Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053, Aug 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
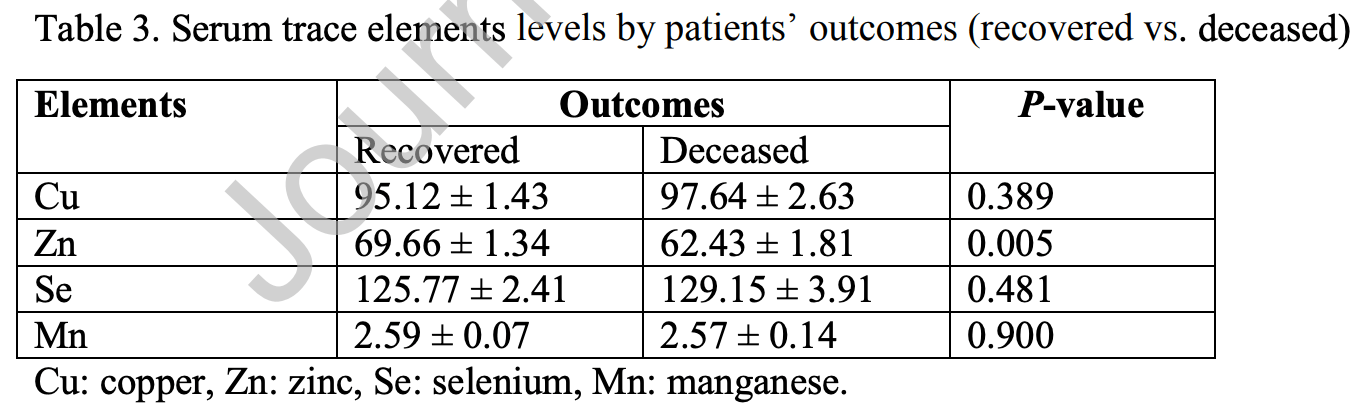
Prospective analysis of 114 ICU patients and 112 matched non-ICU patients in Iran, showing mortality associated with lower zinc levels. There was no significant difference in zinc levels between ICU and non-ICU patients. IR.TBZMED.REC.1399.711.
Study covers selenium and zinc.
Bagher Pour et al., 25 Aug 2021, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 10 October, 2020 - 10 December, 2020.
Contact: karimia@tbzmed.ac.ir, ak.sharif1349@gmail.com.
Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053
Objectives : The relationship between immunity and trace elements levels is well known. We aimed to estimate the association of serum trace elements with severity and outcomes in the Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) patients. Methods: In this single-centered, prospective, observational study, we enrolled 114 patients admitted to severe intensive care units (ICUs) and corresponding 112 sex and aged-matched non-ICU ward patients. Demographic data, clinical characteristics, and outcomes were all collected. We analyzed serum levels of zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), selenium (Se), and manganese (Mn) in both severity groups. Results : The serum levels of Cu, Se, and Mn in both groups were within the normal range while Zn serum levels were lower than normal values. Based on these findings, Zn, Cu, Se, and Mn serum levels were not associated with disease severity ( P > 0.05), while we found Zn serum levels were strongly associated with patient outcomes ( P = 0.005). Our results indicated lower Mn serum levels were associated with age more than 55 years ( P = 0.006). Our results were not in favor of a causal relationship between serum trace elements levels and disease severity. Conclusion : We found Zn level to be a strong indicator for patients' outcomes that can be considered for monitoring patient prognosis. Nutritional measures or supplementation can help reduce poor outcomes caused by low Zn levels in Iranian COVID-19 patients.
Ethics approval This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. It was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran (Ref No: IR.TBZMED.REC.1399.711).
Authors' contributions
Conflicts of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to the content of this article.
References
Andreou, Trantza, Filippou, Sipsas, Tsiodras, COVID-19: The potential role of copper and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in a combination of candidate antiviral treatments against SARS-CoV-2, vivo
Bonham, Connor, Hannigan, Strain, The immune system as a physiological indicator of marginal copper status?, British Journal of Nutrition
Chaturvedi, Shrivastava, Upreti, Viral infections and trace elements: a complex interaction, Current science
Dietz, Santos-Burgoa, Obesity and its implications for COVID-19 mortality, Obesity
Flora, Biomarkers in Toxicology
Harthill, Micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases, Biological trace element research
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Del Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Jamaati, Dastan, Tabarsi, Marjani, Saffaei et al., A fourteenday experience with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): an Iranian treatment protocol, Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review, Diabetes & metabolic syndrome
Jiang, Xia, Ying, Lu, A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome, Cellular & molecular immunology
Karimi, Majidzadeh, Madjd, Akbari, Habibi et al., Effect of Copper Sulfate on Expression of Endogenous L1 Retrotransposons in HepG2 Cells (Hepatocellular Carcinoma), Biol Trace Elem Res
Karimi, Sheervalilou, Kahroba, A New Insight on Activation of Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs) in Malignant Melanoma upon Exposure to CuSO4, Biol Trace Elem Res
Kehl-Fie, Skaar, Nutritional immunity beyond iron: a role for manganese and zinc, Current opinion in chemical biology
Khaerunnisa, Kurniawan, Awaluddin, Suhartati, Soetjipto, Potential inhibitor of COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) from several medicinal plant compounds by molecular docking study
Kong, Yang, Xue, Liu, Wang et al., COVID-19 Docking Server: A meta server for docking small molecules, peptides and antibodies against potential targets of COVID-19, Bioinformatics
Krawczyk-Coda, Determination of Selenium in Food Samples by High-Resolution Continuum Source Atomic Absorption Spectrometry After Preconcentration on Halloysite Nanotubes Using Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Micro Solid-Phase Extraction, Food Analytical Methods
Lee, Bang, Lee, Lee, Kang et al., Serum concentrations of trace elements zinc, copper, selenium, and manganese in critically ill patients, Biological trace element research
Liu, Geng, Mcdermott, Shen, Corbin et al., Copper deficiency in the lungs of TNF-α transgenic mice, Frontiers in physiology
Lv, Chen, Liang, Liu, Gao et al., Association between iron status and the risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19
Maares, Haase, Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation, Archives of biochemistry and biophysics
Majeed, Nagabhushanam, Gowda, Mundkur, An exploratory study of selenium status in healthy individuals and in patients with COVID-19 in a south Indian population: The case for adequate selenium status
Moghaddam, Heller, Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19
Morfeld, Timmermann, Groß, Lewis, Erren, COVID-19: Wie änderte sich die Sterblichkeit?-Mortalität von Frauen und Männern in Deutschland und seinen Bundesländern bis Oktober 2020, DMW-Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift
Organization, Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV
Rahman, Idid, Can Zn be a critical element in COVID-19 treatment?, Biological trace element research
Razzaque, COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance? The Tohoku journal of experimental, medicine
Singer, Nutritional and metabolic management of COVID-19 intensive care patients, Journal of Intensive Medicine
Thurnham, Micronutrients and immune function: some recent developments, Journal of clinical pathology
Uriu-Adams, Keen, Copper, oxidative stress, and human health, Molecular aspects of medicine
Wong, Lui, Sung, Covid-19 and the digestive system, Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Song, A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature
Zeng, Zhang, Wang, Yang, Cheng, Urinary trace elements in association with disease severity and outcome in patients with COVID-19, Environmental research
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053",
"alternative-id": [
"S120197122100686X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagher Pour",
"given": "Ozra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9169-8245",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yahyavi",
"given": "Yahya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1172-8502",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karimi",
"given": "Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khamaneh",
"given": "Amir Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milani",
"given": "Mortaza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalili",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharifi",
"given": "Akbar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"ijidonline.com",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-25T06:30:48Z",
"timestamp": 1629873048000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-04T01:10:29Z",
"timestamp": 1635988229000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-09T11:18:49Z",
"timestamp": 1678360729548
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 13,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629676800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S120197122100686X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S120197122100686X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "164-168",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.11946",
"article-title": "COVID-19: The potential role of copper and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in a combination of candidate antiviral treatments against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Andreou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1567",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "in vivo",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0001",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/BJN2002558",
"article-title": "The immune system as a physiological indicator of marginal copper status?",
"author": "Bonham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "393",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0002",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "Viral infections and trace elements: a complex interaction",
"author": "Chaturvedi",
"first-page": "1536",
"journal-title": "Current science",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0003",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22818",
"article-title": "Obesity and its implications for COVID-19 mortality",
"author": "Dietz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1005",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Obesity",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0004",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Chapter 29 - Metals",
"author": "Flora",
"first-page": "485",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0005",
"series-title": "Biomarkers in Toxicology",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-011-8977-1",
"article-title": "Micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases",
"author": "Harthill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1325",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biological trace element research",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0006",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0007",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A fourteen-day experience with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): an Iranian treatment protocol",
"author": "Jamaati",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0008",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes & metabolic syndrome",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0010",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0372-4",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "554",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cellular & molecular immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0011",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-015-0256-0",
"article-title": "Effect of Copper Sulfate on Expression of Endogenous L1 Retrotransposons in HepG2 Cells (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)",
"author": "Karimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "131",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0012",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-018-1605-6",
"article-title": "A New Insight on Activation of Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs) in Malignant Melanoma upon Exposure to CuSO4",
"author": "Karimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "70",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0013",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.11.008",
"article-title": "Nutritional immunity beyond iron: a role for manganese and zinc",
"author": "Kehl-Fie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "218",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Current opinion in chemical biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0014",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0226.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0015",
"unstructured": "Khaerunnisa S, Kurniawan H, Awaluddin R, Suhartati S, Soetjipto S. Potential inhibitor of COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) from several medicinal plant compounds by molecular docking study. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa645",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Docking Server: A meta server for docking small molecules, peptides and antibodies against potential targets of COVID-19",
"author": "Kong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5109",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0016",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12161-018-1345-4",
"article-title": "Determination of Selenium in Food Samples by High-Resolution Continuum Source Atomic Absorption Spectrometry After Preconcentration on Halloysite Nanotubes Using Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Micro Solid-Phase Extraction",
"author": "Krawczyk-Coda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Food Analytical Methods",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0017",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-018-1429-4",
"article-title": "Serum concentrations of trace elements zinc, copper, selenium, and manganese in critically ill patients",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "316",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biological trace element research",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0018",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2016.00234",
"article-title": "Copper deficiency in the lungs of TNF-α transgenic mice",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "234",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in physiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0019",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "Lv",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0020",
"series-title": "Association between iron status and the risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022",
"article-title": "Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation",
"author": "Maares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Archives of biochemistry and biophysics",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0021",
"volume": "611",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111053",
"article-title": "An exploratory study of selenium status in healthy individuals and in patients with COVID-19 in a south Indian population: The case for adequate selenium status",
"author": "Majeed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif)",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0022",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Moghaddam",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0023",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1334-0586",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Wie änderte sich die Sterblichkeit?–Mortalität von Frauen und Männern in Deutschland und seinen Bundesländern bis Oktober 2020",
"author": "Morfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"issue": "02",
"journal-title": "DMW-Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0024",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0025",
"unstructured": "Organization. WH. World Health Organization.Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200121-sitrep-1-2019-ncov.pdf."
},
{
"article-title": "Can Zn be a critical element in COVID-19 treatment?",
"author": "Rahman",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biological trace element research",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0026",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.251.175",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance?",
"author": "Razzaque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "The Tohoku journal of experimental medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0027",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jointm.2021.01.004",
"article-title": "Nutritional and metabolic management of COVID-19 intensive care patients",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Intensive Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0028",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jcp.50.11.887",
"article-title": "Micronutrients and immune function: some recent developments",
"author": "Thurnham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "887",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Journal of clinical pathology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0029",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2005.07.015",
"article-title": "Copper, oxidative stress, and human health",
"author": "Uriu-Adams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"issue": "4-5",
"journal-title": "Molecular aspects of medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0030",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15047",
"article-title": "Covid-19 and the digestive system",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "744",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0031",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "7798",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0032",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110670",
"article-title": "Urinary trace elements in association with disease severity and outcome in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environmental research",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.08.053_bib0033",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S120197122100686X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Serum trace elements levels and clinical outcomes among Iranian COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "111"
}
