Zinc Deficiency Associated With an Increase in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.77011, Jan 2025
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000016 from 43 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
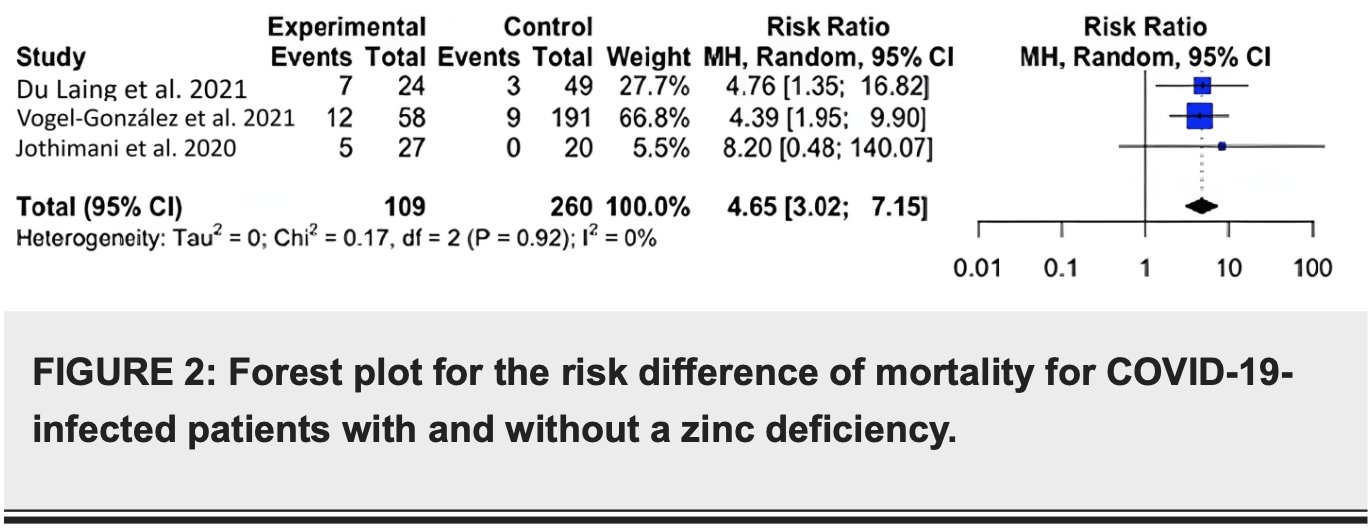
Meta-analysis showing significantly higher COVID-19 mortality and symptomatology with zinc deficiency.
Currently there are 43 zinc treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 33% lower mortality [15‑47%], 40% lower ventilation [-1‑65%], 24% lower ICU admission [-5‑46%], 23% lower hospitalization [6‑38%], and 22% fewer cases [-10‑45%].
1.
Tabatabaeizadeh, S., Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.
3.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
4.
Abuhelwa, Z., Do Zinc Supplements Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19?, Translation: The University of Toledo Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46570/utjms.vol11-2023-749.
5.
Rheingold et al., Zinc Supplementation Associated With a Decrease in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.40231.
Raval et al., 6 Jan 2025, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: cr2359@mynsu.nova.edu.
Zinc Deficiency Associated With an Increase in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.77011
The exact role of zinc in COVID-19-infected patients is not well understood. We examined the effects and outcomes of zinc deficiency on COVID-19-infected patients. We focused on patient outcomes: severity, symptomatology, and mortality. The meta-analysis was performed to examine whether COVID-19-infected individuals suffered greater symptomology and mortality. Secondary outcomes explored included severity and hospital length of stay. For mortality, we found that COVID-19-infected individuals with zinc deficiency had a greater risk of mortality than individuals without zinc deficiency (risk ratio (RR)=5.77; 95% confidence interval (CI): 3.48, 9.54; p=0.004). For symptomology, we found that COVID-19-infected individuals with zinc deficiency had a greater risk of symptomatology than individuals without a zinc deficiency (RR=1.39; 95% CI: 1.13, 1.70; p=0.020). Zinc-deficient individuals are at a greater risk for mortality and symptomatology. Our findings further reinforce the importance of supplementation as a prophylactic agent against viral infections such as COVID-19.
Additional Information Disclosures
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
References
Al-Saleh, Alrushud, Alnuwaysir, Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-021-00355-4
Allard, Ouedraogo, Molleville, Malnutrition: percentage and association with prognosis in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123679
Arentz, Hunter, Yang, Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009
Bagher Pour, Yahyavi, Karimi, Khamaneh, Milani et al., Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053
Bao, Prasad, Beck, Zinc decreases C-reactive protein, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory cytokines in elderly subjects: a potential implication of zinc as an atheroprotective agent, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28836
Barnard, Wong, Bailey, Day, Sidwell et al., Effect of oral gavage treatment with ZnAL42 and other metallo-ion formulations on influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 virus infections in mice, Antivir Chem Chemother, doi:10.1177/095632020701800302
Bösmüller, Matter, Fend, Tzankov, The pulmonary pathology of COVID-19, Virchows Arch, doi:10.1007/s00428-021-03053-1
Carlo, Forni, Lollini, Colombo, Modesti et al., The intriguing role of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in antitumor reactions, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.v97.2.339
Darif, Hammi, Kihel, Idrissi Saik, Guessous et al., The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: what goes wrong?, Microb Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104799
Decoursey, Morgan, Cherny, The voltage dependence of NADPH oxidase reveals why phagocytes need proton channels, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature01523
Grüngreiff, Gottstein, Reinhold, Zinc deficiency-an independent risk factor in the pathogenesis of haemorrhagic stroke?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113548
Haase, Rink, The immune system and the impact of zinc during aging, Immun Ageing, doi:10.1186/1742-4933-6-9
Haase, Rink, Zinc signals and immune function, Biofactors, doi:10.1002/biof.1114
Hasegawa, Suzuki, Suzuki, Nakaji, Sugawara, Effects of zinc on the reactive oxygen species generating capacity of human neutrophils and on the serum opsonic activity in vitro, Luminescence, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-16073-9_8
Ho, Ruffin, Murgia, Li, Krilis et al., Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-kappaB translocation, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7750
Hosseini, Moradi, Marhemati, Firouzian, Ildarabadi et al., Comparing serum levels of vitamin D and zinc in novel coronavirus-infected patients and healthy individuals in Northeastern Iran, Infect Dis Clin Pract, doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051
Ivanova, Pal, Simonelli, Atanasova, Ventriglia et al., Evaluation of zinc, copper, and Cu:Zn ratio in serum, and their implications in the course of COVID-19, J Trace Elem Med Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126944
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Keleş, Çiftdoğan, Çolak, Aksay, Üstündag et al., Serum zinc levels in pediatric patients with COVID-19, Eur J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04348-w
Khalid, Ahmed, Bhatti, Randhawa, Rafaqat, A question mark on zinc deficiency in 185 million people in Pakistan-possible way out, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2011.630541
Kloubert, Wessels, Wolf, Zinc deficiency leads to reduced interleukin-2 production by active gene silencing due to enhanced CREMα expression in T cells, Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.052
Laing, Petrovic, Lachat, Course and survival of COVID-19 patients with comorbidities in relation to the trace element status at hospital admission, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103304
Maywald, Wang, Rink, The intracellular free zinc level is vital for Treg function and a feasible tool to discriminate between Treg and activated Th cells, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19113575
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pinto, Oliveira, Singh, ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.21.20040261
Pormohammad, Monych, Turner, Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: a molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, Int J Mol Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790
Prasad, Bao, Beck, Kucuk, Sarkar, Antioxidant effect of zinc in humans, Free Radic Biol Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.07.007
Prasad, None, doi:10.2119/2008-00033.Prasad
Prasad, Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells, Mol Med, doi:10.2119/2008-00033.Prasad
Quest, Bloomenthal, Bardes, Bell, The regulatory domain of protein kinase C coordinates four atoms of zinc, J Biol Chem
Saaiq, Ashraf, Modifying "Pico" question into "Picos" model for more robust and reproducible presentation of the methodology employed in a scientific study, World J Plast Surg
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Vivier, Tomasello, Baratin, Walzer, Ugolini, Functions of natural killer cells, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/ni1582
Vogel-González, Talló-Parra, Herrera-Fernández, Low zinc levels at admission associates with poor clinical outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020562
Walker, Ezzati, Black, Global and regional child mortality and burden of disease attributable to zinc deficiency, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/ejcn.2008.9
Wessells, Brown, Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050568
Younus, Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase, Int J Health Sci (Qassim)
Zinc, None
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.77011",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.77011",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raval",
"given": "Chirag",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rheingold",
"given": "Spencer Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gordon",
"given": "Antonio M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardigan",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T16:30:44Z",
"timestamp": 1736181044000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T16:30:49Z",
"timestamp": 1736181049000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-06T17:10:09Z",
"timestamp": 1736183409539,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/171424-zinc-deficiency-associated-with-an-increase-in-mortality-in-covid-19-patients-a-meta-analysis",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "WHO COVID-19 dashboard. (2022). Accessed. August 17, 2022: https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0050568",
"article-title": "Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting",
"author": "Wessells KR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Wessells KR, Brown KH. Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting. PLoS One. 2012, 7:e50568. 10.1371/journal.pone.0050568",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2008.9",
"article-title": "Global and regional child mortality and burden of disease attributable to zinc deficiency",
"author": "Fischer Walker CL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Fischer Walker CL, Ezzati M, Black RE. Global and regional child mortality and burden of disease attributable to zinc deficiency. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009, 63:591-7. 10.1038/ejcn.2008.9",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2011.630541",
"article-title": "A question mark on zinc deficiency in 185 million people in Pakistan—possible way out",
"author": "Khalid N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Khalid N, Ahmed A, Bhatti MS, Randhawa MA, Ahmad A, Rafaqat R. A question mark on zinc deficiency in 185 million people in Pakistan—possible way out. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2014, 54:1222-40. 10.1080/10408398.2011.630541",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113548",
"article-title": "Zinc deficiency—an independent risk factor in the pathogenesis of haemorrhagic stroke?",
"author": "Grüngreiff K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Grüngreiff K, Gottstein T, Reinhold D. Zinc deficiency—an independent risk factor in the pathogenesis of haemorrhagic stroke?. Nutrients. 2020, 12:3548. 10.3390/nu12113548",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biof.1114",
"article-title": "Zinc signals and immune function",
"author": "Haase H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biofactors",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Haase H, Rink L. Zinc signals and immune function. Biofactors. 2014, 40:27-40. 10.1002/biof.1114",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104799",
"article-title": "The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: what goes wrong?",
"author": "Darif D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Darif D, Hammi I, Kihel A, El Idrissi Saik I, Guessous F, Akarid K. The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: what goes wrong?. Microb Pathog. 2021, 153:104799. 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104799",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009",
"article-title": "Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review",
"author": "Arentz S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Integr Med",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Arentz S, Hunter J, Yang G, et al.. Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review. Adv Integr Med. 2020, 7:252-60. 10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/2008-00033.Prasad",
"article-title": "Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells",
"author": "Prasad AS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol Med",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Prasad AS. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol Med. 2008, 14:353-7. 10.2119/2008-00033.Prasad",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/095632020701800302",
"article-title": "Effect of oral gavage treatment with ZnAL42 and other metallo-ion formulations on influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 virus infections in mice",
"author": "Barnard DL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antivir Chem Chemother",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Barnard DL, Wong MH, Bailey K, Day CW, Sidwell RW, Hickok SS, Hall TJ. Effect of oral gavage treatment with ZnAL42 and other metallo-ion formulations on influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 virus infections in mice. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2007, 18:125-32. 10.1177/095632020701800302",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"author": "te Velthuis AJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "te Velthuis AJ, van den Worm SH, Sims AC, Baric RS, Snijder EJ, van Hemert MJ. Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6:e1001176. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"article-title": "Zinc and SARS‑CoV‑2: a molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA‑dependent RNA‑polymerase and 3C‑like proteinase enzymes",
"author": "Pormohammad A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Med",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Pormohammad A, Monych NK, Turner RJ. Zinc and SARS‑CoV‑2: a molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA‑dependent RNA‑polymerase and 3C‑like proteinase enzymes. Int J Mol Med. 2021, 47:326-34. 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "Page MJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al.. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 372:n71. 10.1136/bmj.n71",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Modifying \"Pico\" question into \"Picos\" model for more robust and reproducible presentation of the methodology employed in a scientific study",
"author": "Saaiq M",
"journal-title": "World J Plast Surg",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Saaiq M, Ashraf B. Modifying \"Pico\" question into \"Picos\" model for more robust and reproducible presentation of the methodology employed in a scientific study. World J Plast Surg. 2017, 6:390-2.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Zinc. (2022). Accessed. August 19, 2022: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103304",
"article-title": "Course and survival of COVID-19 patients with comorbidities in relation to the trace element status at hospital admission",
"author": "Du Laing G",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Du Laing G, Petrovic M, Lachat C, et al.. Course and survival of COVID-19 patients with comorbidities in relation to the trace element status at hospital admission. Nutrients. 2021, 13:3304. 10.3390/nu13103304",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020562",
"article-title": "Low zinc levels at admission associates with poor clinical outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Vogel-González M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Vogel-González M, Talló-Parra M, Herrera-Fernández V, et al.. Low zinc levels at admission associates with poor clinical outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nutrients. 2021, 13:562. 10.3390/nu13020562",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Jothimani D, Kailasam E, Danielraj S, et al.. COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int J Infect Dis. 2020, 100:343-9. 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-021-00355-4",
"article-title": "Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity",
"author": "Al-Saleh I",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Al-Saleh I, Alrushud N, Alnuwaysir H, et al.. Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity. Biometals. 2022, 35:125-45. 10.1007/s10534-021-00355-4",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123679",
"article-title": "Malnutrition: percentage and association with prognosis in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Allard L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Allard L, Ouedraogo E, Molleville J, et al.. Malnutrition: percentage and association with prognosis in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019. Nutrients. 2020, 12:3679. 10.3390/nu12123679",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051",
"article-title": "Comparing serum levels of vitamin D and zinc in novel coronavirus-infected patients and healthy individuals in Northeastern Iran, 2020",
"author": "Hosseini SJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md)",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Hosseini SJ, Moradi B, Marhemati M, Firouzian AA, Ildarabadi E, Abedi A, Firooz M. Comparing serum levels of vitamin D and zinc in novel coronavirus-infected patients and healthy individuals in Northeastern Iran, 2020. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2021, 29:e390-4. 10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053",
"article-title": "Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Bagher Pour O",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Bagher Pour O, Yahyavi Y, Karimi A, Khamaneh AM, Milani M, Khalili M, Sharifi A. Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2021, 111:164-8. 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04348-w",
"article-title": "Serum zinc levels in pediatric patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Ekemen Keleş Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pediatr",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Ekemen Keleş Y, Yılmaz Çiftdoğan D, Çolak A, Kara Aksay A, Üstündag G, Şahin A, Yılmaz N. Serum zinc levels in pediatric patients with COVID-19. Eur J Pediatr. 2022, 181:1575-84. 10.1007/s00431-021-04348-w",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126944",
"article-title": "Evaluation of zinc, copper, and Cu:Zn ratio in serum, and their implications in the course of COVID-19",
"author": "Ivanova ID",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Trace Elem Med Biol",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Ivanova ID, Pal A, Simonelli I, Atanasova B, Ventriglia M, Rongioletti M, Squitti R. Evaluation of zinc, copper, and Cu:Zn ratio in serum, and their implications in the course of COVID-19. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022, 71:126944. 10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126944",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature01523",
"article-title": "The voltage dependence of NADPH oxidase reveals why phagocytes need proton channels",
"author": "DeCoursey TE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "DeCoursey TE, Morgan D, Cherny VV. The voltage dependence of NADPH oxidase reveals why phagocytes need proton channels. Nature. 2003, 422:531-4. 10.1038/nature01523",
"volume": "422",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1522-7243(200009/10)15:5<321::AID-BIO605>3.0.CO;2-O",
"article-title": "Effects of zinc on the reactive oxygen species generating capacity of human neutrophils and on the serum opsonic activity in vitro",
"author": "Hasegawa H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Luminescence",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Hasegawa H, Suzuki K, Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Sugawara K. Effects of zinc on the reactive oxygen species generating capacity of human neutrophils and on the serum opsonic activity in vitro. Luminescence. 2000, 15:321-7. 10.1002/1522-7243(200009/10)15:5<321::AID-BIO605>3.0.CO;2-O",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-16073-9_8",
"article-title": "Zinc and the immune system",
"author": "Gammoh NZ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Gammoh NZ, Rink L. Zinc and the immune system. Nutrition and Immunity. Mahmoudi M, Rezaei N (ed): Springer, Cham; 2019. 127-158. 10.1007/978-3-030-16073-9_8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(19)50218-6",
"article-title": "The regulatory domain of protein kinase C coordinates four atoms of zinc",
"author": "Quest AF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Quest AF, Bloomenthal J, Bardes ES, Bell RM. The regulatory domain of protein kinase C coordinates four atoms of zinc. J Biol Chem. 1992, 267:10193-7.",
"volume": "267",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.07.007",
"article-title": "Antioxidant effect of zinc in humans",
"author": "Prasad AS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Free Radic Biol Med",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Prasad AS, Bao B, Beck FW, Kucuk O, Sarkar FH. Antioxidant effect of zinc in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004, 37:1182-90. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.07.007",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.28836",
"article-title": "Zinc decreases C-reactive protein, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory cytokines in elderly subjects: a potential implication of zinc as an atheroprotective agent",
"author": "Bao B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Bao B, Prasad AS, Beck FW, et al.. Zinc decreases C-reactive protein, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory cytokines in elderly subjects: a potential implication of zinc as an atheroprotective agent. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010, 91:1634-41. 10.3945/ajcn.2009.28836",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.v97.2.339",
"article-title": "The intriguing role of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in antitumor reactions",
"author": "Di Carlo E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Di Carlo E, Forni G, Lollini P, Colombo MP, Modesti A, Musiani P. The intriguing role of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in antitumor reactions. Blood. 2001, 97:339-45. 10.1182/blood.v97.2.339",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase",
"author": "Younus H",
"journal-title": "Int J Health Sci (Qassim)",
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "Younus H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018, 12:88-93.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7750",
"article-title": "Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-kappaB translocation",
"author": "Ho LH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Ho LH, Ruffin RE, Murgia C, Li L, Krilis SA, Zalewski PD. Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-kappaB translocation. J Immunol. 2004, 172:7750-60. 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7750",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni1582",
"article-title": "Functions of natural killer cells",
"author": "Vivier E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008, 9:503-10. 10.1038/ni1582",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.052",
"article-title": "Zinc deficiency leads to reduced interleukin-2 production by active gene silencing due to enhanced CREMα expression in T cells",
"author": "Kloubert V",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Kloubert V, Wessels I, Wolf J, et al.. Zinc deficiency leads to reduced interleukin-2 production by active gene silencing due to enhanced CREMα expression in T cells. Clin Nutr. 2021, 40:3263-78. 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.052",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00428-021-03053-1",
"article-title": "The pulmonary pathology of COVID-19",
"author": "Bösmüller H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Virchows Arch",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Bösmüller H, Matter M, Fend F, Tzankov A. The pulmonary pathology of COVID-19. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478:137-50. 10.1007/s00428-021-03053-1",
"volume": "478",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.21.20040261",
"article-title": "ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Pinto BG",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Pinto BG, Oliveira AE, Singh Y, et al.. ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19. medRxiv. 2020, 10.1101/2020.03.21.20040261",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1742-4933-6-9",
"article-title": "The immune system and the impact of zinc during aging",
"author": "Haase H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immun Ageing",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Haase H, Rink L. The immune system and the impact of zinc during aging. Immun Ageing. 2009, 6:9. 10.1186/1742-4933-6-9",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19113575",
"article-title": "The intracellular free zinc level is vital for Treg function and a feasible tool to discriminate between Treg and activated Th cells",
"author": "Maywald M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Maywald M, Wang F, Rink L. The intracellular free zinc level is vital for Treg function and a feasible tool to discriminate between Treg and activated Th cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19:3575. 10.3390/ijms19113575",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/171424-zinc-deficiency-associated-with-an-increase-in-mortality-in-covid-19-patients-a-meta-analysis"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zinc Deficiency Associated With an Increase in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article"
}
