetin works against some of the deadliest viruses, such as influenza A, Hepatitis C, Dengue type 2 and Ebola virus, which cause frequent outbreaks worldwide and result in significant morbidity and mortality in humans through epidemics or pandemics. All those have an alarming impact on both human health and the global and national economies. The review extended computing the Quercetin-contained natural recourse and its modes of action in different experimental approaches leading to antiviral actions. The gap in effective treatment emphasizes the necessity of a search for new effective antiviral compounds. Quercetin shows potential antiviral activity and inhibits it by targeting viral infections at multiple stages. The suppression of viral neuraminidase, proteases and DNA/RNA polymerases and the alteration of many viral proteins as well as their immunomodulation are the main molecular mechanisms of Quercetin’s antiviral activities. Nonetheless, the huge potential of Quercetin and its extensive use is inadequately approached as a therapeutic for emerging and re-emerging viral infections. Therefore, this review enumerated the food-functioned Quercetin source, the modes of action of Quercetin for antiviral effects and made insights on the mechanism-based antiviral action of Quercetin.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"molecules28030938"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Environmental and Biological Chemistry, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Shorobi",
"given": "Fauzia Mahanaz",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Chittagong, Chittagong 4331, Bangladesh"
}
],
"family": "Nisa",
"given": "Fatema Yasmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8844-345X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Chittagong, Chittagong 4331, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Saha",
"given": "Srabonti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4601-1074",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Bangladesh Tea Research Institute, Sreemangal-3210, Moulvibazar District, Sylhet 3100, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Muhammad Abid Hasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7421-4410",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Allied Health Sciences, Walailak University, Nakhon Si Thammarat 80160, Thailand"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Srisuphanunt",
"given": "Mayuna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, 9620 Carnegie Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44195, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hossain",
"given": "Kazi Helal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4902-8923",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Allied Health Sciences, Walailak University, Nakhon Si Thammarat 80160, Thailand"
},
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Chittagong, Chittagong 4331, Bangladesh"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rahman",
"given": "Md. Atiar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Molecules",
"container-title-short": "Molecules",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-18T08:04:44Z",
"timestamp": 1674029084000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T10:37:47Z",
"timestamp": 1675247867000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Walailak University, Thailand"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-02T05:34:40Z",
"timestamp": 1675316080110
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673913600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/3/938/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "938",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14020405",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Campos, F.S., de Arruda, L.B., and da Fonseca, F.G. (2022). Special Issue “Viral Infections in Developing Countries”. Viruses, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.732891",
"article-title": "A Review of Medicinal Plants with Antiviral Activity Available in Bangladesh and Mechanistic Insight Into Their Bioactive Metabolites on SARS-CoV-2, HIV and HBV",
"author": "Bachar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732891",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.16774",
"article-title": "Cutaneous manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A clinical update",
"author": "Gisondi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2499",
"journal-title": "J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update",
"author": "Pal",
"first-page": "e7423",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111596",
"article-title": "Antiviral activities of flavonoids",
"author": "Badshah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111596",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/BJN20041327",
"article-title": "Antioxidant capacity of vegetables, spices and dressings relevant to nutrition",
"author": "Ninfali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Quercetin and its derivates as antiviral potentials: A comprehensive review",
"author": "Fais",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods9030374",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Batiha, G.E.-S., Beshbishy, A.M., Ikram, M., Mulla, Z.S., El-Hack, M.E.A., Taha, A.E., Algammal, A.M., and Elewa, Y.H.A. (2020). The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0973-7847.194044",
"article-title": "Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid",
"author": "David",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Pharmacogn. Rev.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S318720",
"article-title": "Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early-Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study",
"author": "Derosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2359",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2012.08.029",
"article-title": "Divergent antiviral effects of bioflavonoids on the hepatitis C virus life cycle",
"author": "Khachatoorian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "346",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "433",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1756-3305-7-130",
"article-title": "Quercetin and quercetin 3-O-glycosides from Bauhinia longifolia (Bong.) Steud. show anti-Mayaro virus activity",
"author": "Kuster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Parasit Vectors",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.08.016",
"article-title": "Inhibition of influenza virus replication by plant-derived isoquercetin",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep11421",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of silymarin against chikungunya virus",
"author": "Lani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11421",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.3687",
"article-title": "Quercetin-induced apoptosis prevents EBV infection",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12603",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01507.x",
"article-title": "Suppression of hepatitis C virus by the flavonoid quercetin is mediated by inhibition of NS3 protease activity",
"author": "Bachmetov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81",
"journal-title": "J. Viral. Hepat.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1743-422X-8-560",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of four types of bioflavonoid against dengue virus type-2",
"author": "Zandi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "560",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00530-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Fanunza, E., Iampietro, M., Distinto, S., Corona, A., Quartu, M., Maccioni, E., Horvat, B., and Tramontano, E. (2020). Quercetin Blocks Ebola Virus Infection by Counteracting the VP24 Interferon-Inhibitory Function. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 64."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40203-022-00132-2",
"article-title": "Quercetin attenuates viral infections by interacting with target proteins and linked genes in chemicobiological models",
"author": "Rahman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Silico Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Review on quercetin and their beneficial properties",
"author": "Verma",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2621.1976.tb00743.x",
"article-title": "Flavonols and flavones in food plants: A review",
"author": "Herrmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "433",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Food Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "11",
"year": "1976"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2012.04.024",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory activity and percutaneous absorption of quercetin and its polymethoxylated compound and glycosides: The relationships to chemical structures",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "857",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c3fo60441a",
"article-title": "Anti-proliferative effects of quercetin and catechin metabolites",
"author": "Delgado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "797",
"journal-title": "Food Funct.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2016.06.001",
"article-title": "Probing the impact of quercetin-7-O-glucoside on influenza virus replication influence",
"author": "Gansukh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "958",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12272-001-1206-5",
"article-title": "Quercetin in a lotus leaves extract may be responsible for antibacterial activity",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "640",
"journal-title": "Arch. Pharmacal Res.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in CD133+ cancer stem cells of human colorectal HT29 cancer cell line and enhances anticancer effects of doxorubicin",
"author": "Atashpour",
"first-page": "635",
"journal-title": "Iran J. Basic Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.005",
"article-title": "Life or death: Neuroprotective and anticancer effects of quercetin",
"author": "Dajas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "J. Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2012.10.030",
"article-title": "Dietary quercetin ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by a high-fat diet in gerbils",
"author": "Ying",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2009.03.002",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on influenza A virus replication",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "329",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/138.4.753",
"article-title": "Serum C-Reactive Protein Concentrations Are Inversely Associated with Dietary Flavonoid Intake in U.S. Adults",
"author": "Chun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-019-2774-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Mehrbod, P., Ebrahimi, S.N., Fotouhi, F., Eskandari, F., Eloff, J.N., McGaw, L.J., and Fasina, F.O. (2019). Experimental validation and computational modeling of anti-influenza effects of quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside from indigenous south African medicinal plant Rapanea melanophloeos. BMC Complement. Altern. Med., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2019.1683810",
"article-title": "A minireview of quercetin: From its metabolism to possible mechanisms of its biological activities",
"author": "Ulusoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3290",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Medicinal plants: Future source of new drugs",
"author": "Shakya",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Herb. Med.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8216435",
"article-title": "Isolation of Quercetin from Rubus fruticosus, Their Concentration through NF/RO Membranes, and Recovery through Carbon Nanocomposite. A Pilot Plant Study",
"author": "Zahoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8216435",
"journal-title": "BioMed. Res. Int.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10826076.2015.1012520",
"article-title": "Application of Sea Sand Disruption Method for HPLC Determination of Quercetin in Plants",
"author": "Wianowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1037",
"journal-title": "J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00217-016-2719-8",
"article-title": "Determining the true content of quercetin and its derivatives in plants employing SSDM and LC–MS analysis",
"author": "Wianowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Eur. Food Res. Technol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "243",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.04.031",
"article-title": "Isolation of quercetin from the methanolic extract of Lagerstroemia speciosa by HPLC technique, its cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells and photocatalytic activity",
"author": "Saraswathi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Sequential extraction of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside from Piliostigma thonningii Schum. leaves using microwave technology",
"author": "Tsague",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "SN Appl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Quercetin synergistically reactivates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 latency by activating nuclear factor-κB",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "2501",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10826070802603369",
"article-title": "Preparative Isolation of Isorhamnetin from Stigma Maydis using High Speed Countercurrent Chromatography",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-018-2246-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Mehrbod, P., Abdalla, M.A., Fotouhi, F., Heidarzadeh, M., Aro, A.O., Eloff, J.N., McGaw, L.J., and Fasina, F.O. (2018). Immunomodulatory properties of quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside from Rapanea melanophloeos against influenza a virus. BMC Complement. Altern. Med., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2019.110985",
"article-title": "Probing the effect of quercetin 3-glucoside from Dianthus superbus L against influenza virus infection- In vitro and in silico biochemical and toxicological screening",
"author": "Nile",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110985",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apjtm.2015.12.002",
"article-title": "Evaluation of antiviral activities of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. extract, quercetin, quercetrin and cinanserin on murine coronavirus and dengue virus infection",
"author": "Chiow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-04358-5",
"article-title": "Identification of a flavonoid isolated from plum (Prunus domestica) as a potent inhibitor of Hepatitis C virus entry",
"author": "Bose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3965",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-019-2695-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Trujillo-Correa, A.I., Quintero-Gil, D.C., Diaz-Castillo, F., Quiñones, W., Robledo, S.M., and Martinez-Gutierrez, M. (2019). In vitro and in silico anti-dengue activity of compounds obtained from Psidium guajava through bioprospecting. BMC Complement. Altern. Med., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-016-2749-3",
"article-title": "Virus-inhibiting activity of dihydroquercetin, a flavonoid from Larix sibirica, against coxsackievirus B4 in a model of viral pancreatitis",
"author": "Galochkina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "Arch. Virol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0115475",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Hung, P.-Y., Ho, B.-C., Lee, S.-Y., Chang, S.-Y., Kao, C.-L., Lee, S.-S., and Lee, C.-N. (2015). Houttuynia cordata Targets the Beginning Stage of Herpes Simplex Virus Infection. PLoS ONE, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2009.08.036",
"article-title": "Neuraminidase inhibitory activities of flavonols isolated from Rhodiola rosea roots and their in vitro anti-influenza viral activities",
"author": "Jeong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6816",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12981-017-0183-6",
"article-title": "The role of the glycosyl moiety of myricetin derivatives in anti-HIV-1 activity in vitro",
"author": "Ortega",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "AIDS Res. Ther.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110298",
"article-title": "Apigenin, flavonoid component isolated from Gentiana veitchiorum flower suppresses the oxidative stress through LDLR-LCAT signaling pathway",
"author": "Dou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110298",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v7041613",
"article-title": "Apigenin Restricts FMDV Infection and Inhibits Viral IRES Driven Translational Activity",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fshw.2018.01.001",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of polyphenol rich plant extracts on herpes simplex virus type 1",
"author": "Salib",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Food Sci. Hum. Wellness",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00307-16",
"article-title": "Prophylactic Efficacy of Quercetin 3-β- O-d-Glucoside against Ebola Virus Infection",
"author": "Qiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5182",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.00867",
"article-title": "Effect of Quercetin Rich Onion Extracts on Bacterial Quorum Sensing",
"author": "Quecan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.10.003",
"article-title": "Ginkgo biloba flavonoid glycosides in antimicrobial perspective with reference to extraction method",
"author": "Sati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "J. Tradit. Complement. Med.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0121610",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Dayem, A.A., Choi, H.Y., Kim, Y.B., and Cho, S.-G. (2015). Antiviral Effect of Methylated Flavonol Isorhamnetin against Influenza. PLoS ONE, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep19095",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Liu, Z., Zhao, J., Li, W., Shen, L., Huang, S., Tang, J., Duan, J., Fang, F., Huang, Y., and Chang, H. (2016). Computational screen and experimental validation of anti-influenza effects of quercetin and chlorogenic acid from traditional Chinese medicine. Sci. Rep., 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60343-6",
"article-title": "Anti—Chikungunya activity of luteolin and apigenin rich fraction from Cynodon dactylon",
"author": "Murali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "352",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2008-1074558",
"article-title": "Anti-Influenza Virus Activities of Flavonoids from the Medicinal Plant Elsholtzia rugulosa",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "847",
"journal-title": "Planta Med.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/2745352",
"article-title": "The Preventive Effects and the Mechanisms of Action of Navel Orange Peel Hydroethanolic Extract, Naringin, and Naringenin in N-Acetyl-p-aminophenol-Induced Liver Injury in Wistar Rats",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2745352",
"journal-title": "Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-52626-3",
"article-title": "The citrus flavonoid naringenin impairs the in vitro infection of human cells by Zika virus",
"author": "Cataneo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16348",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202006.0321.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_62",
"unstructured": "Bellavite, P., and Donzelli, A. (2020). Hesperidin and SARS-CoV-2: New Light on the Healthy Function of Citrus Fruits. Antioxidants, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.26.108",
"article-title": "Anti-Sindbis Activity of Flavanones Hesperetin and Naringenin",
"author": "Paredes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Biol. Pharm. Bull.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/13880209.2010.509734",
"article-title": "Antioxidant capacity of hesperidin from Citrus peel using electron spin resonance and cytotoxic activity against human carcinoma cell lines",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Biol.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.22197",
"article-title": "Apolipoprotein B-dependent hepatitis C virus secretion is inhibited by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin",
"author": "Nahmias",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1437",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/13880209.2010.550054",
"article-title": "Inhibition of TNF-α/IFN-γ induced RANTES expression in HaCaT cell by naringin",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "810",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Biol.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11418-019-01287-7",
"article-title": "Luteolin decreases the yield of influenza A virus in vitro by interfering with the coat protein I complex expression",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "487",
"journal-title": "J. Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2014.12.015",
"article-title": "Flavonoids as noncompetitive inhibitors of Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease: Inhibition kinetics and docking studies",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "466",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep41864",
"article-title": "The citrus flavanone naringenin impairs dengue virus replication in human cells",
"author": "Frabasile",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41864",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1541-4337.12342",
"article-title": "Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation",
"author": "Almeida",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "714",
"journal-title": "Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpregu.2000.279.2.R461",
"article-title": "Accumulation of quercetin conjugates in blood plasma after the short-term ingestion of onion by women",
"author": "Moon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R461",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ecam/neq053",
"article-title": "Quercetin and Cancer Chemoprevention",
"author": "Gibellini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "591356",
"journal-title": "Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "2011",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.018",
"article-title": "Dietary quercetin combining intratumoral doxorubicin injection synergistically induces rejection of established breast cancer in mice",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhibitory Action of Quercetin on Eosinophil Activation In Vitro",
"author": "Asano",
"first-page": "127105",
"journal-title": "Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Overview of hepatitis C virus genome structure, polyprotein processing, and protein properties",
"author": "Reed",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "242",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.26744",
"article-title": "Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "318",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2017). Global Hepatitis Report, 2017, World Health Organization."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature08463",
"article-title": "Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "798",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "461",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Course and outcome of hepatitis C",
"author": "Hoofnagle",
"first-page": "s21",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-136-4-200202190-00008",
"article-title": "Surprisingly small effect of antiviral treatment in patients with hepatitis C",
"author": "Kale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "288",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1316366",
"article-title": "Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Previously Treated HCV Genotype 1 Infection",
"author": "Afdhal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1483",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1402454",
"article-title": "Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Untreated HCV Genotype 1 Infection",
"author": "Afdhal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1889",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.13081",
"article-title": "Cost-effectiveness of all-oral ledipasvir/sofosbuvir regimens in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection",
"author": "Younossi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "544",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S127689",
"article-title": "Hepatitis C treatment: Where are we now?",
"author": "Burstow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40273-015-0373-9",
"article-title": "Systematic Review of Modelling Approaches for the Cost Effectiveness of Hepatitis C Treatment with Direct-Acting Antivirals",
"author": "Chhatwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "551",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoeconomics",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.5518",
"article-title": "A Phase I Dose Escalation Study Demonstrates Quercetin Safety and Explores Potential for Bioflavonoid Antivirals in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "ref_86",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.23232",
"article-title": "The heat shock protein inhibitor Quercetin attenuates hepatitis C virus production",
"author": "Gonzalez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1756",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00645-12",
"article-title": "Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Intracellular Assay for the Conformation of Hepatitis C Virus Drug Target NS5A",
"author": "Bhattacharya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8277",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786419.2015.1020490",
"article-title": "Naringenin and quercetin—potential anti-HCV agents for NS2 protease targets",
"author": "Lulu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "464",
"journal-title": "Nat. Prod. Res.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0278-6915(95)00077-1",
"article-title": "Review of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids",
"author": "Formica",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11745-002-0945-8",
"article-title": "Intestinal apolipoprotein B secretion is inhibited by the flavonoid quercetin: Potential role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and diacylglycerol acyltransferase",
"author": "Casaschi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Lipids",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02167.x",
"article-title": "Quercetin inhibits fatty acid and triacylglycerol synthesis in rat-liver cells",
"author": "Gnoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "761",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.2238",
"article-title": "Efficient hepatitis C virus particle formation requires diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1",
"author": "Herker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1295",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms12064027",
"article-title": "Systematic Approaches towards the Development of Host-Directed Antiviral Therapeutics",
"author": "Prussia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4027",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep31777",
"article-title": "Effect of Quercetin on Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle: From Viral to Host Targets",
"author": "Rojas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31777",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_95",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-010-0357-z",
"article-title": "Dengue virus life cycle: Viral and host factors modulating infectivity",
"author": "Wilschut",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2773",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol. Life Sci. CMLS",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12539-016-0157-8",
"article-title": "Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies to Predict Flavonoid Binding on the Surface of DENV2 E Protein",
"author": "Ismail",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "ref_98",
"unstructured": "(2009). Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control: New Edition, World Health Organization."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0000617",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_99",
"unstructured": "Fried, J.R., Gibbons, R.V., Kalayanarooj, S., Thomas, S.J., Srikiatkhachorn, A., Yoon, I.-K., Jarman, R.G., Green, S., Rothman, A.L., and Cummings, D.A.T. (2010). Serotype-Specific Differences in the Risk of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: An Analysis of Data Collected in Bangkok, Thailand from 1994 to 2006. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis., 4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S22613",
"article-title": "Treatment of dengue fever",
"author": "Rajapakse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "ref_100",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiw423",
"article-title": "Current Status of Dengue Therapeutics Research and Development",
"author": "Low",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S96",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_101",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0003025",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_102",
"unstructured": "Whitehorn, J., Yacoub, S., Anders, K.L., Macareo, L.R., Cassetti, M.C., Van, V.C.N., Shi, P.-Y., Wills, B., and Simmons, C.P. (2014). Dengue Therapeutics, Chemoprophylaxis, and Allied Tools: State of the Art and Future Directions. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1067",
"article-title": "A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle",
"author": "Mukhopadhyay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_103",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.6026/97320630010460",
"article-title": "Molecular Docking Based Screening of Plant Flavonoids as Dengue NS1 Inhibitors",
"author": "Qamar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "Bioinformation",
"key": "ref_104",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00382.x",
"article-title": "Biological characteristics of dengue virus and potential targets for drug design",
"author": "Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin.",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.6026/97320630009889",
"article-title": "Flavonoid from Carica papaya inhibits NS2B-NS3 protease and prevents Dengue 2 viral assembly",
"author": "Senthilvel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "889",
"journal-title": "Bioinformation",
"key": "ref_106",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.22556",
"article-title": "Dietary quercetin potentiates the antiproliferative effect of interferon-α in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activation of JAK/STAT pathway signaling by inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase",
"author": "Igbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113734",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "ref_107",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02188-08",
"article-title": "NS5 of Dengue Virus Mediates STAT2 Binding and Degradation",
"author": "Ashour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5408",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_108",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2014.0136",
"article-title": "Upregulation of the Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling 1 and 3 Is Associated with Arrest of Phosphorylated-STAT1 Nuclear Importation and Reduced Innate Response in Denguevirus-Infected Macrophages",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Viral Immunol.",
"key": "ref_109",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "IL-10 and socs3 Are Predictive Biomarkers of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever",
"author": "Moreno",
"first-page": "5197592",
"journal-title": "Mediat. Inflamm.",
"key": "ref_110",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-015-0383-4",
"article-title": "Interferon lambda inhibits dengue virus replication in epithelial cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_111",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/651018",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of Immune Evasion Induced by a Complex of Dengue Virus and Preexisting Enhancing Antibodies",
"author": "Ubol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "923",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_112",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20130481",
"article-title": "Flavanoids induce expression of the suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS3) gene and suppress IL-6-activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in vascular endothelial cells",
"author": "Wiejak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "ref_113",
"volume": "454",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S210890",
"article-title": "Antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polyphenols on macrophages infected with dengue virus serotypes 2 and 3 enhanced or not with antibodies",
"author": "Dominguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1833",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "ref_114",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.qco.0000244047.31135.fa",
"article-title": "Immunopathological mechanisms in dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "429",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_115",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00035-09",
"article-title": "Dengue Virus Pathogenesis: An Integrated View",
"author": "Martina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_116",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of TNF α, IL-6 and CXCL10 in Dengue disease severity",
"author": "Masood",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Iran. J. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_117",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-010-0814-x",
"article-title": "Proposal for a revised taxonomy of the family Filoviridae: Classification, names of taxa and viruses, and virus abbreviations",
"author": "Kuhn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2083",
"journal-title": "Arch. Virol.",
"key": "ref_118",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep01206",
"article-title": "The spatio-temporal distribution dynamics of Ebola virus proteins and RNA in infected cells",
"author": "Nanbo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1206",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_119",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "ref_120",
"unstructured": "Dapiaggi, F., Pieraccini, S., Potenza, D., Vasile, F., and Podlipnik, Č. (2019). Emerging and Reemerging Viral Pathogens, Academic Press."
},
{
"article-title": "Antiviral Agents Against Ebola Virus Infection: Repositioning Old Drugs and Finding Novel Small Molecules",
"author": "Fanunza",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rep. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_121",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pathol-052016-100506",
"article-title": "The Pathogenesis of Ebola Virus Disease",
"author": "Baseler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis.",
"key": "ref_122",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-017-1068-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_123",
"unstructured": "Di Petrillo, A., Fais, A., Pintus, F., Santos-Buelga, C., González-Paramás, A.M., Piras, V., Orrù, G., Mameli, A., Tramontano, E., and Frau, A. (2017). Broad-range potential of Asphodelus microcarpus leaves extract for drug development. BMC Microbiol., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fitote.2015.09.018",
"article-title": "Quercetin: A flavonol with multifaceted therapeutic applications?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256",
"journal-title": "Fitoterapia",
"key": "ref_124",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.039",
"article-title": "The biology of influenza viruses",
"author": "Bouvier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D49",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "ref_125",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11010010",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_126",
"unstructured": "Mehrbod, P., Hudy, D., Shyntum, D., Markowski, J., Łos, M.J., and Ghavami, S. (2021). Quercetin as a Natural Therapeutic Candidate for the Treatment of Influenza Virus. Biomolecules, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1930",
"article-title": "Nature nominee quercetin’s anti-influenza combat strategy-Demonstrations and remonstrations",
"author": "Gansukh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1930",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_127",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127508",
"article-title": "New insights into antiviral and cytotoxic potential of quercetin and its derivatives—A biochemical perspective",
"author": "Gansukh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127508",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_128",
"volume": "334",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389450033491019",
"article-title": "Recent Strategies in the Search for New Anti-Influenza Therapies",
"author": "Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"journal-title": "Curr. Drug Targets",
"key": "ref_129",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/mi.2014.59",
"article-title": "Targeting the HA2 subunit of influenza A virus hemagglutinin via CD40L provides universal protection against diverse subtypes",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol.",
"key": "ref_130",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v8010006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_131",
"unstructured": "Wu, W., Li, R., Li, X., He, J., Jiang, S., Liu, S., and Yang, J. (2015). Quercetin as an Antiviral Agent Inhibits Influenza A Virus (IAV) Entry. Viruses, 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-48430-8",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of ethanol extract of Geranii Herba and its components against influenza viruses via neuraminidase inhibition",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12132",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_132",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.87",
"article-title": "Influenza virus RNA polymerase: Insights into the mechanisms of viral RNA synthesis",
"author": "Fodor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_133",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "The pharmacological mechanism of quercetin as adjuvant therapy of COVID-19",
"author": "Rizky",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Life Res.",
"key": "ref_134",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2018.12.008",
"article-title": "Plant-derived antiviral drugs as novel hepatitis B virus inhibitors: Cell culture and molecular docking study",
"author": "Parvez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharm. J.",
"key": "ref_135",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0106339",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_136",
"unstructured": "Fatima, K., Mathew, S., Suhail, M., Ali, A., Damanhouri, G., Azhar, E., and Qadri, I. (2014). Docking studies of Pakistani HCV NS3 helicase: A possible antiviral drug target. PLoS One, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187152810793358741",
"article-title": "The Role of Quercetin, Flavonols and Flavones in Modulating Inflammatory Cell Function",
"author": "Chirumbolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets",
"key": "ref_137",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0903991",
"article-title": "Immunosuppressive Effect of Quercetin on Dendritic Cell Activation and Function",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6815",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_138",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019",
"article-title": "Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells",
"author": "Endale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1452",
"journal-title": "Immunobiology",
"key": "ref_139",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.1996",
"article-title": "CD4+ T cell help and innate-derived IL-27 induce Blimp-1-dependent IL-10 production by antiviral CTLs",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_140",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3844/ajidsp.2009.135.141",
"article-title": "The Flavonoid, Quercetin, Inhibits HIV-1 Infection in Normal Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_141",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules21050623",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_142",
"unstructured": "Mlcek, J., Jurikova, T., Skrovankova, S., and Sochor, J. (2016). Quercetin and Its Anti-Allergic Immune Response. Molecules, 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu8030167",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_143",
"unstructured": "Li, Y., Yao, J., Han, C., Yang, J., Chaudhry, M.T., Wang, S., Liu, H., and Yin, Y. (2016). Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients, 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-018-0464-2",
"article-title": "Flavonoid quercetin–methotrexate combination inhibits inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinase expression, providing protection to joints in collagen-induced arthritis",
"author": "Haleagrahara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1219",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_144",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/np1003017",
"article-title": "Quercetin Reduces Neutrophil Recruitment Induced by CXCL8, LTB4, and fMLP: Inhibition of Actin Polymerization",
"author": "Souto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "J. Nat. Prod.",
"key": "ref_145",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C8OB00706C",
"article-title": "Development of oligonucleotide-based antagonists of Ebola virus protein 24 inhibiting its interaction with karyopherin alpha 1",
"author": "Tanaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4456",
"journal-title": "Org. Biomol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_146",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/137.10.2190",
"article-title": "Dietary Flavones and Flavonoles Are Inhibitors of Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Geraets",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2190",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_147",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/MSS.0b013e318199491f",
"article-title": "Effects of Quercetin and EGCG on Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Immunity",
"author": "Nieman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1467",
"journal-title": "Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc.",
"key": "ref_148",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025",
"article-title": "Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes",
"author": "Karki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_149",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C4FO01178C",
"article-title": "Quercetin and related polyphenols: New insights and implications for their bioactivity and bioavailability",
"author": "Kawabata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"journal-title": "Food Funct.",
"key": "ref_150",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.10.008",
"article-title": "Endogenous and exogenous mediators of quercetin bioavailability",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_151",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 151,
"references-count": 151,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/3/938"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Chemistry (miscellaneous)",
"Analytical Chemistry",
"Organic Chemistry",
"Physical and Theoretical Chemistry",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmaceutical Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Quercetin: A Functional Food-Flavonoid Incredibly Attenuates Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections through Immunomodulatory Actions",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}