Insulin and Metformin Administration: Unravelling the Multifaceted Association with Mortality across Various Clinical Settings Considering Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12030605, Mar 2024
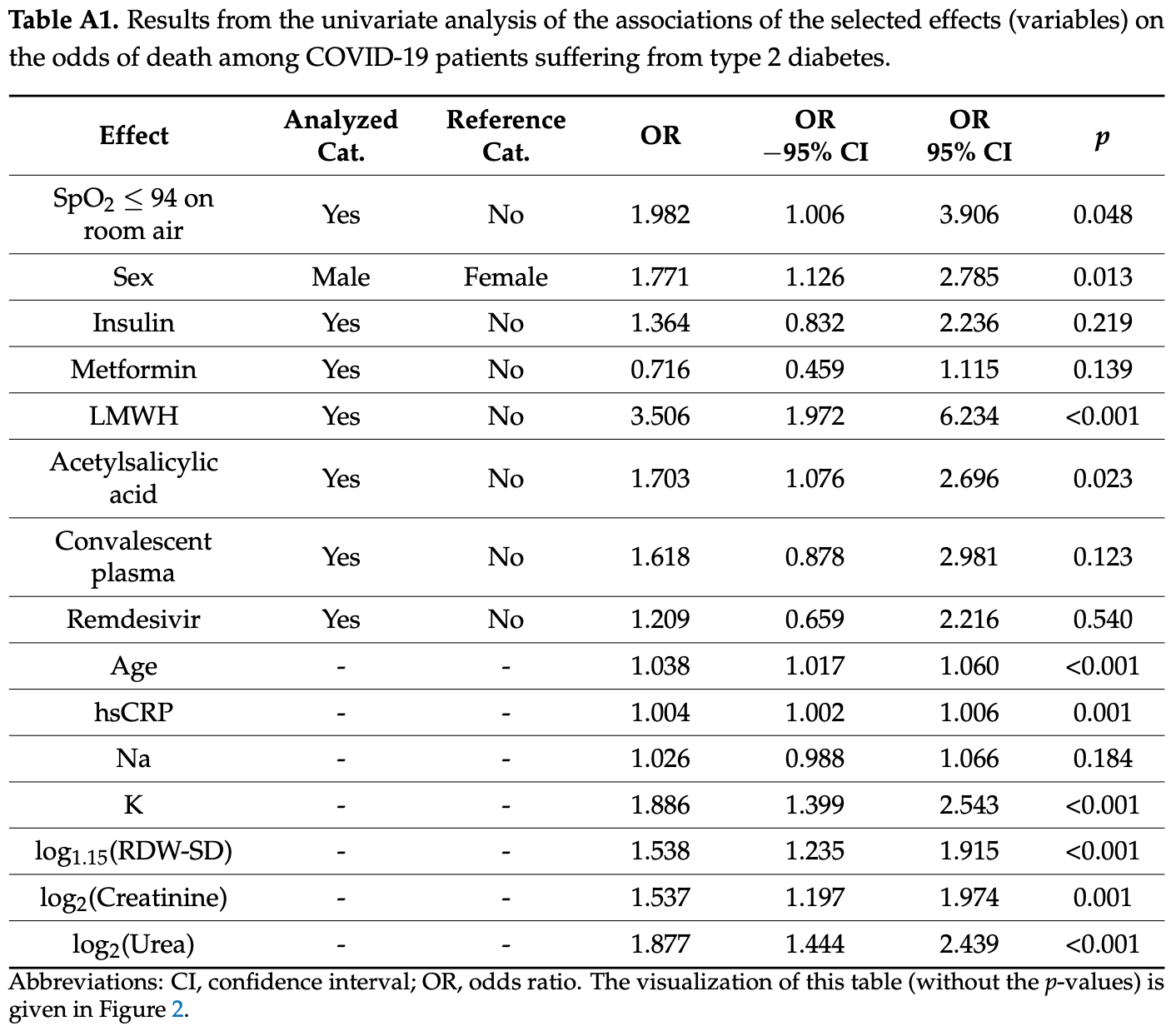
Retrospective 430 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes in Poland showing lower mortality with metformin and higher mortality with remdesivir, convalescent plasma, and aspirin in univariable analysis. These results were not statistically significant except for aspirin, and no baseline information per treatment is provided to assess confounding.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 20.9% higher, OR 1.21, p = 0.55, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Lewandowski et al., 7 Mar 2024, retrospective, Poland, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
Insulin and Metformin Administration: Unravelling the Multifaceted Association with Mortality across Various Clinical Settings Considering Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12030605
Due to the molecular mechanisms of action of antidiabetic drugs, they are considered to be effective in the treatment of both COVID-19 and the post-COVID-19 syndromes. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of administering insulin and metformin on the mortality of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) with symptomatic COVID-19 with the use of logistic regression models. The association between death and insulin and metformin was weak and could not be included in the multivariate model. However, the interaction of both drugs with other factors, including remdesivir and low-molecular-weight heparin (metformin), age and hsCRP (insulin), modulated the odds of death. These interactions hint at multifaceted (anti-/pro-) associations of both insulin and metformin with the odds of death, depending on the patient's characteristics. In the multivariate model, RDW-SD, adjusted with low-molecular-weight heparin treatment, age, sex and K + , was associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 and T2DM. With a 15% increase in RDW-SD, the risk of death increased by 87.7%. This preliminary study provides the foundations for developing further, more personalized models to assess the risk of death in T2DM patients, as well as for identifying patients at an increased risk of death due to COVID-19.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The Wald test was utilized in assessing the value of the factors to be included in the model. The score test (Lagrange multiplier test) was used to check if, at any step, the previously excluded factors should be re-included into the current model. The final model is described in Table 2 and visualized in Figure 3 .
References
Ali, Elevated Level of C-reactive Protein May Be an Early Marker to Predict Risk for Severity of COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26097
Alshnbari, Idris, Can Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitor Reduce the Risk of Adverse Complications Due to COVID-19?-Targeting Hyperinflammation, Curr. Med. Res. Opin, doi:10.1080/03007995.2022.2027141
Alwani, Yassin, Al-Zoubi, Aboumarzouk, Nettleship et al., Sex-based Differences in Severity and Mortality in COVID-19, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2223
Attena, Caturano, Annunziata, Maraolo, De Rosa et al., Remdesivir treatment and clinical outcome in non-severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score matching multicenter Italian hospital experience, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol
Baggen, Jacquemyn, Persoons, Vanstreels, Pye et al., TMEM106B Is a Receptor Mediating ACE2-Independent SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Weaver, Bradley et al., Associations of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes with COVID-19-Related Mortality in England: A Whole-Population Study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Bode, Garrett, Messler, Mcfarland, Crowe et al., Glycemic Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in the United States, J. Diabetes Sci. Technol, doi:10.1177/1932296820924469
Bonora, Avogaro, Fadini, Disentangling Conflicting Evidence on DPP-4 Inhibitors and Outcomes of COVID-19: Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Bugliani, Syed, Paula, Omar, Suleiman et al., DPP-4 Is Expressed in Human Pancreatic Beta Cells and Its Direct Inhibition Improves Beta Cell Function and Survival in Type 2 Diabetes, Mol. Cell Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.mce.2018.01.019
Carino, Moraca, Fiorillo, Marchianò, Sepe et al., Hijacking SARS-CoV-2/ACE2 Receptor Interaction by Natural and Semi-Synthetic Steroidal Agents Acting on Functional Pockets on the Receptor Binding Domain, Front. Chem, doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.572885
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Choudhury, Mukherjee, In Silico Studies on the Comparative Characterization of the Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein with ACE-2 Receptor Homologs and Human TLRs, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25987
Defronzo, Fleming, Chen, Bicsak, Metformin-Associated Lactic Acidosis: Current Perspectives on Causes and Risk, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2015.10.014
Gama, RDW Shows Prognostic Potential in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27764
Gazzaz, Diabetes and COVID-19, Open Life Sci, doi:10.1515/biol-2021-0034
Holman, Knighton, Kar, O'keefe, Curley et al., Risk Factors for COVID-19-Related Mortality in People with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in England: A Population-Based Cohort Study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0
Jung, Choi, Association between COVID-19 and Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality among Patients with Diabetes, Front. Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1230176
Kim, Jeon, Kim, Moon, Cho et al., The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab. J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Levey, Coresh, Greene, Stevens, Zhang et al., Using Standardized Serum Creatinine Values in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Equation for Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-145-4-200608150-00004
Li, Huang, Zou, Yang, Hui et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26424
Li, Zhang, Yang, Lian, Xie et al., The MERS-CoV Receptor DPP4 as a Candidate Binding Target of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101160
Liu, Zhang, Weng, Yang, Jin et al., Association Between Average Plasma Potassium Levels and 30-Day Mortality During Hospitalization in Patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Int. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.7150/ijms.50965
Mahroum, Alghory, Kiyak, Alwani, Seida et al., Ferritin-From Iron, through Inflammation and Autoimmunity, to COVID-19, J. Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102778
Masre, Jufri, Ibrahim, Abdul Raub, Classical and Alternative Receptors for SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Strategy, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2207
Mccarthy, Metformin as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19, Expert. Opin. Pharmacother, doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2215385
Muniyappa, Gubbi, COVID-19 Pandemic, Coronaviruses, and Diabetes Mellitus, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020
Nag, Mandal, Mukherjee, Mukherjee, Kundu, DPP-4 Inhibitors as a Savior for COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes, Future Virol, doi:10.2217/fvl-2022-0112
Norouzi, Norouzi, Ruggiero, Khan, Myers et al., Type-2 Diabetes as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 Infection, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9061211
Pitt, Agarwal, Anker, Ruilope, Rossing et al., Association of Finerenone Use With Reduction in Treatment-Emergent Pneumonia and COVID-19 Adverse Events Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36123
Pouladzadeh, Safdarian, Choghakabodi, Amini, Sokooti, Validation of Red Cell Distribution Width as a COVID-19 Severity Screening Tool, Future Sci. OA, doi:10.2144/fsoa-2020-0199
Rajpal, Rahimi, Ismail-Beigi, Factors Leading to High Morbidity and Mortality of COVID-19 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, J. Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13085
Rakhmat, Kusmala, Handayani, Juliastuti, Nawangsih et al., Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression, Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027
Raman, Bluemke, Lüscher, Neubauer, Long COVID: Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 with a Cardiovascular Focus, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehac031
Schlicht, Rohmann, Geisler, Hollstein, Knappe et al., Circulating Levels of Soluble Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 Are Reduced in Human Subjects Hospitalized for Severe COVID-19 Infections, Int. J. Obes, doi:10.1038/s41366-020-00689-y
Singh, Gillies, Singh, Singh, Chudasama et al., Prevalence of Co-morbidities and Their Association with Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Diabetes Obes. Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14124
Singh, Khunti, COVID-19 and Diabetes, Annu. Rev. Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042220-011857
Solerte, ; D'addio, Trevisan, Lovati, Rossi et al., Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Soni, Gopalakrishnan, Significance of RDW in Predicting Mortality in COVID-19-An Analysis of 622 Cases, Int. J. Lab. Hematol, doi:10.1111/ijlh.13526
Soni, Gopalakrishnan, Vaishya, Prabu, D-Dimer Level Is a Useful Predictor for Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: Analysis of 483 Cases, Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.007
Steenblock, Hassanein, Khan, Yaman, Kamel et al., Diabetes and COVID-19: Short-and Long-Term Consequences, Horm. Metab. Res, doi:10.1055/a-1878-9566
Strollo, Maddaloni, Dauriz, Pedone, Buzzetti et al., Use of DPP4 Inhibitors in Italy Does Not Correlate with Diabetes Prevalence among COVID-19 Deaths, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108444
Tittel, Rosenbauer, Kamrath, Ziegler, Reschke et al., Did the COVID-19 Lockdown Affect the Incidence of Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes in Germany?, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1633
Vankadari, Wilce, Emerging COVID-19 Coronavirus: Glycan Shield and Structure Prediction of Spike Glycoprotein and Its Interaction with Human CD26, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565
Varghese, Samuel, Liskova, Kubatka, Büsselberg, Diabetes and Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): Molecular Mechanism of Metformin Intervention and the Scientific Basis of Drug Repurposing, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009634
Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Lian et al., CD147-Spike Protein Is a Novel Route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Host Cells, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Pichelin, Amadou et al., Predictors of Hospital Discharge and Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19: Updated Results from the Nationwide CORONADO Study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Zelniker, Wiviott, Raz, Im, Goodrich et al., SGLT2 Inhibitors for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines12030605",
"ISSN": [
"2227-9059"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030605",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Due to the molecular mechanisms of action of antidiabetic drugs, they are considered to be effective in the treatment of both COVID-19 and the post-COVID-19 syndromes. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of administering insulin and metformin on the mortality of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) with symptomatic COVID-19 with the use of logistic regression models. The association between death and insulin and metformin was weak and could not be included in the multivariate model. However, the interaction of both drugs with other factors, including remdesivir and low-molecular-weight heparin (metformin), age and hsCRP (insulin), modulated the odds of death. These interactions hint at multifaceted (anti-/pro-) associations of both insulin and metformin with the odds of death, depending on the patient’s characteristics. In the multivariate model, RDW-SD, adjusted with low-molecular-weight heparin treatment, age, sex and K+, was associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 and T2DM. With a 15% increase in RDW-SD, the risk of death increased by 87.7%. This preliminary study provides the foundations for developing further, more personalized models to assess the risk of death in T2DM patients, as well as for identifying patients at an increased risk of death due to COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biomedicines12030605"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7624-631X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry and Immunochemistry, Wroclaw Medical University, Chałubińskiego Street 10, 50-368 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lewandowski",
"given": "Łukasz",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry and Immunochemistry, Wroclaw Medical University, Chałubińskiego Street 10, 50-368 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Bronowicka-Szydełko",
"given": "Agnieszka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Rabczyński",
"given": "Maciej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Bednarska-Chabowska",
"given": "Dorota",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Ophthalmology, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Adamiec-Mroczek",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5472-028X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiology, Faculty of Medicine, 4th Military Hospital, Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Weigla 5 Street, 50-981 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Doroszko",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3951-205X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Trocha",
"given": "Małgorzata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2812-4702",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Statistical Analysis Centre, Wroclaw Medical University, K. Marcinkowski Street 2–6, 50-368 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kujawa",
"given": "Krzysztof",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1064-1237",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Screening of Biological Activity Assays and Collection of Biological Material Laboratory, Wroclaw Medical University Biobank, Faculty of Pharmacy, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 221A, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Matera-Witkiewicz",
"given": "Agnieszka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Kuźnik",
"given": "Edwin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Lubieniecki",
"given": "Paweł",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2434-8725",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, University Hospital, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Madziarski",
"given": "Marcin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Sokołowski",
"given": "Janusz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9202-432X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Heart Diseases, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jankowska",
"given": "Ewa A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3624-3691",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Department of Diabetology and Internal Disease, Wroclaw Medical University, Borowska Street 213, 50-556 Wroclaw, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Madziarska",
"given": "Katarzyna",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedicines",
"container-title-short": "Biomedicines",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-07T16:33:06Z",
"timestamp": 1709829186000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-07T18:17:48Z",
"timestamp": 1709835468000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-08T00:40:31Z",
"timestamp": 1709858431620
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709769600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/3/605/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "605",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2024, January 10). COVID-19 Cases|WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehac031",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 with a Cardiovascular Focus",
"author": "Raman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1157",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042220-011857",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Diabetes",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1878-9566",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: Short- and Long-Term Consequences",
"author": "Steenblock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "Horm. Metab. Res.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2022-0112",
"article-title": "DPP-4 Inhibitors as a Savior for COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes",
"author": "Nag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Future Virol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14124",
"article-title": "Prevalence of Co-morbidities and Their Association with Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1915",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes. Metab.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2",
"article-title": "Associations of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes with COVID-19-Related Mortality in England: A Whole-Population Study",
"author": "Barron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1932296820924469",
"article-title": "Glycemic Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in the United States",
"author": "Bode",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1633",
"article-title": "Did the COVID-19 Lockdown Affect the Incidence of Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes in Germany?",
"author": "Tittel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e172",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"article-title": "Risk Factors for COVID-19-Related Mortality in People with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in England: A Population-Based Cohort Study",
"author": "Holman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03007995.2022.2027141",
"article-title": "Can Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitor Reduce the Risk of Adverse Complications Due to COVID-19?—Targeting Hyperinflammation",
"author": "Alshnbari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "357",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Res. Opin.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009634",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Varghese, E., Samuel, S.M., Liskova, A., Kubatka, P., and Büsselberg, D. (2021). Diabetes and Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): Molecular Mechanism of Metformin Intervention and the Scientific Basis of Drug Repurposing. PLoS Pathog., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.101160",
"article-title": "The MERS-CoV Receptor DPP4 as a Candidate Binding Target of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101160",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X",
"article-title": "SGLT2 Inhibitors for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials",
"author": "Zelniker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2020.572885",
"article-title": "Hijacking SARS-CoV-2/ACE2 Receptor Interaction by Natural and Semi-Synthetic Steroidal Agents Acting on Functional Pockets on the Receptor Binding Domain",
"author": "Carino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "572885",
"journal-title": "Front. Chem.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005",
"article-title": "TMEM106B Is a Receptor Mediating ACE2-Independent SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry",
"author": "Baggen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3427",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"article-title": "CD147-Spike Protein Is a Novel Route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Host Cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2207",
"article-title": "Classical and Alternative Receptors for SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Strategy",
"author": "Masre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "(2024, January 05). Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection When Novel Coronavirus (nCoV) Infection Is Suspected: Interim Guidance, 12 January 2020. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/332299."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-145-4-200608150-00004",
"article-title": "Using Standardized Serum Creatinine Values in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Equation for Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate",
"author": "Levey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2223",
"article-title": "Sex-based Differences in Severity and Mortality in COVID-19",
"author": "Alwani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2223",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Pandemic, Coronaviruses, and Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Muniyappa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E736",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13085",
"article-title": "Factors Leading to High Morbidity and Mortality of COVID-19 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Rajpal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "895",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms9061211",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Norouzi, M., Norouzi, S., Ruggiero, A., Khan, M.S., Myers, S., Kavanagh, K., and Vemuri, R. (2021). Type-2 Diabetes as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 Infection. Microorganisms, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1521",
"article-title": "Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study",
"author": "Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2999",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36123",
"article-title": "Association of Finerenone Use With Reduction in Treatment-Emergent Pneumonia and COVID-19 Adverse Events Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease",
"author": "Pitt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2236123",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2023.1230176",
"article-title": "Association between COVID-19 and Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality among Patients with Diabetes",
"author": "Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/biol-2021-0034",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Gazzaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Open Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26424",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1449",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.50965",
"article-title": "Association Between Average Plasma Potassium Levels and 30-Day Mortality During Hospitalization in Patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "736",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102778",
"article-title": "Ferritin—From Iron, through Inflammation and Autoimmunity, to COVID-19",
"author": "Mahroum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102778",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14656566.2023.2215385",
"article-title": "Metformin as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "MCCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"journal-title": "Expert. Opin. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27764",
"article-title": "RDW Shows Prognostic Potential in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3498",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijlh.13526",
"article-title": "Significance of RDW in Predicting Mortality in COVID-19—An Analysis of 622 Cases",
"author": "Soni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "O221",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Lab. Hematol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2144/fsoa-2020-0199",
"article-title": "Validation of Red Cell Distribution Width as a COVID-19 Severity Screening Tool",
"author": "Pouladzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "FSO712",
"journal-title": "Future Sci. OA",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.007",
"article-title": "D-Dimer Level Is a Useful Predictor for Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: Analysis of 483 Cases",
"author": "Soni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2245",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0146",
"article-title": "The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "602",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. J.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1399",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2015.10.014",
"article-title": "Metformin-Associated Lactic Acidosis: Current Perspectives on Causes and Risk",
"author": "DeFronzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2018.01.019",
"article-title": "DPP-4 Is Expressed in Human Pancreatic Beta Cells and Its Direct Inhibition Improves Beta Cell Function and Survival in Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Bugliani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "186",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "473",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26097",
"article-title": "Elevated Level of C-reactive Protein May Be an Early Marker to Predict Risk for Severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2409",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25987",
"article-title": "In Silico Studies on the Comparative Characterization of the Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein with ACE-2 Receptor Homologs and Human TLRs",
"author": "Choudhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2105",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565",
"article-title": "Emerging COVID-19 Coronavirus: Glycan Shield and Structure Prediction of Spike Glycoprotein and Its Interaction with Human CD26",
"author": "Vankadari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41366-020-00689-y",
"article-title": "Circulating Levels of Soluble Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 Are Reduced in Human Subjects Hospitalized for Severe COVID-19 Infections",
"author": "Schlicht",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2335",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Obes.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor and Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression",
"author": "Rakhmat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01515-6",
"article-title": "Disentangling Conflicting Evidence on DPP-4 Inhibitors and Outcomes of COVID-19: Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Bonora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1379",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w",
"article-title": "Predictors of Hospital Discharge and Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19: Updated Results from the Nationwide CORONADO Study",
"author": "Wargny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "778",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108444",
"article-title": "Use of DPP4 Inhibitors in Italy Does Not Correlate with Diabetes Prevalence among COVID-19 Deaths",
"author": "Strollo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108444",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-023-03499-z",
"article-title": "Remdesivir treatment and clinical outcome in non-severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score matching multicenter Italian hospital experience",
"author": "Attena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "967",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/3/605"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Insulin and Metformin Administration: Unravelling the Multifaceted Association with Mortality across Various Clinical Settings Considering Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
lewandowski