The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846, Nov 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
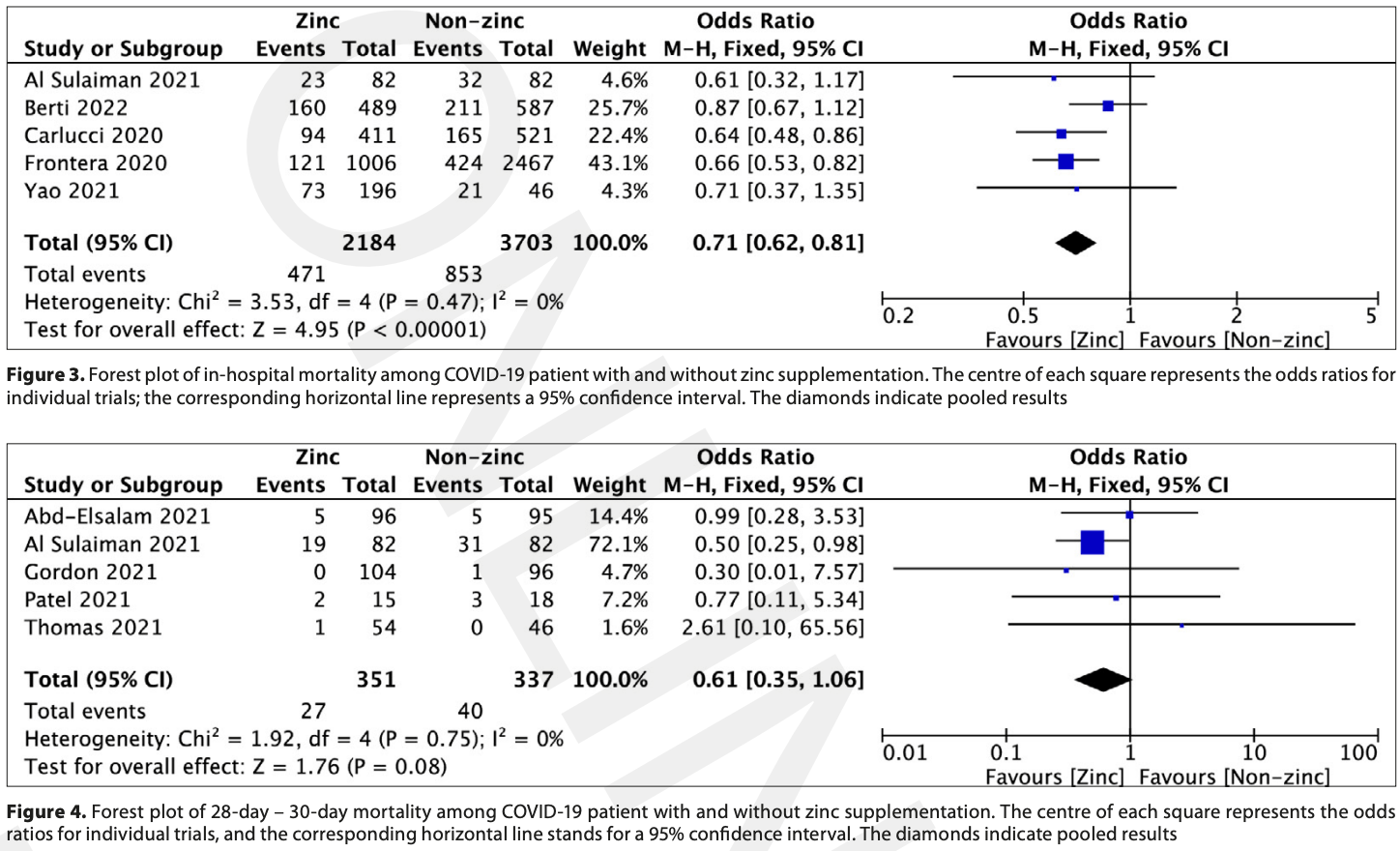
Systematic review and meta analysis of 9 zinc studies, showing significantly lower in-hospital mortality with treatment.
Currently there are 42 zinc treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 33% lower mortality [15‑47%], 40% lower ventilation [-1‑65%], 28% lower ICU admission [-8‑51%], 23% lower hospitalization [6‑38%], and 22% fewer cases [-10‑45%].
|
risk of death, 39.0% lower, OR 0.61, p = 0.08, day 30, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death, 29.0% lower, OR 0.71, p < 0.001, in-hospital mortality, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Tabatabaeizadeh, S., Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.
3.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
4.
Abuhelwa, Z., Do Zinc Supplements Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19?, Translation: The University of Toledo Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46570/utjms.vol11-2023-749.
5.
Rheingold et al., Zinc Supplementation Associated With a Decrease in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.40231.
Olczak-Pruc et al., 3 Nov 2022, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: lukasz.szarpak@gmail.com.
The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis
Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846
Introduction and Objective. Zinc is a trace element that plays a role in stimulating innate and acquired immunity. The aim of the study was to determine the antiviral effect of the administration of zinc in COVID-19 patients.
Materials and Method. A literature search was performed in P Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus and Cochrane databases from 1 January 2020 -22 August 2022. In addition, reference lists of the included articles and their related citations in PubMed were also reviewed for additional pertinent studies. Results. A total of 9 eligible studies were identified. In-hospital mortality in zinc supplementation patients, and patients treated without zinc, varied and amounted to 21.6% vs. 23.04% difference (OR=0.71; 95%CI: 0.62-0.81; p<0.001). 28-day to 30-day mortality in patients treated with zinc was 7.7%, compared to 11.9% for patients treated without zinc (OR=0.61; 95%CI: 0.35-1.06; p=0.08). In-hospital adverse events among patients treated with and without COVID-19 did not show any statistically significant differences in relation to acute kidney injury occurrence (12.8% vs. 12.4%, respectively; OR=0.63; 95%CI: 0.19-2.12; p=0.45, as well as need for mechanical ventilation (13.2% vs. 14.1%; OR=0.83; 95%CI: 0.52-1.32; p=0.43). Conclusions. Zinc supplementation is associated with lower COVID-19 in-hospital mortality. Additionally, it is risk-free in COVID-19 patients since there have been no negative side effects, such as acute renal damage or the requirement for mechanical ventilation compared to patients without COVID-19. Due to scientific evidence and the role it represents in the human body, zinc supplementation should be taken into consideration for COVID-19 patients as an adjunct therapy.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Soliman, Esmail, Do Zinc Supplements Enhance the Clinical Efficacy of Hy-droxychloroquine?: a Randomized, Multicenter Trial, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02512-1
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Ali, Fariha, Islam, Assessment of the role of zinc in the prevention of COVID-19 infections and mortality: A retrospective study in the Asian and European population, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26932
Batra, Effah-Acheampong, Batra, Evolution of SARSCoV-2 variants: A rapid literature scan, J Health Soc Sci, doi:10.19204/2022/VLTN3
Beran, Mhanna, Srour, Clinical significance of micronutrient supplements in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033
Berti, Kale-Pradhan, Giuliano, Clinical Outcomes of Zinc Supplementation Among COVID-19 Patients, Curr Drug Saf, doi:10.2174/1574886317666220317115023
Białorudzki, Izdebski, Changes in the body mass of adult residents of rural and urban areas in the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic vs. their mental, physical and sexual health, Ann Agric Environ Med, doi:10.26444/aaem/143561
Boretti, Banik, Zinc role in Covid-19 disease and prevention, Vacunas, doi:10.1016/j.vacun.2021.08.003
Cakman, Kirchner, Rink, Zinc supplementation reconstitutes the production of interferon-α by leukocytes from elderly persons, J Interferon Cytokine Res, doi:10.1089/jir.1997.17.469
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001250
Chirico, Sagan, Markiwicz, SARS-CoV-2 virus mutation and loss of treatment and preventive measures as we know it now, Disaster Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2021.0025
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hyper-tension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Duncan, Yacoubian, Watson, Morrison, The risk of copper deficiency in patients prescribed zinc supplements, J Clin Pathol, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202837
Dzieciatkowski, Szarpak, Filipiak, COVID-19 challenge for modern medicine, Cardiol J, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2020.0055
Eftekhar, Kazemi, Barary, Effect of Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin on QT Interval Prolongation and Other Cardiac Arrhythmias in COVID-19 Confirmed Patients, Cardiovasc Ther, doi:10.1155/2021/6683098
Fialek, Pruc, Smereka, Diagnostic value of lactate dehydrogenase in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Cardiol J, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2022.0056
Fosmire, Zinc toxicity, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.2.225
Frangos, Maret, Zinc and cadmium in the aetiology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010053
Frontera, Rahimian, Yaghi, Treatment with Zinc is Associated with Reduced In-Hospital Mortality Among COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Center Cohort Study, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-94509/v1
Ghanei, Baghani, Moravvej, Low serum levels of zinc and 25-hydroxyvitmain D as potential risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility: a pilot case-control study, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430
Gordon, Hardigan, A Case-Control Study for the Effectiveness of Oral Zinc in the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.756707
Gozhenko, Szarpak, Jaguszewski, COVID-19 vaccinethird dose, booster dose? What is it and is it necessary?, Disaster Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2021.0027
Higgins, Thompson, Deeks, Altman, Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Hojyo, Fukada, Roles of zinc signaling in the immune system, J Immunol Res, doi:10.1155/2016/6762343
Hozo, Djulbegovic, Hozo, Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample, BMC Med Res Methodol, doi:10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Hunter, Arentz, Goldenberg, Zinc for the prevention or treatment of acute viral respiratory tract infections in adults: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047474
Ibs, Rink, Zinc-Altered Immune function, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/133.5.1452S
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061562
Im, Je, Baek, Chung, Kwon et al., Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Katipoğlu, Sönmez, Vatansev, Can hematological and biochemical parameters fasten the diagnosis of COVID-19 in emergency departments?, Disaster Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2020.0039
Li, Li, Yeu, Wang, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x
Mackiewicz, Lemieszek, Dulkiewicz, COVID 19 -Possible interrelations with respiratory comorbidities caused by occupational exposure to various hazardous bioaerosols. Part II. Clinical course, diagnostics, treatment and prevention, Ann Agric Environ Med, doi:10.26444/aaem/133896
Mcguinness, Higgins, Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments, Res Synth Methods, doi:10.1002/jrsm.1411
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Zinc and COVID-19: Basis of Current Clinical Trials, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020
Patel, Chinni, El-Khoury, A pilot double-blind safety and feasibility randomized controlled trial of high-dose intravenous zinc in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26895
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The Role of Micronutrients in Support of the Immune Response against Viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12103198
Prasad, Lessons learned from experimental human model of zinc deficiency, J Immunol Res, doi:10.1155/2020/9207279
Pruc, Gasecka, Szarpak, Adverse reactions of COVID-19 vaccination: where do they come from? Disaster, Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2021.0004
Schmidt, Jóźwiak, Czabajska, On-admission laboratory predictors for developing critical COVID-19 during hospitalization -a multivariable logistic regression model, Ann Agric Environ Med, doi:10.26444/aaem/145376
Sterne, Hernán, Reeves, ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i4919
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Shaya, Evaluation of zinc sulfate as an adjunctive therapy in COVID-19 critically ill patients: a two center propensity-score matched study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03785-1
Szarpak, Nowak, Kosior, Cytokines as predictors of COVID-19 severity: evidence from a meta-analysis, Pol Arch Intern Med, doi:10.20452/pamw.15685
Szarpak, Pruc, Gasecka, Should we supplement zinc in COVID-19 patients? Evidence from a me-ta-analysis, Pol Arch Intern Med, doi:10.20452/pamw.16048
Szarpak, Pruc, Gasecka, Should we supplement zinc in COVID-19 patients? Evidence from a meta-analysis, Pol Arch Intern Med
Szarpak, Pruc, Nadolny, Role of a field hospital in COVID-19 pandemic, Disaster Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2020.0046
Szarpak, Rafique, Gasecka, A systematic review and metaanalysis of effect of vitamin D levels on the incidence of COVID-19
Szarpak, Zaczynski, Kosior, Evidence of diagnostic value of ferritin in patients with COVID-19, Cardiol J, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2020.0171
Tabatabaeizadeh, Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, Eur J Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Vlieg-Boerstra, De, Meyer, Nutrient supplementation for prevention of viral respiratory tract infections in healthy subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.15136
Wang, Mei, Ren, Plant microRNAs: biogenesis, homeostasis, and degradation, Front Plant Sci, doi:10.3389/fpls.2019.00360
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736
Xue, Moyer, Peng, Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109180
Yaman, Demirel, Yimaz, Retrospective evaluation of laboratory findings of suspected paediatric COVID-19 patients with positive and negative RT-PCR, Disaster Emerg Med J, doi:10.5603/DEMJ.a2021.0023
Yao, Paguio, Dee, The Minimal Effect of Zinc on the Survival of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Observational Study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082
Zheng, Zhangm, Yum, Zinc at cytotoxic concentrations affects post-transcriptional events of gene expression in cancer cells, Cell Physiol Biochem, doi:10.1159/000337599
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.26444/aaem/155846",
"ISSN": [
"1232-1966",
"1898-2263"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.26444/aaem/155846",
"alternative-id": [
"155846"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5718-6828",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Olczak-Pruc",
"given": "Monika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0973-5455",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Szarpak",
"given": "Lukasz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1711-6002",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Navolokina",
"given": "Alla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2606-1656",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chmielewski",
"given": "Jaroslaw",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6210-2887",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Panasiuk",
"given": "Lech",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3597-2048",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Juárez-Vela",
"given": "Raúl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2140-9732",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pruc",
"given": "Michal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5648-4652",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Swieczkowski",
"given": "Damian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7675-0348",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Majer",
"given": "Ryszard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4176-5988",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rafique",
"given": "Zubaid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2352-4176",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Peacock",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Ann Agric Environ Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T11:13:57Z",
"timestamp": 1667474037000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T11:13:57Z",
"timestamp": 1667474037000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-04T05:08:55Z",
"timestamp": 1667538535289
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667433600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667433600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667433600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/pdf-155846-82976",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/pdf-155846-82976",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10974",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.26444",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Institute of Rural Health",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/The-effect-of-zinc-supplementation-on-the-course-of-COVID-19-A-systematic-review,155846,0,2.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Waste Management and Disposal",
"Ecology, Evolution, Behavior and Systematics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article"
}
