Multi-Omics Integration Identifies MT2A as a Biomarker and a Candidate Host Target Linking Zinc Dysregulation to COVID-19 Mortality
et al., Targetome, doi:10.48130/targetome-0026-0006, Feb 2026
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000031 from 44 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
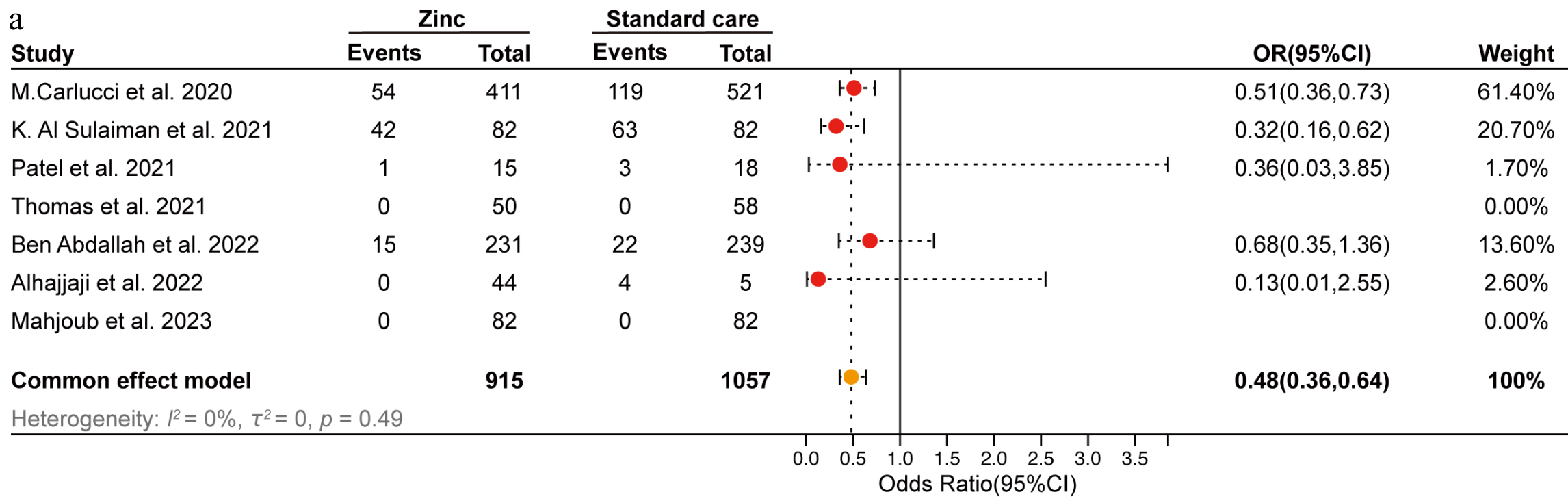
Meta-analysis and multi-omics study showing reduced mortality with zinc supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Authors found that zinc treatment was associated with a significant reduction in mortality (OR 0.48) across seven studies involving 1,972 participants. Through the integration of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data from human blood and respiratory samples, authors identified Metallothionein 2A (MT2A) as a key zinc-regulatory protein that is upregulated in monocytes and macrophages during severe infection. MT2A expression was found to correlate with SARS-CoV-2 entry factors (TMPRSS2, CTSB, CTSL) and innate immune sensing pathways (TLR7, IFIH1), peaking early in the infection course. Authors propose MT2A as a biomarker for zinc-dysregulated immune stress and a potential host target for intervention.
Currently there are 44 zinc treatment for COVID-19 studies, showing 31% lower mortality [12‑46%], 40% lower ventilation [-1‑65%], 24% lower ICU admission [-5‑46%], 23% lower hospitalization [6‑38%], and 22% fewer cases [-10‑45%].
1.
Tabatabaeizadeh, S., Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.
3.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
4.
Abuhelwa, Z., Do Zinc Supplements Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19?, Translation: The University of Toledo Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46570/utjms.vol11-2023-749.
5.
Rheingold et al., Zinc Supplementation Associated With a Decrease in Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.40231.
Li et al., 4 Feb 2026, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
