Real-world clinical outcomes of treatment with molnupiravir for patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic
et al., Clinical and Experimental Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3, Oct 2022 (preprint)
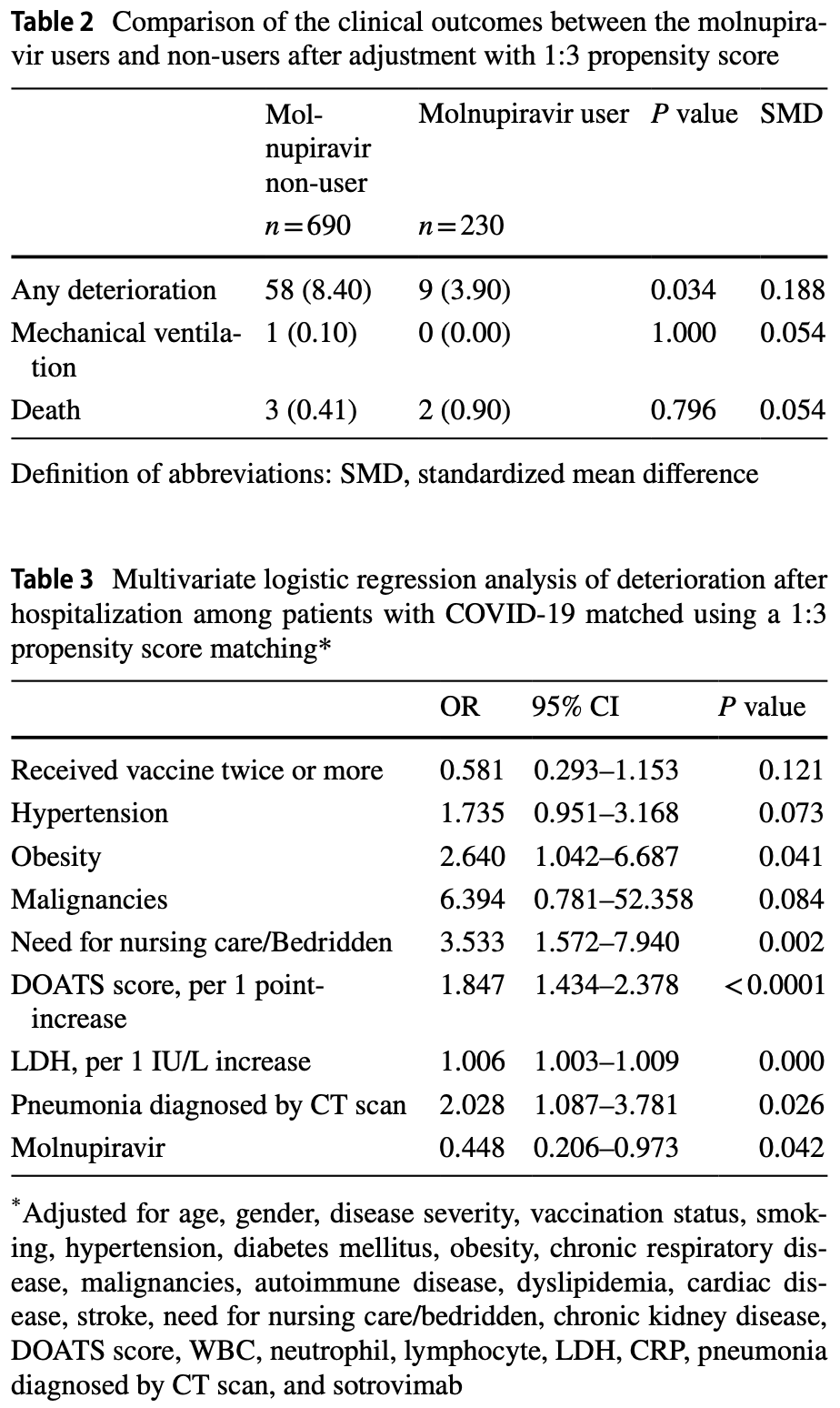
Retrospective 1,921 patients in Japan, showing lower progression with molnupiravir use.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments25.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.60, treatment 2 of 230 (0.9%), control 3 of 690 (0.4%), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 57.1% lower, RR 0.43, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 230 (0.0%), control 1 of 690 (0.1%), NNT 690, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of progression, 53.0% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.04, treatment 9 of 230 (3.9%), control 58 of 690 (8.4%), NNT 22, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Suzuki et al., 5 Oct 2022, retrospective, Japan, peer-reviewed, 53 authors.
Contact: shibatay@fmu.ac.jp.
Real-world clinical outcomes of treatment with molnupiravir for patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic
Clinical and Experimental Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3
It is unclear whether molnupiravir has a beneficial effect on vaccinated patients infected with the Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). We here evaluated the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the Omicron variant surge in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. We enrolled patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who were admitted to hospitals between January and April, 2022. Clinical deterioration after admission was compared between molnupiravir users (n = 230) and non-users (n = 690) after 1:3 propensity score matching. Additionally, we performed forward stepwise multivariate logistic regression analysis to evaluate the association between clinical deterioration after admission and molnupiravir treatment in the 1:3 propensity score-matched subjects. The characteristics of participants in both groups were balanced as indicated by covariates with a standardized mean difference of < 0.1. Regarding comorbidities, there was no imbalance between the two groups, except for the presence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and cardiac disease. The clinical deterioration rate was significantly lower in the molnupiravir users compared to the non-users (3.90% vs 8.40%; P = 0.034). Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that receiving molnupiravir was a factor for preventing deterioration (odds ratio 0.448; 95% confidence interval 0.206-0.973; P = 0.042), independent of other covariates. This real-world study demonstrates that molnupiravir contributes to the prevention of deterioration in COVID-19 patients after hospitalization during the Omicron variant phase.
Keywords Molnupiravir • COVID-19 • Omicron variant • Real-world • Effectiveness Abbreviations CI Confidence interval CKD Chronic kidney disease COVID-19 Coronavirus disease 2019 CRP C-reactive protein CT Computed tomography ECMO Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation IPTW Inverse probability of treatment weighting LDH Lactate dehydrogenase OR Odds ratio SARS-CoV-2 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SMD Standardized mean difference * Yoko Shibata
Author contribution Conception and design: YS and YS. Analysis and drafting the manuscript: YS and YS. Data curation: all authors. Final approval of the manuscript: all authors.
Declarations Conflict of interest Y Shibata and H Minemura received lecture fees and research grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Y Shibata and J Saito received lecture fees from GlaxoSmithKline K.K. The other authors report no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Ethic approval This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the local ethical committee.
Consent to publication The authors have seen the final version of the manuscript and approved submission for publication. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the..
References
Atmosudigdo, Lim, Radi, dyslipidemia increases the risk of severe COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes, doi:10.1177/1179551421990675
Austin, Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies, Pharm Stat, doi:10.1002/pst.433
Austin, Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat Med
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bojkova, Widera, Ciesek, Wass, Michaelis et al., Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in Omicron variant compared to Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9
Callaway, Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03552-w
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2832
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hoffmann, Krüger, Schulz, The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032
Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043
Liu, Rocklöv, The effective reproductive number of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is several times relative to Delta, J Travel Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taac037
Ohashi, Hishiki, Akazawa, Different efficacies of neutralizing antibodies and antiviral drugs on SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105372
Peng, He, Xue, Yang, Liu et al., Role of Hypertension on the Severity of COVID-19: A Review, J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Polack, Thomas, Kitchin, Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
Ren, Nishimura, Tjan, Large-scale serosurveillance of COVID-19 in Japan: acquisition of neutralizing antibodies for Delta but not for Omicron and requirement of booster vaccination to overcome the Omicron's outbreak, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0266270
Rosenke, Okumura, Lewis, MK-4482) is efficacious against Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants in the Syrian hamster COVID-19 model, doi:10.1101/2022.02.22.481491v1
Shiba, Kawahara, using propensity scores for causal inference: pitfalls and tips, J Epidemiol, doi:10.2188/jea.JE20210145
Shibata, Minemura, Suzuki, Development and external validation of the DOAT and DOATS scores: simple decision support tools to identify disease progression among nonelderly patients with mild/moderate COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2021.12.13.21267698v1
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.2, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2201933
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
Wong, Au, Lau, Cowling, Leung, Realworld effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2
Yamamoto, Wada, Ichikawa, Evaluation of biomarkers of severity in patients with COVID-19 infection, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10173775
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3",
"ISSN": [
"1591-9528"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>It is unclear whether molnupiravir has a beneficial effect on vaccinated patients infected with the Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). We here evaluated the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the Omicron variant surge in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. We enrolled patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who were admitted to hospitals between January and April, 2022. Clinical deterioration after admission was compared between molnupiravir users (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 230) and non-users (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 690) after 1:3 propensity score matching. Additionally, we performed forward stepwise multivariate logistic regression analysis to evaluate the association between clinical deterioration after admission and molnupiravir treatment in the 1:3 propensity score-matched subjects. The characteristics of participants in both groups were balanced as indicated by covariates with a standardized mean difference of < 0.1. Regarding comorbidities, there was no imbalance between the two groups, except for the presence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and cardiac disease. The clinical deterioration rate was significantly lower in the molnupiravir users compared to the non-users (3.90% vs 8.40%; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.034). Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that receiving molnupiravir was a factor for preventing deterioration (odds ratio 0.448; 95% confidence interval 0.206–0.973; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.042), independent of other covariates. This real-world study demonstrates that molnupiravir contributes to the prevention of deterioration in COVID-19 patients after hospitalization during the Omicron variant phase.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"949"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "30 September 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "11 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "5 December 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Y Shibata and H Minemura received lecture fees and research grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Y Shibata and J Saito received lecture fees from GlaxoSmithKline K.K. The other authors report no conflicts of interest related to this study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethic approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the local ethical committee."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors have seen the final version of the manuscript and approved submission for publication."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suzuki",
"given": "Yasuhito",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shibata",
"given": "Yoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minemura",
"given": "Hiroyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nikaido",
"given": "Takefumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanino",
"given": "Yoshinori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fukuhara",
"given": "Atsuro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanno",
"given": "Ryuzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Hiroyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suzuki",
"given": "Shuzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inokoshi",
"given": "Yayoi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sando",
"given": "Eiichiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakuma",
"given": "Hirofumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kobayashi",
"given": "Tatsuho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kume",
"given": "Hiroaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamimoto",
"given": "Masahiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aoki",
"given": "Hideko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takama",
"given": "Akira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iizuka",
"given": "Taku",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamiyama",
"given": "Takamichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nakayama",
"given": "Masaru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Kiyoshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanigawa",
"given": "Koichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sato",
"given": "Masahiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waragai",
"given": "Yuichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kambe",
"given": "Toshiyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanzaki",
"given": "Norio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azuma",
"given": "Teruhisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okamoto",
"given": "Hiromasa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakamoto",
"given": "Keiji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nakamura",
"given": "Yuichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ohtani",
"given": "Hiroshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waragai",
"given": "Mitsuru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maeda",
"given": "Shinsaku",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ishida",
"given": "Tokiya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sugino",
"given": "Keishi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abe",
"given": "Wataru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsukada",
"given": "Yasuhiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Tomoyoshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yamada",
"given": "Ryuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sato",
"given": "Riko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Onuma",
"given": "Takumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomita",
"given": "Hikaru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Mikako",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watanabe",
"given": "Natsumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rikimaru",
"given": "Mami",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kawamata",
"given": "Takaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morimoto",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Togawa",
"given": "Ryuichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sato",
"given": "Yuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Junpei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanazawa",
"given": "Kenya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamaguchi",
"given": "Sugihiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iseki",
"given": "Ken",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical and Experimental Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Clin Exp Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T09:03:46Z",
"timestamp": 1670231026000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T09:08:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670231280000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001691",
"award": [
"KAKENHI grant number 19K08658, and 22K10560"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T09:42:34Z",
"timestamp": 1670233354414
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670198400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670198400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"author": "DM Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "238",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "949_CR1",
"unstructured": "Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):238–51. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2035002.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2832",
"author": "A Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1236",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "949_CR2",
"unstructured": "Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al. Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327:1236–46. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.2832.",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR3",
"unstructured": "Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al. Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. N Engl J Med 2022; 386:509–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116044."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "949_CR4",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1397–408. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2118542.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043",
"author": "B Korber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "949_CR5",
"unstructured": "Korber B, Fischer WM, Gnanakaran S, et al. Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell. 2020;182:812-27.e19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03552-w",
"author": "E Callaway",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "949_CR6",
"unstructured": "Callaway E. Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert. Nature. 2021;600:21. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03552-w.",
"volume": "600",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taac037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR7",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Rocklöv J, The effective reproductive number of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is several times relative to Delta. J Travel Med 2022; 29. https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taac037."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0266270",
"author": "Z Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "949_CR8",
"unstructured": "Ren Z, Nishimura M, Tjan LH, et al. Large-scale serosurveillance of COVID-19 in Japan: acquisition of neutralizing antibodies for Delta but not for Omicron and requirement of booster vaccination to overcome the Omicron’s outbreak. PLoS ONE. 2022;17: e0266270. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0266270.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "447",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "949_CR9",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Krüger N, Schulz S, et al. The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell. 2022;185:447-56.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032.",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR10",
"unstructured": "VanBlargan LA, Errico JM, Halfmann PJ, et al. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat Med 2022; 28:490–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR11",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Au ICH, Lau KTK, Cowling BJ, Leung GM. Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2."
},
{
"key": "949_CR12",
"unstructured": "The official website of Fukushima Prefecture. The variant of COVID-19 in Fukushima from January 2022 (in Japanese). https://www.pref.fukushima.lg.jp/site/covid19-portal/variant.html. Accessed 1 June 2022."
},
{
"key": "949_CR13",
"unstructured": "Japan Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare. Clinical Management of patients with COVID-19: A guide for front-line healthcare workers. Available at: https://www.niph.go.jp/h-crisis/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/20200706103735_content_000646531.pdf. Accessed 1 June 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10173775",
"author": "A Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3775",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "949_CR14",
"unstructured": "Yamamoto A, Wada H, Ichikawa Y, et al. Evaluation of biomarkers of severity in patients with COVID-19 infection. J Clin Med. 2021;10:3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173775.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.12.13.21267698v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR15",
"unstructured": "Shibata Y, Minemura H, Suzuki Y, et al. Development and external validation of the DOAT and DOATS scores: simple decision support tools to identify disease progression among nonelderly patients with mild/moderate COVID-19. medRxiv [Preprint] December 14 2021. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.13.21267698v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2188/jea.JE20210145",
"author": "K Shiba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "457",
"journal-title": "J Epidemiol",
"key": "949_CR16",
"unstructured": "Shiba K, Kawahara T. using propensity scores for causal inference: pitfalls and tips. J Epidemiol. 2021;31:457–63. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20210145.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pst.433",
"author": "PC Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Pharm Stat",
"key": "949_CR17",
"unstructured": "Austin PC. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm Stat. 2011;10:150–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/pst.433.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/FJC.0000000000001116",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "949_CR18",
"unstructured": "Peng M, He J, Xue Y, Yang X, Liu S, Gong Z. Role of Hypertension on the Severity of COVID-19: A Review. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2021; 78:e648-e55."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1179551421990675",
"author": "IS Atmosudigdo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes",
"key": "949_CR19",
"unstructured": "Atmosudigdo IS, Lim MA, Radi B, et al. dyslipidemia increases the risk of severe COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179551421990675.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.6607",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "949_CR20",
"unstructured": "Austin PC, Stuart EA. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat Med 2015; 34:3661–79."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9",
"author": "D Bojkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "949_CR21",
"unstructured": "Bojkova D, Widera M, Ciesek S, Wass MN, Michaelis M, Cinatl J Jr. Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in Omicron variant compared to Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Cell Res. 2022;32:319–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR22",
"unstructured": "Takashita E, Kinoshita N, Yamayoshi S, et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.2. N Engl J Med 2022; 386:1475–7. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2201933."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105372",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR23",
"unstructured": "Ohashi H, Hishiki T, Akazawa D, et al. Different efficacies of neutralizing antibodies and antiviral drugs on SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants, BA.1 and BA.2. Antiviral Res. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105372."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.02.22.481491v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "949_CR24",
"unstructured": "Rosenke K, Okumura A, Lewis MC, et al. Molnupiravir (MK-4482) is efficacious against Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants in the Syrian hamster COVID-19 model. medRxiv [Preprint] February 24 2022 Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.22.481491v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"author": "FP Polack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2603",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "949_CR25",
"unstructured": "Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603–15. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2034577.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world clinical outcomes of treatment with molnupiravir for patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}