Low Zinc Levels at Admission Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020562, Oct 2020 (preprint)
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
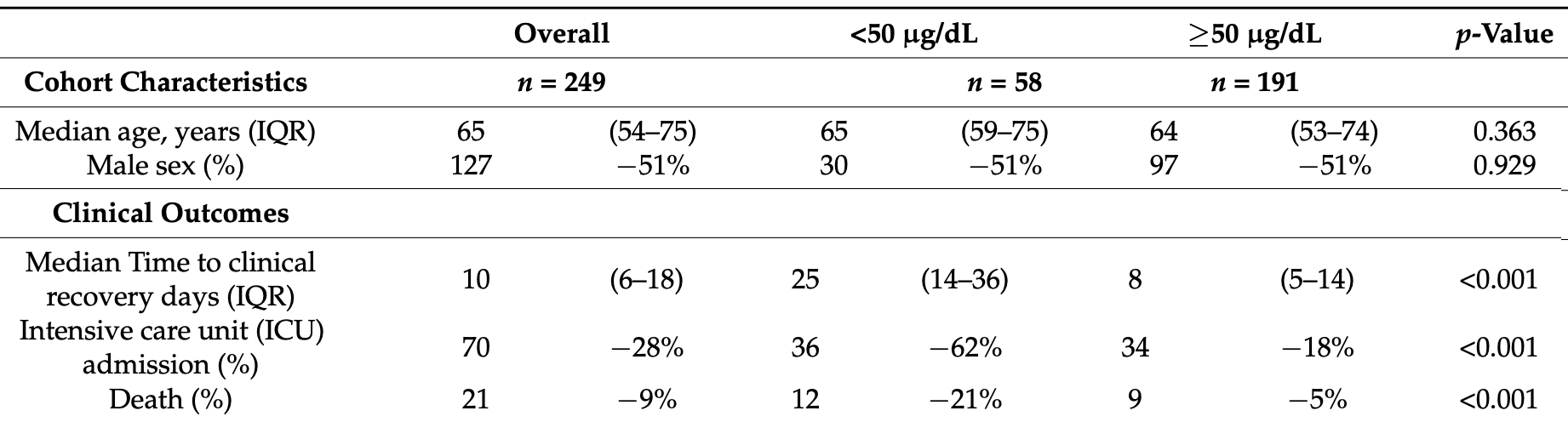
Retrospective 249 PCR+ hospitalized patients in Spain, 58 with zinc levels on admission <50 μg/dL, showing higher mortality and ICU admission, and slower recovery with low zinc levels.
|
risk of death, 77.2% lower, RR 0.23, p < 0.001, high zinc levels 9 of 191 (4.7%), low zinc levels 12 of 58 (20.7%), NNT 6.3, ≥50 μg/dL.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 71.3% lower, RR 0.29, p < 0.001, high zinc levels 34 of 191 (17.8%), low zinc levels 36 of 58 (62.1%), NNT 2.3, ≥50 μg/dL.
|
|
recovery time, 68.0% lower, relative time 0.32, p < 0.001, high zinc levels 191, low zinc levels 58, ≥50 μg/dL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Vogel-González et al., 11 Oct 2020, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
Low Zinc Levels at Admission Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020562
Background: Zinc is an essential micronutrient that impacts host-pathogen interplay at infection. Zinc balances immune responses, and also has a proven direct antiviral action against some viruses. Importantly, zinc deficiency (ZD) is a common condition in elderly and individuals with chronic diseases, two groups with an increased risk for severe severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes. We hypothesize that serum zinc content (SZC) influences COVID-19 disease progression, and thus might represent a useful biomarker. Methods: We ran an observational cohort study with 249 COVID-19 patients admitted in Hospital del Mar. We have studied COVID-19 severity and progression attending to SZC at admission. In parallel, we have studied severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) replication in the Vero E6 cell line modifying zinc concentrations. Findings: Our study demonstrates a correlation between serum zinc levels and COVID-19 outcome. Serum zinc levels lower than 50 µg/dL at admission correlated with worse clinical presentation, longer time to reach stability, and higher mortality. Our in vitro results indicate that low zinc levels favor viral expansion in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Interpretation: Low SZC is a risk factor that determines COVID-19 outcome. We encourage performing randomized clinical trials to study zinc supplementation as potential prophylaxis and treatment with people at risk of zinc deficiency.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB; the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Hospital del Mar of Barcelona (CEIm-2020/9352)). Due to the nature of the retrospective data review, the IRB waived the need for informed consent from individual patients. Informed Consent Statement: Due to the nature of the retrospective data review, the IRB waived the need for informed consent from individual patients.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Bao, Prasad, Beck, Fitzgerald, Snell et al., Zinc decreases C-reactive protein, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory cytokines in elderly subjects: A potential implication of zinc as an atheroprotective agent, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28836
Beck, Prasad, Kaplan, Fitzgerald, Brewer, Changes in cytokine production and T cell subpopulations in experimentally induced zinc-deficient humans, Am. J. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.1997.272.6.E1002
Besecker, Exline, Hollyfield, Phillips, Disilvestro et al., A comparison of zinc metabolism, inflammation, and disease severity in critically ill infected and noninfected adults early after intensive care unit admission, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.008417
Boulware, Pullen, Bangdiwala, Pastick, Lofgren et al., A Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine as Postexposure Prophylaxis for COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2016638
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001250
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Azevedo, Veiga et al., Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI137244
Derwand, Scholz, Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?, Med. Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109815
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, York, COVID-19 outpatients-Early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective case series study, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in infection and inflammation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9060624
Gorshkov, Chen, Bostwick, Rasmussen, Xu et al., The SARS-CoV-2 cytopathic effect is blocked with autophagy modulators, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.16.091520
Hasan, Rink, Haase, Chelation of Free Zn 2+ Impairs Chemotaxis, Phagocytosis, Oxidative Burst, Degranulation, and Cytokine Production by Neutrophil Granulocytes, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0515-0
Hasan, Rink, Haase, Zinc signals in neutrophil granulocytes are required for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps, Innate Immun, doi:10.1177/1753425912458815
Heller, Sun, Hackler, Seelig, Seibert et al., Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764
Jarosz, Olbert, Wyszogrodzka, Młyniec, Librowski, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zincdependent NF-jB signaling, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-017-0309-4
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Liu, Cao, Xu, Wang, Zhang et al., Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0
Liuzzi, Lichten, Rivera, Blanchard, Aydemir et al., Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0502257102
Mauthe, Orhon, Rocchi, Zhou, Luhr et al., Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2018.1474314
Prasad, Beck, Bao, Fitzgerald, Snell et al., Zinc supplementation decreases incidence of infections in the elderly: Effect of zinc on generation of cytokines and oxidative stress, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837
Prasad, Discovery of human zinc deficiency: Its impact on human health and disease, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.3945/an.112.003210
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmz013
Science, Johnstone, Roth, Guyatt, Loeb, Zinc for the treatment of the common cold: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, CMAJ, doi:10.1503/cmaj.111990
Subbe, Davies, Williams, Rutherford, Gemmell, Effect of introducing the Modified Early Warning score on clinical outcomes, cardio-pulmonary arrests and intensive care utilisation in acute medical admissions, Anaesthesia, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2044.2003.03258.x
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Wessells, King, Brown, Development of a Plasma Zinc Concentration Cutoff to Identify Individuals with Severe Zinc Deficiency Based on Results from Adults Undergoing Experimental Severe Dietary Zinc Restriction and Individuals with Acrodermatitis Enteropathica, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.114.191585
Wessels, Haase, Engelhardt, Rink, Uciechowski, Zinc deficiency induces production of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα in promyeloid cells via epigenetic and redox-dependent mechanisms, J. Nutr. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.06.007
Wong, Dashner-Titus, Alvarez, Chase, Hudson et al., Zinc Deficiency and Arsenic Exposure Can Act Both Independently or Cooperatively to Affect Zinc Status, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-019-1631-z
Xue, Moyer, Peng, Wu, Hannafon et al., Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109180
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Cui, Huang et al., In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237
Yasuda, Tsutsui, Infants and elderlies are susceptible to zinc deficiency, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep21850
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020562",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13020562",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Zinc is an essential micronutrient that impacts host–pathogen interplay at infection. Zinc balances immune responses, and also has a proven direct antiviral action against some viruses. Importantly, zinc deficiency (ZD) is a common condition in elderly and individuals with chronic diseases, two groups with an increased risk for severe severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes. We hypothesize that serum zinc content (SZC) influences COVID-19 disease progression, and thus might represent a useful biomarker. Methods: We ran an observational cohort study with 249 COVID-19 patients admitted in Hospital del Mar. We have studied COVID-19 severity and progression attending to SZC at admission. In parallel, we have studied severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) replication in the Vero E6 cell line modifying zinc concentrations. Findings: Our study demonstrates a correlation between serum zinc levels and COVID-19 outcome. Serum zinc levels lower than 50 µg/dL at admission correlated with worse clinical presentation, longer time to reach stability, and higher mortality. Our in vitro results indicate that low zinc levels favor viral expansion in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Interpretation: Low SZC is a risk factor that determines COVID-19 outcome. We encourage performing randomized clinical trials to study zinc supplementation as potential prophylaxis and treatment with people at risk of zinc deficiency.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13020562"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vogel-González",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talló-Parra",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herrera-Fernández",
"given": "Víctor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pérez-Vilaró",
"given": "Gemma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chillón",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5537-1859",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nogués",
"given": "Xavier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5987-068X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gómez-Zorrilla",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Montesinos",
"given": "Inmaculada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arnau-Barrés",
"given": "Isabel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9562-514X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sorli-Redó",
"given": "Maria Luisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horcajada",
"given": "Juan Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6507-0147",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "García-Giralt",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4735-7838",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pascual",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Díez",
"given": "Juana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0401-4808",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vicente",
"given": "Rubén",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Güerri-Fernández",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-14T13:53:56Z",
"timestamp": 1613310836000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-14T14:07:26Z",
"timestamp": 1613311646000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"PI19/00019"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100012619",
"award": [
"CB16/10/00245"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red Fragilidad y Envejecimiento Saludable"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T14:18:44Z",
"timestamp": 1712326724155
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 71,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612828800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/2/562/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "562",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3945/an.112.003210",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9060624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.1997.272.6.E1002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-017-0309-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.06.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753425912458815",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-015-0515-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.111990",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2044.2003.03258.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.114.191585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0109180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2018.1474314",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.16.091520",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep21850",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"article-title": "The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.110.008417",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-019-1631-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.28836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0502257102",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2016638",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109815",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/2/562"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Low Zinc Levels at Admission Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
