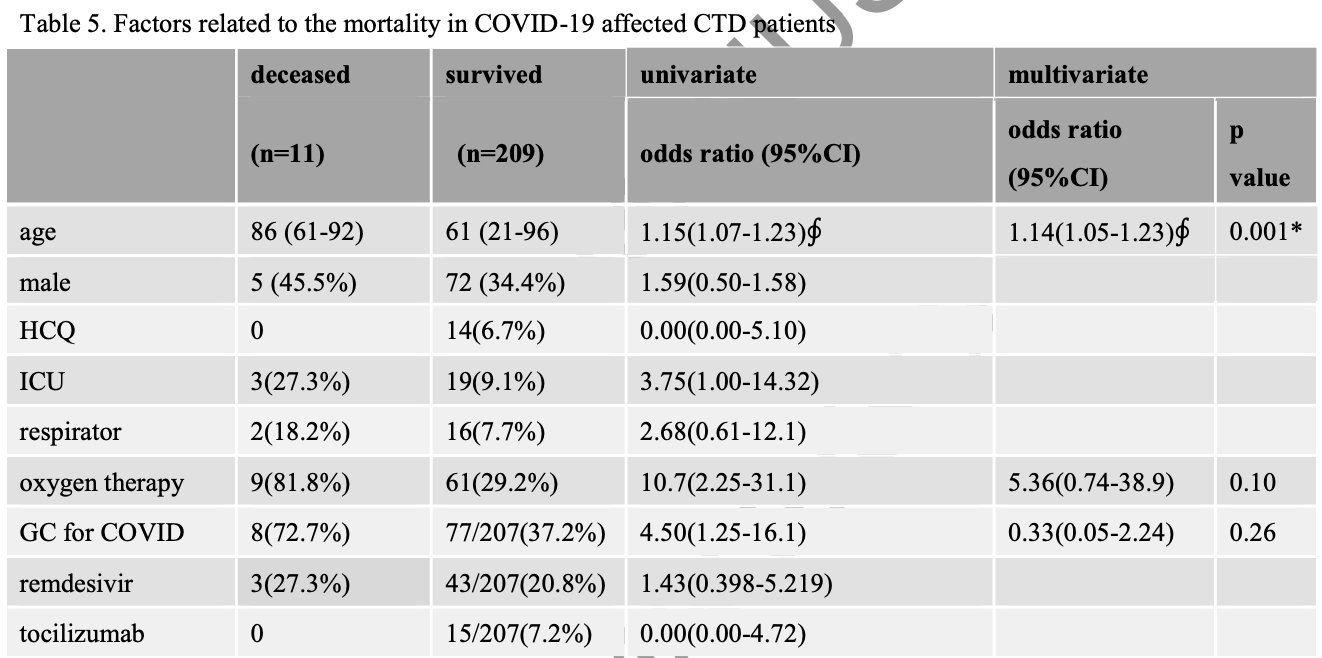
Risk factors for hospitalization or mortality for COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: Results of a nation-wide JCR COVID-19 registry in Japan
et al., Modern Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/mr/roac104, Sep 2022
Retrospective 220 COVID-19 patients with rheumatic disease in Japan, showing no significant difference in mortality with remdesivir treatment.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments15.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
Study covers remdesivir and HCQ.
|
risk of death, 40.2% higher, RR 1.40, p = 0.59, treatment 3 of 46 (6.5%), control 8 of 172 (4.7%), unadjusted, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Oku et al., 6 Sep 2022, retrospective, Japan, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 3 June, 2020 - 30 June, 2021.
Contact: horiuchi.takahiko.191@m.kyushu-u.ac.jp.
MORH-D-22-00049 Received: 20-Jan-2022; Accepted: 4-Aug-2022
doi:10.1093/mr/roac104/6692611
Background: The incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 and rheumatic disease vary among ethnicities and regions. COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic disease patients remain unclear, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. This study aimed to clarify the demographic and clinical factors that may influence COVID-19 prognosis in rheumatic disease patients.
Conflict of interest K. Oku, Y. Kimoto, T. Horiuchi, M. Yamamoto, Y. Kondo, M. Okamoto, and Tatsuya Atsumi have no conflicts of interest to declare. T.Takeuchi has received a speaking fee from Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and a research grant from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.
References
Akiyama, Hamdeh, Micic, Sakuraba, Prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218946
Bozzalla Cassione, Zanframundo, Biglia, Codullo, Montecucco et al., COVID-19 infection in a northern-Italian cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus assessed by telemedicine, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217717
Fernandez-Ruiz, Paredes, Niewold, COVID-19 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: lessons learned from the inflammatory disease, Transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.12.007
Gianfrancesco, Hyrich, Al-Adely, Characteristics associated with hospitalisation for COVID-19 in people with rheumatic disease: data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217871
Hyrich, Machado, Rheumatic disease and COVID-19: epidemiology and outcomes, Nat Rev Rheumatol, doi:10.1038/s41584-020-00562-2
Kutsuna, Clinical Manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019, JMA J, doi:10.31662/jmaj.2021-0013
Listing, Gerhold, Zink, The risk of infections associated with rheumatoid arthritis, with its comorbidity and treatment, Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes305
Matsunaga, Hayakawa, Terada, Clinical epidemiology of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Japan: Report of the COVID-19 REGISTRY JAPAN, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1470
Norena, Fernandez-Ruiz, Aguado, Viral infections in the biologic therapy era, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2018.1521270
Raiker, Deyoung, Pakhchanian, Outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multicenter research network study in the United States, Arthritis Rheum, doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.08.010
Raiker, Pakhchanian, Silva, Short term outcomes of COVID-19 in lupus: Propensity score matched analysis from a nationwide multi-centric research network, J Autoimmun
Schioppo, Argolini, Sciascia, Clinical and peculiar immunological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection in systemic lupus erythematosus patients, Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab611
Schmajuk, Montgomery, Leonard, Factors Associated With Hospitalization and Death After COVID-19 Diagnosis Among Patients With Rheumatic Disease: An Analysis of Veterans Affairs Data, ACR Open Rheumatol, doi:10.1002/acr2.11328
Shin, Shin, Moon, Autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and COVID-19 outcomes in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00151-X
Singh, Cameron, Noorbaloochi, Risk of serious infection in biological treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61704-9
Sparks, Wallace, Seet, Associations of baseline use of biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs with COVID-19 severity in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registry, Ann Rheum Dis
Strangfeld, Schafer, Gianfrancesco, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219498
Thanou, Sawalha, SARS-CoV-2 and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Curr Rheumatol Rep, doi:10.1007/s11926-020-00973-w
Weckerle, Franek, Kelly, Network analysis of associations between serum interferon-alpha activity, autoantibodies, and clinical features in systemic lupus erythematosus, Arthritis Rheum, doi:10.1002/art.30187
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/mr/roac104",
"ISSN": [
"1439-7595",
"1439-7609"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/mr/roac104",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Background: The incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 and rheumatic disease vary among ethnicities and regions. COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic disease patients remain unclear, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. This study aimed to clarify the demographic and clinical factors that may influence COVID-19 prognosis in rheumatic disease patients.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Methods: This was a case series of patients registered with the COVID-19 national registry of Japan College of Rheumatology between June 3, 2020, and June 30, 2021. Multivariable logistic regression was used to estimate the risk of hospitalization or death. Age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic disease diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic disease medications are taken immediately before infection was analyzed.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Results: A total of 220 patients from 55 institutions in Japan were included in the study, among whom 186 (84.5%) were hospitalized and 11 (5.0%) died. COVID-19 treatments were provided to 126 patients (57.3%), and mainly comprised glucocorticoids, favipiravir, remdesivir, and tocilizumab.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>In the multiple logistic regression model, older age and a history of hypertension were associated with hospitalization, while older age was associated with mortality. No specific treatment was correlated with mortality or hospitalization by the multi-variate analysis.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Conclusions: Older age and hypertension were associated with a poor prognosis in Japanese COVID-19 patients with CTD. Factors not directly related to CTD were closely associated with the prognosis.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Infectious Diseases, Kitasato University , Kanagawa, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Oku",
"given": "Kenji",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Kyushu University Beppu Hospital , Oita, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Kimoto",
"given": "Yasutaka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Kyushu University Beppu Hospital , Oita, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Horiuchi",
"given": "Takahiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology and Nephrology, Chubu Rosai Hospital , Aichi, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Yamamoto",
"given": "Mari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1566-2088",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine , Tokyo, Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kondo",
"given": "Yasushi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Medicine and Clinical Immunology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine , Osaka, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Okamoto",
"given": "Masashi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Rheumatology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Faculty of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine , Hokkaido, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Atsumi",
"given": "Tatsuya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine , Tokyo, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Takeuchi",
"given": "Tsutomu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Modern Rheumatology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-06T12:57:08Z",
"timestamp": 1662469028000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-06T12:57:09Z",
"timestamp": 1662469029000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-06T13:12:12Z",
"timestamp": 1662469932803
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1662422400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mr/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/mr/roac104/45718326/roac104.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mr/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/mr/roac104/45718326/roac104.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mr/advance-article/doi/10.1093/mr/roac104/6692611"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Rheumatology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Risk factors for hospitalization or mortality for COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: Results of a nation-wide JCR COVID-19 registry in Japan",
"type": "journal-article"
}
oku