Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis
, S., European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z, May 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
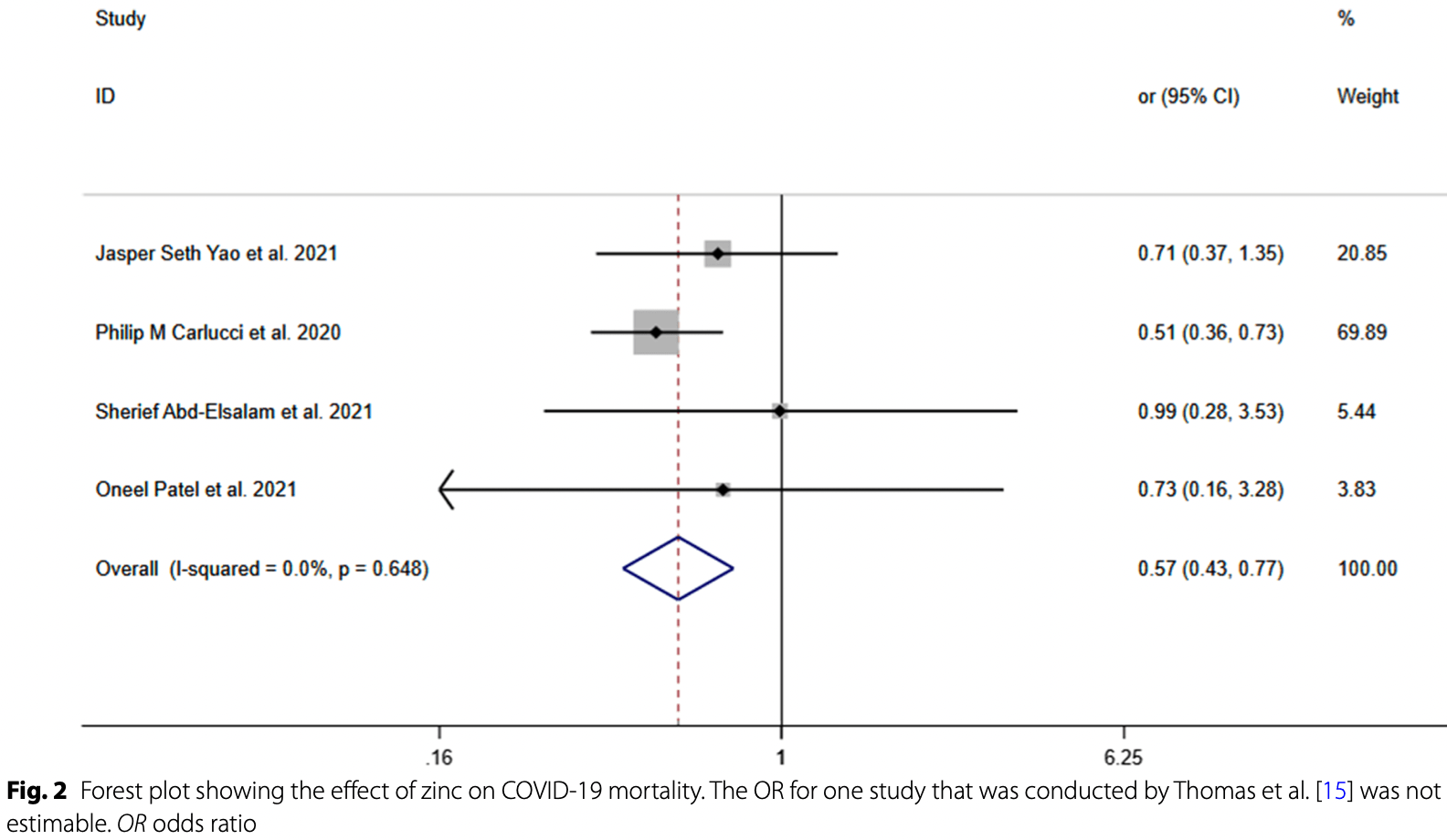
Meta analysis of five zinc treatment studies for COVID-19, showing significantly lower mortality.
Currently there are 42 zinc treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 33% lower mortality [15‑47%], 40% lower ventilation [-1‑65%], 28% lower ICU admission [-8‑51%], 23% lower hospitalization [6‑38%], and 22% fewer cases [-10‑45%].
|
risk of death, 43.0% lower, OR 0.57, p < 0.001, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Tabatabaeizadeh, S., Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.
3.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
4.
Abuhelwa, Z., Do Zinc Supplements Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19?, Translation: The University of Toledo Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46570/utjms.vol11-2023-749.
5.
Rheingold et al., Zinc Supplementation Associated With a Decrease in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.40231.
Tabatabaeizadeh et al., 23 May 2022, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: tabatabaei.amir@yahoo.com (corresponding author).
Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis
European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z
Background and aims: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the agent of a pneumonia outbreak and was called 2019 novel coronavirus disease . COVID-19 emerged in December 2019 and now considered a pandemic. Zinc supplementation can reduce mortality in patients with severe pneumonia. This study aimed at meta-analysis of the results of related studies and evaluate the effect of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 mortality.
Methods: A systematic search has conducted for manuscripts through PUBMED/Medline and Google Scholar (Cochrane guideline has considered it as the gray literature) up to September 2021. This meta-analysis followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) Guideline for evaluation of the effect zinc supplementation on COVID-19 mortality. Based on the heterogeneity a fixed-effect or random-effect model, the OR and 95% CI were used to assess the combined risk. Results: After assessment, five studies with 1506 participants in case and control groups were included in meta-analysis. The OR for one study was not estimable, and the pool OR was estimated for other studies with 1398 participants. The meta-analysis showed that zinc supplementation in cases led to a significant lower risk of mortality when it was compared with the control group; pooled OR (95% CI) was 0.57 [0.43, 0.77] (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis has suggested that zinc supplementation is associated with a lower mortality rate in COVID-19 patients. Zinc supplementation could be considered as a simple way and cost benefit approach for reduction of mortality in COVID-19 patients.
• support for research data, including large and complex data types • gold Open Access which fosters wider collaboration and increased citations maximum visibility for your research: over 100M website views per year
• At BMC, research is always in progress.
Learn more biomedcentral.com/submissions Ready to submit your research Ready to submit your research ? Choose BMC and benefit from: ? Choose BMC and benefit from: Author contributions SAT designed study, did systematic search and selected the studies, analyzed data, prepared manuscript and critically reviewed manuscript; and had primary responsibility for the final content. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable.
Consent for publication The author consented to the publication of the manuscript in European Journal of Medical Research.
Competing interests The author has no conflict of interest to disclose.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Soliman, Esmail, Khalaf, Mostafa et al., Do zinc supplements enhance the clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine?: a randomized multicenter trial, Biol Trace Elem Res
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol
Egger, Smith, Schneider, Minder, Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test, BMJ
Frangos, Maret, Zinc and cadmium in the aetiology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, Nutrients
Herzog, Álvarez-Pasquin, Díaz, Barrio, Estrada et al., Are healthcare workers' intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review, BMC Public Health
Higgins, Altman, Gøtzsche, Jüni, Moher et al., The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Hojyo, Fukada, Roles of zinc signaling in the immune system, J Immunol Res
Hunter, Arentz, Goldenberg, Yang, Beardsley et al., Zinc for the prevention or treatment of acute viral respiratory tract infections in adults: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, BMJ Open
Page, Moher, Evaluations of the uptake and impact of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and extensions: a scoping review, Syst Rev
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Pawar, Rongioletti et al., Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials, Biol Trace Elem Res
Patel, Chinni, El-Khoury, Perera, Neto et al., A pilot double-blind safety and feasibility randomized controlled trial of highdose intravenous zinc in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol
Prasad, Lessons learned from experimental human model of zinc deficiency, J Immunol Res
Shrier, Boivin, Steele, Platt, Furlan et al., Should meta-analyses of interventions include observational studies in addition to randomized controlled trials? a critical examination of underlying principles, Am J Epidemiol
Tabatabaeizadeh, Airborne transmission of COVID-19 and the role of face mask to prevent it: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Med Res
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wang, Song, Efficacy of zinc given as an adjunct to the treatment of severe pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trials, Clin Respir J
Wells, Shea, Connell, Peterson, Welch et al., The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses, Appl Eng Agric
Wu, Lewis, Pae, Meydani, Nutritional modulation of immune function: analysis of evidence, mechanisms, and clinical relevance, Front Immunol
Yao, Paguio, Dee, Tan, Moulick et al., The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study, Chest
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z",
"ISSN": [
"2047-783X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background and aims</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the agent of a pneumonia outbreak and was called 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). COVID-19 emerged in December 2019 and now considered a pandemic. Zinc supplementation can reduce mortality in patients with severe pneumonia. This study aimed at meta-analysis of the results of related studies and evaluate the effect of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 mortality.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A systematic search has conducted for manuscripts through PUBMED/Medline and Google Scholar (Cochrane guideline has considered it as the gray literature) up to September 2021. This meta-analysis followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) Guideline for evaluation of the effect zinc supplementation on COVID-19 mortality. Based on the heterogeneity a fixed-effect or random-effect model, the OR and 95% CI were used to assess the combined risk.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>After assessment, five studies with 1506 participants in case and control groups were included in meta-analysis. The OR for one study was not estimable, and the pool OR was estimated for other studies with 1398 participants. The meta-analysis showed that zinc supplementation in cases led to a significant lower risk of mortality when it was compared with the control group; pooled OR (95% CI) was 0.57 [0.43, 0.77] (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < 0.001).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This meta-analysis has suggested that zinc supplementation is associated with a lower mortality rate in COVID-19 patients. Zinc supplementation could be considered as a simple way and cost benefit approach for reduction of mortality in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"694"
],
"article-number": "70",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "6 March 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "29 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "23 May 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The author consented to the publication of the manuscript in <i>European Journal of Medical Research</i>."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The author has no conflict of interest to disclose."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tabatabaeizadeh",
"given": "Seyed-Amir",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "European Journal of Medical Research",
"container-title-short": "Eur J Med Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T03:44:22Z",
"timestamp": 1653277462000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T03:45:34Z",
"timestamp": 1653277534000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T04:10:57Z",
"timestamp": 1653279057118
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653264000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1653264000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-020-00475-6",
"author": "S-A Tabatabaeizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "694_CR1",
"unstructured": "Tabatabaeizadeh S-A. Airborne transmission of COVID-19 and the role of face mask to prevent it: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):1–6.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/6762343",
"author": "S Hojyo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6762343",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "694_CR2",
"unstructured": "Hojyo S, Fukada T. Roles of zinc signaling in the immune system. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:6762343.",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010053",
"author": "T Frangos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "53",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "694_CR3",
"unstructured": "Frangos T, Maret W. Zinc and cadmium in the aetiology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrients. 2021;13(1):53.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/9207279",
"author": "AS Prasad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9207279",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "694_CR4",
"unstructured": "Prasad AS. Lessons learned from experimental human model of zinc deficiency. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:9207279.",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"author": "AJ Te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "694_CR5",
"unstructured": "Te Velthuis AJ, van den Worm SH, Sims AC, Baric RS, Snijder EJ, van Hemert MJ. Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(11): e1001176.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/crj.12646",
"author": "L Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "857",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Respir J",
"key": "694_CR6",
"unstructured": "Wang L, Song Y. Efficacy of zinc given as an adjunct to the treatment of severe pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trials. Clin Respir J. 2018;12(3):857–64.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13643-017-0663-8",
"author": "MJ Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Syst Rev",
"key": "694_CR7",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, Moher D. Evaluations of the uptake and impact of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and extensions: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):263.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.d5928",
"author": "JP Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "d5928",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "694_CR8",
"unstructured": "Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.",
"volume": "343",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"author": "GA Wells",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Appl Eng Agric",
"key": "694_CR9",
"unstructured": "Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Appl Eng Agric. 2014;18(6):727–34.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "694_CR10",
"unstructured": "Collaboration C. Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5.4 for Windows. Oxford: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629",
"author": "M Egger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "629",
"issue": "7109",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "694_CR11",
"unstructured": "Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.",
"volume": "315",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02512-1",
"author": "S Abd-Elsalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3642",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "694_CR12",
"unstructured": "Abd-Elsalam S, Soliman S, Esmail ES, Khalaf M, Mostafa EF, Medhat MA, et al. Do zinc supplements enhance the clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine?: a randomized multicenter trial. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199(10):3642–6.",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"author": "PM Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1228",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol",
"key": "694_CR13",
"unstructured": "Carlucci PM, Ahuja T, Petrilli C, Rajagopalan H, Jones S, Rahimian J. Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J Med Microbiol. 2020;69(10):1228.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26895",
"author": "O Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3261",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "694_CR14",
"unstructured": "Patel O, Chinni V, El-Khoury J, Perera M, Neto AS, McDonald C, et al. A pilot double-blind safety and feasibility randomized controlled trial of high-dose intravenous zinc in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2021;93(5):3261–7.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"author": "S Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e210369",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "694_CR15",
"unstructured": "Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, Wolski K, Wang Q, Kumar A, et al. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e210369.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"author": "JS Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "694_CR16",
"unstructured": "Yao JS, Paguio JA, Dee EC, Tan HC, Moulick A, Milazzo C, et al. The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study. Chest. 2021;159(1):108–11.",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2458-13-154",
"author": "R Herzog",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "694_CR17",
"unstructured": "Herzog R, Álvarez-Pasquin MJ, Díaz C, Del Barrio JL, Estrada JM, Gil Á. Are healthcare workers’ intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(1):1–17.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9",
"author": "A Pal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2882",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "694_CR18",
"unstructured": "Pal A, Squitti R, Picozza M, Pawar A, Rongioletti M, Dutta AK, et al. Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199(8):2882–92.",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.03160",
"author": "D Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3160",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "694_CR19",
"unstructured": "Wu D, Lewis ED, Pae M, Meydani SN. Nutritional modulation of immune function: analysis of evidence, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Front Immunol. 2019;9:3160.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047474",
"author": "J Hunter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "694_CR20",
"unstructured": "Hunter J, Arentz S, Goldenberg J, Yang G, Beardsley J, Myers SP, et al. Zinc for the prevention or treatment of acute viral respiratory tract infections in adults: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2021;11(11): e047474.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwm189",
"author": "I Shrier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1203",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "694_CR21",
"unstructured": "Shrier I, Boivin J-F, Steele RJ, Platt RW, Furlan A, Kakuma R, et al. Should meta-analyses of interventions include observational studies in addition to randomized controlled trials? a critical examination of underlying principles. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;166(10):1203–9.",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2007"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://eurjmedres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "27"
}
