Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453, Dec 2023
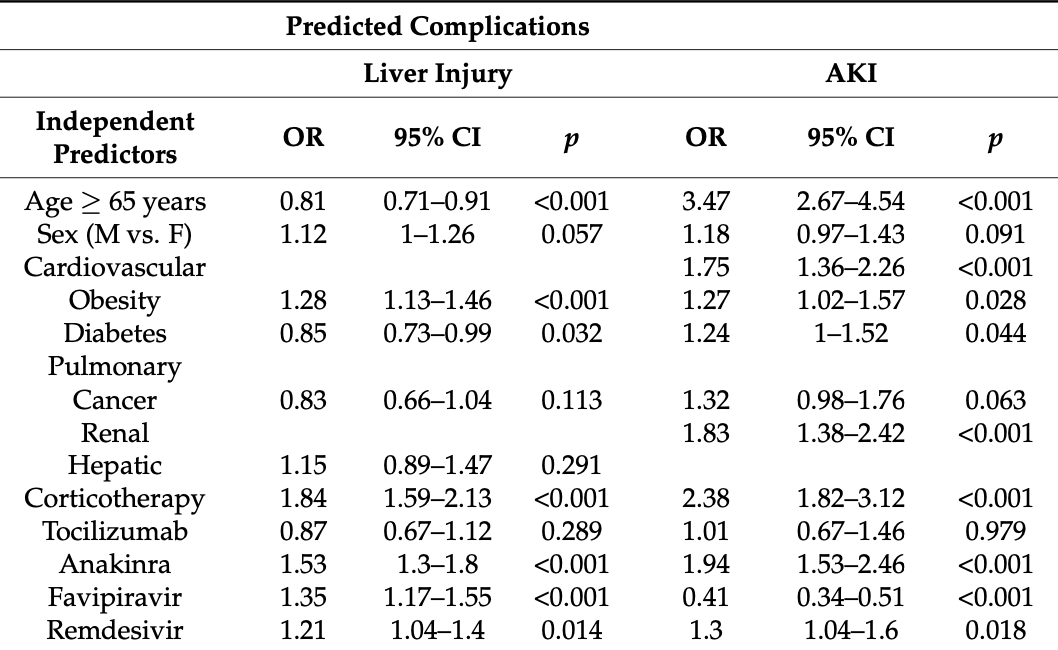
Retrospective 9,049 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Romania showing increased risk of acute kidney injury and liver injury with remdesivir treatment.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Briciu et al., 14 Dec 2023, retrospective, Romania, peer-reviewed, median age 61.0, 11 authors, study period 27 February, 2020 - 31 March, 2023.
Contact: dleucuta@umfcluj.ro (corresponding author), briciu.tincuta@umfcluj.ro, monica.muntean@umfcluj.ro, aradulescu@umfcluj.ro, cristina.cismaru@umfcluj.ro, topan.adriana@umfcluj.ro, melinda.horvat@umfcluj.ro, mihaela.lupse@yahoo.com, herbelucia@yahoo.com, mihai_calinn@yahoo.com, roxidobrota@gmail.com.
Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting
Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453
The aim of this study was to evaluate differences in the clinical manifestations and outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a single Romanian center during four pandemic waves determined by different SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs). A retrospective study on 9049 consecutive hospitalized adult patients was performed between 27 February 2020 and 31 March 2023. The study interval was divided into waves based on national data on SARS-CoV-2 VOCs' circulation. Multivariate logistic regression models were built, predicting death and complications as functions of comorbidities, therapy, wave, severity form, and vaccination status, and adjusted for ages ≥65 years. Pulmonary (pneumothorax/pneumomediastinum, pulmonary embolism) and extrapulmonary complications (liver injury, acute kidney injury, ischemic/hemorrhagic stroke, myocardial infarction, and gastrointestinal bleeding) were present, more frequently in ICU hospitalized patients and with differences between waves. The highest in-hospital mortality was found in patients presenting pneumothorax/pneumomediastinum. All of the evaluated risk factors were significantly associated with death, except for obesity and the Omicron wave. Our study highlights the changing nature of COVID-19 and acknowledges the impacts of viral mutations on disease outcomes. For all four waves, COVID-19 was a severe disease with a high risk of poor outcomes.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Al Ghamdi, Alqahtani, Al Dajani, Alsaedi, Al-Rubaish et al., Pneumothorax in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence, Analysis of Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes, Int. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S387868
Ashktorab, Russo, Oskrochi, Latella, Massironi et al., Clinical and endoscopic outcomes in coronavirus disease-2019 patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, Gastro Hep Adv, doi:10.1016/j.gastha.2022.02.021
Bavishi, Bonow, Trivedi, Abbott, Messerli et al., Special Article-Acute myocardial injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: A review, Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.05.013
Beghi, Giussani, Westenberg, Allegri, Garcia-Azorin et al., Acute and post-acute neurological manifestations of COVID-19: Present findings, critical appraisal, and future directions, J. Neurol, doi:10.1007/s00415-021-10848-4
Bie Ńkowski, Kowalska, Paciorek, Wasilewski, Uliczny et al., The Clinical Course and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 during Three Pandemic Waves in Poland: A Single Center Observational Study, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11247386
Briciu, Topan, Calin, Dobrota, Leucuta et al., Comparison of COVID-19 Severity in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Patients during the Delta and Omicron Wave of the Pandemic in a Romanian Tertiary Infectious Diseases Hospital, Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare11030373
Cappell, Friedel, Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19-Infected Patients, Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am, doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2022.10.004
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Elshazli, Kline, Elgaml, Aboutaleb, Salim et al., Gastroenterology manifestations and COVID-19 outcomes: A meta-analysis of 25,252 cohorts among the first and second waves, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26836
Garcia, Dehghani, Stanberry, Grines, Patel et al., Trends in clinical presentation, management, and outcomes of STEMI in patients with COVID-19, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.345
Guo, Fan, Chen, Wu, Zhang et al., Cardiovascular Implications of fatal outcomes of patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), JAMA Cardiol, doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017
King, Vail, O'leary, Hannan, Brough et al., Anakinra in COVID-19: Important considerations for clinical trials, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30160-0
Kurata, Miyayama, Ogawa, Watanabe, Asano et al., Thromboembolic events in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: Ecological assessment with a scoping review, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066218
Labenz, Toenges, Wörns, Sprinzl, Galle et al., Liver injury in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001827
Legislativ, Protocol of Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Liatsos, SARS-CoV-2 induced liver injury: Incidence, risk factors, impact on COVID-19 severity and prognosis in different population groups, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2397
Louis, Saad, Vijayakumar, Ilyas, Kokkirala et al., The Cardiovascular Manifestations of COVID-19, Heart Fail Clin, doi:10.1016/j.hfc.2022.08.001
Mallhi, Khan, Adnan, Stratification of Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0794
Margos, Meintanopoulos, Filioglou, Ellul, Intracerebral hemorrhage in COVID-19: A narrative review, J. Clin. Neurosci, doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2021.05.019
Matsumoto, Prowle, COVID-19-associated AKI, Curr. Opin. Crit. Care, doi:10.1097/MCC.0000000000000988
Matsuoka, Koami, Shinada, Sakamoto, Investigation of differences in coagulation characteristics between hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variant infection using rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM): Asinglecenter, retrospective, observational study, J. Clin. Lab. Anal, doi:10.1002/jcla.24796
Mărcău, Purec, Niculescu, Study on the Refusal of Vaccination against COVID-19 in Romania, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10020261
Nannoni, De Groot, Bell, Markus, Stroke in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Stroke, doi:10.1177/1747493020972922
Negro, Villa, Rolandi, Lucchini, Bambi, Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Patients: A Rapid Review, Gastroenterol. Nurs, doi:10.1097/SGA.0000000000000676
Noble, Selby, The Changing Nature of COVID-19-Associated AKI: Where Are We Now?, Nephrol. Dial. Transpl, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfab326
Ousseiran, Fares, Chamoun, Neurological manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review and detailed comprehension, Int. J. Neurosci, doi:10.1080/00207454.2021.1973000
Radulescu, Istrate, Flonta, Lupse, Antibody and viral RNA kinetics in SARS-CoV2 infected patients admitted to a Romanian University Hospital of Infectious Diseases, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.067
Radulescu, Istrate, Muntean, Treatment with Tocilizumab in Adult Patients with Moderate to Critical COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Single-Center Retrospective Study, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.01.048
Redruello-Guerrero, Ruiz-Del-Pino, Jiménez-Gutiérrez, Jiménez-Gutiérrez, Carrascos-Cáliz et al., COVID-19-associated lung weakness (CALW): Systematic review and meta-analysis, Med. Intensiv, doi:10.1016/j.medine.2023.06.001
Salahuddin, Afreen, Sheikh, Lateef, Dawod et al., Neurological predictors of clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Front. Neurol, doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.585944
Shams, Kazemi, Jafaryan, Morowvat, Peymani et al., Acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients receiving remdesivir: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Clinics, doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100200
Sullivan, Lees, Drake, Docherty, Oates et al., Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK Study: A prospective, multi-centre cohort study, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfab303
Wu, Luo, Wu, He, Li et al., Acute kidney injury associated with remdesivir: A comprehensive pharmacovigilance analysis of COVID-19 reports in FAERS, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828
Zellmer, Hanses, Muzalyova, Classen, Braun et al., Gastrointestinal bleeding and endoscopic findings in critically and non-critically ill patients with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Results from Lean European Open Survey on SARS-CoV-2 (LEOSS) and COKA registries, United Eur. Gastroenterol. J, doi:10.1002/ueg2.12165
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens12121453",
"ISSN": [
"2076-0817"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121453",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The aim of this study was to evaluate differences in the clinical manifestations and outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a single Romanian center during four pandemic waves determined by different SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs). A retrospective study on 9049 consecutive hospitalized adult patients was performed between 27 February 2020 and 31 March 2023. The study interval was divided into waves based on national data on SARS-CoV-2 VOCs’ circulation. Multivariate logistic regression models were built, predicting death and complications as functions of comorbidities, therapy, wave, severity form, and vaccination status, and adjusted for ages ≥65 years. Pulmonary (pneumothorax/pneumomediastinum, pulmonary embolism) and extrapulmonary complications (liver injury, acute kidney injury, ischemic/hemorrhagic stroke, myocardial infarction, and gastrointestinal bleeding) were present, more frequently in ICU hospitalized patients and with differences between waves. The highest in-hospital mortality was found in patients presenting pneumothorax/pneumomediastinum. All of the evaluated risk factors were significantly associated with death, except for obesity and the Omicron wave. Our study highlights the changing nature of COVID-19 and acknowledges the impacts of viral mutations on disease outcomes. For all four waves, COVID-19 was a severe disease with a high risk of poor outcomes.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"pathogens12121453"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Briciu",
"given": "Violeta",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4218-8622",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Informatics and Biostatistics, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400349 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leucuta",
"given": "Daniel-Corneliu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Muntean",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Radulescu",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Cismaru",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3339-9711",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Topan",
"given": "Adriana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Herbel",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Horvat",
"given": "Melinda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Calin",
"given": "Mihai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Dobrota",
"given": "Roxana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
},
{
"name": "The Clinical Hospital of Infectious Diseases, 400348 Cluj-Napoca, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Lupse",
"given": "Mihaela",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pathogens",
"container-title-short": "Pathogens",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T08:16:33Z",
"timestamp": 1702628193000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T09:39:02Z",
"timestamp": 1702633142000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"40PFE/30.12.2021"
],
"name": "project PDI-PFE-CDI 2021, entitled Increasing the Performance of Scientific Research, Supporting Excellence in Medical Research and Innovation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-20T09:54:30Z",
"timestamp": 1703066070223
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1702512000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/12/12/1453/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1453",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2397",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 induced liver injury: Incidence, risk factors, impact on COVID-19 severity and prognosis in different population groups",
"author": "Liatsos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2397",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0794",
"article-title": "Stratification of Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19",
"author": "Mallhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2164",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00207454.2021.1973000",
"article-title": "Neurological manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review and detailed comprehension",
"author": "Ousseiran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "754",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hfc.2022.08.001",
"article-title": "The Cardiovascular Manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Louis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Heart Fail Clin.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "(2023, November 24). World Health Organization Romania Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/region/euro/country/ro."
},
{
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Our World in Data (2023, August 03). Romania: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus/country/romania?country=ROU~OWID_WRL#daily-confirmed-deaths-how-do-they-compare-to-other-countries."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10020261",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Mărcău, F.C., Purec, S., and Niculescu, G. (2022). Study on the Refusal of Vaccination against COVID-19 in Romania. Vaccines, 10."
},
{
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "ECDC (2023, November 23). COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker. Available online: https://vaccinetracker.ecdc.europa.eu/public/extensions/COVID-19/vaccine-tracker.html#uptake-tab."
},
{
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2022, December 01). Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/report-of-the-who-china-joint-mission-on-coronavirus-disease-2019-(covid-19)."
},
{
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "(2023, June 06). The Romanian National Institute of Public Health. Available online: https://www.cnscbt.ro/index.php/analiza-cazuri-confirmate-covid19?limit=10&limitstart=20."
},
{
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "R Core Team (2013). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing."
},
{
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation (2023, June 06). Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—8 February 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---8-february-2022."
},
{
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2023, March 14). COVID-19 Medical Conditions, Available online: cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/healthcare11030373",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Briciu, V., Topan, A., Calin, M., Dobrota, R., Leucuta, D.C., and Lupse, M. (2023). Comparison of COVID-19 Severity in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Patients during the Delta and Omicron Wave of the Pandemic in a Romanian Tertiary Infectious Diseases Hospital. Healthcare, 11."
},
{
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Portal Legislativ (2023, March 14). Protocol of Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/249520."
},
{
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2023, January 13). Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living Guideline. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-therapeutics-2023.1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.01.048",
"article-title": "Treatment with Tocilizumab in Adult Patients with Moderate to Critical COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Single-Center Retrospective Study",
"author": "Radulescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30160-0",
"article-title": "Anakinra in COVID-19: Important considerations for clinical trials",
"author": "King",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e379",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency (2023, March 14). EMA Recommends Approval for Use of Kineret in Adults with COVID-19. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-approval-use-kineret-adults-covid-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.067",
"article-title": "Antibody and viral RNA kinetics in SARS-CoV2 infected patients admitted to a Romanian University Hospital of Infectious Diseases",
"author": "Radulescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066218",
"article-title": "Thromboembolic events in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: Ecological assessment with a scoping review",
"author": "Kurata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e066218",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcla.24796",
"article-title": "Investigation of differences in coagulation characteristics between hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variant infection using rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM): Asingle-center, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Matsuoka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e24796",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Lab. Anal.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated lung weakness (CALW): Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"first-page": "552",
"journal-title": "Med. Intensiv.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S387868",
"article-title": "Pneumothorax in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence, Analysis of Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes",
"author": "Alqahtani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8249",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000001827",
"article-title": "Liver injury in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Labenz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1194",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCC.0000000000000988",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated AKI",
"author": "Matsumoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "630",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ndt/gfab303",
"article-title": "Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK Study: A prospective, multi-centre cohort study",
"author": "Sullivan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Nephrol. Dial. Transplant.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ndt/gfab326",
"article-title": "The Changing Nature of COVID-19-Associated AKI: Where Are We Now?",
"author": "Noble",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Nephrol. Dial. Transpl.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.692828",
"article-title": "Acute kidney injury associated with remdesivir: A comprehensive pharmacovigilance analysis of COVID-19 reports in FAERS",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692828",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100200",
"article-title": "Acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients receiving remdesivir: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials",
"author": "Shams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100200",
"journal-title": "Clinics",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2020.585944",
"article-title": "Neurological predictors of clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Salahuddin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585944",
"journal-title": "Front. Neurol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00415-021-10848-4",
"article-title": "Acute and post-acute neurological manifestations of COVID-19: Present findings, critical appraisal, and future directions",
"author": "Beghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2265",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "269",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1747493020972922",
"article-title": "Stroke in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nannoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Stroke",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jocn.2021.05.019",
"article-title": "Intracerebral hemorrhage in COVID-19: A narrative review",
"author": "Margos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2020.05.013",
"article-title": "Special Article—Acute myocardial injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: A review",
"author": "Bavishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "682",
"journal-title": "Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular Implications of fatal outcomes of patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "811",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.345",
"article-title": "Trends in clinical presentation, management, and outcomes of STEMI in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Garcia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2236",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SGA.0000000000000676",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Patients: A Rapid Review",
"author": "Negro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterol. Nurs.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gtc.2022.10.004",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19-Infected Patients",
"author": "Cappell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26836",
"article-title": "Gastroenterology manifestations and COVID-19 outcomes: A meta-analysis of 25,252 cohorts among the first and second waves",
"author": "Elshazli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2740",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.02.021",
"article-title": "Clinical and endoscopic outcomes in coronavirus disease-2019 patients with gastrointestinal bleeding",
"author": "Ashktorab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "487",
"journal-title": "Gastro Hep Adv.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ueg2.12165",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal bleeding and endoscopic findings in critically and non-critically ill patients with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Results from Lean European Open Survey on SARS-CoV-2 (LEOSS) and COKA registries",
"author": "Zellmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1081",
"journal-title": "United Eur. Gastroenterol. J.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11247386",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Bieńkowski, C., Kowalska, J.D., Paciorek, M., Wasilewski, P., Uliczny, P., Garbacz-Łagożna, E., Pihowicz, A., Mrozińska, M., Dyda, T., and Makowiecki, M. (2022). The Clinical Course and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 during Three Pandemic Waves in Poland: A Single Center Observational Study. J. Clin. Med., 11."
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/12/12/1453"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Immunology and Microbiology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}