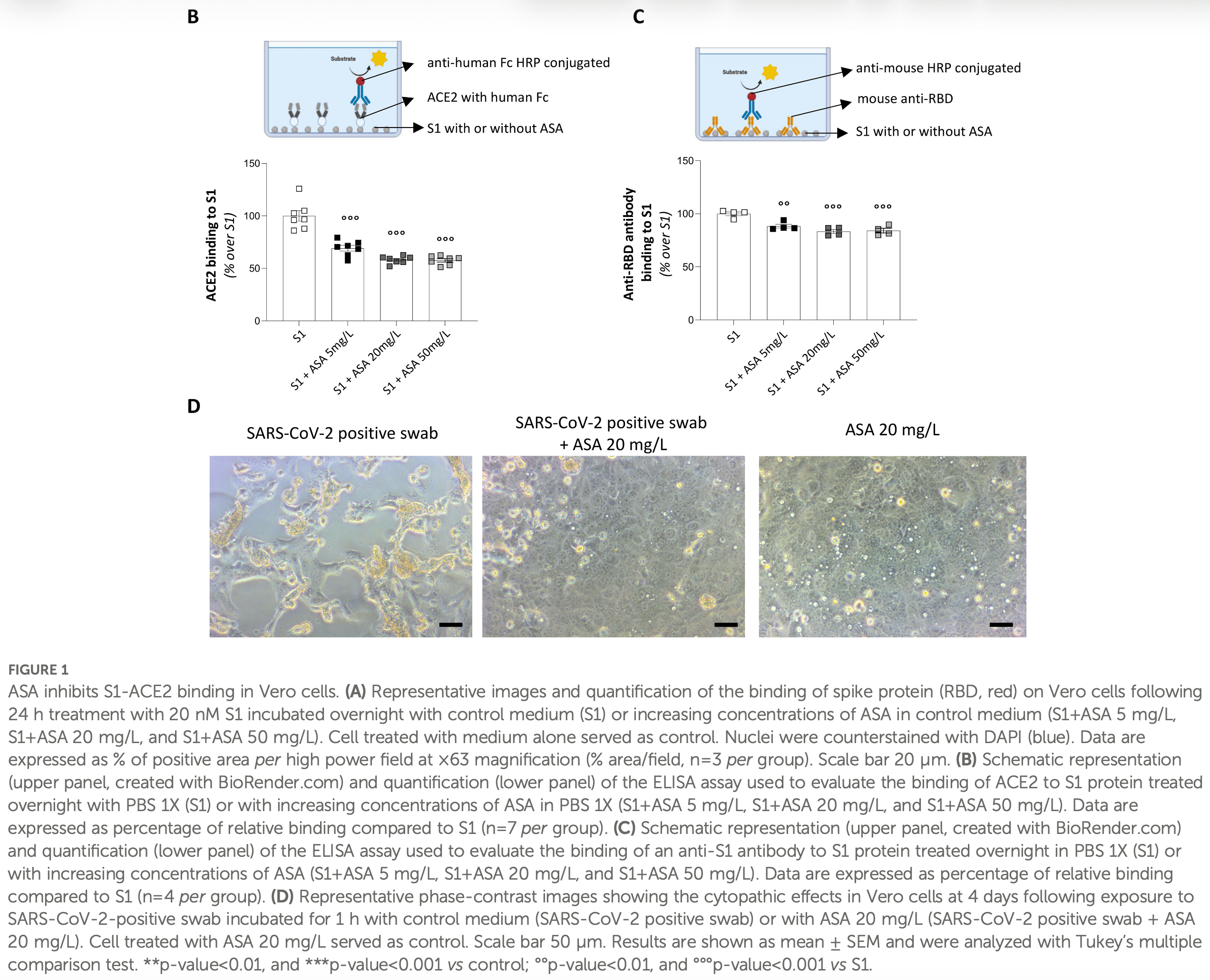
Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycosylation and selectively impairs binding to ACE2
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997, Jan 2026
In vitro and mouse study showing that acetylsalicylic acid (ASA/aspirin) inhibits SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit binding to ACE2 in a dose-dependent manner.
4 preclinical studies support the efficacy of aspirin for COVID-19:
1.
Eissa et al., Identification of Potential FDA-Approved Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Helicase Through a Multistep In Silico Approach: A Promising Prospect for COVID-19 Treatment, Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/0115734064318640241112071225.
2.
Perico et al., Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycosylation and selectively impairs binding to ACE2, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997.
Perico et al., 7 Jan 2026, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: luca.perico@marionegri.it.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycosylation and selectively impairs binding to ACE2
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997
Preclinical and clinical evidence suggested the potential benefits of treatment with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in mitigating COVID-19 severity. While available studies largely focused on the intracellular pathways through which ASA impairs viral replication or dampens host immunoresponse stimulated by SARS-CoV-2, whether ASA directly affects the interaction between the viral spike protein and its cellular receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) remains unexplored. This question is clinically relevant, as circulating spike S1 has been shown to persist in patients with acute and long COVID-19, where its interaction with the broadly expressed ACE2 drives systemic manifestations and tissue damage. Here, we demonstrate that pre-incubation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike subunit 1 (S1) with ASA dose-dependently impaired ACE2 binding on Vero cells. The functional relevance of this finding was confirmed in transgenic mice with human ACE2, in which intratracheal administration of ASA-treated S1 markedly reduced lung injury, fibrosis, and inflammation compared to untreated S1. Glycoproteomic profiling revealed that ASA altered the glycosylation landscape of S1, particularly N-glycosylation at N61 and O-glycosylation at S325. Site-directed mutagenesis of these two residues confirmed the critical role of their glycosylation in S1-ACE2 binding in vitro. Consistently, the glycosylation-insensitive S1 had limited effect in inducing lung injury, fibrosis, and inflammation in transgenic mice compared to WT S1, phenocopying the protective effects of ASA. These findings unveil a previously unrecognized antiviral activity of ASA, providing a molecular rationale for its repurposing as a low-cost, readily available intervention to prevent the progression from mild to severe COVID-19.
Ethics statement Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. The animal study was approved by Italian Ministry of Health (approval number 371/2023-PR). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The author(s) declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declared that generative AI was not used in the creation of this manuscript. Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found..
References
Aghajani, Moradi, Amini, Tehrani, Pourheidar et al., Decreased in-hospital mortality associated with aspirin administration in hospitalized patients due to severe COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27053
Ahmed, Merrell, Ismail, Joudeh, Riley et al., Rationales and uncertainties for aspirin use in COVID-19: a narrative review, Fam Med Com Health, doi:10.1136/fmch-2020-000741
Alamdari, Afaghi, Rahimi, Tarki, Tavana et al., Mortality risk factors among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a major referral center in Iran, Tohoku J Exp Med, doi:10.1620/tjem.252.73
Andersen, Rambaut, Lipkin, Holmes, Garry, The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9
Antonopoulos, Broome, Sharov, Ziegenfuss, Easton et al., Site-specific characterization of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain, Glycobiology, doi:10.1093/glycob/cwaa085
Bagdonaite, Thompson, Wang, Søgaard, Fougeroux et al., Site-specific O-glycosylation analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein produced in insect and human cells, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13040551
Bassetti, Andreoni, Santus, Scaglione, NSAIDs for early management of acute respiratory infections, Curr Opin Infect Dis, doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000001024
Bonaventura, Vecchiéa, Dagna, Martinod, Dixon et al., Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9
Calvaresi, Wrobel, Toporowska, Hammerschmid, Doores et al., Structural dynamics in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36745-0
Casalino, Gaieb, Goldsmith, Hjorth, Dommer et al., Beyond shielding: the roles of glycans in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, ACS Cent Sci, doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01056
Catanzaro, Fagiani, Racchi, Corsini, Govoni et al., Immune response in COVID-19: addressing a pharmacological challenge by targeting pathways triggered by SARS-CoV-2, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0191-1
Cheng, Liu, Li, Sun, Liu et al., Protein post-translational modification in SARS-CoV-2 and host interaction, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1068449
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Yamane, Levine et al., Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Anesth Analg, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292
Chow, Rahnavard, Gomberg-Maitland, Chatterjee, Patodi et al., Association of early aspirin use with in-hospital mortality in patients with moderate COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3890
Consolaro, Suter, Rubis, Pedroni, Moroni et al., A h o m e -t r e a t m e n t a l g o r i t h m b a s e d o n a n t i -i n fl a m m a t o r y d r u g s t o prevent hospitalization of patients with early COVID-19: A matched-cohort study (COVER 2), Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.785785
Conway, Mackman, Warren, Wolberg, Mosnier et al., Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00762-9
Craddock, Mahajan, Spikes, Krishnamachary, Ram et al., Persistent circulation of soluble and extracellular vesicle-linked Spike protein in individuals with postacute sequelae of COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28568
Dong, Chen, Yan, Zhang, Li et al., Comprehensive O-glycosylation analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with biomimetic trp-arg materials, Anal Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04634
Du Sert, Ahluwalia, Alam, Avey, Baker et al., Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411
Eikelboom, Jolly, Belley-Cote, Whitlock, Rangarajan et al., Colchicine and aspirin in community patients with COVID-19 (ACT): an open-label, factorial, randomised, controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00299-5
Geiger, König, Oberwinkler, Roll, Diesendorf et al., Acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in precision-cut lung slices, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10101619
Ghazanfari-Sarabi, Habibi-Rezaei, Eshraghi-Naeeni, Moosavi-Movahedi, Prevention of haemoglobin glycation by acetylsalicylic acid (ASA): A new view on old mechanism, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0214725
Glatthaar-Saalmüller, Mair, Saalmüller, Antiviral activity of aspirin against RNA viruses of the respiratory tract-an in vitro study, Influenza Other Respir Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12421
Gong, Qin, Dai, Tian, The glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor ACE2, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00809-8
Gorog, Storey, Gurbel, Tantry, Berger et al., Current and novel biomarkers of thrombotic risk in COVID-19: a Consensus Statement from the International COVID-19 Thrombosis Biomarkers Colloquium, Nat Rev Cardiol, doi:10.1038/s41569-021-00665-7
Gracie, Lai, Newsome, Cellular signalling by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Microbiol Aust, doi:10.1071/MA24005
Gu, Tyagi, Jain, Gu, Lee et al., Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation, Nat Rev Cardiol, doi:10.1038/s41569-020-00469-1
Huang, Dietsch, Anti-influenza viral activity of aspirin in cell culture, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejm198809223191218
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Huang, Yang, Xu, Xu, Liu, Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacol Sin, doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4
Hun-Opfer, Mata-Segreda, Non-enzymatic acetylation of proteins by aspirin as protection against the secondary complications of diabetes mellitus, Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam
Jin, Yang, Chen, Zhang, Duan, Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: from basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00454-7
Kosik, Ince, Gentles, Oler, Kosikova et al., Influenza A virus hemagglutinin glycosylation compensates for antibody escape fitness costs, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006796
Li, Jiang, Li, Lin, Wang et al., Clinical and pathological investigation of patients with severe COVID-19, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.138070
Li, Wang, Sun, Knopf, Herrmann et al., Immune response in COVID-19: what is next?, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-022-01015-x
Liao, Lin, Wu, Tsao, Wang et al., Salicylates inhibit flavivirus replication independently of blocking nuclear factor kappa B activation, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.75.17.7828-7839.2001
Liu, Huang, Li, Zhou, Liang et al., Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19, Med, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000024544
Lodigiani, Iapichino, Carenzo, Cecconi, Ferrazzi et al., Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy, Thromb Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024
Ma, Su, Sun, Lowe, Zhou et al., Does aspirin have an effect on risk of death in patients with COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00228-022-03356-5
Martha, Pranata, Lim, Wibowo, Akbar, Active prescription of low-dose aspirin during or prior to hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjusted effect estimates, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.016
Mazur, Wurzer, Ehrhardt, Pleschka, Puthavathana et al., Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) blocks influenza virus propagation via its NF-kappaBinhibiting activity, Cell Microbiol, doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00902.x
Meizlish, Goshua, Liu, Fine, Amin et al., Intermediatedose anticoagulation, aspirin, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A propensity score-matched analysis, Am J Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.26102
Merzon, Green, Vinker, Golan-Cohen, Gorohovski et al., The use of aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease is associated with a lower likelihood of COVID-19 infection, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15784
Nagelschmitz, Blunck, Kraetzschmar, Ludwig, Wensing et al., Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous and oral administration to healthy volunteers, Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.2147/CPAA.S47895
Nguyen, Mccord, Bui, Bouwman, Kitova et al., Sialic acid-containing glycolipids mediate binding and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Chem Biol, doi:10.1038/s41589-021-00924-1
Osborne, Veigulis, Arreola, Mahajan, Röösli et al., Association of mortality and aspirin prescription for COVID-19 patients at the Veterans Health Administration, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246825
Ou, Lan, Wu, Zhao, Duan et al., Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Omicron diverse spike gene mutations identifies multiple inter-variant recombination events, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00992-2
Oudit, Wang, Viveiros, Kellner, Penninger, Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2-at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.039
Parsons, Acharya, Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113444
Peluso, Swank, Goldberg, Lu, Dalhuisen et al., Plasmabased antigen persistence in the post-acute phase of COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00211-1
Perico, Benigni, Casiraghi, Ng, Renia et al., Immunity, endothelial injury and complement-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19, Nat Rev Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-020-00357-4
Perico, Benigni, Remuzzi, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: from a vasoactive peptide to the gatekeeper of a global pandemic, Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000692
Perico, Benigni, Remuzzi, SARS-CoV-2 and the spike protein in endotheliopathy, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2023.06.004
Perico, Benigni, Remuzzi, Should COVID-19 concern nephrologists? Why and to what extent? The emerging impasse of angiotensin blockade, Nephron, doi:10.1159/000507305
Perico, Cortinovis, Suter, Remuzzi, Home as the new frontier for the treatment of COVID-19: the case for anti-inflammatory agents, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00433-9
Perico, Morigi, Pezzotta, Locatelli, Imberti et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces lung endothelial cell dysfunction and thromboinflammation depending on the C3a/C3a receptor signalling, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-38382-5
Perico, Tomasoni, Peracchi, Perna, Pezzotta et al., COVID-19 and lombardy: TESTing the impact of the first wave of the pandemic, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103069
Pezzotta, Bovio, Imberti, Locatelli, Corna et al., Mesenchymal stromal cell secretome reduces lung injury and thrombo-inflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Stem Cell Res Ther, doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04472-6
Primache, Binda, Benedittis, In vitro activity of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella-zoster virus, New Microbiol
Rong, Mai, Ebert, Kapoor, Puelles et al., Persistence of spike protein at the skull-meninges-brain axis may contribute to the neurological sequelae of COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2024.11.007
Sanda, Morrison, Goldman, and O-glycosylation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Anal Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03173
Santoro, Nuñez-Gil, Vitale, Viana-Llamas, Mc et al., Antiplatelet therapy and outcome in COVID-19: the Health Outcome Predictive Evaluation Registry, Heart, doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2021-319552
Santoro, Nuñez-Gil, Vitale, Viana-Llamas, Romero et al., Aspirin therapy on prophylactic anticoagulation for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A propensity score-matched cohort analysis of the HOPE-COVID-19 registry, J Am Heart Assoc, doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.024530
Sańchez-Garcıá, Rıós-Ibarra, Rincoń-Sańchez, Ortiz-Loṕez, Garza-Juaŕez et al., Use of proteomic analysis tools to identify HCVproteins down-regulated by acetylsalicylic acid, Ann Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31313-4
Shajahan, Pepi, Kumar, Murray, Azadi, Site specific N-and Oglycosylation mapping of the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-33088-0
Shajahan, Supekar, Gleinich, Azadi, Deducing the N-and Oglycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Glycobiology, doi:10.1093/glycob/cwaa042
Speir, Yu, Ferrans, Huang, Epstein, Aspirin attenuates cytomegalovirus infectivity and gene expression mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 in coronary artery smooth muscle cells, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/01.res.83.2.210
Srivastava, Kumar, Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14515
Sun, King, Hamlin, Saniepay, Gorshkov et al., Identification of a fibronectin-binding protein signature associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Cells Dev, doi:10.1016/j.cdev.2024.203941
Suter, Consolaro, Pedroni, Moroni, Pastò et al., A simple, home-therapy algorithm to prevent hospitalisation for COVID-19 patients: A retrospective observational matched-cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100941
Swank, Borberg, Chen, Senussi, Chalise et al., Measurement of circulating viral antigens post-SARS-CoV-2 infection in a multicohort study, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2024.09.001
Swank, Senussi, Manickas-Hill, Yu, Li et al., Persistent circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike is associated with post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac722
Tan, Chia, Qin, Liu, Chen et al., A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2spike protein-protein interaction, Nat Biotechnol, doi:10.1038/s41587-020-0631-z
Tian, Li, Zhang, Bai, Yuan et al., O-glycosylation pattern of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reveals an "O-Follow-N" rule, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-021-00545-2
Tian, Parsons, Jankowska, Cipollo, Site-specific glycosylation patterns of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein derived from recombinant protein and viral WA1 and D614G strains, Front Chem, doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.767448
Trujillo-Murillo, Rincoń-Sańchez, Martıńez-Rodrıǵuez, Bosques-Padilla, Ramos-Jimeńez et al., Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits hepatitis C virus RNA and protein expression through cyclooxygenase 2 signaling pathways, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.22215
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Winskill, Whittaker et al., Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7
Walz-Cicconi, Weller, Dose-related effect of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella zoster virus. vitro, Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A, doi:10.1073/pnas.81.16.5223
Wang, Baudys, Bundy, Solano, Keppel et al., Comprehensive analysis of the glycan complement of SARS-coV-2 spike proteins using signature ions-triggered electron-transfer/higher-energy collisional dissociation (EThcD) mass spectrometry, Anal Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03301
Wang, Wu, Hu, Hao, Yang, Impact of expressing cells on glycosylation and glycan of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c01785
Warner, Nylander, Whatling, Anti-platelet therapy: cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the use of aspirin with particular regard to dual anti-platelet therapy, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03943.x
Watanabe, Allen, Wrapp, Mclellan, Crispin, Site-specific glycan analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb9983
Wijaya, Andhika, Huang, Purwiga, Budiman, The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Epidemiol Glob Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883
Wu, Lin, Tsai, Lee, Chuang et al., Influenza A surface glycosylation and vaccine design, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1617174114
Yang, Hughes, Kelkar, Yu, Cheng et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 viral entry upon blocking N-and O-glycan elaboration, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.61552
Yang, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Wan et al., COVID-19: immunopathogenesis and immunotherapeutics, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00243-2
Yin, Zhang, Aspirin inhibits hepatitis C virus entry by downregulating claudin-1, J Viral Hepat, doi:10.1111/jvh.12446
Yuan, Chen, Li, Chen, Wang et al., Mortality and prehospitalization use of low-dose aspirin in COVID-19 patients with coronary artery disease, J Cell Mol Med, doi:10.1111/jcmm.16198
Zhang, Schmidt, Muecksch, Wang, Gazumyan et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike glycosylation affects function and neutralization sensitivity, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01672-23
Zhang, Tecson, Mccullough, Role of endothelial cell receptors in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent), doi:10.1080/08998280.2021.1874231
Zhang, Zhao, Mao, Chen, Wang et al., Site-specific Nglycosylation characterization of recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins, Mol Cell Proteomics, doi:10.1074/mcp.RA120.002295
Zhao, Li, Yu, Liu, Liu et al., Aspirin inhibits rotavirus replication and alters rat gut microbial composition, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02199-5
Zhao, Praissman, Grant, Cai, Xiao et al., Virusreceptor interactions of glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 spike and human ACE2 receptor, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004
Zhu, Wu, Lu, Jiao, Liu et al., Acute lung injury induced by recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 in mice, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-025-03143-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n Preclinical and clinical evidence suggested the potential benefits of treatment with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in mitigating COVID-19 severity. While available studies largely focused on the intracellular pathways through which ASA impairs viral replication or dampens host immunoresponse stimulated by SARS-CoV-2, whether ASA directly affects the interaction between the viral spike protein and its cellular receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) remains unexplored. This question is clinically relevant, as circulating spike S1 has been shown to persist in patients with acute and long COVID-19, where its interaction with the broadly expressed ACE2 drives systemic manifestations and tissue damage. Here, we demonstrate that pre-incubation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike subunit 1 (S1) with ASA dose-dependently impaired ACE2 binding on Vero cells. The functional relevance of this finding was confirmed in transgenic mice with human ACE2, in which intratracheal administration of ASA-treated S1 markedly reduced lung injury, fibrosis, and inflammation compared to untreated S1. Glycoproteomic profiling revealed that ASA altered the glycosylation landscape of S1, particularly N-glycosylation at N61 and O-glycosylation at S325. Site-directed mutagenesis of these two residues confirmed the critical role of their glycosylation in S1-ACE2 binding\n <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic>\n . Consistently, the glycosylation-insensitive S1 had limited effect in inducing lung injury, fibrosis, and inflammation in transgenic mice compared to WT S1, phenocopying the protective effects of ASA. These findings unveil a previously unrecognized antiviral activity of ASA, providing a molecular rationale for its repurposing as a low-cost, readily available intervention to prevent the progression from mild to severe COVID-19.\n </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997"
],
"article-number": "1706997",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perico",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bovio",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomasoni",
"given": "Susanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trionfini",
"given": "Piera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cerullo",
"given": "Domenico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corna",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pezzotta",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Locatelli",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alberti",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benigni",
"given": "Ariela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Remuzzi",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-07T06:59:07Z",
"timestamp": 1767769147000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-07T06:59:12Z",
"timestamp": 1767769152000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100021856",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100021856",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100003196",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Ministero della Salute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-07T07:02:27Z",
"timestamp": 1767769347448,
"version": "3.48.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1767744000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"article-title": "Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis",
"author": "Verity",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.138070",
"article-title": "Clinical and pathological investigation of patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00762-9",
"article-title": "Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy",
"author": "Conway",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08998280.2021.1874231",
"article-title": "Role of endothelial cell receptors in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent)",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41569-021-00665-7",
"article-title": "Current and novel biomarkers of thrombotic risk in COVID-19: a Consensus Statement from the International COVID-19 Thrombosis Biomarkers Colloquium",
"author": "Gorog",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cardiol",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41569-020-00469-1",
"article-title": "Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cardiol",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00243-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19: immunopathogenesis and immunotherapeutics",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-0191-1",
"article-title": "Immune response in COVID-19: addressing a pharmacological challenge by targeting pathways triggered by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Catanzaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-022-01015-x",
"article-title": "Immune response in COVID-19: what is next",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QCO.0000000000001024",
"article-title": "NSAIDs for early management of acute respiratory infections",
"author": "Bassetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Infect Dis",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00433-9",
"article-title": "Home as the new frontier for the treatment of COVID-19: the case for anti-inflammatory agents",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100941",
"article-title": "A simple, home-therapy algorithm to prevent hospitalisation for COVID-19 patients: A retrospective observational matched-cohort study",
"author": "Suter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.785785",
"article-title": "A home-treatment algorithm based on anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent hospitalization of patients with early COVID-19: A matched-cohort study (COVER 2)",
"author": "Consolaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.26102",
"article-title": "Intermediate-dose anticoagulation, aspirin, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A propensity score-matched analysis",
"author": "Meizlish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Hematol",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27053",
"article-title": "Decreased in-hospital mortality associated with aspirin administration in hospitalized patients due to severe COVID-19",
"author": "Haji Aghajani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"article-title": "Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Anesth Analg",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.16198",
"article-title": "Mortality and pre-hospitalization use of low-dose aspirin in COVID-19 patients with coronary artery disease",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cell Mol Med",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15784",
"article-title": "The use of aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease is associated with a lower likelihood of COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024",
"article-title": "Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy",
"author": "Lodigiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.252.73",
"article-title": "Mortality risk factors among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a major referral center in Iran",
"author": "Alamdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Tohoku J Exp Med",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "252",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14515",
"article-title": "Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Srivastava",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e14515",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3890",
"article-title": "Association of early aspirin use with in-hospital mortality in patients with moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e223890",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-022-03356-5",
"article-title": "Does aspirin have an effect on risk of death in patients with COVID-19? A meta-analysis",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246825",
"article-title": "Association of mortality and aspirin prescription for COVID-19 patients at the Veterans Health Administration",
"author": "Osborne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0246825",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.016",
"article-title": "Active prescription of low-dose aspirin during or prior to hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjusted effect estimates",
"author": "Martha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883",
"article-title": "The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wijaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Epidemiol Glob Health",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000024544",
"article-title": "Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e24544",
"journal-title": "Med (Baltimore)",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.121.024530",
"article-title": "Aspirin therapy on prophylactic anticoagulation for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A propensity score-matched cohort analysis of the HOPE-COVID-19 registry",
"author": "Santoro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e024530",
"journal-title": "J Am Heart Assoc",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/heartjnl-2021-319552",
"article-title": "Antiplatelet therapy and outcome in COVID-19: the Health Outcome Predictive Evaluation Registry",
"author": "Santoro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heart",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01825-0",
"article-title": "Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00299-5",
"article-title": "Colchicine and aspirin in community patients with COVID-19 (ACT): an open-label, factorial, randomised, controlled trial",
"author": "Eikelboom",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03943.x",
"article-title": "Anti-platelet therapy: cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the use of aspirin with particular regard to dual anti-platelet therapy",
"author": "Warner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/fmch-2020-000741",
"article-title": "Rationales and uncertainties for aspirin use in COVID-19: a narrative review",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Fam Med Com Health",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.22215",
"article-title": "Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits hepatitis C virus RNA and protein expression through cyclooxygenase 2 signaling pathways",
"author": "Trujillo-Murillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31313-4",
"article-title": "Use of proteomic analysis tools to identify HCV-proteins down-regulated by acetylsalicylic acid",
"author": "Sánchez-García",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Hepatol",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jvh.12446",
"article-title": "Aspirin inhibits hepatitis C virus entry by downregulating claudin-1",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Viral Hepat",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.75.17.7828-7839.2001",
"article-title": "Salicylates inhibit flavivirus replication independently of blocking nuclear factor kappa B activation",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-02199-5",
"article-title": "Aspirin inhibits rotavirus replication and alters rat gut microbial composition",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12421",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of aspirin against RNA viruses of the respiratory tract-an in vitro study",
"author": "Glatthaar-Saalmüller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir Viruses",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00902.x",
"article-title": "Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) blocks influenza virus propagation via its NF-kappaB-inhibiting activity",
"author": "Mazur",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Microbiol",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejm198809223191218",
"article-title": "Anti-influenza viral activity of aspirin in cell culture",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "797",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "319",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"article-title": "In vitro activity of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella-zoster virus",
"author": "Primache",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "New Microbiol",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.81.16.5223",
"article-title": "Dose-related effect of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella zoster virus",
"author": "Walz-Cicconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.res.83.2.210",
"article-title": "Aspirin attenuates cytomegalovirus infectivity and gene expression mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 in coronary artery smooth muscle cells",
"author": "Speir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "83",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101619",
"article-title": "Acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in precision-cut lung slices",
"author": "Geiger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00211-1",
"article-title": "Plasma-based antigen persistence in the post-acute phase of COVID-19",
"author": "Peluso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2024.09.001",
"article-title": "Measurement of circulating viral antigens post-SARS-CoV-2 infection in a multicohort study",
"author": "Swank",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28568",
"article-title": "Persistent circulation of soluble and extracellular vesicle-linked Spike protein in individuals with postacute sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Craddock",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e28568",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac722",
"article-title": "Persistent circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike is associated with post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae",
"author": "Swank",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2024.11.007",
"article-title": "Persistence of spike protein at the skull-meninges-brain axis may contribute to the neurological sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Rong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2112",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2023.06.004",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and the spike protein in endotheliopathy",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00454-7",
"article-title": "Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: from basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-020-00357-4",
"article-title": "Immunity, endothelial injury and complement-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Nephrol",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MNH.0000000000000692",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: from a vasoactive peptide to the gatekeeper of a global pandemic",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000507305",
"article-title": "Should COVID-19 concern nephrologists? Why and to what extent? The emerging impasse of angiotensin blockade",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nephron",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CPAA.S47895",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous and oral administration to healthy volunteers",
"author": "Nagelschmitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-020-0631-z",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2–spike protein–protein interaction",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0214725",
"article-title": "Prevention of haemoglobin glycation by acetylsalicylic acid (ASA): A new view on old mechanism",
"author": "Ghazanfari-Sarabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0214725",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cdev.2024.203941",
"article-title": "Identification of a fibronectin-binding protein signature associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cells Dev",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1068449",
"article-title": "Protein post-translational modification in SARS-CoV-2 and host interaction",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00809-8",
"article-title": "The glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor ACE2",
"author": "Gong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "396",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-36745-0",
"article-title": "Structural dynamics in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Calvaresi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1421",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.0c01056",
"article-title": "Beyond shielding: the roles of glycans in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Casalino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "ACS Cent Sci",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1071/MA24005",
"article-title": "Cellular signalling by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Gracie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Aust",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-025-03143-7",
"article-title": "Acute lung injury induced by recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 in mice",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.039",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2—at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Oudit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb9983",
"article-title": "Site-specific glycan analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike",
"author": "Watanabe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03173",
"article-title": "and O-glycosylation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Sanda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Anal Chem",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsomega.1c01785",
"article-title": "Impact of expressing cells on glycosylation and glycan of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "ACS Omega",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4",
"article-title": "Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13040551",
"article-title": "Site-specific O-glycosylation analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein produced in insect and human cells",
"author": "Bagdonaite",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00545-2",
"article-title": "O-glycosylation pattern of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reveals an “O-Follow-N” rule",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "B74",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/glycob/cwaa042",
"article-title": "Deducing the N- and O-glycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shajahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Glycobiology",
"key": "B75",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.767448",
"article-title": "Site-specific glycosylation patterns of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein derived from recombinant protein and viral WA1 and D614G strains",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Chem",
"key": "B76",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.61552",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 viral entry upon blocking N- and O-glycan elaboration",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e61552",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "B77",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004",
"article-title": "Virus-receptor interactions of glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 spike and human ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "586",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "B78",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03301",
"article-title": "Comprehensive analysis of the glycan complement of SARS-coV-2 spike proteins using signature ions-triggered electron-transfer/higher-energy collisional dissociation (EThcD) mass spectrometry",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Anal Chem",
"key": "B79",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9",
"article-title": "The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Andersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B80",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04634",
"article-title": "Comprehensive O-glycosylation analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with biomimetic trp-arg materials",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Anal Chem",
"key": "B81",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-021-00924-1",
"article-title": "Sialic acid-containing glycolipids mediate binding and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Nat Chem Biol",
"key": "B82",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/mcp.RA120.002295",
"article-title": "Site-specific N-glycosylation characterization of recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100058",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Proteomics",
"key": "B83",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/glycob/cwaa085",
"article-title": "Site-specific characterization of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain",
"author": "Antonopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Glycobiology",
"key": "B84",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01672-23",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike glycosylation affects function and neutralization sensitivity",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "B85",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Non-enzymatic acetylation of proteins by aspirin as protection against the secondary complications of diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Hun-Opfer",
"journal-title": "Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam",
"key": "B86",
"volume": "36",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113444",
"article-title": "Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike",
"author": "Parsons",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113444",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "B87",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00992-2",
"article-title": "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Omicron diverse spike gene mutations identifies multiple inter-variant recombination events",
"author": "Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B88",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-33088-0",
"article-title": "Site specific N- and O-glycosylation mapping of the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern",
"author": "Shajahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10053",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B89",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1617174114",
"article-title": "Influenza A surface glycosylation and vaccine design",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "B90",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006796",
"article-title": "Influenza A virus hemagglutinin glycosylation compensates for antibody escape fitness costs",
"author": "Kosik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1006796",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "B91",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-38382-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces lung endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombo-inflammation depending on the C3a/C3a receptor signalling",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11392",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B92",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13287-025-04472-6",
"article-title": "Mesenchymal stromal cell secretome reduces lung injury and thrombo-inflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Pezzotta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "324",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Res Ther",
"key": "B93",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411",
"article-title": "Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0",
"author": "Percie du Sert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3000411",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol",
"key": "B94",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103069",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and lombardy: TESTing the impact of the first wave of the pandemic",
"author": "Perico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103069",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B95",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 95,
"references-count": 95,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycosylation and selectively impairs binding to ACE2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}